Glioma, which affects parts of the brain, is a heterogeneous tumor that develops from neuronal precursor cells. This is the most common type of primary malignant neoplasm in the head cavity. The total number of malignant lesions of the central nervous system is 60%.
In photographs it often looks like a nodule with poorly defined, blurred boundaries. It is localized mainly in the area of the optic nerve or ventricles, less often in the brain stem structures. Dimensions range from 2-50 mm. Usually grows slowly with no metastasis process.
Causes of tumor
Scientists have found that neoplasms appear due to the rapid proliferation of immature glial cells.
This is how benign and cancerous gliomas appear. Tumors form in the gray or white matter around the central canal, in the posterior part of the pituitary gland, cells in the cerebellum, or in the retina. Glioma develops slowly from the volume of a small grain to a round body with a diameter of 10 cm. Metastases spread in rare cases.
The exact reasons for the growth of cancerous glioma have not been determined, but scientists are inclined to believe that they lie at the genetic level when the structure of the TP53 gene is disrupted.
It is difficult to treat this disease precisely because it is poorly understood. This tumor has clear contours and affects one area of the brain. Metastases almost never develop.
Symptoms and signs of glioma
Brain tumors are characterized by signs of neuralgia, the shape and strength of which depend on the degree of development of the pathology. The first symptoms of the disease are:
- intense pain in the head area;
- nausea and epilepsy attacks;
- speech disorder;
- blurred vision or complete blindness;
- temporary memory loss;
- thinking disorder.
As the tumor grows, irreversible changes begin to occur in the patients' brains, which affect their behavior. Over time, a person becomes aggressive, irritable and uncontrollable.
The symptoms of the disease depend on the type and degree of development of glioma:
- A tumor in the frontal part of the brain is caused by the appearance of pain on one side of the head, which provokes convulsions during its movements. Atrophy of the optic nerve often occurs, which leads to visual impairment, the appearance of visual and taste hallucinations, and hearing impairment.
- A tumor of the medulla oblongata is characterized by the presence of mental disorders as a result of high intracranial pressure. In this case, vomiting, loss of coordination of movements, development of hoarseness, hallucinations, and paralysis of the limbs are observed.
- Midbrain glioma causes disruption of signal conduction, which leads to paralysis of the limbs and failure of the human motor system. The patient begins to have difficulty oriented in space, and severe dizziness appears.
- Brainstem glioma is the most dangerous, as it compresses structures that are important for the functioning of the body. In this case, the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid is disrupted, which leads to increased pressure inside the skull and the development of hydrocephalus.
- Glioma of the corpus callosum manifests itself in impaired coordination of movements, the upper limbs cease to obey, so the patient is not able to perform simple actions. As a result of nerve damage, he experiences mental disorders.
Malignant glioma is very difficult. In this case, paralysis and constant relapses are added to all of the above symptoms.
Note! Timely diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors allows the patient to live another nine years.
Related tumor entities
Gliomas are tumors of different types depending on the type of cells that have undergone painful changes. Types of tumor formations:
- diffuse astrocytoma - 50% of diseases, it is formed in the white matter - this is a glioma of the brain stem;
- ependymoma occurs in the ventricles – 8%;
- oligodendroglioma – 10%;
- mixed tumors arise in any part of the brain space;
- tumors in the vessels of the brain are rare and affect the walls of the blood vessel;
- neuroma is a benign formation that can degenerate into a malignant tumor that affects the optic nerve;
- a rare type of disease - neuronal glial tumor .
Brain gliomas - classification
Intracerebral glial tumor is, in most cases, an intracerebral primary tumor of the cerebral hemispheres. Sometimes it is localized in the area of the chiasm, the wall of the cerebral ventricle, and nerve trunks, for example, in the optic nerve. Brain glioma rarely grows into the skull bones or meninges, but it is characterized by infiltrative growth, so it is difficult to detect the border between the tumor and unaffected tissues even with a microscope.
