Diagnostics
Often we have to face problems in the “proper functioning” of our body, which takes us out of the usual cycle of life. Both the simplest, average person and those most susceptible to various diseases can come face to face with such difficulties: such a predisposition in most cases is inherent at the genetic level.
Often, all those tendencies to one or another disease that your ancestors were sick with are inherited. Therefore, it will not be difficult to find out the likelihood of developing any ailments in the future, make sure of the guesses made, and also contact specialists in time and begin to eliminate this problem.
However, in our time, people do not notice the little things happening in their body, devoting their entire attention to work in the bustle of the city. Poor nutrition and lifestyle, stress, lack of exercise and inattention to one’s own health lead to all sorts of complications in the digestive system, which suffers the most from these factors.
All this hurts our gastrointestinal tract, which is extremely sensitive to any digestive problems. A person goes to the doctor and is told that he needs a colonoscopy of the intestines. What is the preparation for the procedure, is the process itself safe, and is it painful during the procedure? The patient has many questions. Is it possible to diagnose the intestines under and without anesthesia?
Dive into theory
Colonoscopy is a diagnostic procedure that allows the doctor to “get to know each other better” and examine the condition of the patient’s intestines using a small camera - a probe (endoscopic device) designed to examine the colon.
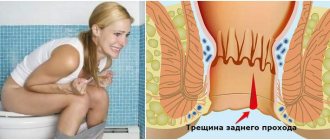
In order for this probe to penetrate the human body, it is inserted through the anus directly into the intestine. A characteristic feature of this procedure is that the examined area is the entire large intestine (120-155 cm long).
In another way, colonoscopy is usually called “endoscopic examination”. It provides the opportunity to take the biopsy cells necessary for diagnosis or immediately begin therapeutic actions.
Indications for the study
The examination procedure can be prescribed by the following doctors:
- proctologist;
- coloproctologist;
- endoscopist.
Colonoscopy evaluates:
- diameter of the intestinal lumen;
- vessels of the submucosal layer;
- mucous color;
- inflammatory changes and motor activity of the walls.
The method allows:
- Find ulcers, polyps, perform biopsies and heal remaining wounds.
- Painlessly remove polyps up to 1 mm (the procedure is called polypectomy), followed by examination of the material for the presence of an oncological component.
When is a colonoscopy needed?
Colonoscopy is used to examine, diagnose, and treat the colon. The procedure is worth going through when:
- it is necessary to identify the cause of abdominal pain or hemorrhage in the rectum;
- treatment of colon cancer and polyps is necessary;
- Need a biopsy for laboratory testing;
- response to treatment should be monitored if inflammatory bowel disease occurs;
- there is a change in the consistency of the stool and the presence of blood in it;
- alternating constipation and diarrhea;
- involuntary weight loss or persistent diarrhea;
- a decline in blood diabetes mellitus below normal has been noticed;
- there is frequent bloating;
- The patient is already 45 years old.
Important! If your closest relatives have had cases associated with oncology of the colon and rectum, then you should definitely systematically conduct a colonoscopy examination for the presence of a source of malignant tumors.
How to behave after a colonoscopy?
After a colonoscopy, it will take some time for your intestines to begin fully functioning again. Therefore, the patient is recommended to adhere to the diet for another two to three days.
In the first days after a colonoscopy, the patient may experience discomfort in the abdomen; nagging pain and flatulence may occur. To relieve unpleasant symptoms, it is allowed to use painkillers and enterosorbents prescribed by a doctor. The latter is usually activated carbon (5-6 tablets per dose), which is washed down with plenty of warm water.
Important! Colonoscopy is a fairly safe examination method that rarely leads to serious complications. However, be sure to consult your doctor if after your colonoscopy procedure:
- the high temperature remains stable for several days;
- pain symptoms manifest themselves for more than a week;
- bloody discharge from the anus appeared;
- there is a sharp deterioration in health: severe nausea or vomiting, weakness, dizziness, breathing problems, etc.
