Ultrasound is the oldest diagnostic method after radiography. Until recently, it was not used to examine the intestines, since the air inside it greatly distorted the result due to its low echogenicity. Modern diagnostic medicine capabilities have changed beyond recognition - now you can do an ultrasound of the small or large intestine without the risk of missing pathological changes.
Topographic anatomy of the abdominal organs
In what cases is ultrasound performed?
A referral for examination of the small or large intestine using ultrasound can only be obtained if there are symptoms that indicate the presence of pathologies in them. The list of indications for the procedure includes:
- chronic constipation;
- systematic fecal incontinence;
- painful bowel movements, especially if blood is visible in the stool;
- gas formation not related to dietary habits;
- chronic pain in the intestines.
Also, an ultrasound of the small and large intestines is performed when the patient has a displacement of the internal organs, and upon palpation, compactions are detected in the abdomen. In men, an ultrasound examination is performed in the presence of a diagnosed prostate tumor, and in women - in case of retrocervical endometriosis.
Patients at risk for oncology and people diagnosed with chronic diseases of the terminal intestine also need regular examination of the large and small intestines using an ultrasound machine.
Abdominal pain - indication for sonography
Ultrasound of the fetal intestine
When examining the fetal intestines, the doctor can determine its echogenicity. The detection of increased echo density indicates the accumulation of feces in the intestines. This is not a direct pathological sign, since it can be observed in both healthy babies and patients with chromosomal diseases. In combination with a discrepancy between the size of the fetus and the gestational age, hyperechogenicity of the intestine indicates a delay in the development of the child.
If such a phenomenon has been identified, the doctor will refer the woman to an appointment with a geneticist, and will also prescribe a blood test for antibodies to TORCH infection. A repeat ultrasound is performed a month later.
What does diagnostics show?
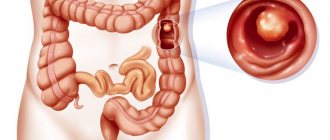
If pathological changes in the intestine are suspected, ultrasound helps to identify many types of pathologies, including changes in the position of its loops relative to other internal organs, neoplasms in the mucous and submucosal layers, inflammatory and other processes. An ultrasound diagnostic doctor using an ultrasound machine can see:
- sizes and shapes of intestines;
- the thickness of the intestinal walls, the condition of their layers and echogenicity;
- the lumen of the intestine, the structure of its internal surface;
- the position of various parts of the intestine relative to other organs (uterus, bladder, prostate);
- condition of regional lymph nodes, their size and density;
- inflammatory foci inside the intestine and in nearby tissues;
- structural anomalies (congenital and acquired - scars, strictures, injuries);
- neoplasms (polyps, tumors, metastases), their location, size.
Radiology doctors claim that ultrasound shows even small-sized altered areas of the digestive tract. This allows you to make a correct diagnosis without using more expensive methods (MRI and CT).
When examined by ultrasound, the resulting image will indicate the presence of the following pathologies:
- paraproctitis acute and chronic;
- colitis, appendicitis;
- source of intestinal bleeding, hematomas of the intestinal wall;
- diverticulosis, polyps;
- intestinal adhesions, intussusception;
- tumors in the walls of the digestive tract and in the perirectal tissue;
- Crohn's disease.
It is recommended to perform an ultrasound of the intestine in a child who exhibits symptoms of disorders such as ulcerative colitis, congenital anomalies in the structure of the terminal region, IBS, Hirschsprung and Crohn's disease, dolichosigma.
Indications
An intestinal ultrasound for a child, like an adult, is prescribed to confirm the following diagnoses:
- peritonitis (general inflammation of the peritoneum);
- acute or chronic appendicitis (ultrasound of appendicitis is necessary to clarify);
- colitis of unknown etiology;
- intussusception;
- to determine the presence and degree of complications after surgery;
- if there is a suspicion of peritoneal pathology;
- if a neoplasm is suspected or under dynamic observation;
- to determine free fluid in the retroperitoneal space.
An ultrasound of the rectum is performed in the following conditions:
- chronic constipation or, conversely, fecal incontinence;
- blood impurities in stool;
- suspicion of a neoplasm detected by palpation;
- when determining the displacement of organs on an x-ray image;
- detection of colon deformation during rectoscopy;
- for dynamic monitoring of rectal cancer;
- in case of endometriosis, it is carried out to exclude pathology;
- in men with prostate cancer;
- after surgical treatment for a tumor to exclude recurrence of the tumor.