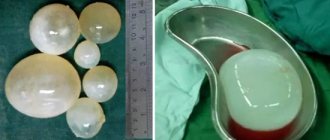
Brain glioma looks like a small round or spindle-shaped tumor of grayish-white or dark red color with a diameter of 2-3 millimeters to the size of a tennis ball. This formation often grows slowly and is characterized by the absence of metastasis, but the development of glioma is accompanied by degeneration of surrounding tissues, which leads to a discrepancy between the size of the tumor and the severity of neurological deficit.
Classification of brain glioma:
- According to the type of glial cells from which glioma grows
- astrocytoma (about 50% of all gliomas), oligodendroglioma (about 10%), ependymoma (5-8%), the rest are mixed, for example, oligoastrocytoma, as well as tumors of unknown origin and choroid plexus tumors. - By malignancy
- I degree (slowly growing benign glioma), II degree ("borderline" glioma, which has one sign of malignancy, often this sign is cellular atypia), III degree (brain glioma has 2 of 3 signs of malignancy - nuclear atypia, figures mitoses or microproliferation of the endothelium), grade IV (glioma has areas of necrosis).
How does a tumor progress and grow?
Stages of disease development:
- The first stage is a non-cancerous, slowly developing lump. It can also be a natural benign glioma. With successful therapy, the patient lives 7-9 years.
- The second stage is the slow growth of the tumor and degeneration into a malignant tumor. Specific signs of a neurological disease are observed.
- The third stage is anaplastic glioma. Symptoms confirm the presence of cancer. Even in the absence of metastases, tumor growth affects neighboring parts of both hemispheres of the brain. The prognosis for survival is from 2 to 5 years.
- The fourth stage is a rapidly growing tumor. The patient usually lives no more than 1 year. This tumor cannot be cured surgically.
Diffuse glioma in young patients is treated radiologically. After a short-term improvement, the disease returns in a more severe form.
Glioma is an incurable disease, the prognosis in any case is disappointing. Excision of the tumor through surgery provides temporary improvement. Then the tumor appears again. All treatment has the goal of reducing the patient's pain and suffering and improving his quality of life. On average, it is possible to extend it for 5-10 years.
Is it possible to prevent the development of glioma?
There is no specific prevention for brain cancer, since the causes that cause it are unclear. Precautionary measures in this case would be regular consultation and examinations with a neurologist if you are worried about unpleasant symptoms from the nervous system or if there are cases of the disease in your family history. To prevent a relapse of an existing disease, you must strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations.
The likelihood of glioma recurrence even after surgery is very high.
Establishing diagnosis
For each patient, the doctor selects an individual treatment strategy.
It is related to the location of the formation, the intensity of tumor growth, and the degree of its malignancy. Examination and treatment are prescribed by a neurosurgeon.
To determine the diagnosis, the following hardware examinations are performed:
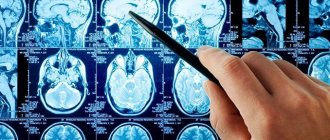
- The most informative method for studying tumor processes is magnetic resonance imaging . It allows you to accurately determine the position of the tumor and its size even at the onset of the disease. This method examines the baby's brain in the womb to identify possible changes.
- Computed tomography allows us to determine the nature of the tumor. A marker is injected into the tissue. It is excreted by healthy cells, but tumor tissues accumulate it.
- Spectroscopy examines the tumor to determine whether further surgery is necessary.
Diagnostics
When making a diagnosis, the neurologist conducts neurological tests, studies the medical history, and prescribes additional instrumental examination. Diagnostics is performed using the following methods:
- MRI and CT of brain structures.
- Biopsy is a sample of tumor tissue.
- Echoencephalography, electroencephalography, vascular angiography, ophthalmoscopy, lumbar puncture are auxiliary diagnostic methods that provide additional information and allow us to clarify the details of damage to brain structures.
Positron emission tomography helps determine the degree of aggressiveness and rate of tumor growth. Neoplasms detected at an early stage are easier to treat.
There is no cure, but life can be extended
Surgery is the most effective way to help patients with glioma. The operation is performed by a neurosurgeon. This is a very complex intervention that requires the utmost precision and skill of the doctor. A doctor’s mistake can lead to disruption of many vital functions, paralysis, and death of the patient.