Colonoscopy is one of the most informative diagnostic procedures. As a screening procedure, it is recommended for men and women over 50 years of age.
Classification
An intestinal colonoscopy can be performed both to examine the condition of the patient’s intestines and to cleanse the intestinal walls of polyps if surgery is then scheduled.
Often, an endoscopic examination is carried out to take a tissue biopsy in order to accurately identify the likely presence of inflammatory processes, hereditary abnormalities, or even signs of a benign tumor, if the patient has suspicions or complaints.
Then, thanks to this procedure, it became possible to remove foreign bodies from the rectum, eliminate tumors, and stop hemorrhage in the intestinal cavity. However, colonoscopy is classified not only by the purpose of the procedure.
The process of inserting an endoscope into the body is not a pleasant procedure. It is often performed using anesthesia and anesthesia: the patient’s “vigilance” is “put to sleep,” due to which you fall into a shallow sleep and do not feel any discomfort or pain during the examination.
This medical procedure is called a “sleep colonoscopy.” But is it worth asking for general anesthesia, because it has an unfavorable effect on the body, when a colonoscopy is not even considered an operation and may not cause any pain during the procedure?
Moreover, endoscopic examination is expressed in the vast majority of cases only in an unpleasant sensation of the movement of a foreign object in the body. In any case, this examination is carried out using painkillers. It is probably possible to do without the use of anesthesia if:
- you will be examined by an experienced specialist and expert;
- the individual structure of the intestine and its ruggedness favor easy passage of the probe;
- the patient has an increased pain threshold;
- the psychological and emotional background of the person being examined is high - you should be patient and relax before the procedure without anesthesia;
- The patient has no pathologies that could make the procedure painful and unpleasant.
If such arguments are not convincing, and it seems to you that you cannot do without a colonoscopy in your sleep, then you should think about whether you need anesthesia, which negatively affects the health of the nervous system, or general anesthesia, when there is an alternative to this.
Since several types of anesthesia are used during endoscopic examination, local anesthesia is a good replacement for anesthesia. In this case, a local gel anesthetic is applied to the end of the endoscope probe, which reduces sensitivity at the site of passage of the device - the sensations are dulled, there is practically no pain, but the patient continues to feel the movement of the endoscope probe.
The advantage of this method of pain relief is that the patient is given the opportunity to independently control the progress of the colonoscopy, thereby reducing the likely risk of intestinal damage.
There is another effective way to make the procedure more comfortable - colonoscopy with sedation, during which the patient remains half-conscious/half-asleep. Acts as a sedative, suppressing any sensations. Sedation involves either the drug Midazolam or Propofol. After completing an endoscope examination, sometimes people regain the memory of how the procedure proceeded.
Patients' opinions about the procedure
As you know, how many people, so many opinions. Some say good things, some say not so much, everyone can be understood, and they are all right in their own way. Someone ended up with an unqualified specialist, or was simply deceived, and this happens. Some, on the contrary, easily endured the procedure under the strict supervision of a doctor. However, most agree on one thing - undergo the procedure only under anesthesia. Almost everyone who has dared to do this without anesthesia speaks of unpleasant and even painful sensations. Choosing the anesthesia option is easier for both the patient and the doctor conducting the study. He will not be distracted by noise from the patient and will be able to focus on observing and determining what the colonoscopy shows. In this case, the reviews will be more positive, and the patient himself will forget about the procedure and will not worry.
For some, it is not the procedure itself that causes fear, but the preparation for it. It will be especially difficult for those who eat poorly and are used to eating a lot. You will have to limit yourself for a few days. But even this food can be balanced and tasty, the main thing is to prepare everything correctly.
To reduce irritation from frequent urges to go to the toilet, patients recommend waiting a little and not going there right away, so there will be less pain.
The consequences and sensations from the procedure also depend on the individual characteristics of the structure of your intestines, so no one can say for sure what sensations you will have. You should not be afraid of this procedure, because what a colonoscopy shows cannot be shown by any test. It’s worth going through this and moving on with a calm life.
