One of the most common oncological diseases of the female reproductive system is cervical cancer, for early diagnosis of which a cytology smear is performed. What it is? This is a cytological analysis of scrapings from the cervix, the so-called Papanicolaou test, or, as the doctor usually writes in the referral for the study, a PAP test.
It is recommended that all women over 18 years of age undergo a cytology smear.
In 1943, the scientific work of the Greek physician G. Papanikolaou, “Diagnosis of uterine cancer using smears,” was published in a specialized medical publication. It aroused great interest among the medical community, and the proposed diagnostic method began to be widely used in clinics. After the name of its creator, a cytology smear from the cervix began to be called a Papanicolaou smear or PAP test for short. By watching the video on YouTube, you can learn more about Georgios Papanikolaou and his discovery, which made it possible to reduce mortality from cervical cancer tenfold.
Every adult woman who is not vaccinated against HPV before sexual activity has a risk of cervical cancer.
What is cervical cytology
The objectives pursued by this research are very diverse. It all depends on what kind of biomaterial was taken and what needs to be found or refuted. In any case, it is assessed whether the collected material corresponds to what is normal for a healthy human individual. This is the configuration of the cytoplasm, their structure and the absence or presence of negative inclusions in each cell studied. Cytology allows you to find abnormalities in biomaterial from the cervix, find cancerous inclusions or abnormal precancerous inclusions preceding it.
In gynecology
Cytology in gynecology plays a serious role in determining many diseases, not only cancerous tumors. This examination will help to recognize structural transformations in the structure of cells and determine inflammation or infection in the first days or weeks of the disease.
What is cytological analysis - a relatively short, inexpensive and highly accurate way to determine the appearance of atypical cells. Atypical cells in cytology indicate the development of an inflammatory or infectious disease, or changes in the structure of the cells themselves. To check women's health, you need to scrape the cervix. This is especially important if a woman had relatives who died from cancer of the cervix or other part of the genitourinary system. If a woman has previously had cancer, then it is necessary to be examined for the likelihood of relapse at least annually or more often on the recommendation of the attending physician.
What can liquid-based cytology show?
When deciphering a cytological analysis, the following is considered to be the norm:
- Cells of unchanged columnar epithelium are detected.
- Multilayer vaginal cells without disturbing their structure.
- Small changes that may indicate the initial stage of inflammation are within normal limits.
- A small number of leukocytes (up to 15 units), acidity is 4.0-4.5. The main part of the bacteria is Doderlein bacillus.
- Small mucus impurities.
- Flat cell epithelium does not exceed 10 units.
- The degree of vaginal cleanliness is within the second stage.
Pathological changes are detected if the following deviations are observed in the smear:
- An increase in acidity over 5.0.
- The presence of trichomonas, Neisser gonococci, fungi of the genus candida, gardnerella, chlamydia, papillomavirus indicates the presence of an infectious pathology.
- The detection of several types of lactobacilli at once, against the background of an increase in acidity to 7.0, or if it becomes alkaline, may indicate the initial form of dysplasia. The degree of vaginal cleanliness can move into the third or fourth category.
- The complete absence of lactobacilli, the development of an alkaline environment, with a high concentration of columnar and squamous epithelial cells raise the suspicion of the probable development of a cervical form of uterine cancer. Such changes are most often observed against the background of an increased content of leukocytes, with large amounts of mucus, and a change in vaginal cleanliness to the fifth degree.
Atypical cells are considered to be when the following changes occur in the cellular structure:
- The volume of the core increases significantly.
- Its configuration and coloring are disrupted.
- Morphological abnormalities appear in the cytoplasm.
It should be noted that even significant deviations do not always provide grounds for making a diagnosis indicating the development of an oncological process.
To achieve a reliable diagnosis, prescribe:
- Repeated cervical cytology.
- Colposcopy in combination with biopsy.
- Diagnostic curettage.
- Complete blood test using tumor markers.
When undergoing this type of study, a positive result is quite common. But this does not always mean that a woman develops cancer.
Very often, a positive result may indicate the presence of an infectious process, which can occur as a result of diseases of the genital area, erosion, or vaginal dysbiosis.
After treatment for sexually transmitted infections, repeated cytological analysis usually returns to normal.
To establish a final diagnosis and exclude oncopathology, colposcopy, biopsy, and histology are required. A diagnostic curettage is required.
In addition to the above studies, the woman is prescribed anti-inflammatory therapy followed by cauterization of the affected areas. If the disease is viral, it is recommended that both partners undergo a full course of therapy. This will prevent re-infection.