The tumor is removed using several methods:
- Surgical . Using an endoscope, a video camera and surgical instruments are inserted into the cranial space. Using them, the neurosurgeon removes the tumor. After the operation, a course of chemicals is given. More than half of the cases end in re-intervention.
- Radiotherapy - radiation is used in the initial stages of cancer or after surgery as a preventive measure.
Glioma has genetic causes of formation. Therefore, after surgery, the tumor may form again. The use of genetic engineering drugs can reduce the size of a malignant tumor and facilitate surgery.
These newer drugs target cancer cells, killing them. The size of the tumor does not change, the patient can live longer without pain. Genetic engineering drugs make it possible to avoid repeated surgery.
Be careful, video of the operation! Click to open
As the last hope - alternative medicine
The life of a patient with diffuse glioma causes suffering for the patient and his family. Sometimes folk unconventional methods help prolong life and improve its quality.
Surgery is an extremely dangerous and unpredictable treatment event. The ability to postpone it until later is provided by folk recipes. They do not cancel medical prescriptions, but can alleviate the patient’s condition.
The following methods may help:
- Decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs - collections from sage, hemlock, Caucasian discorea improve blood supply to the brain, make metabolic processes more intense, restoring cell functions.
- Green coffee – removes free radicals from cells, which contribute to the development of cancer cells. It is used for preventive purposes, to reduce benign formations.
- dietary supplements.
Diet
Foods rich in carcinogens have an extremely adverse effect on the composition of the blood. These are fatty, fried and smoked foods. Carcinogens impair blood flow.
Healthy foods include fresh vegetables and fruits, seafood. You should eat in moderation. Smoking and alcohol are prohibited.
Treatment
To treat glioma, like any other cancer, the following methods are used:
- surgical method;
- chemotherapy;
- radiation therapy;
- radiosurgery.
Surgical method
This treatment method is one of the oldest methods of tumor removal. This is an effective method for removing benign tumors, but there is a risk of tumor recurrence due to remaining abnormal cells.
The operation is dangerous due to damage to healthy brain tissue, which will lead to neurological disorders. A malignant neoplasm is characterized by invasive growth, which makes it impossible to remove it without damaging surrounding tissues.
Chemotherapy
This treatment method is not used for benign tumors. This is due to the difficulty of selecting the drug due to the blood-brain barrier. The drugs used for treatment are cytostatics; they block DNA replication in the tumor cell, thereby disrupting its division.
It is possible to use Methotrexate, a substance that disrupts the functioning of the thymidylate synthase complex, which blocks cell division.
The consequences of chemotherapy are such unpleasant symptoms as nausea, vomiting, headache, hair loss due to the effects of the drugs on healthy cells.
Radiation therapy
It can be performed before or after surgery, or can be used independently if surgery is not possible. Its action is aimed at suppressing the proliferation of tumor cells. Consequences may also include nausea, vomiting, headaches, hair loss, and dermatitis.
Radiosurgery
This is an innovative method that can be used to remove even inoperable gliomas. The method involves exposing the tumor to beams of radiation while minimizing the penetration of healthy tissue.
The patient is conscious, and the surgeon controls his actions via MRI or CT, which reduces the likelihood of error to a minimum. The leading technique is cyberknife
Folk remedies
Glioma cannot be treated with folk remedies; they can only support the patient’s condition during medical interventions.
But there are several tips that will help make therapy more effective:
- refusal or reduction of salt intake;
- the use of lotions made of clay diluted with table vinegar, which should be applied to the temples;
- compliance with the regime, a calm lifestyle;
- eating foods rich in potassium, calcium, and magnesium.
Everything is very bad
Glioma is a congenital disease that occurs at the genetic level, so the life prognosis is disappointing. Complete removal of the tumor is impossible. After the operation it increases again.
Repeated surgery can only prolong the patient's life and alleviate suffering. If the glioma is malignant and grows rapidly, the patient does not live for more than a year. If, nevertheless, it is possible to completely excise the tumor with maximum preservation of brain tissue, then almost 80% of patients live more than 5 years.
