Physiological causes of pain
If you have a tightening in your lower abdomen in the middle of your cycle, this pain is recognizable and visits you every month with enviable regularity, then perhaps this is due to the ovulation process.
There is no threat to health and no treatment is required. Pain during ovulation is localized in the lower abdomen and is dangerous because it can be confused with serious problems. If this is your first time encountering such symptoms, visit your gynecologist. It will help eliminate intestinal inflammation, pelvic infectious diseases, and life-threatening conditions.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GYRUPwsafbg
Ovulation is the birth of a mature egg. This process occurs monthly and is the main indicator of a woman’s reproductive health and capabilities.
Knowing the nature of what is happening simplifies a woman’s life both in terms of protection from unwanted pregnancy and in terms of conceiving a long-awaited baby.
The menstrual cycle – its regularity and completeness – depends on ovulation (its presence, time).
It is believed that in a healthy woman, ovulation occurs in the middle of the monthly cycle. However, even for one woman, the time of this process can “walk” from the beginning of the cycle to its end. It is impossible to predict this moment. The time for the release of an egg is influenced by the woman’s health status, moving, temperature changes, stress, physical activity and even the intensity of a particular sexual act.
The last “method” for determining the time of ovulation is the most accurate, but not available to everyone. Most women do not feel this process or do not pay attention to the discomfort that arises. The ability to recognize the moment of ovulation by the accompanying signs becomes an excellent tool for family planning.
There are no clear criteria for “normal” pain during ovulation. Most often, women go to the gynecological office with complaints of vague, nagging pain in the lower abdomen and discomfort. Sometimes complaints of heavy discharge at this time are added.
The doctor carries out diagnostic procedures - laboratory blood tests, smears, ultrasound of the pelvic organs. If no pathology is found, the gynecologist may assume that the symptoms are associated with ovulation. Only the woman herself can definitively understand whether this is true by observing the reaction to ovulation over several cycles.
Less than half of women are able to feel the process of ovulation. Painful sensations are caused by rupture of the ovarian follicle during the release of the egg. This occurs with damage to the blood vessels and slight bleeding. The process of releasing the egg itself lasts no more than a few minutes. The accompanying pain can last up to two days.
Depending on which ovary produces the cell, the pain is localized on the right or left. It is believed that the right ovary “works” more intensely than the left.
The pain is nagging, sometimes sharp, and continuous. Its scale ranges from “slight discomfort” to “severe, unbearable.”
The duration and intensity of pain during ovulation can be influenced by:
- the presence of adhesions in the pelvis;
- endometriosis;
- scarring;
- inflammatory processes.
A woman can only determine why her stomach hurts in the middle of her cycle with the help of her gynecologist.
It is not immediately possible to determine the time of ovulation and recognize the characteristic pain in the future. You will need to monitor yourself over several menstrual cycles. Necessary:
- Find out the exact duration of menstruation. The length is counted from the first day of the start of menstruation to the first day of the start of the next cycle.
- “Take” a few days (2 – 3) of expected ovulation in the middle and carefully observe your sensations.
- Changing your basal temperature will help you accurately determine the day.
Measure your basal temperature upon waking. A thermometer (not electronic) is inserted into the anus. In the period before ovulation, the temperature ranges from 36.3 to 36.8. On the day the egg is released, it rises to 37.0 - 37.2 and remains at this level until the start of menstruation.
This method of determining the time of final maturation of a female cell is considered the most accurate. An ovulation test can provide insurance.
Additional symptoms that indicate ovulation is approaching:
- Copious, clear mucous discharge, similar to egg white.
- Noticeable increase in libido.
- Mood swings.
- Heaviness in the mammary glands.
If you managed to “catch” the feeling of the egg leaving the follicle, then you will no longer confuse it with any symptoms. This means that you are one of the lucky few who know the periods of possible conception without additional research.
As a rule, healthy ovulation, even if accompanied by pain, does not require drug treatment. To alleviate the condition, it is recommended to drink more fluids, include more vegetables in the diet, and avoid strong emotional and physical stress. Ideally, find reasons to stay at home for a couple of days.
Particularly sensitive women, after consultation with a gynecologist, can take painkillers such as ibuprofen, analgin, and aspirin to relieve the condition.
Ovulation disorders
Ovulation disorders (misses, absence) affect the course of menstruation. This relationship allows the specialist to determine ovulatory dysfunction.
