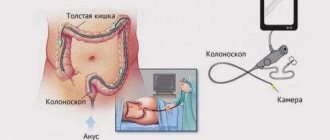
Traditional colonoscopy is the optimal method for diagnosing most diseases of the large intestine. It is carried out with a special endoscope, which is inserted through the anus and moves along the entire intestine, which causes a lot of inconvenience for the patient. Not so long ago, virtual colonoscopy began to be used in our country - a method of radiation diagnostics that allows high-quality visualization of all parts of the intestine without the need to use a traditional colonoscope and conduct the necessary research, unlike, for example, ultrasound diagnostics.
Difference between virtual and classic colonoscopy
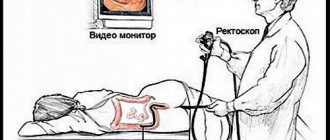
In classical fibrocolonoscopy (FCS), a special device is used - an endoscope, which is inserted into the colon. This type of study allows you to visually assess the condition of the mucous membrane and intestinal lumen, and, if necessary, perform a biopsy, stop internal bleeding, or remove a polyp. Despite the high information content, the technique is uncomfortable and painful for the patient, and therefore sometimes requires the use of anesthesia.
Using virtual colonoscopy, the intestines are examined without insertion into its cavity. In this case, the patient is placed in a computed tomograph, which, thanks to ionizing radiation, scans the intestinal tube layer by layer. Unlike classic FCS, tomography does not cause pain and provides a more accurate image of the organ. However, in the process of virtual diagnostics it is impossible to perform a biopsy and other minor operations.
Let's sum it up: which is better - CT scan of the intestines or colonoscopy?
Now both of these procedures are used quite often. The choice of any of them is made by the doctor. At the same time, all risks from the procedure are calculated and weighed against the benefits of the research. In each case, one or another research method is necessary, and they are not always interchangeable. There may be cases when it is necessary to perform a colonoscopy, because a CT scan is not informative and will not give the desired effect. The decision to conduct this type of diagnostic research should be made only by a doctor.
https://youtu.be/fQO8S63TtQc
Indications for the procedure
- suspicion of a tumor in the colon (polyps, adenocarcinoma, etc.);
- identification of chronic intestinal diseases such as ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease;
- confirmation of the presence of diverticula - pathological “pouches” from the intestinal walls that can become inflamed and bleed;
- establishing the source of internal bleeding - the segment of the colon in which the destruction of the wall and its vessels occurred;
- control of surgical treatment of polyposis and tumors.
Also, computer colonography is annually prescribed to patients over 40-45 years of age with a family history of colon cancer and the presence of contraindications to the endoscopic examination method.
We recommend reading:
How to check the intestines for oncology?
Who is prescribed the procedure?
The appropriateness of the procedure is determined by the attending physician.
Experts advise people with risk factors to undergo diagnostics: colon cancer in close relatives, blood in the stool.
MSCT of the intestine recommends:
- for chronic inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- if neoplasms are suspected;
- mature patients;
- patients with ulcerative lesions;
- with increased flatulence, persistent constipation or diarrhea;
- to investigate the causes of frequent abdominal pain;
- to detect the source of intestinal bleeding.
Advantages and disadvantages of the study
| Advantages | Flaws |
|
|
The possibility of conducting a study with contrast can be attributed to both advantages and disadvantages. In the first case, the information content and accuracy of the diagnostic manipulation increases, in the second, intravenous administration of a contrast agent can lead to the development of a severe allergic reaction. Also, this type of study is prohibited in persons with impaired renal function.
In general, standard fibrocolonoscopy is considered more informative. With its help, the doctor independently examines the intestinal mucosa, removes polyps and other small tumors, and stops bleeding by “cauterizing” or “suturing” the vessels. The main advantage of the method is a biopsy (taking a piece of mucous membrane) with further histological analysis of the collected tissues. This makes it possible to identify the presence of chronic inflammation or determine the degree of malignancy of the tumor.
Virtual colonoscopy is used to confirm colorectal cancer (colon cancer), polyposis and chronic intestinal ulcers. The technique is in demand for patients with contraindications to endoscopic examination.
We compare the safety of methods and possible complications
Advantages of CT:
- painless procedure (the patient does not need anesthesia);
- the diagnostic information content is not inferior to the results obtained during colonoscopy;
- there is no possibility of intestinal perforation;
- the device is not inserted into the body;
- the effectiveness of diagnosis in the presence of strictures and polyps in the intestine, which do not allow inserting a colonoscope and thoroughly studying the features of the intestinal wall;
- availability of clear photographs;
- no need for anesthesia;
- Diagnosis of a patient of any age.
Disadvantages of CT:
- cannot be used during pregnancy;
- it is impossible to take a biopsy sample for analysis;
- it is impossible to evaluate the fine mucous structure;
- not very informative in obese patients;
- it is impossible to evaluate the shade of the mucous membrane.
Complications during CT scans are rare, last a short time and disappear almost the next day.
Among them:
- general weakness;
- allergy to contrast injection;
- abdominal pain.
Advantages of using colonoscopy:
- the ability to identify the slightest pathological foci;
- taking a biopsy;
- reliability of research information;
- simultaneous implementation of therapeutic measures (removal of polyps, elimination of the source of bleeding).
Possible complications from colonoscopy:
- pain in the abdominal area after manipulation;
- reaction to drugs administered for anesthesia;
- risk of bleeding;
- intestinal perforation is possible.