Surgery in cases of oncology is inevitable and is the preferred method of treatment. Open operations involve craniotomy. Success depends on how accessible the tumor is. If it is possible to remove it without damaging neighboring areas of the brain, then the effectiveness of treatment reaches 90%.
If cancer cells remain in the tissues, after surgery the patient undergoes a course of chemical and radiation therapy.
Symptoms of glioblastoma
At the initial stage of the disease, there are practically no symptoms, so it is difficult to diagnose it in the early period. Pronounced signs are observed when the tumor has already grown significantly and puts pressure on the brain. The first manifestations of glioblastoma are common dizziness and memory impairment. In some cases, the fingertips become permanently numb.
As the disease progresses, cerebral and neurological manifestations develop.
The development of cerebral symptoms is associated with increased intracranial pressure and progression of intoxication. These are the following manifestations:
- Severe headaches that become more intense when the person lies down.
- Constant feeling of dizziness.
- Nausea that has nothing to do with eating; vomiting, after which there is no relief.
- Constant weakness, drowsiness, severe fatigue.
- Deterioration of mental abilities, lethargy.
- Depression , apathy , irritability.
The manifestation of neurological symptoms depends on the location of the tumor. The following signs may be observed:
- Cramps.
- Impaired vision, hearing, speech, smell.
- Decreased sensitivity or paralysis of the limbs.
- Auditory and tactile hallucinations
- Movement coordination disorder.
- Respiratory depression.
Since neurological symptoms are similar to those of a stroke , this may be the reason for an incorrect diagnosis.
Unfortunately, in the later stages, when these symptoms appear, it is no longer possible to cure the patient. Doctors can only prolong his life.
Symptoms of oligodendroglioma also depend on its location. In all types of oligodendroglioma, intracranial pressure increases. Other symptoms similar to the manifestations of glioblastoma described above also develop.
Therapy methods
Glial tumors are most amenable to therapeutic treatment due to their sensitivity to chemotherapy and radiation. If an inoperable glioma is discovered or the patient has strict contraindications to surgical treatment, therapy becomes the main method of combating the disease. Also, therapeutic procedures are prescribed before and after surgery.
Chemotherapy is a method of drug treatment for cancer. Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor selects the most effective and safe regimen. Cytotoxic and cytostatic drugs are used that directly destroy tumor structures and slow down the growth of tumors. This method does not completely eliminate the pathological focus in the brain, but it is possible to relieve unpleasant symptoms and prolong the patient’s life in the later stages. Chemotherapy almost always causes side effects, but oncologists prescribe medications to improve tolerability of treatment.
Radiation or radiation therapy involves the targeted effect of ionizing radiation on a tumor. This type of treatment is carried out to reduce the size of the pathological lesion, eliminate symptoms and prepare the patient for surgery. In the case of glial tumors, stereotactic radiosurgery is especially effective, in which small foci of cells are targeted with ionizing radiation. This procedure makes it possible within several months to almost completely get rid of tumors that do not grow into neighboring tissues.
Surgery
Surgeries are most effective for benign tumors. In this case, the neurosurgeon can separate the altered tissues from healthy neurons and perform complete excision of the pathological focus. Borderline and malignant tumors grow into adjacent tissues, so in this case surgery is ineffective. Modern methods of tomographic control and microsurgery have slightly improved the effectiveness of such treatment.
The operation can be performed in combination with therapeutic treatment. Often, oncologists must first use radiation and chemotherapy after surgery to destroy any residual cancer. Surgical treatment is not performed if hydrocephalus and multifocal neoplasm are detected.
Causes and risk factors
Gliomas are a poorly understood type of cancer. Doctors do not know the exact causes of tumors. At the same time, numerous studies have allowed specialists to discover risk factors for the growth of brain tumors associated with lifestyle, individual and family history of patients.
Glial tumors are not formed from mature cells. Slowly developing gliocytes undergo malignant degeneration, which over time must replace old tissue. The mechanism of change in young neuroglia is due to the already mentioned genetic defects. Mutant genes can be present in DNA from the moment of conception or appear throughout life due to exposure to negative factors.