2 - 3 “misses” of egg release per year are considered an acceptable norm. This trend increases with a woman's age. The closer the reproductive ability is to complete extinction, the more often ovulation skips occur. Menstruation continues, although it may be scanty.
The absence of ovulation at the height of fertile age signals problems in the body and the impossibility of conception. The absence of an egg for two or more months is a reason for a visit to the gynecological clinic. The cause may be both hormonal disorders and pathological processes in the pelvic organs.
Important! Pain in the lower abdomen during healthy ovulation is constant and remains recognizable throughout the reproductive period of a woman’s life. The “adding” of new symptoms or a sharp change in pain indicates possible health problems.
Treatment
Treatment of ovulation syndrome depends on the degree of menstrual disruption and the woman’s life goals during this period. Symptomatic is prescribed when full ovulation is maintained and there is a desire to become pregnant. A woman is prescribed analgesics and antispasmodics to relieve pain during ovulation.
Conservative treatment varies depending on the pathology. This may be inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis by the drugs ibuprofen and indomethacin. They are prescribed on the eve of ovulation, 1-2 days before. In parallel, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out.
In case of pathological changes in hormonal levels, oral contraceptives are used. If a woman is not planning a pregnancy, then this approach allows her to stabilize hormones while simultaneously suppressing the process of egg maturation. Ovulation stops and the pain goes away.
If an ovarian rupture is detected, then surgical treatment is considered the only justifiable option. The operation is performed laparoscopically. This allows, with minimal tissue trauma, to “remove” all the consequences of apoplexy, avoiding the further formation of adhesions.
What treatment is required is decided by the attending physician after a comprehensive examination. Your task is to tell in detail about the symptoms that bother you.
Perhaps the abdominal pain and ovulation are not connected in any way, but coincided in time. Next to the genital organs in the abdominal cavity are the urinary system (bladder, ducts, kidneys) and intestines. Diseases of these organs, chronic or acute, often accompany women of childbearing age.
Acute pain in the lower abdomen can be caused by an inflammatory process in the bladder, intestines, or the passage of a kidney stone. On the right side there is appendicitis, which, when inflamed, can lead to peritonitis. Problems with the pancreas are manifested by acute pain in any part of the abdomen. These are just a few examples of possible ailments, the main symptom of which is abdominal pain.
Remember! Unauthorized use of painkillers for abdominal pain complicates diagnosis, which often leads to death (for example, in the case of appendicitis, ectopic pregnancy, rupture of a cyst).
You will need emergency help if:
- The intensity of the pain prevents you from getting out of bed;
- It was accompanied by high fever, weakness, chills;
- The pain is accompanied by nausea, vomiting;
- Intensifies over time;
- Blood appeared in the urine;
- Breathing problems;
- An unusual color (red, black, green with mucus) stool was added;
- There is loss of consciousness.
Nagging pain after ovulation in most cases is considered normal, which is explained by the physiological characteristics of the process and the woman’s menstrual cycle. This pain is reminiscent of the sensations before menstruation: a woman’s lower abdomen feels tight, and cramping pain may appear.
If discomfort does not disappear within three days after ovulation or is accompanied by abnormal discharge, fever and other warning symptoms, you should go to the hospital.
The cause may be gynecological diseases and pathologies of the genitourinary system, as well as the onset of a malignant process.
After ovulation, the stomach feels like before menstruation
If a woman has no health problems, ovulation occurs exactly in the middle of the menstrual cycle. For most women, the cycle lasts 28-30 days, that is, the rupture of the dominant follicle occurs on the 14-15th day of the cycle. In some cases, the cycle can be 26 days or 32-34 days.
You can determine the exact date of ovulation using an ultrasound (this method is used during pregnancy planning) or by keeping a basal temperature chart. The second method is less accurate, since the indicators are affected by hormonal fluctuations, endocrine problems and infectious diseases.
The egg matures and prepares for fertilization during the first half of the cycle. For follicle growth to occur, a woman's brain produces FSH.
Hormonal disbalance
In the case when a woman experiences constant stress , does not have a sexual partner, and also suffers from systemic diseases (diabetes mellitus, thyroid diseases), hormonal disruption may occur. Absolutely all processes occurring in the body are controlled by the hormonal system. When it is adversely affected by external factors, the production of one or another hormone is inhibited, and the production of another is carried out twice as much.