After all treatment measures, it is recommended to undergo an annual cytological examination for the presence of cervical cancer.
Stage 1 – no atypia is detected, there is a normal cytological picture.
Stage 2 – abnormal cells are present, but in small quantities. If there is an inflammatory process in the genital area, a certain number of atypical cells can be considered a variant of the norm.
Stage 3 – atypical cells are detected, their nucleus and cytoplasm are changed. But such results do not always indicate oncology. Only histology will help in establishing an accurate diagnosis.
Stage 4 - in this case, it is discovered that the cells have begun their malignant transformation. The nucleus, cytoplasm, and chromosomes change. Possible dysplasia. An accurate diagnosis can only be made with additional research.
Stage 5 - if a very large number of atypical cells are involved in transformation, most likely there is oncology.
Liquid-based cytology is a standard test with a well-established technique.
First, they take the material, after which it is transferred to the laboratory for detailed study.
If a person is interested in the question of how many days the result is deciphered, then the answer is two weeks.
When to take a smear for cytology
The reasons that indicate the need to get tested are varied. The first time the study is recommended is 3 years after the start of sexual activity. Girls over 18 years of age are required to undergo a cytology test annually in order to promptly identify the onset of a deviation. There are also direct indications for which a cytological examination of scrapings from the cervix and cervical canal should be taken unscheduled:
- If you plan to become pregnant in the near future;
- If infertility is in question or is being treated;
- Distortions of the menstrual cycle have been identified and the reasons need to be established;
- Genital herpes has been detected or there is a suspicion that it will appear soon;
- Obesity has been diagnosed and the cause is being sought;
- Suspicion of human papillomavirus;
- Hormonal contraception was taken for a long time;
- Promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- More than two sexual partners at the same time or in a row;
- It is planned to insert an intrauterine device.
In addition, a doctor can prescribe a cytological smear at his own discretion or if he suspects a whole range of diseases.
When should you take a smear for cytology?
There are some conditions of the body in which it is necessary to take a smear monthly in order not only to identify atypical cells, but also to monitor the health status of a person at risk:
- There are indirect signs of human papillomavirus;
- Venereal diseases;
- Genital warts;
- Cancer is in remission;
- Genital herpes;
- Severely weakened immunity.
For cervical erosion and human papillomavirus infection, smears must be performed every six months to monitor health and the onset of negative manifestations. It is important to maintain healthy microflora. During pregnancy, the test will have to be carried out three times - during the first visit and registration with the LCD, at 30 weeks, when you need to undergo an examination to receive an exchange card. And at 36 weeks, the last study before the maternity hospital is carried out to identify diseases and try to cure them before birth. In every case when a pregnant woman’s discharge changes sharply, itching and burning appears, you need to consult a doctor.
If the woman is not pregnant, then the test should be taken on day 4-5 of the cycle. During pregnancy - when the doctor says within the specified weeks. Why else do they take a cytological test before the maternity hospital? The presence of sexually transmitted diseases, AIDS or HIV, genital herpes, or life-threatening diseases for the child transfers the mother to a special group. In this case, she will come under the close supervision of specialists and will give birth in the second department of the maternity hospital, where everyone with similar diseases is collected.
Indications
Diagnostic liquid-based cytology is not performed on every woman. A gynecologist recommends it for a number of patients with special indications:
- A woman complains of discharge from the genitals, which is atypical. Discharge increases in volume after sexual intercourse, which can frighten patients and cause serious concern.
- During a manual examination, the gynecologist identified erosion of the cervix. The situation is aggravated by histological detection of abnormal cells. The study helps confirm or refute oncological pathology or a precancerous condition. The procedure is indicated for women who have a genetic predisposition to cervical cancer, that is, representatives of the fair sex in the family were ill or died from this disease.
- The woman’s menstrual cycle has become irregular: periods have become painful, the volume of menstrual blood has changed, the intervals between bleeding have become longer or shorter. Menstruation may be absent for a long time.
- During preconception preparation of a woman for the purpose of diagnosing sexually transmitted and other types of diseases. Shows liquid cytology and some causes of infertility, recurrent miscarriage or other reproductive disorders.
- For viral infection of the genital tract or generalized forms. HIV infection is also an indication for cervical cytology. Immunodeficiency as a side effect can be caused by hormone therapy, in which liquid-based cytology is indicated.
- During menopause, it is also useful for women to be examined using this method in order to avoid the appearance of chronic latent diseases.
If the doctor has established one of the indications for a woman, then the diagnostic method is used at least once a year. If the patient’s condition worsens, the examination can be performed more often without fear for the condition of the genital organs and general level of health.
