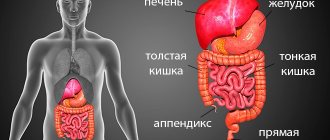
The essence of endoscopic examination of the gastrointestinal tract
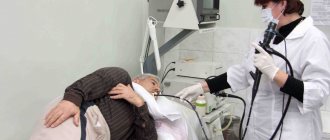
During a colonoscopy, special endoscopic equipment is used.
The key to obtaining a reliable examination result is full compliance with the rules of preparation for it. The manipulation itself, in addition to being simply unpleasant, can be quite painful in the presence of severe stomach pathologies. For this reason, most patients who need to undergo a diagnosis want to know how to check their intestines without a colonoscopy. The essence of this study is that a medical tube with an endoscopic camera on the tip is inserted into the patient's anus, which displays an image on the doctor's monitor screen. During a colonoscopy, the specialist performs the following manipulations:
- analyzes structural changes and condition of the intestinal walls;
- takes biomaterial for biopsy;
- removes outgrowths of the mucous membrane of the intestinal wall, which can be either single or multiple.
Colonoscopy is accompanied by slight bloating, which then gradually goes away. A significant advantage of this method for studying gastric pathologies is its efficiency. A medical report with information about the identified problems is issued immediately upon completion of the procedure.
In addition to the unaesthetic nature of the procedure, many patients do not want to undergo multi-stage preparation for the examination, which consists of following a dietary diet, cleansing the rectum with laxatives and microenemas. In such situations, it is recommended to take gentle sedative medications.
At the preliminary consultation, doctors warn that colonoscopy is generally tolerable, but in some patients it is accompanied by extremely unpleasant symptoms.
Thus, if there is an alternative to intestinal colonoscopy, patients prefer it. The doctor insists on endoscopic fibrocolonoscopy only if there are appropriate indications. It is allowed to replace it with a similar study in the absence of signs of cancer of the digestive organ.
Variations of instrumental examinations
According to medical statistics, about 95% of the population should be periodically diagnosed by a gastroenterologist. This is due to the fact that pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract are quite often diagnosed in different categories of people. Modern medical technologies make it possible to detect the disease at an early stage. Qualified doctors will tell patients in detail what kind of intestinal examination they should undergo in their case and what the preparation for it will be based on.
If it is possible to replace colonoscopy, doctors offer various hardware diagnostic methods for intestines, which can be used either individually or in combination. Hardware analysis of the stomach is prescribed only according to indications. Based on the clinical picture of the disease.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the following instrumental methods of intestinal examination are used:
1. X-ray.
2.Echography.
3.CT and MRI.
4. Capsule endoscopy.
5.Virtual colonoscopy.
Each technique acts as a means of assessing the deformation of the walls of the digestive tract, and has its own characteristics.
Bowel examination methods
The following common methods for diagnosing intestinal diseases can be identified:
- irrigoscopy;
- capsule endoscopy;
- PET scan;
- ultrasonography;
- hydrogen test;
- CT colonography (virtual colonoscopy).
The listed methods are not ideal and cannot fully become an alternative to colonoscopy. However, each of them has a number of advantages over the “gold standard” of diagnosis, which will be discussed below.
X-ray of the stomach
Fluoroscopy is a highly effective analogue of gastric colonoscopy. The essence of irrigoscopy is that during the examination a visual image of the affected organ is displayed on the screen of an x-ray monitor. Indications for this method of diagnosing the intestines are: frequent heartburn, impaired swallowing function, the presence of blood in the stool, rapid weight loss.
This type of examination should not be confused with radiography. Digital fluoroscopy is a more informative method that involves studying the stomach in real time and does not require the creation of numerous images. In addition, the radiation dose is much lower than in radiography.
No special preparation is required before this procedure, and it involves eliminating foods that increase gas formation from the daily diet. Before the examination begins, the patient takes a solution with barium sulfate, which coats the gastric mucosa. During irradiation, X-rays will be retained in the digestive organ, due to which a clear visual image will be provided on the monitor screen. After the stomach is filled, the patient will have to take various positions, while the doctor's assistant takes pictures. During the process of removing barium sulfate, vomiting may occur, which usually disappears after 2-3 days.
