Modern medicine has become a leading field, taking as a basis the diagnosis and treatment of quite complex diseases. Experts have learned to recognize various pathologies that previously resulted in death.
If we talk about gynecology, then this area of science is not in last place. Thanks to a number of diagnostic tests, today it is possible to prevent the development of such a terrible disease as cervical cancer. With the advent of the Pap test, it became possible to detect cancer 4 times more often in the fairer sex, thereby reducing the mortality threshold.
Many women do not understand how important it is to undergo regular gynecological examinations and not ignore the cytological smear (PAP smear) in the diagnosis. Often girls are stopped by fear of the unknown. But these are completely unfounded fears. In order to understand in detail what the affected manipulation is, it is worth more clearly describing what it is.
PAP test, what is it?
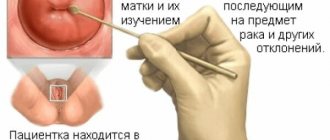
This procedure is a screening test that is performed on every woman over 21 years of age during a visit to the gynecologist for the purpose of a preventive examination. To do this, the doctor takes a smear from the cervix and cervical canal. Samples of the resulting material are applied to a glass slide and sent to the laboratory for staining of the material, as well as further examination.
Pap test - detection of precancerous or cancerous cells in the vagina and cervix
The diagnostic procedure is named after its founder Georgios Papanicolaou test, Pap test or Pap smear. Thanks to his work, laboratory assistants can examine any cells, but they use the technique more often in gynecology.
What is a cytology smear in gynecology?
Georgios (George) Papanikolaou is a Greek scientist and pioneer of cytology.
He spent most of his professional life in the USA, where he developed the field of early diagnosis of cancer. A doctor back in 1928 argued that a cytology smear is useful in identifying cervical cancer at the very beginning of the process.
The pioneering scientist's colleagues considered the work unfounded and refused to publish it. Later, the Pap smear became known as the main method for early diagnosis of cervical cancer.
Today, there are international standards that require regular examination with a Pap smear or Pap smear.
A cytology smear should be done annually from the age of 21. If, based on the results of three years, the condition of the epithelial tissues of the cervix is consistently good, then the study can be carried out every two to three years.
After the age of 65 (provided you have had good cytology smears within the last ten years), you can stop taking the Pap test.
An annual cytology smear should be done if a woman is at risk - she suffers from immunodeficiency, has undergone chemotherapy or organ transplantation, or is constantly taking steroid medications.
In Russia, the tradition of self-medication is deeply rooted, and prevention and diagnosis are at an extremely low level.
Therefore, domestic doctors refer for a cytological smear at every opportunity - during pregnancy or planning it, when contacting a gynecologist about an irregular menstrual cycle.
Cervical cancer is one of the most common malignant diseases among women. Women aged 35–55 years are at risk.
Earlier and later cases of the disease are relatively rare. It is better to do a smear for cytology occasionally than not at all.
Malignant formations in the cervix respond well to treatment if detected in a timely manner, possible thanks to a cytology smear.
Even if a single smear may give an inaccurate result, regular testing is the key to confidence.
Many women do not want to undergo a cytology smear, citing its inaccuracy. Indeed, when performing a Pap smear, too much depends not only on the professionalism, but also on the experience and intuition of the doctor.
This does not mean that it is useless to take a smear for cytology; on the contrary, if you do it regularly, then changes in the cervix can be observed over time.
Cytology helps determine erosion (dysplasia) of the cervix, however, these diagnoses have not existed in the global medical space for decades.
https://youtu.be/d106CGDP0LU
Domestic doctors not only use them, but also indiscriminately call them precancerous conditions. In combination with HPV (human papillomavirus), cervical erosion from the lips of a doctor almost sounds like a death sentence.
Frightened by the prospect of cervical cancer, women agree to any treatment offered by the doctor.
In many cases, cervical erosion is generally diagnosed by eye during a gynecological examination.
