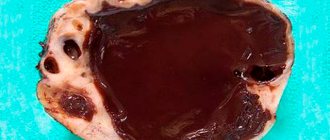
What is husking?
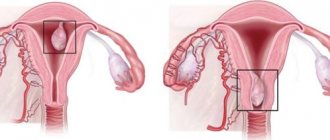
Husking the capsule of an ovarian cyst is a surgical intervention that allows you to preserve a woman’s reproductive function.
In this case, only the tumor (cyst) is removed along with the capsule, and healthy ovarian tissue is not affected. In order for the enucleation (husking) of a cyst to be successful, the patient should not have acute or exacerbation of chronic inflammatory diseases of the genital organs at this time.
Enucleation of the cyst
Benefits of laser cyst removal
The use of laser beams in medical practice has a number of advantages over other methods of surgical removal of tumors:
- the laser cyst removal procedure does not take much time (small formations are removed in just a few minutes);
- when using a laser, the surgeon has the opportunity to selectively influence tissue and dose the degree of exposure to laser beams as accurately as possible, which allows him to remove only the tumor itself and damaged areas of neighboring tissues, without affecting surrounding healthy tissues and organs;
- Patients experience virtually no swelling, so rehabilitation after surgery proceeds without significant pain;
- surgery to remove a cyst with a laser is low-traumatic and almost never leads to bleeding, after which rapid healing of the wound is observed;
- laser removal is characterized by high precision and minimal trauma, which prevents the formation of pronounced scars on the skin;
- Laser beams have a bactericidal effect, so the risk of infection in the surgical wound is minimal.
What to do before surgery
For the diagnosis of neoplasms and dynamic monitoring of them, ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the pelvic organs with Doppler measurements using a transvaginal sensor is preferable. It is recommended to study the concentration of tumor markers in blood serum (CA-125 and HE4). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) provide more informative images of the pelvic organs.
The patient passes the clinical minimum and is admitted to the hospital. On the eve of the operation, the woman must shave the hair growing in the groin area. She is given consent for medical intervention, which contains information about possible complications.
Complications of ovarian cysts
Frequent complications that occur due to ovarian cysts include:
- Ovarian cancer. Each benign ovarian cyst can transform into a malignant neoplasm;
- Necrotic changes in ovarian cysts. Very often, an ovarian cyst undergoes twisting in the projection of its pedicle, the clinical manifestation of which is severe pain. In practical surgery, this condition is called “acute abdomen.” Pain occurs due to poor circulation in the ovarian area, resulting in necrosis of the cyst. Against the background of a necrotic process in the ovary, inflammation of the peritoneum, or peritonitis, may begin. With the development of such a pathological condition, there is a risk of removing the entire ovary. Severe and prolonged course of ovarian cysts can lead to the impossibility of conception - infertility;
- Rupture of the cyst capsule. With the development of this complication, massive bleeding into the pelvic cavity is observed. Clinically, this condition is characterized by severe pain localized in the lower abdomen. The pain may often radiate to the rectum and be accompanied by nausea and dizziness. Rupture of the cyst capsule requires urgent surgical treatment.
Indications for ovarian cyst removal (cystectomy)
- The presence of an ovarian cyst on the left or right side .
- Lack of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
- The cyst should be mobile, movable, small or medium in size.
- The tumor marker CA-125 must be in an acceptable, non-pathological concentration.
- A pelvic ultrasound should reveal a single-chamber homogeneous cyst. Any inclusions are not allowed. The cyst wall should not be rough, the contours should not be blurred.
Diagnosis of ovarian cyst
A woman alone, without the help of specialists, will not be able to identify such a pathology in her body. This is explained by the fact that the formation of an ovarian cyst often passes without any clinical manifestations. For example, cases have been described in which women did not even experience menstrual irregularities due to cysts. Only a small percentage of women could complain that menstruation lasts longer than before and is accompanied by pain. Most women think that such violations are a variant of the norm and do not pay attention to them. The main method for diagnosing ovarian cysts is ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
Laparoscopic method
Endoscopic removal of the cyst is the least traumatic. Before choosing a laparoscopic approach, it is necessary to ensure that there is no malignant process.
Indications for cyst removal using laparoscopy are any ovarian cysts, provided cancer is excluded and the tumor is relatively small. The operation takes place under general anesthesia. Usually 3 holes with diameters up to 10 mm are made.