What material is used in the study?
Cytological research methods involve taking three types of biomaterial in the same way. To collect biomaterial, a brush is passed along the tissue of the cervical canal. Using another similar sterile spatula, a smear is examined in the vagina, and a third one is used to examine a smear from the mouth of the paraurethral ducts.
The biomaterial is sent to the laboratory. There it is placed on glass, stained and the cytoplasm is examined using specialized equipment. Cytological examination of the cervix of the cervical canal, if necessary, is accompanied by another analysis using a Petri dish.
How to prepare for a smear test
To conduct cytological studies of a smear, you need to prepare.
You need to refrain from any sexual contact and not use any vaginal products for one or two days before collecting the material. The use of creams, lubricants, suppositories and douching is also prohibited within two days before the day of delivery. You can swim, but without adding medications to the water, which can destroy normal flora, and not in hot water. On the day of the smear test, you cannot visit the toilet 2-3 hours before the appointment, you cannot urinate, wash yourself or use wet wipes for intimate hygiene. You cannot take the test if you experience severe itching in the vagina or an unpleasant-smelling discharge, since the collection of biomaterial is accompanied by microtrauma of the cervix. This can trigger the development of infection in the genital tract. It is important to remember on what day of the cycle it is possible to submit the material for research. You can take the test only on the 4-5th day of the cycle, immediately after your period ends.
Preparing for the test: How to take a smear correctly
A smear for cytology is taken immediately after the end of menstruation. Doctors recommend not taking the test if there are various replenishments in the body: colds, runny nose, sore throat. Also, you should not take cytology during menstrual bleeding, as this will distort the results of the analysis. One to two days before taking the test, it is worth following a number of recommendations from the gynecologist:
- You can't have sex for two days.
- Use douching and vaginal suppositories.
- Use lubricants and creams.
- 2 hours before the test you should not relieve yourself.
The test procedure itself does not seem difficult. The patient sits in the gynecological chair, as during a routine examination with a gynecologist. Using a speculum, the doctor opens access to the cervix.
Theory for deciphering the results
It is better to entrust the decoding of cytology to a specialist, but sometimes it is necessary to study the data yourself. The level of flora living in different girls can be very different, cytological studies differ. There is a norm, although it is quite difficult to establish its boundaries.
The normal level of leukocytes does not exceed 10 cells per field of view in the urethra, and 30 in the cervix and its canal. In a pregnant woman, these indicators will be greater; the assessment of their characteristic volume depends on the condition of the pregnant woman herself. Types of cytological studies include work with different materials - sputum, mammary gland secretions, amniotic fluid and others, depending on the need to identify the disease. Such studies help to detect positive dynamics in treatment.
The type of epithelium that lines the tissue is also being studied. If you analyze a smear from the vagina or urethra, you can see traces of stratified squamous epithelium. When studying biomaterial from the cervical canal, most of the prismatic epithelium will be depicted; its binucleate cells change their number according to the days of the cycle. But in normal quantities it should not be more than 10 units.
In a normal state, traces of mucus should be found in small quantities in the biomaterial. This component should be in moderation, because both the vagina and the cervical canal secrete it. Large amounts of mucus can be a symptom of bacterial vaginosis. In a normal smear, the flora should be rod-like with occasional inclusions of cocci.
Labeling of test results
The results of the examination are subject to mandatory marking - changes must have a number from 0 to 5. The number 0 is given if the material was collected incorrectly or is of poor quality. It is not suitable for research and must be taken again. Other indicators:
- Normal cells without atypical inclusions;
- There are atypical changes;
- Beginning of dysplastic changes;
- Precancerous cells;
- Ivasive cancer.
Degrees of dysplasia
Dysplastic changes in cervical cells are divided into three large groups. The first stage is considered mild and reflects the appearance and active development of the inflammatory process. The second stage is accompanied by moderate dysplastic changes and signals an increased likelihood of cancer cells appearing. The third stage corresponds to a severe condition of the cells and is diagnosed before the appearance of precancerous cells.
Terms used in diagnosis
When collecting material such as a smear for oncocytology or suspicion of other diseases, liquid cytology of the cervix is performed. This type of research allows you to collect only the material necessary for the study. At the same time, such thin-layer smears will not show whether there are leukocytes in the mucus, inflammation or destroyed cells. This does not allow assessing the cell environment and performing an intermediate stage of the study.
Before taking a smear for cytology of women, you must definitely come to see a doctor and undergo an examination. A cytological examination is not prescribed at the request of the patient, only for direct indications or suspicions of them.