In this case, the doctor sees only redness of the tissue of the cervix, which can have many causes, at least 50% of which are ectopia - a normal physiological condition of many women of childbearing age.
Every patient should know that if the doctor’s speech refers to her with the word “cancer” based on the results of only a visual examination, then this is a signal that the doctor needs to be changed.
All precancerous conditions are a laboratory diagnosis, which must be confirmed by cytology (smear or biopsy).
Changes in the structure of the epithelium (intraepithelial neoplasia) detected as a result of a cytology smear have three degrees:
- mild – in 90% of women it goes away on its own and does not require treatment;
- intermediate-moderate degree requires observation by a doctor, and in special cases treatment;
- severe - can become malignant, requires treatment and regular cytology smears.
HPV is another doctor's bogeyman, the result of global panic over the discovery of a link between some forms of the virus and some types of cancer.
Only a few types of HPV have oncogenic activity, but each type has subtypes that are not related to oncology.
HPV refers to viruses that the human immune system can cope with on its own. True, this does not happen in seven days, as in the case of the flu, but in 3 to 18 months.
There is no cure for HPV, just like for the flu. Therefore, if a doctor scares you about HPV and insists on treatment, then he is, to put it mildly, exaggerating. Many doctors are so confused that the HPV vaccine is called the cervical cancer vaccine.
Menstrual irregularity (hormonal imbalance) is another concept in gynecology, which, even with a stretch, can hardly be called a diagnosis.
Cytological analysis in gynecology refers to microscopic examination of samples taken from the vagina and cervical canal to determine the typical cellular composition.
This diagnosis allows doctors to draw conclusions about the presence of inflammatory processes, precancerous diseases or cancer in the patient’s reproductive organs.
https://youtu.be/A1vPFeGszDc
Unlike histological examination, the cytological method is non-invasive. That is, when taking biological material there is no need to perform a biopsy or puncture, and the integrity of the tissue is not compromised at all.
Samples taken using a fingerprint or swab are analyzed. To obtain accurate results, you must carefully follow the rules for preparing for the examination.
Cytological analysis usually takes no more than a day to complete. If a precancerous condition or an oncological process is discovered, invasive diagnostic techniques are used to clarify the diagnosis - biopsy.
Cytology is especially important when biopsy is contraindicated and when examining a large number of patients (when it is necessary to identify women at risk for developing malignant pathology).
— Inflammation in the cervical canal, cervix, especially if they occur chronically.
— Menstrual cycle disorders.
- Reproductive problems.
— Preparation for surgical interventions and other medical procedures.
— Planning pregnancy.
— Preparation for installation of the spiral.
— Taking hormonal drugs.
- Diabetes.
— 2nd and 3rd degree obesity.
— The presence of certain viruses in the body (human papilloma, genital herpes).
READ MORE: Cytology of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
- Frequent change of sexual partners.
Cytology smears are not taken during menstruation. If you need to evaluate the presence of atypical cells, you should not conduct the analysis during inflammation of the vagina and cervix.
The cervix of a healthy woman is covered with columnar epithelium, and the vagina is flat. As for the vaginal microflora, it is not cocci, but rods.
Some indicators depend on the phase of the cycle - karyo-pyknotic and acidophilic indices, basal and parabasal cells, the number of leukocytes. They provide information about the functioning of the ovaries.
Class 1. Absence of pathological changes in the examined material. The cells are of normal size and shape and are correctly located.
Class 2. The morphological norm of some cellular elements is reduced, which is a sign of inflammation or infection. This result may be a sign of vaginosis.
Class 3. The material contains single cells with disturbances in the structure of the nucleus and cytoplasm (dysplasia or hyperplasia). The number of such pathological cells is small. The patient is sent for repeat cytology.
Class 4. The examined smear reveals cells with malignant changes in the nucleus, chromatin and cytoplasm. These pathological changes indicate that the patient has a precancerous condition.
Class 5. The presence of a large number of atypical cells in the smear (they are much more than normal). In this case, the initial stage of cancer is diagnosed.