Instructions for preparing for a colonoscopy
If you have been scheduled for an endoscopic examination, then you need to start preparing for it. Preparation for the procedure is an integral part of the endoscopic examination. The sequence of your actions:
- Be sure to tell your doctor about any allergic reactions you have to medications.
- The next, most serious step in preparing for a colonoscopy should be a complete refusal to eat any food: fruits, cereals, vegetables, especially meat dishes, for 12-14 hours. Otherwise, undigested food particles remaining in the stomach will have an extremely negative impact on the assessment of the condition of the colon and the accuracy of the diagnosis.
- The day before, you can drink more liquids: mineral water (still), tea without sugar.
Important! On the appointed day of the intestinal colonoscopy procedure, it is forbidden to eat absolutely everything, including even water.
Next comes the stage of “cleansing”, but not of the soul, but of the intestines with the help of an enema or special means. Most often it is recommended to take Duphalac, Senade, Regulax.
Cleaning using an enema
Modern medicine offers several methods for cleaning the colon at home, and, in addition to the usual enema method, which is familiar to many, you can use effective medications. Here everyone chooses the most acceptable one for themselves.
How often can I have a bowel colonoscopy?
To prepare for the procedure, you don’t have to spend money on enemas, but as a disadvantage of this method, the patient will need an assistant, since someone will have to hold Esmarch’s mug or a combined heating pad, commonly called enemas. In order to properly prepare for the study, you need to carry out water procedures the evening before the diagnosis and in the morning 3-4 hours before it.
In the evening, you should do two enemas - at 19.00 and 20.00 hours (you can shift the administration by an hour or two) of 1.5-2 liters each. An excellent way to get rid of fecal matter is to take 40-60 ml of castor oil or 100-150 mg of magnesium sulfate 2-4 hours before evening washing, which will act as a strong laxative and speed up the cleansing process. It is optimal to take it at 15.00–16.00 hours.
In the morning, 2 more enemas are given at 7 and 8 o'clock, but if after them the rinsing waters do not become clear, the cleansing should be repeated until the emerging waters are clear. This method has certain contraindications - for anal fissures and hemorrhoids, it is better to use special cleaning preparations. Therefore, before preparing for a colonoscopy or even when prescribing this procedure itself, you should find out in detail from the attending physician all the details of the procedure and notify him of the presence of existing obstacles to the examination.
During bowel cleansing, an intestinal enema procedure should be carried out until clean rinsing waters are used.
Working on camera
Virtual colonoscopy is somewhat different from the usual one. Firstly, the technique is non-invasive (without penetrating organ tissue or mucous membranes directly into the organs themselves with a piercing instrument), but it will be impossible to immediately eliminate the source of the disease.
That is, virtual colonoscopy can only study the condition of the intestines (1.5 m deep), and in two- and three-dimensional images displayed on the doctor’s monitor. Secondly, it is a completely safe and proven method. The downside is that virtual colonoscopy does not allow you to diagnose and evaluate the intestinal tract with the same accuracy as a regular one.
This version of colonoscopy has contraindications:
- slight risk of injury to the intestinal wall when air is pumped into its cavity;
- strong radiation, so it is recommended to do it no more than once every 6-7 years;
- contraindicated for pregnant and breastfeeding women;
- If polyps are detected, an additional colonoscopic examination will have to be performed.
Preparation for the procedure is absolutely similar to a regular colonoscopy and takes about 2-3 days.
The procedure (no more than 20 minutes) begins with the subject being asked to lie on his stomach. Through the rectum, pumping air to widen the passage, an inserted tube-probe with a tiny chamber at the end is inserted into the intestine.
The next step is to move the table on which the patient is located inside the scanner, where a series of images are taken. When the tube with the camera is removed from the rectum, having previously pumped out all the air from there, the doctor will vividly describe the condition of the intestines to you based on several “successful” frames.
Important! Because the test is performed without underwear, most patients experience shame and great discomfort. To prevent such things from distracting you and causing discomfort, doctors recommend purchasing special panties for this procedure made of non-woven fabric with a ready-made hole for inserting the probe tube.