Interpretation of abbreviations and abbreviations
After receiving the research results, you should not try to decipher all the data yourself, much less prescribe treatment. It is better to wait for a consultation with a specialist and entrust all this to him. The main values that may appear on the results form are:
- NILM - absence of malignant cells or lesions in the body;
- AGC—presence of atypical cells in the biomaterial;
- ASC - the presence of atypical cells in the squamous epithelium;
- NOS or US - unclear purpose of cells;
- AIS—endocervical adenocarcinoma;
- CIS - carcinoma;
- SIL - damage to squamous epithelial cells with H - high degree, with L - low degree;
- VaIN—vaginal neoplasia;
- VIN is a neoplasia found in the vulva.
Inflammatory type of smear for cytology - what is it?
The presence of an inflammatory type of cytology smear indicates that inflammation is occurring in the body. If this type of smear was diagnosed, then it is necessary to identify the cause of the inflammation. It can be hidden in a fungal, viral or protozoal infection. Then you need to undergo treatment, which will be prescribed by a specialist after he sees the test results. It is not worth treating with folk remedies or herbs, as this can only waste time and aggravate the disease and the body’s own condition. After the full course of treatment, you need to be re-examined for cure.
Analysis Tools
Having noticed the definition “for cito!” in the referral form for testing, a woman of any age becomes confused. Sometimes the anxiety is not unfounded. Cytology analysis in gynecology is deciphered by the doctor and explains to the patient what it is.
A method for identifying atypical (cancerous) cells, developed in the middle of the last century, is today used to diagnose precancerous conditions. Even a slight deviation from normal values is a reason to repeat the analysis.
A control examination of the body every 3 months will reduce the likelihood of progression of the pathological process and the growth of atypical cells into deeper layers.
Of course, liquid cytology is not performed on all women when visiting a gynecologist. There are certain indications. Let's look at them in more detail:
- The appearance of atypical discharge from a woman’s genital tract, often worsening after sexual intercourse.
- Cervix with cellular abnormalities.
- To diagnose pathology of the mucous membranes.
- When a failure occurred and the menstrual cycle became irregular.
- For viral diseases.
- Infertility.
- Cervical erosion.
- With long-term treatment with hormonal drugs.
- If you plan to become pregnant in the near future.
- During multiple births in a woman.
- If a woman gave birth at an early age.
- With frequent changes of sexual partners.
- When did menopause occur?
- If it is necessary to install an intrauterine device.
- In case of prolonged absence of examination by a gynecologist.
- If the previous smear deviates from the norm.
- In case of pathological changes in the cervix, which are discovered by the gynecologist during examination.
- If a woman is diagnosed with HIV.
- Genetic predisposition.
Liquid cytology of the cervix is a test that must be repeated once a year. But if cellular abnormalities are detected, it is carried out more often.
This analysis requires some preparation. To make it as informative as possible, a woman should not neglect the doctor’s recommendations.
MORE ABOUT: Urinary incontinence due to alcohol intoxication
So what needs to be done? Before the procedure, the following rules must be observed:
- Stop having sex in two days.
- You can't douche.
- The body must be kept clean. This is required by liquid-based cytology. The preparation doesn't end there.
- Sprays, vaginal suppositories, tablets should be excluded. You should also avoid using tampons. All this can affect the result of the study, and it will be inaccurate.
- It is not recommended to go to the toilet 2 hours before the analysis itself.
- Avoid taking antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and oral contraceptives in advance.
- During menstrual bleeding, liquid cytology is not performed, since during this period it will be uninformative. If there are less than five days left before the start of menstruation, the test cannot be performed.
- If a woman has any infection, she must first be cured and then scraped (wait about 10 days after recovery).
The attending physician will help you sort out all the preparatory measures.
Liquid cytology of the cervix - a simple analysis.
The material for research is taken with special sterile instruments:
- An Eyre spatula is convenient for scraping from the mucous membrane and uterus, or rather its upper part.
- Endobrush - with this probe the cervical canal is expanded and a sample is removed.
- Spirette – this instrument is used to take aspirate.
- A special brush can be used to take a smear from the cervix.
- The Volkmann spoon detects cervical infection.
A smear is taken instantly, and these manipulations are absolutely painless for the woman.
How exactly is liquid-based cytology performed? What does it show? More on this later.
Once abnormalities in cytology are detected, additional tests may be prescribed:
- repeat scraping for cytology;
- a biopsy of the affected area is performed;
- colposcopy;
- scrape the cervix;
- an extensive blood test is prescribed;
- a smear is taken for human papillomavirus;
- cauterize dysplasia;
- for various viral diseases, it is recommended that the woman and her partner undergo complex treatment.