- Normal. The absence of pathology does not have any special designation.
— Vaginosis, koilocytosis – HPV.
- Cervical dysplasia depending on the degree - CIN I, CIN II or CIN III.
— Cervical cancer — Carcinoma (pax).
— CBO. Normal indicators, no pathological changes.
- Cytogram of inflammation. Indicators indicating the development of the inflammatory process (cervicitis).
— Leukocyte infiltration – increased number of leukocytes. This is a sign of vaginosis, exocervitis or endocervitis.
— Koilocytes – the presence of cells indicating HPV.
— Proliferation – acceleration of cell division. This condition is typical for the inflammatory process in the uterus. With strong proliferation, advanced inflammation occurs.
— Leukoplakia – the smear contains pathologically altered (but not cancerous) cells.
Why is a Pap smear performed?
A cytological examination is carried out to identify abnormalities in the structure of the cells of the cervix and vagina. In order to detect malignant tumors in time, you should not neglect the diagnostic procedure, if only because health should always come first.
Do not forget that cancer can progress over a short period of time, and this can lead to its metastasis and inoperability of the tumor. This is why it is so important for women to have a smear, which helps diagnose any pathological changes in the structure of cells at an early stage of the disease, and also enables patients to begin timely treatment.
After the Pap smear procedure
The time it takes to receive your smear results varies from clinic to clinic, your doctor will tell you when to come get your results.
Negative or normal test results mean that the cervix appears healthy and is of a healthy shape and size.
Positive or abnormal smear results mean that something is unusual in the sample, with abnormal cells of varying sizes and shapes found.
An abnormal Pap smear result does not always mean cancer. The cells sometimes appear abnormal but are not cancerous. The woman will have to return to the clinic for follow-up examination. Remember that abnormal cells do not always become cancerous, but some factors (such as HPV detection) are more dangerous than others. Cervical infections may result in positive test results. Yeast, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, or gonorrheal infection can cause inflammation in the cells of the cervix. Once the infection is treated, the Pap smear result usually returns to normal. Human papillomavirus (HPV) can also make a smear test positive. This virus can live on the cervix or vagina and causes genital warts. Many types of HPV have been identified, and some are associated with cervical cancer. If a woman has HPV, she has a higher risk of developing cervical cancer. The smear test may be positive because it shows changes that could develop into cervical cancer. If a woman has an abnormal repeat Pap smear result, smears should be taken by a doctor every 4 to 6 months for 2 years until 3 consecutive negative tests are obtained. If a positive Pap test is due to an infection, the underlying cause must be treated. PAP - The test should be repeated within 2-3 months because cervical cancer may be hidden by infection. Although the Pap smear is the best method for early detection of cervical cancer, it is not perfect because even the best laboratories may miss some cellular changes; a woman should have a pap smear every year. Recently, 2 computerized systems (PAPNET and AutoPap) have been approved in the United States for the detection of abnormal Pap smear cells. To ensure the accuracy of the tests, they use computer technology to double-check Pap smears, in which abnormal cells may not be detected by the cytologist. These tests are more expensive than the cost of a normal Pap smear, but they may be useful if a woman is at high risk of developing cervical cancer. Talk to your doctor about these methods.
Goals and indications for laboratory testing
The goals are understood as diagnostics of the reproductive system and quality control of treatment results. Any type of research is carried out for medical reasons. Often a woman undergoes a smear for cytology in the following cases:
- during or after treatment;
- when diagnosing infertility;
- while using hormonal contraception;
- with frequent changes of sexual partners;
- with human papillomavirus infection and detection of genital genital warts;
- during periods of frequent infectious diseases of the reproductive system;
- during a preventive examination.
Diagnosis of women's health using the cytological smear method.
Risk group
Women at risk should undergo a gynecological examination and undergo a cytological smear once every six months. Persons at risk include:
- those who started sexual activity early;
- having multiple sexual partners;
- women with a medical history of viral and latent infections;
- ladies with a history of cancer of the reproductive system;
- lovers of bad habits (smoking, alcoholism);
- with a hereditary predisposition to cancer.