The research procedure requires high-quality preparation to obtain reliable data and can be carried out in two ways.
Types of ultrasound diagnostics
There are several types of this diagnosis, depending on how the intestinal ultrasound is performed - through the abdominal wall or through the rectum. There are two types of examination:
- Transabdominal examination - is carried out through the anterior abdominal wall using a wide sensor, rounded on one side. In some cases, to obtain an accurate diagnosis, special preparation for an ultrasound of the intestine in the form of an enema with a contrast solution is not required, but the bladder must be full.
- Transrectal ultrasound of the rectum is performed through the anus using a narrow, elongated probe. This type of study requires more careful preparation (sometimes psychological), and is used only in the absence of pathological narrowing in the intestines and stenosis of the rectal sphincter. Bladder filling is not required for this type of examination.
Transrectal examination is considered more informative, since during abdominal diagnosis the rectal area is less visualized, especially when the patient has not filled the bladder well enough. However, it is always performed after an external, abdominal examination.
transrectal and transabdominal diagnostic sensors
What to choose: ultrasound examination of the intestine or colonoscopy
An ultrasound scan uses high-frequency waves to move a transducer (which both emits a signal and picks up a response electrical impulse) along the abdominal wall or inserted into the anus to examine the rectum.
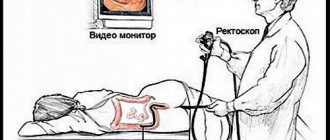
Colonoscopy is the name of diagnosis, which is carried out using an endoscope placed inside the rectum and is highly informative. During the examination, the patient is placed on his back and a special tube with an optical device at the end is inserted into the anus.
When choosing a research method, most people prefer ultrasound, since colonoscopy is a rather painful diagnostic option (although recently it is increasingly being performed with anesthesia). Still, for children it is better to choose ultrasound because of painlessness and comfort.
How to prepare for the examination
If you do not prepare, an ultrasound of the digestive tract will not show the real picture - particles of undigested food and fecal stones will interfere with a good view. To reduce the likelihood of receiving unreliable results, preparation for the procedure should begin at least one day before visiting the ultrasound diagnostic room. You can clarify all the points on how to prepare for the study more effectively with the doctor who issued the referral.
Standard training should include:
- dietary adjustments - it is not advisable to eat heavy, difficult-to-digest foods, smoked and fatty foods, as well as drink alcoholic and carbonated drinks before an ultrasound;
- stimulation of the digestive process with enzyme preparations - Pancreatin, Mezim, Creon;
- elimination of gases in the intestines with Espumisan, Smecta in adults, and Bobotik is suitable for children;
- cleansing the intestines using the drugs White Coal, Enterosgel, Smecta.
It is advisable to take medications at the preparation stage on the recommendation of a doctor in individually selected doses. To find out whether a particular product can be used, it is necessary to have a preliminary appointment with the attending physician or an ultrasound diagnostic specialist who will conduct the examination.
If a patient has problems with stool in the form of constipation, he faces an additional problem: how to clean the intestines before an ultrasound so that solid stool does not interfere with the diagnosis. Doctors recommend using cleansing enemas or saline laxatives 6-12 hours before the procedure.
The diet should be followed for 2-3 days, and 6-8 hours before visiting the ultrasound diagnostic room, you should completely stop eating. If an external (abdominal) examination is planned, an hour before it you must drink at least a liter of water without gases and sugar, or herbal unsweetened tea.
Note! Smoking, sucking lollipops or chewing gum is prohibited until the diagnosis is carried out!
If your doctor insists that you need to check your digestive tract with a rectal probe, you should not drink a lot of fluids. Food is also avoided 6-8 hours before the examination. Also, on the eve of the diagnostic procedure, you should do a cleansing enema (preferably in the evening if the diagnosis is scheduled for the morning).
Diet and cleansing procedures
Diet plays an important role in preparation. It should be followed for 2-3 days. Let's take a closer look at how you should eat and what you can eat and drink before an ultrasound of the intestine?
To reduce gas formation, you should exclude from your diet:
- Vegetables and fruits in any form; it is allowed to use potatoes, carrots, and beets for cooking.
- All types of legumes (lentils, peas, beans) and corn. You can cook porridge from any other cereal products.
- Fatty meat, fish. The amount of protein should be limited, for example, use no more than 1 egg per day.