If therapy is chosen correctly and is timely, cervical cancer can be avoided. But you need to constantly monitor the condition of this organ to prevent its pathology.
Any woman over 18 years old has visited a gynecologist at least once in her life and had tests done. A regular vaginal smear is the most common form of examination that is offered in gynecological offices.
But sometimes the doctor writes a referral for another test with the mysterious combination “cytology test in gynecology.” The young woman does not know what it is and why it is prescribed, and is often perplexed as to what it is and why the doctor gave a referral for this test.
MORE ABOUT: The use of chamomile in gynecology
What if this is some kind of new infection or the name of a serious and dangerous disease?
Before you carry it out, you need to follow a few simple rules.
- Take the test 4-5 days after the end of menstruation. At this time, you will receive the most accurate result of the study, since in the second half of the cycle or before the onset of menstruation, the uterus may be slightly larger, which will allow you to obtain unreliable data or an inaccurate result, as well as not fully understand the origin of the pathology.
- Stop using vaginal suppositories and contraceptives for 2 days. They can disrupt hormonal levels and prevent an accurate result from being determined, even if your doctor prescribed them for the treatment of an inflammatory process.
- Two days before the study, do not engage in vaginal sex, but it is better to generally refrain from intimate contact with your partner. This must be done before any examination and taking a gynecological smear.
- You should not empty your bladder 2 hours before the test. This rule applies to any smear taking for gynecological examination.
The result of the analysis will indicate “negative” and “positive”. It is clear that receiving a result with the word “negative” means an absolutely healthy cervix.
What does a cytology smear show? This question is asked by every woman who is sent for a cytological analysis. This test is a highly informative analysis that allows you to diagnose cervical diseases and vaginal pathology.
The procedure itself is absolutely painless and simple. Cells are taken from the plane of the cervix, which are subject to further study. Using the cytological method of examination, atypical cells are determined that may indicate dysplasia (cellular modification) of the cervix.
By examining the entire epithelial layers of the uterine cervix, it is possible to determine dysplasia, which leads to neoplasms of the uterus and cervix. A cytological smear allows you to identify pathology in the early stages.
Very often, neoplasms begin to develop in the internal areas of the vagina, progressing over time and becoming a life-threatening disease. A smear from the upper layers of the epithelium can diagnose the disease when the disease has reached its final stage.
Cytological analysis can examine all cells, which distinguishes it from the histological method, where individual material is subject to examination.
If cancer is suspected, doctors use invasive methods to test cells. There are a number of situations when it is also necessary to take a smear for cytology:
- Planned pregnancy.
- Menstrual fight.
- Infertility.
- Increased body weight.
- Diabetes.
- Erosion. A common disease in women.
- Frequent change of sexual partners.
- Installation of the uterine device.
A smear for this type of study may also be prescribed when there has been a long and continuous use of hormonal drugs. Women of all ages are recommended to take this test once a year. It is advisable to begin the study immediately after the woman has had her first sexual experience.
A smear for cytology is taken immediately after the end of menstruation. Doctors recommend not taking the test if there are various replenishments in the body: colds, runny nose, sore throat.
Also, you should not take cytology during menstrual bleeding, as this will distort the results of the analysis. One to two days before taking the test, it is worth following a number of recommendations from the gynecologist:
- You can't have sex for two days.
- Use douching and vaginal suppositories.
- Use lubricants and creams.
- 2 hours before the test you should not relieve yourself.
MORE ABOUT: Trimetazidine indications for use reviews
The test procedure itself does not seem difficult. The patient sits in the gynecological chair, as during a routine examination with a gynecologist. Using a speculum, the doctor opens access to the cervix.
Then special instruments are used - a medical spatula or brush - and material is taken from the walls of the cervix. If there is a suspicious inflammatory area, then a scraping is taken from it.
Next, the taken material is applied to a special glass and sent to the laboratory for research. The procedure does not take more than fifteen minutes. In the laboratory, a specialist directly examines all the cells and gives an opinion about the inflammatory process or oncology.
A cytological smear allows you to identify all pathological changes occurring in a woman’s body. This is a very accurate study that gives a hundred percent result.
The material applied to a glass slide is dried and fixed using special solutions, and then tested in laboratory conditions.
As a rule, this analysis is ready within one hour, but results are always given the next day. But there are cases when the test can take several days, it depends on the laboratory itself.
The patient will be able to come at the appointed time and pick up the results, and the doctor will do the decoding.