When is the best time to get tested?
The period recommended for screening begins on the fifth day of the menstrual cycle and ends 5 days before the expected start date of menstruation. Do not forget that any physiological processes in the vagina during bleeding may indicate the presence of a disease. That is why situations arise when material is collected regardless of the recommended period, but this is done only as prescribed by a doctor.
Screening is not performed for women who have had a hysterectomy and who have not had cervical cancer in the past 20 years.
Are there any contraindications for taking a smear?
This study has no contraindications. However, it is not performed if patients have cervical inflammation, since the test result will be incorrect.
2.What increases the risk of an abnormal test result?
According to statistics, the risk of becoming infected with the human papillomavirus is higher in those people who have more than one sexual partner (or a partner who, in turn, has other sexual partners). There is also a risk of infection associated with having sex without a condom, especially if the first condition is present. And the risk of HPV infection automatically increases the risk that after the next smear from the cervix, the test results will show a deviation from the norm.
In addition, smoking and disorders of the immune system increase the chance of developing abnormal cells in the cervix.
Visit our Gynecology page
Table with recommendations for different age categories for performing a Pap smear
| Recommended group of people | Recommendations for screening frequency |
| Age category 21-29 years | Every 3 years, carry out a smear for cytology |
| Age category 30-65 years | Every 3 years, carry out a cytological smear, or every 5 years, do a test for the presence of papillomavirus along with a cytological smear. |
| Age category over 65 years | Completion of the study in the absence of positive test results. |
Preparation for a smear for cervical cytology
- Shape of the epithelium.
- Papanicolaou class 1 - normal cytological picture (healthy)
- Papanicolaou class 2 - changes in cell morphology. As a rule, this is directly related to the inflammatory process in the vagina or inflammation in the cervix. It is necessary to find out the causes of inflammation. After treatment, the smear result returns to normal.
- Papanicolaou class 3 - single abnormal cells are detected (anomaly of nuclei or cytoplasm). In this case, colposcopy and histological examination of tissues are additionally performed.
- 4th class - individual cells were identified in which signs of malignancy were clearly expressed. Only in this case is there a suspicion of cancer. Further studies are carried out by a gynecological oncologist.
- Class 5 - a large number of typical cancer cells (cancer) are detected.
Different clinics use different Pap smear scoring systems. Along with the Pap test, the Bethesda scoring system is common. Using our table, you can compare Papanicolaou classes and the results of the Bethesda system and independently decipher the result of a cytology smear.
A positive smear does not always mean a malignant neoplasm.
Atypical cells can appear for the following reasons - the presence of inflammation - chlamydia, herpes, gonorrhea, etc., as well as human papillomavirus. With this result, treatment is carried out and the smear is repeated after 3 months.
Stage 1: there are no cells with any abnormalities, a normal cytological picture is observed. This stage is typical for completely healthy women.
Stage 2: there are slight changes in the structure of cells, however, due to the inflammatory process of the internal genital organs. This stage is also the norm, but at the same time, the doctor will definitely recommend you a more thorough examination to identify the causes of inflammation and eliminate them.
Stage 3: there are cells with abnormalities in the structure of the nuclei, but their number is extremely small. In this situation, it is necessary to take a second smear or conduct a special histological examination of the changed tissue.
Stage 4 - Individual cells with clearly malignant changes (such as increased mass of cell nuclei, changes in chromosomes and cytoplasm) can be detected.
Stage 5 - a large number of typical cancer cells are observed in the smears.
The reliability of vaginal cytological smears (Pap test) is high when it comes to changes in the cervix. However, this test does not say anything about the condition of the uterus, ovaries or fallopian tubes.
And in 20-30% of cases, the Pap test gives false negative results. A guarantee of reliable interpretation of data is provided only by a comprehensive examination (colposcopy of the cervix, biopsy of the mucous membrane, etc.).
