How to prepare for an ultrasound scan of the gland?
Accurate results of this diagnostic method are achieved by following some simple rules. Preparation for liver ultrasound has certain specifics. Before the study, patients are prescribed fractional meals in small portions up to 4 times a day. The last meal (dinner) is taken 2 hours before bedtime. The drinking regime is reduced to 1.5 liters per day. The best time for the study is on an empty stomach in the morning. If the study is scheduled for the afternoon, only a light breakfast is allowed. At least 8-10 hours should pass between the procedure and food intake. 48 hours before diagnosis, foods that increase gas formation are excluded from the menu. Such products include:
- high-calorie dishes;
- black bread;
- legumes;
- raw fruits, vegetables;
- milk;
- sweets: cakes, pastries;
- fish;
- products containing yeast;
- fat meat;
- cabbage;
- fiber;
- sparkling water;
- alcohol.
If the patient’s body is prone to gas formation, you should take activated charcoal the evening before the test. If the patient has a tendency towards obesity, he should do a cleansing enema in the morning and evening the day before the diagnosis. When the patient is taking any medications, it is necessary to consult with the doctor about rescheduling the medication to a later time. This is required to avoid diagnostic errors, since some medications can cause a slight enlargement of the liver or its structure.
Return to contents
How do they do it?
The child will lie on the couch. It is most convenient to dress it in such a way that it is easy to expose the abdominal area. The doctor will lubricate the child’s skin with a hypoallergenic gel in the area where the examination will be performed and move the sensor over the skin. During the examination, the doctor will move the sensor over the child’s abdomen, turn small children on their sides, and older children will be able to do this themselves.
Additionally, the doctor may ask them to hold their breath from time to time . All the time he will also look at the computer monitor and make special notes. Then the gel is easily removed with a damp cloth.
Preparing for an ultrasound examination of the gallbladder
If it is necessary to perform an ultrasound of the liver and gallbladder, study the ducts, determine the degree of contraction of the organ, the level of bile production as a response to food intake, the intestines are prepared for the procedure, it should not interfere with the scanning.
For several days before the ultrasound, you should limit your food intake and take medications to help reduce gas formation. Ultrasound of the gallbladder is performed on an empty stomach to facilitate the examination, since bile accumulates in the gallbladder and allows for an objective assessment of its condition. Before an ultrasound scan of the gallbladder, a cleansing enema is performed. Ultrasound of the liver and gall bladder is performed by people with a traumatized abdominal cavity, suspected cholecystitis, gall bladder cancer, polyps, blockage of the biliary tract, or cirrhosis of the liver. The following violations are detected:
- congenital cysts;
- tumors of benign and malignant nature;
- metastatic lesions that spread from the stomach, intestines, pancreas, skin, genitals, prostate, kidneys, lungs, soft tissues, etc.
Often metastasis to the liver occurs due to tumor formations of the small and large intestines, pancreas, and stomach. Less commonly, the kidneys, lungs, and prostate gland metastasize to the liver. Ultrasound diagnostics, in combination with other examination methods, makes it possible to judge whether a patient has serious oncological complications, liver cirrhosis, or hepatitis. Doctors compare the results obtained with the norm, evaluate the structure, contours and tissues of the organ. Ultrasound allows you to accurately assess the size, shape, location of the abdominal organs (liver, spleen, gallbladder), identify focal formations, bile duct stones, and evaluate changes in the bile ducts.
Today, ultrasound examination makes it possible to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate therapy.
Rate this article:
For the correct diagnosis of hepatological diseases, as well as routine examinations of internal organs, the state of the digestive tract on the eve of the procedure is of great importance. Therefore, it is important to follow some rules before an ultrasound scan of the liver: the preparation is not complicated and consists of a few simple steps that will help the radiologist make an appropriate description and interpretation of the results.
How to prepare for a liver ultrasound?
During an ultrasound examination, it is important that there is no large accumulation of gases and feces in the intestines. Therefore, the examination must be performed on an empty stomach, preferably in the morning. It is recommended that the last meal be taken the night before, 8-10 hours before the ultrasound.