The final stage of the analysis is its decoding. What does a cytological smear show? When deciphering the test, doctors use terminology - stages. And there are five stages according to which a preliminary conclusion is made, a diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed.
- First stage - cytological analysis did not reveal any abnormalities, the patient is healthy.
- Second stage – a slight change in the structure of the cells was detected. This may also be inflammatory processes in the body, this is also considered normal.
- The third period - a small number of cells with an abnormal structure were identified. This requires re-analysis.
- The fourth stage means that cells that are malignant have been identified. For example, the mass of nuclei was increased and changes occurred in the cytoplasm. But it is worth noting that the fourth stage is not final for the approval of cancer. Further diagnosis and research is required.
- The fifth and final stage is the presence of cancer cells in the smear in quantities significantly exceeding all norms. In this case, prompt treatment and a fight for the patient’s life are required.
The reliability of a smear for a cytological test is very high, this is especially applicable to the study of the cervix. The test shows all the changes and identifies cancer cells that are progressing in the woman.
What does a cytology smear show?
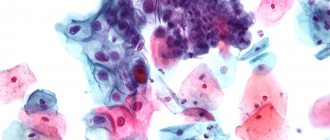
The analysis can make it possible to assess the size, shape and number of cells, as well as the nature of their arrangement.
With this test, background cells, precancerous and cancerous, can be seen. This is very helpful in diagnosing cancer in the early stages, when treatment is close to 100 percent. Cytology smear - what does it show?
In the laboratory, the material for cytological analysis of the cervix is carefully assessed. It is checked whether there is enough material for analysis and whether it is applied too thin or thick. It is important to check before starting the test that the material is not contaminated with mucus, blood, semen or other liquid. Poor cervical cytology will also occur in the presence of inflammatory exudate in the biomaterial.
Cytological diagnosis determines the presence of atypical cells or other pathologies in the body. A cytological smear does not diagnose diseases, but with the help of additional studies it becomes possible to make accurate diagnoses, such as vaginitis, vaginosis, cancer, Trichomonas, genital herpes and other diseases.
Additionally, the patient usually undergoes a blood test, which can confirm or deny the presence of inflammation in the body. Mucus in cytology is normal if it is in the body in small quantities. The normal number of indicators can be determined by a gynecologist.
A smear for cervical cytology has a transcript that can only be carried out by a specialist. Independent interpretation of the results may result in an incorrect diagnosis and treatment, which means taking useless drugs when the body is healthy. There may also be the opposite result - without understanding what the analysis shows, a person does not detect the onset of a malignant tumor and misses the time when it was possible to quickly get rid of the disease.
Decoding using the Betsed method
In the transcript of a cytological examination of the cervix using this method, one can see a low or high degree of transformation. Low will show koilocytosis and CIN I. With a high degree, CIN II or III can be detected, and carcinoma can also be detected, which correlates with Pap smear grade 3-5. A description of the obtained values with an explanation will either be at the end of the sheet, or it must be obtained from the specialist who prescribed the analysis.
The results may have the following values:
- NILM—normal cell state;
- ASCUS - atypical inclusions of unknown etiology;
- LSIL—small number of cells with transformations, HSIL—increased volume;
- High-grade SIL - squamous cell carcinoma;
- AGC - low-quality glandular inclusions.
Interpretation of the Papanicolaou method PAP test
Analysis in the form of cervical cytology is performed for girls over 21 years of age.
The results make it possible to identify cervical cancer or dysplasia in the early stages. You can get results at the clinic after 1-2 weeks. If you do the analysis through a private laboratory, you can get the finished analysis after a couple of days. A cytology smear showed inflammation, what does this mean - the development or appearance of inflammatory processes, the cause may be different. This is both a protozoal disease and a viral or fungal infection. Treatment is carried out in accordance with the doctor’s prescription, depending on the diagnosis.
Cell transformations that can occur with this type of test are divided into five different classes:
- Class I - normal cells without pathological changes;
- Class II - an inflammatory process in the cervix or vagina, accompanied by minor cellular changes;
- Class III - some cells have changes in the nucleus, there is a suspicion of the formation of malignant cells;
- Class IV - some of the cells have obvious signs of malignant formations;
- Class V - the appearance of a malignant tumor with a significant number of cancer cells not only at the site of tumor formation, but also nearby.
It is important to remember that the white blood cell count in a pregnant woman’s blood will be higher than what should be normal in a non-pregnant woman. In addition, in some cases it is necessary to repeat the study or conduct other clarifying diagnostic studies.