- Dairy products, especially those with a high fat content (cream, sour cream). It is allowed to use fermented milk products (ryazhenka, kefir).
- Bakery yeast products, pastries, sweets; Yesterday's bread can be eaten in small quantities.
- Carbonated drinks, juices, strong coffee. Lightly brewed tea is allowed.
- Alcohol.
How is the diagnosis carried out?
The examination takes place in the ultrasound diagnostic doctor’s office. First, the patient is placed on a couch and a conductive gel is applied to the abdomen. A wide transabdominal probe is used to examine the intestines. If during the procedure it was not possible to establish the nature of the symptoms, a transrectal examination is performed. To do this, the patient frees the lower part of the body from clothes, lies on his left side and pulls his knees towards his stomach. The doctor inserts an endorectal probe into the rectum and examines the intestinal walls, their lumen and surrounding tissues. During the procedure, the specialist moves it to different depths and periodically turns it. The procedure lasts about 10 minutes.
Standard bowel examination procedure
Since checking the intestines for the presence of pathological foci located inside it using the method described above is not enough, the doctor may recommend ultrasound irrigoscopy. To do this, a sterile saline solution is injected through the anus through a rectal catheter. The liquid creates pressure inside the intestine, its walls straighten, and the internal surfaces are better visible during an abdominal ultrasound.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of changes recorded during an ultrasound examination. This is usually done by a gastroenterologist, but in order to make a final verdict, consultations with other specialized specialists, for example, an oncologist, are sometimes required.
Intestinal ultrasound is the safest diagnostic method, which is suitable for examining children in the first year of life and pregnant women. It has a minimum of contraindications and is highly informative.
Features of colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is a direct visual method that allows you to directly see the inner walls of the colon, identify polyps, tumors and other lesions of this organ.
Examination of the small intestine is difficult, but possible. The procedure is carried out thanks to a camera, which is located at the end of the endoscope tube, about 1.45 m long, with a diameter of 5-7 mm. In this way, it is possible not only to diagnose polyps and neoplasms at an early stage, but also to remove them, avoiding surgical intervention. It is also possible to do a biopsy for diagnostic purposes, cauterize erosions, and administer medications. The manipulation is painful and is performed under anesthesia. The patient, who lies on his side, has an endoscope inserted through the anus. Advantages of the endoscopic method:
- It has the ability to detect the smallest formations of the colon and is distinguished by its efficiency and accuracy.
- The doctor has the opportunity to see the entire internal cavity of the intestine, assess the condition of the walls, while receiving a clear color image.
- During the examination, biopsies and treatment procedures are also possible.
Disadvantages of colonoscopy:
- long preparation of the patient before manipulation;
- the risk of injury and cracks in the intestinal walls;
- the need for anesthesia;
- for children and elderly people, use is limited, only when absolutely necessary;
- inaccessibility of examination of the upper sections;
- risk of complications.
Types of endoscopic method
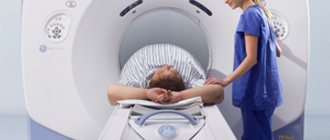
Virtual (tomographic) colonoscopy is performed using a tomograph and lasts 10 minutes. The diagnosis is made based on the creation of a 3D model of the intestine. The procedure is painless, the contraindications are similar to colonoscopy, but the method is not used during pregnancy.
Capsule endoscopy is indicated for examining the small intestine using a special capsule with a video camera, which moves through the gastrointestinal tract and transmits information to a special medium. It is recommended to conduct the study on an empty stomach.
Balloon enteroscopy is performed for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. The endoscope is inserted through the anus or mouth. It is performed under general anesthesia. Using this method, a biopsy is also performed, foreign bodies are removed, and tumors are removed.
Rectosigmoidoscopy is used to diagnose pathologies of the sigmoid colon and rectum.
Who is the procedure indicated for?
Typically, instrumental diagnostics, along with laboratory tests, are part of a comprehensive study of the gastrointestinal tract. This is carried out if there are relevant complaints. This method is gradually replacing FGS (in cases where it is optional). Ultrasound examination is prescribed in case of suspected diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in the presence of symptoms such as:
Sometimes doctors prescribe the procedure for preventive purposes. This type of examination is indicated for people suffering from chronic gastrointestinal diseases. This helps to avoid exacerbations in a timely manner. Sonography helps in identifying acute appendicitis.