Most laboratories in the United States use a standard set of terms called the Bethesda classification (cervicovaginal cytology diagnosis) to report or interpret Pap smear results.
According to the Bethesda classification, Pap smear samples that do not have abnormal cells are interpreted as "negative for an intraepithelial or malignant lesion" (that is, women do not have cancer).
Specimens with cellular abnormalities are classified into the following categories (as outlined by the National Cancer Institute): ASC (atypical squamous cells): Squamous cells are thin, flat cells that form the surface of the cervix.
https://youtu.be/URhiUJkJldw
The Bethesda system divides this category into the following 2 groups: ASC-US (atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance): The squamous cells do not appear completely normal, but doctors are not sure if the changes mean cancer.
Sometimes these changes are associated with HPV infection. ACS-US is considered a soft anomaly. ASC-H (atypical squamous cells; squamous intraepithelial lesions cannot be ruled out): The cells are not normal, but doctors are not sure if the changes mean cancer.
ASC-H often indicates a precancerous condition. AGC (atypical glandular cells): Glandular cells are mucus-producing cells found in the endocervical canal (in the center of the cervix) or in the lining of the uterus.
The glandular cells are not normal, but doctors are not sure what the cellular changes mean. AIS (endocervical adenocarcinoma): precancerous cells in glandular tissue.
LSIL (low grade squamous intraepithelial lesions): Low grade means there are some early changes in cell size and shape.
The word lesion refers to an area of abnormal tissue. Intraepithelial refers to the layer of cells that form the surface of the cervix. LSILs are considered minor abnormalities resulting from HPV infection.
HSIL (high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions): High-grade means that there are more noticeable changes in the size and shape of the abnormal (precancerous) cells, that is, the cells are very different from normal cells.
Early stages of cervical precancer and cancer often have no signs or symptoms. Therefore, it is very important to have regular Pap smears.
If you experience the following symptoms, consult your doctor immediately:
- Unusual vaginal discharge
- Blood stains or light bleeding outside of your normal period
- Bleeding or pain during sex
These symptoms do not clearly indicate cancer; other factors may cause these symptoms, but testing is necessary to determine the cause. If the Pap smear result is normal, the woman will continue with routine screening.
If her Pap smear result is atypical (could not be classified as normal or abnormal), a repeat smear should be done after 4 months.
If the repeat test is abnormal, the doctor will do a colposcopy. During this test, the doctor looks at the cervix through a colposcope (a special microscope) instrument, looking for an explanation for the abnormality in the Pap smear.
It doesn't hurt at all and has no side effects. It is possible to perform this procedure during pregnancy. If there are abnormal cells on the cervix, the doctor will perform a biopsy (taking a tissue sample to look at under a microscope).
If a woman's smear result is abnormal, a colposcopy and biopsy should be performed immediately. A biopsy is the only way to determine whether a precancerous condition is cancerous or not.
Several types of biopsies are performed under different types of anesthesia. To treat precancerous tissue or very early stage cancer, the doctor may remove the abnormal tissue entirely during a biopsy.
If the biopsy and Pap test results are normal, the Pap smear should be performed again after 4 months. If the biopsy is normal but the Pap test is abnormal, the doctor will repeat the colposcopy and biopsy.
Useful tips
READ MORE: Cytology what is it in animals
1. All women who are sexually active or over 19 years of age are recommended to undergo a gynecological examination once a year with a cytological analysis of the Papanicolaou smear (Pap test).
After receiving a negative result twice, you can undergo this test less frequently - once every three years, until you reach age sixty-five.
2. If you use hormonal contraceptives or have had genital herpes, it is recommended to undergo the following test - a Pap test twice a year.
3. Infertility, uterine bleeding, overweight (obesity), genital herpes, genital warts, frequent changes of sexual partners, taking estrogen hormones are factors for more frequent cytological smears.