Known risk factors:
- Elderly age. According to epidemiological data, glioma is most often diagnosed at the age of 45-70 years. In children, this disease is rarely detected. Age-related risk can be explained by the gradual accumulation of genetic errors in the DNA of new cells.
- Radiation exposure. Radiation is the main factor in the appearance of genetic mutations in cells. Patients undergoing radiation therapy are at risk.
- Unfavorable heredity. The genes DRD5, WDR1, NOMO1, PDXDC1, which are responsible for the malignant degeneration of neuroglia, are passed on to children from parents.
- Congenital diseases. An increased risk of brain cancer is typical for patients suffering from neurofibromatosis and tuberous sclerosis.
- Features of the diet. Eating foods containing large amounts of nitroso compounds increases the likelihood of tumor growth. These substances are found in vegetables and fruits grown on low-quality fertilizers.
- Cytomegalovirus infection. Every second person is a hidden carrier of this virus. The infection accelerates the growth of the tumor.
The available data is insufficient to create an effective scheme for the prevention and screening of the disease.
Danger of malignant forms
Benign and malignant tumors differ in morphological characteristics and growth characteristics. Benign neuroglia form an isolated pathological focus that can compress adjacent anatomical structures. This disease is dangerous, but surgical and therapeutic methods of treatment in this case are very effective. If the tumor is located in a well-accessible place, the surgeon can easily separate the changed tissues from the healthy ones during the operation.
Malignant neoplasms have one fatal feature that causes an unfavorable prognosis. These pathological structures are able to “grow” into neighboring tissues and quickly spread within the organ. Gliomas not only compress different parts of the brain, but also gradually destroy neurons. In later stages, surgical options are limited due to extensive damage to the brain.
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy
Life expectancy with brain glioma largely depends on how successful the treatment was. Methods such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy are used to treat malignant neoplasms. Such methods are used quite widely both as the main method of treatment and after surgery. They help curb tumor growth.
Similar therapy methods are used if it is not possible to perform surgery for certain medical reasons. Such indications include the following:
- the tumor is localized in both hemispheres of the brain;
- several types of cancer are observed;
- the patient is unstable;
- the glioma is located in an inoperable location.
Modern radiotherapy involves the use of a linear accelerator, which directs rays to a malignant tumor from different directions. The entire treatment process using radiotherapy is controlled using computer programs. In this way, the maximum possible effectiveness of therapy is achieved. Computer programs help regulate the shape and intensity of each radiation beam.
Chemotherapy is carried out using new generation drugs that help slow down tumor growth. Treatment of brain stem glioma in children is carried out using radiation therapy methods. However, if possible, surgery is recommended, since after irradiation there is a risk of relapse of the disease with a subsequent increase in existing symptoms. Radiotherapy is not able to completely remove the tumor, but is aimed solely at curbing its subsequent growth.
Alarm Signals
The exact cause of glioma has not been established. It is very important to pay attention to your well-being. If you suspect that some pathological process has begun, it is better to go to the doctor and get a diagnosis. This way it is possible to detect cancer at a very early stage. This is the key to successful treatment.
Symptoms of glioma development are very similar to neurological pathologies. This is why most patients put off going to the doctor. They attribute everything to fatigue, pressure changes, migraines, etc. Meanwhile, the tumor continues to grow little by little. It also happens that the doctor himself made the wrong diagnosis. This happens especially often in the first stages of pathology development.
Signs of glioma directly depend on its location. This is the result of compression of nerve endings due to tissue proliferation, local destruction, and disruption of the endocrine system.
When the tumor is localized in the crown, convulsions are disturbing, sensory functions are disrupted, and the ears may often become blocked. If the neoplasm is located in the dominant hemisphere, disruptions in speech activity, agraphia, and finger agnosia appear. The most severe symptoms appear if the cancer has affected the pons.
When localized in the temple area, convulsions, fits, and hallucinations may develop. Aphasia and anomia may appear. With occipital localization, flashes of light and seizures may periodically appear.