Performing a virtual colonoscopy
Preparing for the examination
Before the examination, the patient is prescribed preliminary preparation 2-3 days before the procedure. It includes following a diet and cleansing the intestines. The diet involves excluding from the diet foods that can increase gas formation in the intestines: legumes, fresh baked goods, fresh fruits, vegetables, fast food.
We recommend reading:
Preparation and performance of intestinal sigmoidoscopy
To cleanse the intestines, you can use regular cleansing enemas (the evening before and the morning of the test day) or medications like Fortrans (prescribed only by a doctor, taken according to the schedule). A lactulose-based product, Duphalac, has a milder laxative effect, which should be taken the day before the examination in the morning.
Read more: Using laxatives to prepare for a bowel examination
Algorithm
- The patient is placed on a special tomograph couch (on the left side with bent legs or on the stomach).
- Using a sigmoidoscope, the doctor pumps air into the intestine so that during the examination all its sections and bends are visible.
- After the patient experiences discomfort in the abdomen, he is placed in a computed tomography scanner, which, constantly rotating, takes a series of images of the organ being examined.
- While the scanner is operating, it is important to listen to and follow all the recommendations of the doctor, who is in a nearby room and monitors the progress of the procedure.
- After 15-30 minutes of scanning, the device turns off, and the previously pumped air is removed from the patient’s intestines using a gas outlet tube and they are helped to get up from the couch.
- Then, within an hour, the doctor examines the received images and makes a conclusion, which is entered into the protocol. If necessary, all photographs are copied onto digital media and printed onto special film.
Thus, the manipulation takes no more than half an hour and causes virtually no discomfort, except for the moment of pumping air into the intestines.
With a negative examination result, the doctor did not find any pathology in the intestines. In the absence of a hereditary predisposition to colon cancer, the procedure can be repeated no earlier than after 5 years.
A positive result may be if polyps or other space-occupying formations are detected. If a histological examination of the tumor is necessary, the doctor will prescribe a classic colonoscopy with biopsy.
We recommend reading:
Diagnostic laparoscopy: how and why is it performed?
Preparing for the study
Knowing how to prepare for a traditional colonoscopy, it is easy to prepare for a virtual one. The patient begins to prepare three days before the procedure. The main thing is to follow a slag-free diet - it allows you to minimize the amount of feces in the intestines.
At the discretion of the doctor, medication may be prescribed. It allows you to do without strict dietary restrictions. They use drugs such as Duphalac, Fortrans, and other drugs. You must inform your doctor about the presence of any somatic diseases before the examination.
Contraindications to virtual colonoscopy
The procedure can be prescribed by a physician, gastroenterologist, oncologist or surgeon, subject to the mandatory exclusion of contraindications for the patient.
| Absolute contraindications | Relative contraindications |
|
|
If there are relative contraindications, the patient may be admitted to the examination only with the permission of the attending physician.
Features of CT examination
Computerized intestinal colonoscopy is a non-invasive, x-ray examination method. Similar to X-rays, CT scans take a series of images through sections of the body, which can be converted into a virtual image of the colon using a special computer program.
The advantages of CT scanning are as follows:
- has high accuracy, since images of sections are every 2-5 mm, this depends on the type of device, neoplasms (cancer) can be detected at the earliest stage of development;
- it is possible to diagnose interstitial formations that grow from the inside of the intestinal wall, not only tumors located in the lumen, but also in the abdominal cavity;
- is carried out without the use of anesthesia, which is important for weakened patients, elderly people with concomitant pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- to improve visualization, sometimes it is necessary to introduce a barium mixture or gas into the rectum, which is done using a thin, soft probe, so there is no risk of complications such as perforation or damage to the walls;
- Computed tomography is performed if there are contraindications to colonoscopy (anal fissures, hemorrhoids).
The disadvantages of CT include:
- inability to perform the study if the patient is overweight (more than 120 kg);
- ionizing radiation, which prohibits CT scanning for pregnant women and limits its use in children;
- inability to visually determine the color of the mucous membrane or take a biopsy.
Therefore, when choosing, the doctor takes these points into account.
Possible complications
In rare cases, systemic allergic reactions to the administration of a contrast agent occur. X-ray radiation is harmful to humans, but a single examination poses virtually no threat. It is extremely rare that perforation (rupture) of the intestine is possible due to the injection of air into it by a sigmoidoscope.
In continuation of the topic, be sure to read:
- How to check the intestines for oncology?
- Preparation and performance of intestinal ultrasound
- Preparation and performance of computed tomography (CT) of the intestine
- Fistulography of the fistula: preparation and examination
- Plain radiography of the abdominal cavity: what it shows, preparation and implementation
- X-ray of the intestines with contrast (barium): what does it show and how is it done?
- X-ray of the intestines: the essence of the procedure, preparation and implementation
- Intestinal ultrasound or colonoscopy: comparison of techniques and their information content
- Irrigoscopy and colonoscopy: which test is better?
- MRI of the intestine and colonoscopy: which study is better?
Which method is better?
What to choose: virtual colonography or colonoscopy?
Which method is better - virtual colonography or colonoscopy? Doctors say that colonoscopy is a more informative method in the presence of pathologies associated with the inner wall of the intestine. The choice of technique always depends on the indications, the presence of clinical symptoms and the goals that the doctor wants to achieve.
To clarify the location and extent of tumors, it is better to perform virtual colonography, and to determine the malignancy of the tumor, colonoscopy, since only this makes it possible to take material for histological examination. When choosing a diagnostic method, it is very important to take into account all contraindications - it is possible that the specialist has grounds for conducting a certain type of examination. The decision is always made by the attending physician, even when choosing a colonoscopy - the procedure should not be ignored, it can lead to dire consequences.