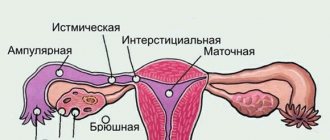
So, the cervix is a narrow tube, which at its outer end opens into the vagina, thereby communicating with the uterine cavity. The outside of the cervix is covered with stratified squamous epithelium (consists of four layers of different cells), and the inside is covered with columnar epithelium, which is a single row of cylindrical cells.
The PAP test in gynecology is used to study the structure of cells that are located both inside and outside the cervix. In essence, this procedure is a scraping with further cytological examination of the resulting samples.
By the way, this procedure is often called a Papanicolaou smear in honor of the Greek doctor who first began conducting such studies in the 50s of the 20th century. There is another name for the test - “cervical cytology”.
- Cytological sampling is carried out in the first few days after the end of menstruation - this is the only way to count on reliable results.
- Two days before the procedure, doctors recommend stopping the use of intravaginal medications. The use of vaginal lubricants and spermicidal contraceptives is contraindicated. All these means can distort information about the true structure of the cells of the uterine cervix.
- Also, scraping should not be performed if the patient has signs of an inflammatory/infectious disease of the genital organs, for example, itching, uncharacteristic vaginal discharge. In such cases, you first need to determine the cause of the symptoms and undergo a full course of treatment. Only after complete recovery can the procedure be performed.
- Type I. The results correspond to the norm; no pathological features were found in the studied material.
- Type II. An inflammatory process takes place. Possible hyperplasia and proliferation of glandular epithelium.
- Type III. Suspicion of cervical dysplasia.
- Type IV. Suspicion of cancer.
- Type V. There is a high probability of having cervical cancer.
Of course, such results only provide information about the possible presence of a particular pathology. To make an accurate diagnosis, additional research is necessary.
How to prepare for research?
There is no special preparation for taking a cytology test. However, there are general recommendations that must be followed 48 hours before the procedure:
- you should refrain from sexual relations with your partner;
- it is necessary to exclude the use of vaginal suppositories (suppositories) and vaginal creams;
- It is not recommended to douche and take a bath;
- you need to give up sanitary tampons;
- You should not skip other diagnostic tests.
How the procedure is performed
Before the medical procedure begins, the woman must undress (remove everything below the waist) and lie on the edge of the gynecological chair. The doctor then inserts a speculum into the vagina and provides a good visual view of the cervix. If there is discharge from the uterus, the gynecologist cleans the cervix with a tampon.
Material for research is collected from several areas. This:
- vaginal vaults;
- outer surface of the neck;
- cervical canal.
The collected material is placed on a glass slide and fixed with alcohol, or a special test tube with an alcohol solution is used.
What to avoid after the test
After a medical procedure, a woman is advised to adhere to several recommendations to prevent the development of complications:
- you should avoid taking a bath for 5 days after screening;
- you need to abstain from sexual intercourse for up to 5 days;
- It is necessary to abandon vaginal suppositories, creams and douches.
Possible complications
Complications after screening rarely occur, since the diagnostic procedure is minimally invasive and specialists use sterile instruments. However, it should be remembered that exceptions to the rules are possible, such as:
- bloody discharge of low intensity;
- infection.
Obtaining diagnostic results
Receipt of hand test results may vary depending on the health care facility where the woman was screened. In public hospitals, waiting times can range from 1 to 2 weeks. In modern clinics and medical centers, equipped with the latest technology, you can pick up the results of a PAP smear the very next day.
Having received the results in hand, the woman should contact her gynecologist in order to find out the Pap test decoding. It is possible to read and understand what the screening results indicate on your own, but there are fears that if interpreted incorrectly, the patient will miss valuable time.
Why is a Pap test prescribed, how is it performed, interpretation of the analysis
Papanicolaou testing has a number of indications.