If the session takes place in the afternoon, a very light breakfast is allowed, for example, a few spoons of oatmeal without fat or vegetable soup. At the same time, it is undesirable to consume foods that cause flatulence:
- fiber;
- cabbage;
- whole milk;
- legumes
- Rye bread;
- fresh fruits.
A person’s tendency to increase the formation of gases in the intestines requires taking more serious measures - taking any sorbent the day before ultrasound examinations, and taking drugs like Espumisan 2-3 days before. In some cases, 1 or 2 cleansing enemas are prescribed on the eve of the procedure.
Preparing the patient for ultrasound of the liver and gallbladder
The difficulty of examining the gallbladder lies in the fact that it is necessary to carefully examine its ducts, as well as to identify the degree of contraction of the organ and the level of bile production in response to food intake.
Thus, the first stage of preparation for an ultrasound examination is similar to the previously given rules for describing the condition of the liver. At the second stage, the gallbladder is examined after eating, usually a small amount of any fatty dairy product (sour cream). This allows you to determine whether the organ contracts correctly, how much bile is produced, and how clean the ducts are.
Preparation for ultrasound of the liver and pancreas
Often, together with hepatological studies, diagnostics of the pancreas is carried out, especially if hepatitis A or Botkin’s disease (“jaundice”) is suspected.
To properly prepare for an ultrasound, you need:
- Do not eat food 5-6 hours before the procedure.
- In case of increased flatulence, 3-4 days before the ultrasound, do not eat poorly tolerated foods, as well as foods that cause gas formation.
- Take enzymatic drugs (Enzistal, Pancreatin, Festal).
- Drink Espumisan 2 days before ultrasound diagnostics.
- Cleanse the intestines once using a mild laxative or enema.
Preparation before ultrasound of the liver and spleen
In case of liver diseases and toxic lesions of the body, acute intoxication syndrome or viral hepatitis, an additional examination of the spleen is carried out. If an ultrasound examination is performed exclusively for this organ, then no special preparation measures are required, but, as a rule, the spleen is studied together with other components of the digestive tract. Therefore, it is advisable to adhere to the same rules as before an ultrasound of the liver:
- Have your last meal 8 hours before the procedure.
- Do not eat milk, fresh vegetables and fruits, bread made from dark flour, fatty, fried foods, legumes, mushrooms, carbonated drinks, strong coffee or tea.
- In case of gas formation, use a sorbent (activated carbon, Enterosgel, Polysorb).
- Make a cleansing microenema or take a natural laxative once.
The development of medicine does not stand still. Over the years, specialists have managed to create a fairly simple way to diagnose human internal organs. This method is called “ultrasound examination”. It is quite accurate and reliable. Most often, patients are prescribed a study of the digestive organs, including an ultrasound of the liver. Preparation for the procedure is required in each case. However, it may differ slightly for different patients. From this article you can find out what indications a liver ultrasound has. Preparation for the procedure will also be presented to your attention.
Terms used to describe the liver on ultrasound
To make a correct diagnosis, you should know what an ultrasound of the liver shows.
Each transcript contains digital values (dimensions) and description.
In conclusion, the following concepts can be seen:
- Calcification is an area of the liver impregnated with salts that occurs as a result of an infectious disease of the organ.
- A cyst is a cavity in the structure of an organ containing fluid. Refers to benign formations.
- A tumor is a malignant formation of a dense structure that grows deep into the tissues of an organ, possibly spreading beyond the capsule.
- Diffuse changes in the liver may be a sign of organ disease or reflect natural aging of the body. This term refers to changes in the tissue of the entire organ. Diffuse changes during diagnosis can be detected in hepatitis or cirrhosis.
- Increased echogenicity indicates the presence of areas in the structure that do not transmit the ultrasound wave and thereby prevent a full examination.
- The “white liver” symptom indicates a fatty lesion, the hepatocytes are replaced by non-functional adipose tissue and do not reflect ultrasound waves well. In the photographs, areas of light-colored liver appear.
It is worth remembering that deciphering ultrasound diagnostics is for a doctor; only he can make the correct diagnosis. The same indicator may indicate different diseases or be the norm.
In addition to the listed indicators, sometimes in the transcript of the liver you can find the following terms indicating the disease:
- Spots on the liver are areas of compaction, indicating the presence of foci of the disease; they often indicate damage to the organ by Giardia.