Important! Glandular cells of a benign nature are a normal condition of a woman’s body. This is considered a normal option in girls with a normal menstrual cycle.
Decoding
Cytological examination of a smear from the vaginal mucosa is one of the simplest but most reliable methods for determining the presence of oncopathology. Using the technique makes it possible to identify mutated cells in the early stages of their spread, when there are no obvious symptoms.
Interpretation of diagnostic results is carried out based on the state of the epithelial cells. Depending on their appearance, stage, class and other features, five conditions are distinguished:
- Norm. There are no changes.
- The morphology of certain cell elements is reduced. An inflammatory process or infection is possible. In order to establish the exact cause of this condition, additional diagnostics are required. In this case, colposcopy and biopsy are more often prescribed.
- Pathological changes are observed in individual cells. A repeat analysis is ordered.
- Precancerous condition. Changes have been detected. Related to a precancerous condition.
- A high content of mutated cells, which indicates the initial stage of cancer pathology.
To accurately indicate the results, specialists use the Bethesda system. An accurate diagnosis is established after obtaining data on the presence of changes in the cell nucleus and their location.
How long to wait for results and expiration date
There is a slight difference in the time it takes to do a smear for flora and cytology at a paid research laboratory or at a antenatal clinic. In the first case, the conclusion can be received in hand in 1-4 days. If necessary, you can do an urgent study, which will be somewhat more expensive, but the result will be within two to three hours.
How many days the cervical cytology is done, if taken at a antenatal clinic, will depend on where the test is taken. The clinic usually does not have its own laboratory that can handle such research, among other things. Therefore, the material is prepared and transported to a laboratory that cooperates with the clinic.
You can check with the gynecologist after the test to determine how long the cytology test is done and when the results will be available, but usually this period reaches 8 working days. This time includes transportation of the biomaterial, the time at which the result will be prepared, and sending the results back to the clinic. Regardless of where the material is submitted, the result will be valid for three months. After this period you will have to retake the analysis.
Urogenital tract in women. Ecosystem Features
Leukocytes are by no means the only cells in a woman’s smear taken for both flora and cytology. Moreover, they only reflect the body’s reaction to changes in the ecosystem of a woman’s urogenital tract, such as changes in hormonal levels and various types of inflammation. As you know, their number increases with the phase of the cycle, and therefore, when collecting, the day of the beginning of the last menstruation is always indicated.
Inflammation is diagnosed not only by the quantitative indicator of leukocytes, but also by closely studying their nuclei. Having entered into a reaction, leukocytes try to absorb the “harmful creature”, but destroy themselves. Neutrophilic (destroyed) leukocytes are not indicated in the study transcripts. But the presence of many destroyed leukocytes along with a rich coccal or cocco-bacillary flora provides grounds for diagnosing inflammation.
The anatomy and ecosystem of the female body (epithelium of the vagina, cervical canal, cervix) suggest the presence of microorganisms: obligate or obligatory and acquired from the outside. The latter are the cause of inflammatory processes.
Also, disorders and inflammations can be provoked by other external or internal factors. This promotes the displacement of natural microorganisms by external microbes. A good example of this phenomenon is the dominance of gardnerella, which has replaced lactobacilli, and the consequence of this process is widespread gardnerellosis or bacterial vaginosis.
What does a gynecological smear look like normally?
Despite all the abundance of microorganisms that live in the female flora, the norms for them are, of course, determined. We will try to introduce the reader to the main indicators:
- leukocytes. For the norm in the field of view during viewing, quantitative indicators were determined: 10 for the urethra and 30 for the cervix. If the quantitative indicators exceed the specified values, the presence of inflammation can be suspected;
- epithelium. For this criterion, the norms also differ depending on where the material for the study is taken from. For the vagina, urethra and cervix, the epithelium is normally characterized by the MPE obtained in the preparation. The material from the cervical canal is a cylindrical epithelium. At the same time, in different phases of the female cycle, the number of cells varies (the average normal value is up to 10 cells). These indicators are still very conditional, since everything needs to be considered in context - the morphology of cell nuclei is of great importance in this sense (shows a smear on cytology);
- slime. To be normal, this component must be present (this is the work of the cervical canal and vagina), but in small quantities. If sampled during the ovulatory phase, the mucus has a crystallized structure resembling a leaf pattern. In cytology this is called the “fern sign”;
- rod flora. The presence of single cocci and lactobacilli indicates normality; their quantitative increase indicates pathology.
Norm and pathology in opportunistic flora
Lactobacilli, which are normally always present in small quantities, perform a “sanitary” function by cleaning the vagina. But a smear can also show the presence of other microorganisms.