Hormones that control the functioning of the genital organs contribute to the establishment of a certain cycle. If there is a lack of their production, menstruation may disappear, or they may acquire an increased intensity of bloody discharge. In this case, the cycle shortens or, on the contrary, lasts more than 45 days.
A disruption in the production of one hormone leads to disruptions in the functioning of other hormones, so this pathology should be treated as early as possible.
The first symptoms of hormonal imbalance are:
- absence of menstruation for more than 2 months (in the absence of pregnancy);
- sudden weight gain with the usual diet;
- hot flashes and heat;
- lack of sexual desire.
Type of pain Aching pain in the lower back, which is accompanied by increased fatigue, irritability and aggression. Localization: Lower back and lower abdomen. Diagnostics A blood test for hormones will help determine the presence of a hormonal imbalance, as well as identify which hormones are produced in insufficient (excess) quantities. Blood is drawn from a vein, after which it is examined for all types of hormones. It is also important to establish what exactly is the cause of the failure (diseases, pathologies, disorders). Treatment Corrective therapy is used, prescribing to the woman those hormones that are lacking, as well as suppressing the synthesis of those that are produced in excess. To eliminate lower back pain, antispasmodics and analgesics (non-opioid group) can be used, which will help eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
It is important to establish the root cause of hormonal imbalance and eliminate it.
https://youtu.be/qqBR_7hVDnI
Ovarian apoplexy
Even physiological processes sometimes end in disaster. So, sometimes during ovulation, not only the follicle ruptures, but also the entire ovary. This life-threatening and reproductive health disease is called apoplexy and requires urgent medical intervention. If the ovary ruptures, massive bleeding develops, which can lead to significant blood loss.
If, after sexual intercourse in the middle of the menstrual cycle, you suddenly develop severe nagging pain in the abdominal cavity, especially in its lower part, accompanied by weakness, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, decreased blood pressure and pallor, immediately call an ambulance and go to the hospital for treatment. Here it is important to provide assistance within several hours and prevent the development of shock.
Onset of pregnancy
Such a wonderful event as pregnancy is accompanied by a massive restructuring of the body. At first, the female body, oddly enough, tries to reject the fertilized egg, perceiving it as a foreign agent. The second half of pregnancy, on the contrary, is aimed at keeping the fetus inside for as long as possible.
After fertilization, the egg, now called an embryo, must find a place in the uterine cavity and attach to the prepared endometrium, rich in blood vessels. The moment of implantation of the embryo into the wall of the uterus is called implantation. This event occurs 5–6 days after fertilization, that is, right in the middle of the menstrual period.
Changing the balance of hormones and implantation itself becomes the answer to why the stomach hurts in the middle of the cycle, like before menstruation. If on the 13-20th day from the beginning of menstruation you notice this symptom (some women also experience slight spotting at the same time), consider taking a pregnancy test or donating blood to determine the concentration of hCG.
Do not forget that sometimes the fertilized egg is not attached to the wall of the uterus, but in the cavity of the fallopian tube or even somewhere in the pelvic cavity. This condition is called an ectopic pregnancy, which is always terminated surgically or spontaneously.
What can determine the intensity of pain?
First of all, from the receptivity and sensitivity of a woman. Also, in the presence of gynecological diseases, the pain of all processes is aggravated.
It is important to note that in rare cases, egg maturation is observed in both ovaries. If fertilization occurred, the woman would have a multiple pregnancy. And during ovulation, the pain is not localized in one side, but “spreads” in the lower abdomen. This is how abdominal pain manifests itself in the middle of the cycle.
Why does libido increase in the middle of the cycle? This condition is natural, since ovulation is the best time for conception.
The nature of the discharge from the genital tract changes - it becomes absolutely transparent, like egg white. This allows sperm to more easily penetrate the woman's uterine cavity. In rare cases, there is blood in the discharge, but in a very small amount. This occurs due to the detachment of a small endometrium as a result of the cessation of production of estrogen and progesterone at the same time.
Breast pain occurs as a result of hormonal changes in a woman’s body, that is, the mammary glands begin to prepare for the process of feeding the unborn baby. But this may not be observed. And most often the lower abdomen hurts in the middle of the cycle.