Colonoscopy results and interpretation
Examination of the intestine through colonoscopy allows you to detect almost all pathologies of the large intestine known in medicine already at the time of examination. Therefore, preliminary results become known during the inspection. Upon completion, the doctor who diagnoses the disease (endoscopist) begins to draw up a conclusion. It includes:
- description of the appearance of the intestinal mucous membranes (normal, hyperemia, erosion, edema, neoplasms);
- localization of areas where pathological changes are visible;
- nature, size and extent of pathological areas;
- the nature of the contents and discharge of the intestine;
- the presence or absence of intestinal narrowing.
After the examination is completed, a detailed transcript of the results is compiled, which is then transferred to the gastroenterologist or coloproctologist along with printed images of the pathological areas. If the doctor took a biopsy during the study, the final results of the colonoscopy become known after 1-2 weeks, when the results of laboratory tests of the biopsy are ready.
Contraindications and possible complications
Contrary to popular belief that anyone can undergo an endoscopic procedure, the opposite is being proven. Colonoscopy has contraindications and is not performed if the subject has:
- various forms of serious condition requiring urgent medical intervention;
- ulcerative and ischemic colitis, Crohn's disease;
- peritonitis, urgent for emergency surgery;
- low blood clotting;
- advanced stages of heart failure - complex cases unacceptable for the procedure;
- acute myocardial infarction with an increased risk of death;
- pregnancy - high probability of premature birth or miscarriage (in the early stages).
No matter how safe and harmless intestinal colonoscopy may seem, complications may begin after it: perforation or rupture of the intestinal wall (frequency 1.2%); hemorrhage in the intestines (0.09%); risk of respiratory arrest due to general anesthesia (0.4%); a rise in body temperature from 37-37.80 C for 1-3 days (when polyps are removed from the intestines).
If you notice these signs after an endoscopic procedure, consult your doctor immediately:
- feeling of apathy;
- irritability;
- decreased vigor and strength, constant drowsiness;
- dizziness;
- increased headache or migraine;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- nausea and vomiting;
- blood is seen in loose stools;
- temperature above 380 C.
In what cases is intestinal colonoscopy performed?
Since colonoscopy is an invasive examination method, it has its indications and strict contraindications. It is important to take them into account in order to avoid unwanted reactions and complications. The examination itself is carried out in a specialized office by an endoscopist together with a nurse and sometimes an anesthesiologist.
Who is a diagnostic colonoscopy indicated for:
- persons with suspected infiltrative or growing tumor of the colon according to an objective examination, ultrasound, radiography or CT;
- patients with suspected polyposis, intestinal diverticulosis (polyps are small pedunculated neoplasms from the mucous membrane; diverticula are pathological “pockets” of the intestine);
- patients who are suspected of having ulcerative enterocolitis, Crohn's disease, irritable bowel syndrome;
- persons with frequent, painful constipation, a foreign body in the rectum or sigmoid colon;
- patients with internal intestinal bleeding, inflammation in this area;
- patients who need a biopsy, removal of small tumors, hemorrhoids.
It is possible to carry out the procedure with low intestinal obstruction or incomplete fecal impaction. The study is strictly prohibited during an acute intestinal infection, if peritonitis or ischemic colitis is suspected. Colonoscopy is not prescribed in cases of severe respiratory or heart failure, pathology of the blood coagulation system and massive ulcerative colitis.
Conclusion
The colonoscopy procedure must be done at least once in your life to make sure that your intestinal microflora is healthy or, conversely, to doubt it and think about starting a course of treatment for ailments in a timely manner. After all, it is very important to track this or that disease in time in order to prevent the deterioration of the condition of your own body.
But often the disease does not manifest itself in any way, and therefore it is impossible to do without the intervention of experienced specialists and medical equipment. Colonoscopy serves precisely this purpose - to accurately diagnose all abnormalities in the intestinal area in the early stages and build a plan with the attending physicians to eliminate the problem.