- Liver compaction is also a diagnostic term indicating the presence of neoplasms; to clarify malignancy, a biopsy is performed followed by histological examination.
https://youtu.be/skB_jkqkx3E
What is the liver?
Before finding out how an ultrasound of the liver is performed, preparation for the study and what indications there are for this, it is worth saying a few words about the organ itself.
The liver is recognized as one of the largest formations in the human abdominal cavity. It performs vital functions. The organ is involved in hematopoiesis. The liver also passes through itself all medications, junk food, alcohol and other products entering the human body. During this process, the organ cleanses all beneficial substances from toxins and poisons. This is why people so often have to deal with liver diseases. To identify this or that pathology, doctors conduct research. They consist of palpation, blood and urine tests. An ultrasound of the liver is also often prescribed. Preparation for the procedure includes several stages. You will learn about them further.
Decoding the results: what pathologies will an ultrasound of the liver reveal?
When deciphering liver ultrasound indicators, the following pathologies can be detected:
- Various types of hepatitis (acute, chronic). They are characterized by a heterogeneous structure of the liver tissue, indicating an inflammatory process and an increase in the size of the organ.
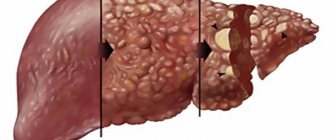
- Cirrhosis . This is the result of long-term inflammation and death of liver cells. Characteristic echo signs are uneven edges, lumpy surface, and heterogeneous structure.
- Cysts. On ultrasound, a parasitic liver cyst appears as a round formation with a dense hyperechoic capsule. The cavity is filled with liquid, sometimes the structure is heterogeneous and contains dense inclusions.
- Hemangiomas . They are found more often in women and represent a tangle of intertwined blood vessels.
- Malignant tumors formed from liver tissue or resulting from metastasis from other organs.
Also, ultrasound can detect calcifications in the liver that have formed as a result of infectious diseases. This is a dense structure formed as a result of the deposition of calcium salts in places of hemorrhage. Typically, the formation of calcifications is caused by infections such as tuberculosis, malaria, and amoebiasis.
Ultrasound of the liver helps to detect most pathologies of the liver tissue, as well as evaluate secondary changes associated with damage to other body systems. Ultrasound is a fast, accessible and informative examination method that allows timely detection of diseases and initiation of treatment.
Indications for diagnostics
Most often, the study is prescribed to older people. This is explained by the fact that various liver pathologies occur with age. However, the study cannot be ruled out in young people. Indications for the procedure are the following cases:
- yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes;
- bright-colored urine combined with pale-colored feces;
- poor laboratory results;
- long-term medication use;
- state of the body after radiation exposure and chemotherapy;
- abdominal pain localized in the right hypochondrium;
- heaviness in the peritoneum after eating;
- alcohol abuse and addiction to bad habits;
- suspicion of the formation of tumors in an organ of various types;
- after severe trauma to the peritoneum;
- during certain diseases at the stage of selecting a correction;
- for preventive examination.
In fact, the list of indications can go on for a very long time. The listed points are the most popular reasons why a doctor prescribes such a study. This allows you to find out the cause of the pathology and make the correct diagnosis.
Why does the liver enlarge?
An enlarged liver is called hepatomegaly. For preschoolers, the norm is when it protrudes beyond the hypochondrium by about 1 cm; these are age-related characteristics (acceptable moderate increases). Then it “hides”, and can protrude beyond the edge if there is some kind of disease.
Symptoms:
- most often, palpation reveals a protruding liver;
- pain and heaviness in the liver area;
- very light stools, even white, and dark urine;
- vascular network in the liver area, yellow sclera and mucous membranes;
- abdominal circumference is visually increased.
Causes:
- inflammatory processes and congenital infections;
- metabolic disorders, genetic disorders;
- hepatitis, hypervitaminosis, sepsis;
- violation of the outflow of blood and bile;
- primary liver damage;
- malignant liver lesions.
Ultrasound of the liver: preparation
Preparing the patient for such a study should begin several days before the scheduled diagnosis. It includes several stages. The patient must follow a certain diet and drinking regimen. In some cases, it becomes necessary to use medications.