An endoscope is used to view the organs. The ovary is held and fixed in the most convenient form for access to the ligaments. Where the contours of the cyst are most clearly visible, an incision is carefully made so as not to damage the contained follicles. It is advisable to remove the cyst without damaging its capsule so that the contents do not get on healthy tissue. The contents are removed into a special container so that it does not spill inside the body during extraction. Bleeding from small damaged vessels is stopped using an electric coagulator. In this case, it is permissible to leave the ovary itself without stitches, or they can put a couple of stitches.
Sometimes the contents are aspirated using a needle to facilitate removal of larger cysts. Then a camera is inserted into the hole and the cyst is examined from the inside. If the examination of the inside of the cyst is satisfactory, the incision made is subjected to coagulation. Then they separate what remains of the cyst and the ovary.
Features and effectiveness of enucleation of ovarian cysts
Enucleation of an ovarian cyst is one of the types of cyst removal. This procedure involves dissecting the ovarian tissue, leaving the organ itself intact. It is important to note that enucleation of the formation is carried out only if the tissue of the ovary is not affected by the disease.
The procedure is indicated for functional cysts that do not resolve over several months, for formations whose size exceeds 8 centimeters and have pronounced symptoms, as well as for bilateral tumors.
This operation is only effective for women of childbearing age. During this procedure, small incisions are made in the abdominal wall through which trocars are inserted. This allows the doctor to monitor the progress of the operation on a large screen.
Enucleation involves the separation of the tumor capsule from the organ tissue. The surgeon uses small scissors and a clamp to do this. If blood vessels are damaged during surgery, they are cauterized with a coagulator. In order to reduce the trauma of the procedure, the doctor can use a laser or radiofrequency scalpel, which reduces the likelihood of inflammation or bleeding.
After surgery, the wounds must be sutured. A woman can move around the ward after just a few hours. She is discharged after a couple of days. A week later, the patient must come to the hospital where her stitches will be removed. If a woman experiences pain after surgery, the doctor prescribes antibiotics and painkillers.
We recommend learning: Cystectomy of an ovarian cyst and What is ovarian drilling
Laparotomy method
The anterior abdominal wall is treated with antiseptic substances. The incision is made more extensive according to Pfannenstiel. This cosmetic incision is made inconspicuous after the postoperative wound has healed. Using a scalpel, an incision is made 3-4 cm above the pubic symphysis along the suprapubic skin fold with an average length of 11 cm. At the same time, the skin and subcutaneous fatty tissue are dissected. Vessels that begin to bleed are treated with an electric coagulator.
The aponeurosis is carefully cut and separated using scissors so as not to touch the muscles. Next, the fibers of the rectus abdominis muscle are separated and the peritoneum is opened.
The Pfannenstiel laparotomy incision provides convenient access for enucleation even for large ovarian cysts. After removing the cyst, the tissue is sutured in layers and suturing is performed.
What types of cysts can be removed with laser?
It is possible to accurately determine the most optimal method of cyst removal only after a thorough examination. In each individual case, the surgeon chooses a surgical intervention method that corresponds to the type of cyst, size and location, and also takes into account possible complications. Not all pathologies are amenable to laser therapy, but most diseases with “plus tissue” syndrome (growths diagnosed as new tissue) can be treated with laser radiation.
There are also some contraindications for laser cyst removal, which do not depend on the type of formation. In particular, laser treatment of cysts is not used in the presence of malignant tumors of internal organs or skin cancers, diseases of the nervous system accompanied by increased excitability, acute infectious and viral diseases, or a febrile state. In addition, in patients with angina pectoris, severe heart rhythm disturbances, diabetes mellitus, hypertension and some other diseases, laser therapy is used with caution.
Postoperative period
2 hours after the operation, the patient can drink fluids, eat food, and with a relatively satisfactory condition and a laparoscopic incision, she is allowed to get out of bed to go to the toilet. After the enucleation of the cyst has been successful, the woman is discharged home on the 2nd day after surgery. After discharge, if indicated, the patient takes painkillers and antibacterial agents. Full bathing is allowed 1 week after surgery.
If the work of the operated patient does not involve heavy physical labor, after 2 weeks from the day of the operation, she can receive a certificate of temporary disability. You should refrain from lifting weights and heavy physical work for at least 2-3 months. Sexual rest after enucleation of the cyst is necessary for 4 weeks.
If necessary, the gynecologist prescribes hormonal medications that will need to be taken for 3 to 6 months.
After 1 month, the patient will need to undergo an examination by her gynecologist and examine the pelvic organs using an ultrasound. The next ultrasound and visit to the doctor should take place 3 months from the date of surgery, and then six months later. After this, the woman needs to undergo a preventive examination with pelvic ultrasound once every 6 months.
Important! Pregnancy should be planned no earlier than 3 months after the cyst has been removed.