This is mandatory for every patient, because the intestinal tract plays a huge role in the human body, without it the proper functioning of the entire human body is unthinkable. That is why you should not be afraid of the endoscopic procedure, because health is the key to your success. And for the sake of this you can be patient.
Specialized equipment
Diagnosis using the colonoscopy method is performed using innovative endoscopic equipment, which means examination using a special lighting device - a colonoscope.
Colonoscopy instruments
- The main element of a colonoscope is a flexible probe with a streamlined microscopic illuminating video camera at the end. Its design and dimensions are designed to make the procedure as comfortable as possible.
Photo: Rectoscope
2. A digital video camera transmits to the screen an enlarged image of the internal cavity of the rectum and large intestine with high resolution, which guarantees an accurate diagnosis even in the early stages of the disease.
Detection of worms using colonoscopy
There are many people who are planning to undergo a whole-body diagnostic. They ask themselves: “Do you see parasites during a colonoscopy?” An examination method such as colonoscopy can show worms in the intestines even when there are small numbers of them and detect the oviposition of worms.
The diagnosed stage and form of the disease is much easier to cure. Moreover, some types of worms (worms such as bovine tapeworms, roundworms and tapeworms) can remain inside the human body for a long time. In some cases, worms live in the human intestines for several years, reaching gigantic sizes. Of course, “neighborhood” with worms can have disastrous consequences. That is why, if parasites are identified in a timely manner through a colonoscopy, this will save the patient’s health, and sometimes even his life.
Now you have learned how things really are with the diagnosis of parasites, and whether worms are visible during colonoscopy. And you yourself can advise an interested person on this issue.
Reviews
Lyudmila: “They recently showed me, I was very afraid, but it turned out not to be scary. Before I started, I went on a diet and cleansed myself with carry-out tablets. The colonoscopy went very quickly.”
Nikolai: “At the end of the procedure, I felt bloating in the intestines, as they pumped air, but soon everything went away after drinking activated charcoal.”
Marina: “Because I’m afraid of pain, I chose anesthesia. I felt absolutely nothing. When the anesthesia wore off, I felt discomfort, but it did not last long.”
Distinctive subtleties of the procedures
In addition to the peculiarities of preliminary preparation, there are technical differences when performing colonoscopy and irrigoscopy.
The total duration of irrigoscopy can vary from half an hour to 45 minutes. Before examining the patient, he is taken an X-ray in a horizontal position on his back. Next, the patient is placed on the left or right side, it is recommended to bend the lower limbs at the knees and cross the arms behind the back. After this, a solution of barium sulfate is injected into the rectum, which acts as a radiopaque substance. In some situations, contrast is administered orally. When taking barium sulfate orally, several hours should pass, which will ensure uniform distribution of the component throughout all parts of the intestine. The substance used is safe for the body, since it acts locally without being absorbed into the systemic bloodstream.
By analogy with irrigoscopy, during colonoscopy the patient is recommended to take a horizontal position on the left side, with the lower limbs bent at the knees and pressed against the body. Next, the medical specialist performs an antiseptic treatment of the patient’s anus, applies a lubricant and inserts an endoscopic tube, systematically moving it through the intestines. In order to improve the visualization of the organ, air is pumped into its lumen, which straightens the physiological folds. Thanks to the built-in camera, the intestinal lumen is visualized on a special monitor in real time. Unlike irrigoscopy, the total duration of this diagnostic procedure ranges from 10 minutes to half an hour.
An increase in colonoscopy time occurs if the patient undergoes a biopsy or polypectomy. Unlike irrigoscopy, colonoscopy is invasive and presents symptoms such as discomfort and pain. Very often, patients are prescribed pain management techniques such as general anesthesia or drug-induced sleep (sedation). If a colonoscopy is performed using one of the anesthesia techniques, then its price increases markedly.
Do they do it for hemorrhoids?