If your doctor has ordered a liver ultrasound, preparations for the procedure will be explained to you in advance. Otherwise, you need to ask your doctor yourself and find out what needs to be done before the manipulation. Let's consider the main points of preparation for diagnosis.
Normal organ sizes in adults and children
To decipher an ultrasound of the liver, special tables are used that indicate the norm and average size of the organ in adults and children. Sizes vary depending on the age of the child. In adult women and men they are approximately the same. Of course, there may be exceptions related to the height, weight, and constitution of the subject. In such cases, the doctor takes into account the possible error.
Ultrasound determines the size of each lobe separately: length, width, as well as oblique vertical and craniocaudal dimensions. A separate examination of each lobe makes it possible to identify focal changes (tumors) that do not spread to others.
Three days before the test
So, you are preparing for an ultrasound of the liver. What can you eat? There are no special dietary restrictions three days before the procedure. However, during this period of time it is worth giving up fatty foods, smoked foods and pickles. Also limit your consumption of fast food and instant foods. Three days before the procedure, you must completely eliminate alcohol and carbonated drinks from your diet.
During this time, try to eat soups made with low-fat broth. Instead of plain bread, use bran or crispbread. Porridge, boiled potatoes, steamed meat - you can eat all this. Limit your consumption of raw vegetables and fruits. If desired, you can steam cabbage, eggplant, and broccoli and then consume them. Plain water should enter the body in unlimited quantities.
Ultrasound in newborns and infants
In this case, the task is somewhat simplified. Milk is quickly absorbed in a child’s stomach, so it’s worth booking an examination so that it happens 3 hours after feeding. If the baby eats formula, then 3.5-4 hours should pass after eating , since the mixture stays in the stomach longer.
Nursing mothers should also change their diet and exclude gas-forming foods, otherwise the baby will also develop gas. This means that mom should even give up sweet tea .
During this period, the baby should be given clean, unsweetened water; any tea is prohibited.
The day before diagnosis
If you are overweight, then most likely your doctor will recommend you do a cleansing enema. As an alternative method of cleansing the body, you can take a laxative. However, this should not be done on the eve of the event, but approximately 24 hours in advance.
In addition, it is recommended to take several tablets of activated carbon. The sorbent will cleanse your body of harmful substances that may affect the results of the study. In case of increased gas formation, you need to use appropriate medications, for example, Espumisan. However, before doing this, you should consult your doctor.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of the ultrasound method for diagnosing the liver are:
- non-invasiveness,
- safety,
- multidimensionality of research
- the ability to assess vascular blood flow in Doppler mode,
- relative speed and low cost of the procedure.
Disadvantages include deterioration in image quality in people with developed subcutaneous fat and patients with severe intestinal bloating, and lower spatial resolution compared to radiological methods (CT, MRI).
On the day of the study
Preparations for liver ultrasound are almost complete. Is it possible to drink water on the day of diagnosis?
Doctors recommend performing the procedure on an empty stomach. That is why most studies are scheduled for the morning. Drinking water is not contraindicated. However, this should not be liters of liquid. Limit yourself to one glass. If the procedure is scheduled for the evening or lunchtime, then a light breakfast is allowed. Remember that at least six hours must pass from your last meal to the start of the study.
Normal indicators
The data obtained during an ultrasound of the liver and gallbladder are compared with normal values. In adults, a normal liver should have smooth and clearly defined edges, a uniform structure and certain parameters (in cm):
- width up to 27 (minimum 23);
- length – from 14 to 20 cm;
- diameter – minimum 20, maximum 22.5;
- right lobe – 12.5;
- left side – 6-8.
The common duct of the organ is 3-5 mm, the inferior vein is up to 15 mm. Normal values of the gallbladder (in cm): width – from 3 to 5, length – minimum 7, maximum 10, diameter – from 3 to 3.5. The diameter of the main duct is up to 8 mm, the lobar duct is up to 3 mm, the wall thickness is up to 4 mm.
Ultrasound is a simple diagnostic method. The cost of the examination is much less than a CT or MRI; the body does not receive a dose of radiation. There is no need to lie still during the scan, which is a big advantage for the use of ultrasound in pediatrics.