Echography of the stomach
In situations where the patient wants to know how to check the intestines other than colonoscopy, the gastroenterologist may suggest undergoing an ultrasound examination. However, it should be understood that this form of stomach examination is not very informative. Sonography does not allow the entire pathology to be identified. Due to the specifics of its implementation, the doctor cannot take biopsy material for laboratory analysis.
As medical practice shows, examination of the intestines without colonoscopy is carried out for young children using an ultrasound procedure. It is with this procedure that the diagnosis begins due to the fact that it causes the least discomfort.
Preparatory measures include the need to exclude the following foods from the diet 3 days before the examination:
- cellulose;
- legumes;
- dairy products;
- carbonated drinks;
- bread and flour products.
The duration of echography is on average 7-15 minutes. The essence of the procedure is that the doctor applies a special gel to the anterior abdominal wall and moves the sensor over the skin to obtain a visual image. According to indications, in some situations the patient is required to drink about 500 ml of distilled water and undergo ultrasound again. An ultrasound examination is absolutely painless and does not have any negative effects on the body. For this reason, this diagnostic method is used even for newborn children.
CT and MRI
Instead of a colonoscopy, the colon can be examined using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This diagnostic technique is based on the use of magnets and radio waves. The generated energy is returned in the form of impulses. When doctors decide how to check the intestines for cancer without a colonoscopy, an MRI is just right. During this study, the doctor can identify large tumor-like neoplasms of a malignant nature, as well as foreign objects.
Before the procedure begins, the patient is injected with the substance gadolinium, which allows one to visually distinguish growths of the mucous membranes of the stomach from healthy tissue. Using MRI, a gastroenterologist can make a final diagnosis and plan further therapeutic intervention. Its only drawback is its rather high cost.
Computed tomography (CT) is an additional alternative that can be used to check the bowel. However, this research method does not allow identifying diseases associated with small tumor-like neoplasms, which is why it is inferior in terms of information content. At the same time, this procedure is completely non-invasive, which makes it so popular among patients with gastric pathologies. The examination is carried out using a special medical tomograph that produces X-ray radiation.
Hydrogen test
This diagnostic method does not require invasive intervention in the patient's body. It is based on recording the time of increase in the amount of hydrogen in different parts of the intestine. As you know, the intestines contain a large number of bacteria that produce hydrogen. Thus, sections of the intestinal tube with a high amount of this element are precisely those areas where the pathological process is localized.
This method cannot be called a full-fledged alternative to colonoscopy examination due to its low information content, however, it can be used to diagnose the following diseases:
- dysbacteriosis with establishment of the exact cause;
- lactase deficiency;
- congenital fructose intolerance.
Capsule endoscopy
Colonoscopy of the intestine can be replaced by an endoscopy procedure. This fundamentally new diagnostic technique is carried out using a special capsule with a built-in video camera. It is this form of research that makes it possible to identify diseases of the small intestine, which until recently was quite difficult to diagnose due to the specifics of its anatomical structure. Previously popular X-ray examination techniques can only reveal severe pathology.
Before the endoscopy begins, the patient swallows a miniature capsule with a built-in video camera. This device transmits an image to the monitor screen while passing through the entire gastrointestinal tract. The procedure itself lasts from 4 to 10 hours, depending on the expected diagnosis and doctor’s testimony. At the same time, a significant advantage of capsule endoscopy is that the patient does not disturb his usual lifestyle and goes about his daily activities.
After the allotted time, the capsule is removed naturally, and the doctor receives images of the small intestine, which are used for further analysis of its condition. In addition to the high cost, significant disadvantages include the inability to collect biomaterial for subsequent biopsy. This means that if a pathology is detected, additional invasive manipulation will be required.
Ultrasonography
Almost everyone knows what ultrasound diagnostics is. But the fact that intestinal examination can also be carried out using ultrasound is a new thing for most. To do this you need to prepare specially:
- 12 hours before the ultrasound do not eat;
- do an enema a few hours before, or take a laxative at night;
- Do not urinate two hours before the ultrasound.
The examination itself is carried out using an ultrasound machine and contrast injected into the intestines through the anus.
Doctors look at the bowel before urinating (with a full bladder) and after bowel movement to see how the intestinal wall reacts as it stretches and contracts.
Which is better, ultrasound or colonoscopy?