This is a screening smear that is taken from every woman in the examination room. The test is often used for rapid diagnosis in women over 30 years of age. Among the most common indications for Pap testing for HPV are:
- undergo an annual examination for early detection of cervical epithelial dysplasia and prescription of therapy;
- after a course of treatment for STDs;
- immunodeficiency conditions and chronic gynecological pathology;
- cervical erosion, which may affect the likelihood of HPV infection;
- family history of cancer of the reproductive organs.
Before conducting the study, you must inform your doctor about taking hormonal medications or oral contraceptives.
Among the general principles of preparing for a Pap test for HPV are:
- hygiene procedures on the day of analysis without the use of soap and gels with fragrances;
- 48 hours before the smear test, refrain from sexual intercourse;
- do not douche;
- do not use tampons or vaginal suppositories for several days;
- You cannot take a smear during menstruation or non-cyclical bleeding, the result will be inaccurate or false negative.
On the day of the Pap test procedure, the patient undergoes the following manipulations:
- the woman lies down in the gynecological chair;
- a speculum is inserted into the vagina for a complete view of the transition zone and pharynx of the cervix;
- the cervical area is first cleaned with a sterile cotton swab;
- a cervical spatula with a brush is inserted and epithelial cells are layered in a circular motion, including those with condylomas due to HPV;
- the material is placed on a glass slide.
Used in gynecology, the Papanicolaou smear is a simple, painless test that is used to diagnose endometrial and cervical cancer. It is based on the work of George Papanicolaou, who discovered that cancer cells shed into vaginal secretions.
Every year, 500 thousand women are diagnosed with cervical cancer worldwide. Over the past 30 years, the incidence has decreased by more than 2 times. This is largely due to the widespread use of screening cytological examination.
The mainstay of early detection of cervical cancer in large populations for the last 60 years has been the Papanicolaou smear.
What is a Pap test (also called a Pap smear)?
This is an exfoliative cytological procedure with staining of the resulting material.
In other words, a Pap smear is a scraping of the tissues of the superficial layer of the cervix and examination of the resulting cells under a microscope after treatment with special dyes.
The method is also used to detect cancer of the bladder, stomach and lungs. Any body secretions (urine, feces, sputum, prostate secretions), as well as biopsy material, are suitable for it.
However, the Pap smear is most often used to diagnose the early stages of cervical cancer.
The material is taken from the transition zone of the cervix, where the columnar epithelium of the cervical canal borders the squamous stratified epithelium lying on the vaginal part of the cervix.
The resulting sample is placed on a glass slide, stained, and examined under a microscope to look for abnormal or malignant cells.
What does it show?
It detects precancerous and malignant changes (cancer) of the cervix. In a few minutes, the analysis can detect cancer of the uterus or its cervix at a stage when the tumor is not accompanied by external changes and damage to surrounding tissues. At this time, the malignant neoplasm is successfully cured.
Liquid cytology based Pap test helps in detecting Human Papilloma Virus. At the same time, additional research is being carried out to identify the DNA of the virus. This pathogen is a major risk factor for the development of cervical cancer. When using the liquid cytology method, the material is placed not on a glass slide, but in a test tube with a liquid preservative.
A smear for the human papillomavirus is prescribed in case of doubt about the results of a cytological examination. Both traditional analysis and liquid-based cytology have equal diagnostic effectiveness. Both of these methods can be used in practice.
Although the interpretation of results largely depends on the qualifications and experience of the doctor, there are objective ways to improve diagnostic accuracy. Thus, special computer programs are being developed. Some clinics retest some swabs for quality control.
Much depends on the woman’s proper preparation for the study.
Preparing for the test
The analysis is carried out during a routine examination by a gynecologist. You should tell your doctor about any contraceptives or other hormonal medications you are taking.
Special preparation for the Pap test:
- refrain from vaginal intercourse for 48 hours before the test;
- at the same time, do not use vaginal tampons, douche, or use medications or contraceptives inserted into the vagina;
- It is advisable to first treat cervicitis, if present.
Pap test, in other words Pap smear
On what day of the cycle should I take the test?
There are no special restrictions. The only condition is the absence of menstrual or other uterine bleeding. However, the analysis can be taken even during menstruation, but its accuracy is reduced.