Summarizing
You now know how to prepare for a procedure called “ultrasound examination of the liver.” Often during the manipulation, the doctor examines neighboring organs. The data obtained allow us to judge possible pathologies or their absence. Remember that a conclusion is never a diagnosis. In the research protocol, the doctor describes only what he sees on the monitor of the diagnostic device. The final verdict must be made by the attending physician. That is why after the manipulation it is advisable to contact a specialist and get an appointment. Good luck with your research results!
In modern medicine, ultrasound diagnostics of internal organs is one of the most informative ways to determine organic and functional pathology. Modern ultrasound diagnostic equipment allows you to successfully assess the functional and structural state of all organs of the digestive system.
Using this method, it is possible to timely detect benign and malignant neoplasms, abscesses and cysts of these organs.
The reliability of the data obtained depends not only on the qualifications of the doctor and the technical characteristics of the ultrasound machine, but also on the quality of preliminary preparation for the study. Below we will present the basic rules for preliminary preparation for ultrasound examination of the liver and pancreas, which will make the results of this procedure as accurate as possible.
Application of ultrasound
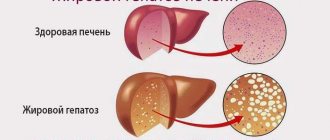
Hepatic steatosis
Hepatic steatosis is the most common pathology of this organ. The sensitivity and specificity of detecting hepatic steatosis by ultrasound is very high. In transabdominal ultrasound, hepatic steatosis is characterized by increased echogenicity.
Cirrhosis of the liver
The accuracy of ultrasound in diagnosing liver cirrhosis in patients is high (>90%). In the initial stages and with micronodular cirrhosis, the accuracy can drop to 30%. Sonographic features of cirrhosis include heterogeneous echostructure and irregular nodular structure of the liver surface and a variety of other possible findings, including disrupted vascular architecture, also depending on the etiology of the diseases.
Chronic viral hepatitis
With hepatitis B and C, signs of diffuse liver damage are revealed.
Primary biliary cirrhosis
The echo texture of the parenchyma in patients with stage I and II primary biliary cirrhosis is often unremarkable. Stage IV shows typical signs of liver cirrhosis.
Liver cyst
Cysts are common. They are easily diagnosed using conventional ultrasound. Liver cysts are characterized by strong posterior wall echogenicity and postcystic enhancement due to pulse differences.
Hemangioma
It is known that hepatic hemangiomas are the most common benign liver tumors.
Abscess
If a liver abscess is suspected, ultrasound can identify a pathological focus in the parenchyma of the organ.
Ultrasound examination may be indicated in such cases if:
- pain appears in the right hypochondrium, which occurs and intensifies after drinking alcohol, fatty and fried foods, or after physical activity;
- the skin changes its color, acquires a yellow or yellow-gray color;
- there is a history of diseases of the pancreas or gall bladder;
- there is a suspicion of the presence of a tumor in the liver;
- there was an abdominal injury and there is suspicion of liver damage;
- there is a suspicion of a liver abscess;
- the patient has a history of drug or alcohol abuse;
- the patient takes medications for a long time that can damage the liver;
- the patient has laboratory signs of liver disease;
- disease treatment monitoring is required.
Doppler ultrasound is used to diagnose the following conditions:
- hypoplasia and aplasia of the common hepatic artery and/or its branches with atrophy of the associated liver segments;
- aneurysms of the common hepatic artery and its branches;
- atypical vascular directions;
- arteriovenous and arterioportal shunts;
- abnormal vascular malformations are more common in association with vascular changes in other organs (heart, lungs, brain and kidneys), which usually determine the clinical course and prognosis.
Ultrasound examination of the liver is rarely performed separately; most often, diseases of the hepato-biliary tract are diagnosed, which includes, in addition to the liver, the gallbladder and bile ducts, since their pathology is often interrelated. Or, to diagnose various disorders of the digestive tract, a comprehensive ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs is performed. Ultrasound of this organ is also carried out together with ultrasound diagnostics of the pancreas.
Preparation for liver ultrasound
In the process of preparing for an ultrasound examination of the liver, two main points play a key role: diet and the level of gas formation in the lumen of the large intestine. Increased levels of carbon dioxide in the intestines can distort the results of the study. The diet prescribed the day before helps reduce the processes of fermentation and gas formation, and also stimulates the cleansing of the intestinal lumen.