Even an experienced specialist will not be able to answer this question for you. Why? Because these are two different types of bowel examination that can complement, rather than replace, each other. You can make a list of the advantages and disadvantages of these examinations, but what is more significant is up to you to decide.
| Ultrasonography | Colonoscopy | ||
| Advantages | Flaws | Advantages | Flaws |
| Painless | Difficulty in preparation | Less expensive | Difficulty in preparation |
| No side effects such as pain or even internal injuries | The gaps in the folds are not always visible | Possibility of biopsy and removal of polyps | There are unpleasant and even painful sensations |
| The entire intestine is examined completely, even remote areas | Tumors smaller than 1cm are difficult to detect | Detection of tumors at early stages | Possibility of injuring the intestinal mucosa |
| Unlimited number of examinations | Information content | ||
It is impossible to say which of these intestinal examinations is better. But you can choose priority indicators for yourself and focus on them.
Virtual colonoscopy
The stomach can also be examined using virtual colonoscopy. The essence of the procedure is that a tube is installed directly into the rectum through which air is pumped. After the lumen has fully expanded, the patient is asked to hold his breath, while the doctor scans the organs. Gastroenterologists say that this procedure is inferior in terms of information content to classical colonoscopy. However, due to the straightening of the rectum, small polyps are revealed in the folds of the mucous membranes, which were not diagnosed during other examinations.
Doctors do not recommend replacing a virtual colonoscopy if they suspect the presence of a flat-shaped, malignant tumor-like neoplasm that does not protrude into the lumen as growths. For this reason, at the moment, doctors do not prescribe it to patients for the purpose of primary diagnosis of stomach pathologies, especially those with cancerous degeneration. The basic indication for virtual colonoscopy continues to be the need to conduct an intestinal examination in patients who cannot tolerate the classical form of the procedure.
Pros and cons of gut testing
Diseases associated with the intestines significantly affect a person’s quality of life. When choosing a diagnostic method, you should not postpone the study, and you need to choose only a high-quality examination.
Colonoscopy can be compared to tomography, and it provides more opportunities for in-depth examination and detection of a large number of pathologies. She also helps take biopsy samples and assists in treatment. This method is considered the most difficult; after it, the patient has the impression for some time that his stomach is swollen, but after a short period of time all symptoms disappear.
Irrigoscopy also has its advantages - this procedure is not so painful, and the degree of injury from it is minimal. This method is well suited in cases where it is difficult to check certain areas of the intestine – bends and pockets – using another method.
And the main disadvantages of diagnostics are contraindications to its implementation:
- intussusception;
- severe form of diverticulosis.
In cases where there is a suspicion of obstruction in the intestine, then irrigoscopy is performed using water-soluble substances, and this greatly affects the quality of the images.
Choosing a method for diagnosing gastric pathologies
In gastroenterology, colonoscopy is considered one of the most informative diagnostic methods. At the initial consultation, the attending physician must warn the patient about the existing advantages and disadvantages of this examination:
| Advantages | Weak sides |
| The study allows you to obtain the most complete information about the condition of the mucous membranes and walls of the digestive organ. | Multi-stage preparation for the procedure |
| High degree of visualization provides a complete view of the stomach | Psycho-emotional discomfort arising during the diagnosis of gastric pathologies |
| During a colonoscopy, polyps can be removed and biomaterial taken for biopsy at the same time. | There may be painful symptoms during the advancement of the endoscopic device in the rectum |
| During the diagnostic process, doctors cauterize bleeding vessels, thereby avoiding surgical intervention | Requires sedative medications and, in some cases, anesthesia for patients with excessive excitability and sensitivity |
| The total duration of the manipulation is 30 minutes | In rare cases, medical practice has encountered such a complication of colonoscopy as perforation of the intestinal wall. This is due to the lack of experience of the doctor |
If the patient is concerned about how to examine the intestines without a colonoscopy, then various alternative hardware techniques can be offered. Each instrumental method for diagnosing gastric pathologies has its own positive and negative characteristics. It should be understood that not all of them can fully replace classic colonoscopy.
Some alternative methods for examining the intestines are used in a narrow specialization; some cannot be used due to the individual sensitivity of the patient’s body to contrast agents.
There are often situations when in any case you will have to undergo a colonoscopy, since this is the only way to take a biopsy material and surgically remove small growths of the mucous membrane. The decision to use one or another diagnostic method is made by the doctor based on the clinical picture, the patient’s age and the presence of concomitant diseases. If gastric carcinoma is suspected, the specialist will insist on a colonoscopy, since only this study will provide such complete information about the tumor.