Colonoscopy for hemorrhoids is prescribed in the following cases:
- to confirm the diagnosis previously made by a specialist;
- to identify the extent of the inflammatory process caused by hemorrhoids;
- to determine existing complications;
- to stop existing heavy rectal bleeding;
- as a preparatory study for the upcoming operation;
- to conduct a diagnostic assessment of hemorrhoids and existing tumors formed in the rectal cavity in the presence of characteristic symptoms in the form of sudden loss of body weight, signs of intoxication, changes in stool, etc.
- for the purpose of collecting tissues for further histological or microbiological laboratory studies.
Under anesthesia or not - which is better?
Carrying out diagnostics using colonoscopy under anesthesia does not cause the patient much discomfort and relieves pain. This method is especially effective for those patients who experience panic fear before any medical procedure, including the use of a colonoscope. All equipment of a modern device is made taking into account the human body; the hose with which the probe is directed and the image is transmitted to the monitor is flexible, has a minimal cross-section and is almost imperceptible as it moves through the intestines. All received data is stored in a computer, recorded on a digital medium, and the patient can at any time receive advice on the results obtained in any clinic from a specialist of his choice.
However, when using local anesthetics, although the insertion of the probe will be painless, when further moving through the bends of the intestine or when encountering any formations in its cavity, the patient may feel quite significant pain. Often these symptoms can manifest themselves with such force that further examination has to be interrupted without completing it.
Carrying out manipulations under anesthesia greatly simplifies the procedure and allows you to examine the problem areas of interest in more detail. The patient under anesthesia is in a relaxed state, completely open for penetration and does not interfere with the advancement of the probe throughout the entire intestine by possible involuntary spasms. Moreover, the use of anesthesia makes it possible to perform the necessary surgical removals according to indications that emerged as a result of the examination. There is no need to use additional painkillers for this; everything happens during one colonoscopy session.
As for complicated situations when conducting an examination under anesthesia, there is only a risk of damage to the intestinal wall, since the patient is asleep and is not able to inform the specialist about the occurrence of severe pain during intestinal perforation. Otherwise, the use of anesthesia does not pose any danger, especially since the dose of the anesthetic drug is calculated correctly.
It is also recommended to think about other options for pain relief in cases where general anesthesia is contraindicated for the patient due to existing individual contraindications. An experienced specialist performing a colonoscopy will always suggest a possible pain relief option that will make the examination procedure less painful.
Where and how best to do it: expert advice
The main rule in conducting a safe study is a good doctor. In many ways, the diagnostic result depends on the experience and professionalism of the physician. And to a greater extent this concerns not so much the procedure itself, but the ability to decipher or see the resulting picture. Experts recommend choosing comprehensive and specialized clinics, well-known and specialized companies.
Find out which doctor will examine you and talk to him or her before going for a colonoscopy. This will help dispel all worries and doubts, discuss the preparation and features of the procedure. Be sure to clarify why the check is dangerous in your specific case, what the benefits and harms are in general.
Also make sure that the result is recorded on disk or take endophotographs that can be shown to another specialist.
Colonoscope device
The appearance of a colonoscope resembles a black tube. The length of the standard device is 2 m. The inner layer consists of an optical fiber that transmits the image to the monitor. In Latin, fibers would be called fibers. Due to this feature, endoscopic research methods are also called fiberoscopy.
The outer layer of the device is represented by a protective shell that prevents damage to the fiber optic elements. In addition, there are cables running through the protective layer, thanks to which the distal end of the colonoscope can move in two planes. The outer shell also contains a backlight cable and air supply tubes. Due to the nature of the preparatory stage, the intestinal walls may collapse, so a jet air supply is used to straighten them, allowing the device to be advanced further.
What is fiberoscopy? As stated above, a fiberscope is a general concept that includes all devices based on the use of fiber optics.
The head also has special forceps, thanks to which it is possible to collect biological material for further examination by a histologist. New models of colonoscopes are equipped at the end with a camera necessary for recording “interesting” areas of the colon mucosa. The diameter of a conventional device is no more than 1.5 cm.
Does it hurt?
Those patients who are afraid of the procedure due to fear of pain are given anesthesia in the following ways:
- administering local anesthesia;
- sedation, that is, being in a state similar to sleep;
- use of general anesthesia.