Diet
The main preparatory measures for an ultrasound examination of the liver imply compliance with the following food intake rules:
- Food intake should be in small portions, several times a day (4-5). Evening meals should be consumed at least 3 hours before bedtime.
- Water consumption should be moderate and not exceed 2 liters per day.
- Ultrasound diagnosis should be carried out on an empty stomach, and the last meal before diagnosis should be at least 8-9 hours before the diagnosis.
The following list of foods should be excluded from your daily diet:
- products containing increased amounts of plant fiber and yeast (white cabbage, peas, beans, soy, flour products, baked goods);
- confectionery products;
- sweet and carbonated drinks;
- whole milk;
- fatty varieties of meat and fish;
- Rye bread;
- caffeinated drinks;
- raw plant foods.
The list of permitted food products includes:
- cereals in the form of porridges (barley, flaxseed);
- fish and meat varieties with reduced fat content (boiled);
- The consumption of chicken eggs is permissible in the amount of 1 piece. per day (soft-boiled);
- hard cheeses with a low fat content.
If the proposed diet did not help reduce gas production in the intestines, then there is a need to take special medications. Such drugs include activated carbon, Mezim and Festal, as well as Espumisan.
People with excess body weight need to undergo a deep cleansing enema on the eve of the liver ultrasound procedure. Also, ultrasound diagnostics should not be carried out immediately after endoscopic examinations of the gastrointestinal tract and x-ray diagnostics using contrast agents.
On the eve of the procedure, you should completely stop smoking, chewing gum and caramel candies. The optimal time to conduct the study is the first half of the day. You should inform your doctor and diagnostician in advance about taking any medications. It is strictly forbidden to take antispasmodic drugs before the study.
Features of preparing children
For most parents, the most pressing question is how to prepare their children for a liver test. In pediatric practice, it is recommended to adhere to the following tips:
- Children from birth to 1 year should skip one meal, and this corresponds to 3 hours before the test. The last drink of water should be 1 hour before the procedure.
- Children from 1 to 3 years of age should be given food no later than 4-5 hours before diagnosis. The last intake of liquid is 1-1.5 hours before.
- The last meal before the study in children over 3 years old should be 6-8 hours before, and liquids should be 1.5 hours before.
You should have a clean disposable diaper, dry wipes, as well as data from previous studies with you.
Norms
During the examination, the doctor will look at the structure of the liver, its uniformity, and whether the vessels are clearly visible. Size is also important. They depend on the age of the child.
Right lobe:
- 1 year - 60 mm, each subsequent year + 6 mm;
- 15 years - 100 mm;
- 18 years old - 120 mm.
Left lobe:
- 1 year - 33-40 mm, each subsequent year 2 mm;
- 15 years - 50 + 1.5 mm;
- 18 years old - 50 + 1.5 mm.
After the study, parents will be provided with a transcript of the study, which will indicate all detected violations or the absence thereof.
Anatomy of the liver
The liver is the largest gland in the human digestive tract. In the vast majority of people it is located in the right hypochondrium. An anomalous location is less common - on the left. The weight of an adult human liver ranges from 1.2 to 1.5 kg.
The organ is divided into 4 lobes:
Adjacent to the liver are other organs of the abdominal cavity - the tail of the pancreas, part of the duodenum, the gallbladder, and the right kidney.
On ultrasound, several segments of the liver are distinguished:
- caudate lobe;
- left side upper;
- left side lower;
- left middle;
- right front upper;
- right front lower;
- right rear upper;
- right rear lower.
Thus, the liver has 8 segments (photo). This is taken into account when making a diagnosis.
Norms and anomalies
The diagnostician evaluates the size, shape, echogenicity and echostructure of the liver. Additionally, the relative position of the liver with other organs and structures is assessed.
To assess the echogenicity of the liver parenchyma, the doctor compares it with the echogenicity of the kidney and spleen: normally, the liver parenchyma is somewhat more echogenic than the renal cortex, as well as the parenchyma of the spleen and pancreas.
On an ultrasound machine, the liver is normally fine-grained, which is due to point and linear formations distributed throughout the organ.