It is most dangerous if the tumor is located in the center of the brain. Its growth can lead to coma, paralysis, breathing problems, heart rhythm disturbances, pupil fixation, and circulatory arrest. If intracranial pressure is elevated for a long time, false symptoms may begin (paralysis of the eye muscle, visual fields are impaired, hemiplegia develops).
Symptoms
A tumor such as glioma is almost always accompanied by neurological manifestations. Symptoms of the pathology may differ depending on the stage of the disease and the degree of malignancy. Most patients will experience the following general symptoms of the disease:
- Periodic headaches.
- Feeling sick and vomiting.
- The appearance of epilepsy attacks.
- Speech deterioration (problems with forming sentences and impaired diction).
- Deterioration of vision, periodic memory loss.
- Blindness.
When the growth begins to increase in size, the person’s behavior may change greatly: he will become more aggressive, irritable, and will also suffer from psycho-emotional disorders.
Types of gliomas
Optic nerve glioma (optic nerve glioma) is formed from glial elements that surround the optic nerve. It is characterized by gradual development and the fact that there are no pronounced symptoms at the onset of the disease.
Important! Optic nerve glioma can cause decreased vision.
The location of this type of glioma can be within the orbit, and then this tumor is intraorbital and is treated by ophthalmologists. A glioma on the part of the optic nerve that is in the skull is called intracranial, and is treated by neurosurgeons. This pathology is usually benign, but if detected late it can lead to blindness. This disease often occurs in children.
Diffuse glioma of the brainstem
The usual location of brain stem glioma is the point of articulation of the spinal cord with the brain. The centers of the nervous system that are responsible for heartbeat, breathing, movement and other human functions are collected here. Diffuse brainstem glioma spreads to some parts of the brain and can affect the chiasm, midbrain peduncles, and quadrigeminal. A tumor in this area leads to disruption of the vestibular apparatus, dysfunction of speech and hearing, and other symptoms.
ethnoscience
If a person is determined to fight a neoplasm that has arisen in him - a glioma, then he tries to use all the possibilities. Various traditional medicine recipes help to significantly reduce neurological symptoms:
- healing infusions and decoctions - extracts of St. John's wort, Caucasian dioscorea, and hemlock are actively used: they improve cerebral blood supply and correct metabolic processes;
- a source of natural antioxidants - green coffee, is able to cleanse the body of accumulated free radicals, which significantly affects the well-being of cancer patients;
- Various dietary supplements also have a beneficial effect on the course of neoplasms; official medicine does not welcome them, but there is no reliable information about their ineffectiveness.
An important role is also played by the patient’s proper nutrition - it is necessary to exclude from the diet dishes that contribute to the concentration of negative substances in the blood that impair cerebral blood flow. The primary emphasis is on the principles of healthy eating - the predominance of various vegetables, fruits, lean meats, fish, cereals, and seafood in the diet.
It is recommended to completely abandon existing bad habits - tobacco, alcohol, drugs. This will immediately affect your well-being - it will improve.
The correct psychological attitude will also help to cope with pathologies - the patient should be supported by relatives and friends. Motivation to recover is half the success.
How long do people live with glioma?
Unfortunately, the prognosis of this disease is, for the most part, unfavorable. Partial removal of a glioma leads to its rapid recurrence and only slightly prolongs the patient’s life. If the degree of malignancy is high, then half of cancer patients die within a year, and only a quarter of them live for more than 2 years. With grade I malignancy and complete removal with the least postoperative neurological deficit, the life expectancy of patients is about 5 years (80% of patients).
The question of whether it is possible to cure glioma completely must be approached with caution - on the one hand, the availability of modern methods can completely get rid of such a tumor, on the other, the effect of treatment also depends on the stage of the cancer and the general health of the patient. Only by taking all these points into account can we make more accurate predictions about the consequences of glioma treatment.
Reasons for the development of the disease
The exact causes of glioblastoma and similar tumors in the brain have not been established. The leading role of hereditary factors in the development of pathology has not been confirmed. No more than 5-10% of cases are associated with hereditary predisposition. According to some doctors, the appearance of glioblastoma correlates with alcoholism. Other causes:
- Past viral infections (herpes virus, polyomavirus, cytomegalovirus).