Diagnostic procedures
The first doctor a woman should contact with a complaint of pain in the lower abdomen is a therapist. After an initial examination, which consists of palpation of the peritoneum, he refers the patient to a gynecologist or surgeon, sometimes to both specialists at the same time. In addition, laboratory tests of blood and urine are prescribed to identify signs of an inflammatory process in the body.
Gynecological examinations include:
- Colcoscopy is an examination of the cervix to detect pathological changes in the tissue. After applying a special composition to the mucous membrane, healthy cells change color, but sick cells remain the same. Changes are detected during examination using a speculum inserted into the vagina.
- Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive technique for examining the intrauterine cavity using a special device - a hysteroscope. Since its insertion requires maximal expansion of the cervical canal - the cervix, the manipulation is carried out under general anesthesia. The technique allows you to combine examination with minimally invasive surgery - removal of polyps, remnants of the fertilized egg or intrauterine contraceptive device (IUD). Using a hysteroscope, tissue samples are taken for further examination.
If a sexually transmitted infection is suspected, a scraping of the mucous membrane is made for bacterial culture. This way chlamydia and gonorrhea are detected.
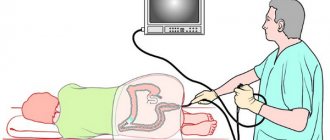
An ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs is also carried out, which makes it possible to detect functional and structural disorders in the organs of the urinary and reproductive systems. Ultrasound in women is performed in two ways: abdominal - through the anterior wall of the abdominal press (pathologies of the kidneys and bladder, or inflammation of the appendix are determined), and transvaginal - through the vaginal entrance (if gynecological diseases are suspected). To clarify the results, ultrasound of the pelvic organs is supplemented with computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
When to see a doctor
If you suspect that your stomach hurts due to errors in your diet, it is recommended to improve your diet and cleanse your body of waste and toxins. Nutritionists advise reducing your intake of solid foods at first and drinking more water.
Cases when specialist consultation is necessary:
- pain appeared for the first time;
Bladder diseases are often accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen
- discomfort persists for more than a week;
- the pain does not go away within 1-2 days;
- persistent flatulence does not go away for several days;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- burning and stinging when going to the toilet;
- diarrhea lasting more than 3 days;
- pain with fever;
- pain radiates to the shoulder, neck or chest.
During pregnancy, discomfort in the lower abdomen is a dangerous symptom. It may indicate a threat of miscarriage, and therefore requires immediate medical attention.
Other conditions requiring emergency medical attention:
- severe and sharp pain;
- pain syndrome is accompanied by lethargy and apathy;
- vomit;
- lack of appetite;
- constipation;
- cold sweat;
- cardiopalmus;
- pale skin;
- abdominal wall tone.
Pulling in the lower abdomen - the reasons for women may be different. Depending on the nature of the pain and other symptoms, you may need help from different specialists. Consultation with a gastroenterologist is necessary if there is a suspicion of gastrointestinal dysfunction.
A doctor can determine the exact cause of nagging pain in the lower abdomen in women
, especially if the pain occurs after eating. If the discomfort radiates to the groin, a proctologist and urologist are involved in the treatment. A consultation with the latter will be needed if you have problems with the urinary system.
In case of painful critical days and disruption of the menstrual cycle, it is necessary to visit a gynecologist. He will diagnose and prescribe treatment for diseases of the reproductive system. In other situations, you will need to see a GP first. He will collect anamnesis and, if necessary, refer to other specialists.
Menstrual irregularities
Normally, the period of menstruation lasts from 28 to 32 days. However, during puberty (when the first menstruation usually appears) and shortly before the onset of menopause, hormonal disruptions occur, and the cycle begins to “dance”: it lasts either 21 days or 40. That is why pain on the left or right side of the lower abdomen in the middle of the cycle is perceived as pathology, whereas in fact it foreshadows the onset of the next menstruation. The same changes can occur during reproductive age due to hormonal imbalance.
Therapy and prevention
Pain in the hypogastric region, explained by physiological causes, does not require special treatment and goes away on its own as the situation normalizes. If necessary, short-term use of non-narcotic painkillers - Analgin, Pentalgin, Baralgin - is acceptable.
Therapy for pathological pain in the lower abdomen depends on its etiology and nature. For endometriosis, as well as in the early stages of fibromatosis, the course of treatment includes hormonal agents. Inflammatory processes are extinguished by antibiotic or antibacterial drugs taken as prescribed and under the supervision of a physician.