If a woman has bleeding or cervicitis (inflammation of the cervix), this is not a contraindication for the study. These symptoms may be caused by precancer or malignancy, which can be detected during screening.
Indications
For timely diagnosis of malignant tumors, a simple method that has no contraindications is needed. A cervical Pap test is a screening test that allows most women to be examined regularly.
According to the latest recommendations of the American Cancer Society and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the test should be performed starting at age 21, regardless of the onset of sexual activity.
Table. When is the best time to do a Pap test?
HPV vaccine
Some women have a higher than average risk of developing cancer. They may need more frequent testing.
At-risk groups:
- women infected with HPV or HIV;
- survivors of chlamydia and sexually transmitted diseases;
- patients with weakened immune systems;
- early onset of sexual life;
- multiple sexual partners;
- having cervical dysplasia;
- smoking or drug use.
A Pap test during pregnancy is mandatory to exclude infections and precancerous diseases. It does not pose any danger to the expectant mother and baby.
How is it carried out?
To carry out the analysis the following are used:
- gynecological chair and lamp;
- metal or plastic vaginal dilator;
- examination gloves;
- cervical spatula and special brush;
- test tube or slide.
How is a Pap smear performed?
The patient is positioned on a gynecological chair. Her tailbone should be at the edge of the chair to ensure a good view when inserting the dilator.
A speculum is placed into the vagina. It is first recommended to warm it in warm water for the woman’s comfort. Some clinics use a small amount of special lubricant if necessary to facilitate insertion of the dilator.
The surface of the cervix should be completely open and thoroughly examined by the doctor. It is necessary to visualize the squamous epithelium, transition zone and external os. The transition zone is the area where squamous epithelium transforms into glandular epithelium. HPV affects this area. Therefore, cell selection is carried out in this zone. In addition, material is taken from the surface of the cervix and from the area of the external pharynx.
If necessary, the cervix is cleaned of secretions with a soft swab. The material is taken with a spatula or a special brush, turning them around its axis.
Depending on the equipment used, the resulting material is either placed in a special solution, which is in a test tube, or on a glass slide, onto which a fixative is then applied and placed in an alcohol solution.
The study is completed within a few minutes. It's painless. After the analysis, it is better to avoid sexual intercourse, use of tampons and douching for 5 days.
Can I take a bath after a Pap test?
It is recommended to do this no earlier than 5 days after the procedure.
Adverse effects from a Pap smear are very rare. The woman should be warned about the possibility of light bleeding. This is fine. Another complication is the addition of an infection. However, its likelihood is very low, since the procedure does not damage blood vessels and sterile instruments are used.
Although the Pap smear is one of the best screening methods, it has its limitations. The sensitivity of a single Pap test in detecting cervical dysplasia averages 58%.
This means that the existing disease will be detected in only half of the women who actually have it.
HPV testing has higher sensitivity. In the group of women over 30 years of age, it allows diagnosing dysplasia in 95% of cases. However, in younger women such analysis becomes less informative.
results
If the results of the Pap test show the presence of abnormal cells, the patient is scheduled for colposcopy. This test helps detect precancerous and malignant changes through a biopsy - removing a piece of tissue for microscopic analysis. If a precancerous disease is detected and treated in time, this will save the patient from cancer.
How many days does the analysis take?
The result is ready in 1-3 days; when using automatic analyzing systems, the time to obtain the result is reduced. In some public clinics, the waiting time for results increases to 1-2 weeks.
How many days does a smear cytology test take?
Cytological analysis of a smear usually takes from 1 to 5 days.
It is important to remember that the oncological process does not occur in a few days. Quite a long time passes from the first pathological changes to malignant degeneration.
Therefore, timely detection of atypical cells in a woman’s body makes it possible to prevent the development of cervical cancer. For these purposes, an accessible and simple method for the early diagnosis of malignant cells was introduced everywhere - a cytological examination of a smear.