- Past malaria.
- Ionizing radiation (rare).
- Chronic intoxication with harmful chemicals (including salts and vapors of heavy metals).
Malignant tumors of the primary form account for 2% of the total mass of oncological diseases. Scientists identify risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing a malignant neoplasm of neuroepithelial etiology. Among them:
- Male gender.
- Age 40-60 years.
- Diagnosed astrocytoma of I, II degree of malignancy.
- Genetic mutations.
- Diagnosis of neurofibromatosis (about 15% of cases).
Statistics show that people of the white race are more susceptible to pathology. In order to never personally find out how people die from glioblastoma, it is worth paying attention to the first signs of pathology.
List of sources
- A.P. Romodanov, N.M. Mosiychuk. Neurosurgery. - Kyiv: Vyshcha School, 1990. - P. 16. - 105 p.
- Zemskaya A.G. Glioblastoma multiforme of the brain. - L: Medicine, 1976.-S. 192.
- Pishel Y.V. Glioblastomas of the brain. (Pathomorphology, clinical picture, diagnostics, comparative assessment of treatment methods): Abstract of thesis. dis. . Dr. med. Sci. - Kharkov, 1971. P. 32.
- Savchenko A.Yu. Brain gliomas. Omsk: Publishing house. Omsk State Pedagogical University, 1997. - P. 312.
- Fadeev B.P., Zhabina PM Combined treatment of glial and metastatic brain tumors // Bulletin of Surgery named after. I.I. Grenova. - 2005. - No. 1. — P. 80-82.
Low-grade glioma, what is it?
Low-grade glioma (LGG) is a neoplasm, grade 1-2 tumor according to the WHO classification.
They are characterized by a slow increase: several years may pass from the onset of tumor formation to the first symptoms. In most cases, they are formed in the cerebellum and in the cerebral hemispheres. Occurs in children and young people under the age of 20.
There are several groups of low-grade gliomas that differ by cell lineage:
- Infiltrative astrocytoma grade 2 (fibrillar and protoplasmic).
- Oligodendroglia from astrocytes and oligodendroglia (oligoastrocytomas).
This disease is divided into 3 groups, regardless of histology:
- Solid tumors that do not infiltrate the brain tissue. Most often, when such a neoplasm forms, surgical intervention is possible, removal occurs completely, and the prognosis for life expectancy is most favorable. These include gangliogliomas, pilocytic astrocytomas, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytomas, and some protoplasmic astrocytomas (oligodendrogliomas do not belong to this group).
- Dense formations that are surrounded by a zone of infiltration of brain tissue. Surgical intervention is possible, but complete removal can only be done from the site of origin. They exist as low-grade astrocytomas.
- Infiltration by tumor cells, no tumor node. Due to the risk of neurological deficits, resection of infected tissue may not be possible. Forms as an oligodendroglioma.
Nutritional Features
Diet for glioblastoma is one of the methods of complex treatment. Properly organized nutrition cannot cure a person from a terrible disease, but it helps the body mobilize its own strength and actively resist the progression of tumor processes. Diet for glioblastoma in the brain includes foods low in carbohydrates, high in fat and moderate in protein.
The ketogenic (low-carbohydrate) diet is actively used to treat epilepsy in childhood. If the patient adheres to such a diet, the amount of glucose entering the brain decreases, due to which the nutrition of tumor cells deteriorates and the process of their division slows down. Products are shown that help strengthen the immune system, improve blood composition, and remove toxic substances from the body. You can eat fish and seafood, lean beef and poultry, legumes (beans, peas, lentils).
Vegetable oils are useful, including coconut, olive, sunflower, and corn. The diet should contain fermented milk products - cheese, fermented baked milk, sour cream, cottage cheese. You need to eat soy, vegetables, herbs, unsweetened fruits, and drink green tea. It is necessary to limit alcohol consumption, give up bad dietary habits (abuse of refined sweets, fast food, sweet carbonated drinks).