- Gardanella. As a rule, Gardanella does not show itself normally, but when the pH changes, it quickly becomes active. Almost always, after the manifestation of the activity of the gardanella, the activity of the mobiluncus begins. In this case, changes occur in the flora, and the smear shows a significant increase in cocci. This coccobacilli flora is called “bacterial sand” because it covers the epithelium. Such a diagnostic picture may indicate the presence of bacterial vaginosis.
- Candida fungi of yeast-like origin can be seen in a smear, since the normal flora also contains them, but does not allow them to develop and multiply. As soon as the situation becomes favorable for the fungi, Candida will quickly begin to multiply, and this will not go unnoticed for the woman. Itching, inflammation, and thrush will immediately appear.
- Leptothrix is a union of multiple species of microorganisms acting as a united front. This community has a certain "intelligence": they can imitate chains of mycelium threads or resemble lactobacilli. Therefore, culture is necessary to differentiate Leptothrix.
- Actinomycetes - bacteria that resemble cubes and blots in the preparation, almost never cause inflammatory reactions. The exception is when a woman uses an intrauterine contraceptive device.
- Other opportunistic forms. Enterococcus faicalis and Escherichia coli may also be present in the smear. The reason for this is the anatomy of the female body - the genitourinary system is located close to the lower gastrointestinal tract.
Also included in the group of other opportunistic forms that can normally be present in small quantities in the female genital tract are corynebacteria, staphylococci, mycoplasmas, streptococci and ureaplasmas. To differentiate these forms, they turn to other research methods, since they cannot always be clearly identified in a smear on the flora.
The listed representatives of the female microflora may be present in a healthy body and not manifest themselves in any way until a certain moment. When the situation for microorganisms becomes favorable, inflammatory processes occur. It must be said that even lactobacilli can become a source of inflammation - the extremely unpleasant disease lactobacillus occurs when there is an excess of lactobacilli with a simultaneous rich bacterial flora.
What diseases cause deviations in results
A cytological report will not show an accurate picture and will not make a diagnosis. After receiving the results, they need to be taken to a specialist who will decipher the indicators not only taking into account cytology, but also based on other studies, examination, anamnesis and heredity.
A negative cytological analysis may indicate the presence of:
- Bacterial vaginosis;
- Inflammation in the urethra or vagina;
- Invasive or non-invasive cancer;
- Trichomonas, candida, herpes, coccal infection;
- Metaplasia;
- Hyperkeratosis, colpitis, metaplasia.
Many other diseases are also possible, which negative cytology will show. In some cases, the doctor will ask you to redo the study in the hope that it was performed poorly or an error was made during the collection of biomaterial.
Where to go and what to do if there is a deviation in the results
After a cytology smear and receiving the results, you need to go to the doctor, who will correctly decipher the indicators and tell you what to do next. Depending on what cells were found, additional studies are performed to clarify the diagnosis and confirm it. If bloody discharge appears after taking a smear, this is normal for 1-2 days. If the discharge continues for more than 2 days, then this is a reason to consult a doctor unscheduled. In rare cases, untimely treatment threatens the patient with reactive changes in the body and rapid deterioration of the condition.
Cytological examination is never prescribed just like that, only for direct indications. After the results have been received, you should not decipher the text yourself, but seek help from a doctor. He will check all the indicators, correlate them with your medical history and complaints, and conduct additional studies if necessary. Then treatment will be prescribed. After its completion, it will be necessary to conduct a cytological examination again.
How the analysis is carried out
A cytological smear (Pap test, Papanicolaou smear, oncocytology smear) is performed during a gynecological examination. The doctor uses a mirror to examine the vagina, the entrance to the cervical canal and the cervical mucosa. If there is a suspicion of an anomaly, cells are collected with a special brush from 3 areas: from the walls of the vagina, the cervical canal, and the entrance to the cervix. The procedure is comfortable, painless and does not require special preparation.
The mucus is applied evenly onto a glass slide, dried and sent to the laboratory.
A laboratory technician uses reagents to stain a smear and examine it through a microscope. This method determines the following indicators:
- cell structure;
- cell size;
- epithelial shape;
- mutual arrangement;
- number of cells per unit area;
- pathological changes in cell structure.
A cytology smear allows you to identify most inflammatory diseases, precancerous pathologies of the epithelium (dysplasia), and malignant tumors. After taking a smear, spotting is often observed for 2-3 days, which is normal. Extremely rare - severe bleeding, abdominal pain, chills, increased body temperature. In this case, an urgent examination by a gynecologist is required.