Before making a choice, it is necessary to take into account all the reasons that could affect the patient’s sensations during the period of manipulation, as well as the general condition of the patient’s body.
- The experience of the specialist who will carry out the promotion of the device is of great importance in conducting the examination and the sensations during it.
- The modern equipment of the device is also important; the comfortable sensations during the procedure and the results of the information received depend on it.
- The individual characteristics of the patient’s body also largely determine the painlessness of the procedure, such as existing diseases of the internal organs, the patient’s pain threshold, and the structure of his intestines.
- Painful sensations and discomfort during the examination depend on the interaction between the doctor and the patient, on their coordination in actions.
Before a colonoscopy, you can discuss with your doctor the method of pain relief and the need for its use, taking into account all possible risks.
Biopsy
Only after collecting biological material and based on the results of histological examination can the presence of a malignant process be established. It is impossible to confirm the diagnosis based only on the results of imaging studies, so a biopsy is an important step in the treatment of cancer. Depending on the result obtained, treatment tactics are selected and the issue of the volume of surgical manipulation is decided. To increase the success of biopsy, it is recommended to combine it with chromendoscopy. Some neoplasms, which have a flat shape, cannot be distinguished from areas of healthy tissue, so touch-up is extremely necessary. Thanks to the design of the device, it is possible to perform surgical procedures of minor complexity. If polyps, adenomas and other small benign neoplasms are detected, the endoscopist removes the tumor. This procedure is considered to be of very high quality, because unlike standard operations that require opening the abdominal cavity, endoscopic removal of polyps is less traumatic for the patient.
Alternative Methods
The procedure helps to identify various intestinal diseases. Several methods can be an alternative:
- Irrigoscopy. The use of a contrast agent helps to see pathological changes in the organ, but will not reveal the initial processes in the tumor.
- Sigmoidoscopy. The procedure is identical to colonoscopy, but it allows you to examine only 30 centimeters of the colon.
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the intestine. Images of the abdominal cavity are taken with a scanner on both sides, then a three-dimensional model of the intestine is created. The method is gentle and does not cause discomfort, but it detects pathological formations up to 1 cm in size.
Medical history: ovarian cyst - intestinal tumor
The girl is a 22-year-old student at one of the economic universities in the Krasnodar region. I came in with severe abdominal pain. They thought it was gynecology, did tests, began laparoscopically removing the cyst in the ovary and realized that it was not a cyst, but a metastasis. Upon closer examination, it became clear that a tumor of the transverse colon had metastasized to the ovary.
Well done doctors - they carried out all the necessary examinations on time to identify a malignant neoplasm. During the operation, the intestine was brought out to the side, but the continuity of the intestine was not restored at the next stage. The girl arrived in Moscow and went to a private clinic for additional surgery and subsequent chemotherapy.
We must pay tribute to the doctors who showed sensitivity and care for the patient (which, unfortunately, is rare for Russian healthcare): since the patient was of childbearing age, she was offered the prospect of preserving a healthy egg for possible subsequent IVF. After a complete recovery, the girl managed to undergo a successful embryo transfer. Now her baby is growing, everyone is alive and well. This is a happy story when doctors managed to help on time.
Back to contents
Case history: not just hemorrhoids
A business-like, energetic, practical woman, 55 years old, head of a regional division of a global IT company. It would seem that everything in her life was good - an interesting job, an active lifestyle, high income. But hemorrhoids bothered me, and - lo and behold! — the time has come to go to the clinic for his treatment.
There was no bad heredity in the family, and there were no chronic diseases. Based on the initial examination, it was recommended to perform a computed tomography scan of the abdominal cavity. The image revealed metastases in the liver... Then they did a colonoscopy and discovered a tumor. We carried out embolization of lesions in the liver and a course of chemotherapy, but the tumor could not be completely destroyed - the stage was too advanced and it had extensive metastasis. Prospects - maximum 3-4 years of life, palliative treatment, rest of life - with a removed colostomy. It's a sad story.
Back to contents