The norm for the right hepatic lobe along the midclavicular line is about 130 mm, and in asthenics this parameter can reach up to 140 mm. In cross-section, the thickness of the right lobe reaches 110–125 mm. The size of the liver from the edge of the right lobe to the most distant point of the diaphragmatic dome is up to 149 mm.
The norm of the left lobe of the liver varies within the following limits: vertical size - up to 60 mm, thickness - no more than 100 millimeters. The angle of the lower edge of the left lobe is less than 30°.
The gallbladder is a pyriform organ with anechoic contents. The wall of the gallbladder does not exceed 4 mm in thickness. Normally, the contents of the gallbladder are homogeneous, anechoic, the internal contour is clear and even, the presence of a physiological inflection is allowed in tall patients.
How is the procedure performed?
An ultrasound examination of the liver is performed with the patient in a supine position. If necessary, the doctor may ask him to turn over a little. A special gel is applied to the skin of the abdomen, acting as a conductor between the body and the ultrasound machine. The rays reflected from the organs are returned to the device, converted and displayed on the device’s monitor. More often, the liver is examined with a two-dimensional black and white image. However, there is equipment capable of displaying three-dimensional, color, three-dimensional images. With a 4D examination, the specialist is able to rotate the image, which helps evaluate the organ from all sides. This ultrasound is done when there are difficulties in diagnosing, as well as before surgical interventions.
The examination begins with the right upper abdomen, gradually affecting other areas. During the procedure, the gallbladder is also examined, the patency of the excretory canals is determined, and the vessels of the liver are studied. The process lasts up to half an hour. After analyzing the data, the specialist issues a conclusion based on the ultrasound results.
Indications for ultrasound examination of the liver in a child
Under normal conditions, in the absence of complaints and significant disturbances in the development of the newborn, liver examination is not required. Most often, a general examination of the internal organs is carried out using an ultrasound machine at the age of 1-1.5 months, during which the condition of the liver is also checked. But in some cases, diagnosing the child’s liver may be necessary several times, especially with the following factors:
- the risk of hereditary liver diseases (if there are cases of severe diseases in the family history - hepatitis, cirrhosis, malignant tumors);
- with increased bilirubin;
- with a visual enlargement of the organ detected by palpation;
- for symptoms of blood diseases;
- if there are complaints of pain (crying, restless behavior of the child);
- problems with stool of unknown nature.
The liver ultrasound procedure in children is completely safe. An examination is also carried out in addition to a general blood test, blood tests for biochemistry and liver enzymes. The procedure does not require special preparation, because... the organ is easily visible on the monitor during the procedure. However, 2-3 days before the examination, it is recommended to adjust the child’s diet, excluding from it foods that contribute to the formation of gases and digestive disorders. If necessary, after a doctor’s prescription, the child is given medications that normalize intestinal function.
Children under 6 months of age who are fed breast milk or formula do not require preparation for a liver ultrasound procedure.
If you don’t know where to get an ultrasound of your child’s liver, consult with the specialists of our medical center by phone, or make an appointment with a doctor through the feedback form on the website.
What does the procedure diagnose?
Ultrasound of the liver allows you to determine, first of all, the volume of the liver, as well as its structure. The procedure consists of examining different parts of the organ and measuring the following parameters:
- anteroposterior size of the right lobe;
- anteroposterior size of the left lobe;
- common bile duct;
- diameter of the portal vein.
In addition, this procedure is aimed at detecting foreign entities, such as:
- tumors;
- cysts;
- cancer metastases;
- calcifications;
- hemangiomas;
- cystic formations, etc.
Depending on what the liver looks like, ultrasound can reveal:
- hepatitis,
- cirrhosis (viral, alcoholic, biliary, toxic, congenital and congestive),
- steatosis (fatty liver),
- Budd-Chiari syndrome (hepatic vein thrombosis), etc.
First of all, the doctor who conducts the diagnosis should pay attention to the edges of the liver, as well as the uniformity of its structure.
When performing an ultrasound of the liver, you should also pay attention to neighboring organs. These include the gallbladder and bile ducts. Diseases can affect several organs together. In addition, changes in the liver often suggest pathologies in the gallbladder or bile ducts. Also, in this organ of the human body, some waste products of the body can accumulate due to pathologies and deviations from standard sizes.