Diseases of the large intestine are common among the population. Moreover, their spectrum covers both absolutely harmless conditions, for example, single polyps, and tumor lesions of the intestine with a poor prognosis. In this regard, it becomes especially relevant to conduct periodic examinations, for which intestinal FCS is most often used. FCS is a fibrocolonoscopy, an endoscopic research method based on the examination of the large intestine using a special probe with an installed light source and a video camera. Like any diagnostic procedure, colonofibroscopy has certain indications and contraindications for its implementation.
FCS is one of the most common types of endoscopic analysis of the gastrointestinal tract.
FCS is one of the most informative methods for diagnosing proctological diseases
What is the procedure
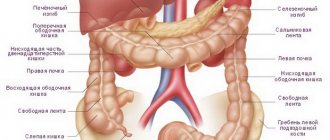
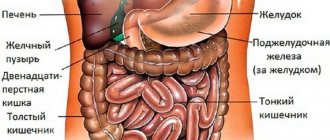
A colonoscope is a special flexible tourniquet, which is equipped on all sides with all kinds of medical instruments, lighting devices and a camera. Due to the fact that the colonoscope is quite flexible, this device can penetrate into the most remote parts of the intestinal tract without any difficulty. The fibers that make up the medical device have conductive particles, with the help of which data and the resulting image are transmitted to the monitor screen. Subsequently, the specialist assesses the condition of the person’s intestines.
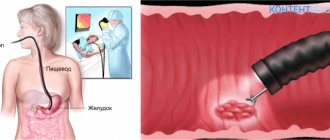
Fibercolonoscopy of the intestine allows the doctor to assess the position in which all parts of the large intestine are located. At the same time, determine the condition of the distal intestinal tract, which is located in the ileal region. Using a colonoscope, you can not only visually examine parts of the small intestine, but also, if necessary, perform radical manipulations, such as a biopsy (taking a sample of tissue located in the intestine for further laboratory examination).
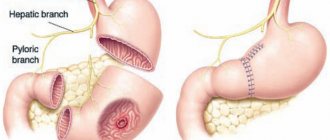
If various neoplasms, such as polyps and small tumors, were found in the cavity of the intestinal tract, then their resection (removal) is performed using the same device. Such medical manipulation is carried out with great precision and is carried out quite quickly, almost instantly. The accuracy and speed of resection using a colonoscope allows the patient undergoing the procedure, if necessary, to avoid performing any surgical operation on this internal organ and, accordingly, performing preparatory and rehabilitation processes associated with surgical intervention.
In addition, the colonoscope can take pictures as it moves through the intestinal tract, as well as perform all kinds of local therapeutic manipulations. Fibercolonoscopy is performed under general anesthesia, but can also be performed without it. This procedure is painless and safe for the patient.
Indications and contraindications for using the procedure
A fibrocolonoscopy of the intestine is prescribed to a patient if:
- The patient experiences the appearance of clinical signs indicating a disease such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). These signs include the occurrence of any disorders of the human digestive system, which can manifest themselves in the form of periodically appearing or constant stool disorders, characterized by constipation and diarrhea. In this case, a person may experience pain in the abdomen and a feeling of heaviness that occurs during the process of excessive accumulation of digestive gases in the intestinal tract (flatulence).
- Foreign impurities such as mucus and blood have been found in human feces.
- The patient complains of loss of appetite and a constant feeling of weakness.
- There was a sharp decrease in a person’s body weight without any well-defined reasons.
In addition, FCS of the intestinal tract is prescribed for those patients who have tumor tumors of various etiologies in any part of the large intestine, the presence of foreign objects in the lumen of the abdominal region and inflammatory processes. The use of a colonoscope is also prescribed in case of internal bleeding in the intestinal tract that requires urgent medical attention.
Although fibrocolonoscopy is a safe diagnostic procedure, it cannot be used if the person being examined has the following pathologies:
- cardiopulmonary failure;
- ulcerative or ischemic colitis, which has a severe pathological process;
- recent stroke;
- hypertension occurring in the third degree of severity;
- Crohn's disease, which has a chronic stage of development of the pathological process or occurs in a severe form;
- the development of any inflammatory processes in the rectal area that are acute in nature;
- peritonitis (presence of inflammatory processes in the visceral and parietal abdominal cavity);
- various problems that disrupt blood clotting processes;
- adhesions in the intestines;
- the course of diseases such as thrombosis of blood vessels and acute hemorrhoids.
In addition, this kind of diagnostic procedure cannot be performed on those patients who have recently undergone any surgical operations in the intestinal tract and are undergoing a postoperative recovery period.
Colonoscopy results are normal
The following can be considered positive indicators of the study:
- Pale pink or yellowish color of the mucous membrane of all parts of the intestine. The presence of growths changes its shade.
- When exposed to light, the mucous membrane should shine; this indicator indicates normal mucus secretion. Dullness indicates the presence of pathological processes.
- The surface of the shell should be as smooth as possible. Lumps, protrusions, and growths are immediately noticeable during the procedure.
- Accumulations of mucus should not contain pus, fibrin or accumulations of dying tissue; in normal condition they are visible in the form of light-colored small lumps.
- The vascular pattern should be uniform and clearly visible throughout the entire intestine, have a uniform pattern.
Any deviation indicates a particular disease, which is determined by the proctologist.
Preparatory procedures for the implementation of the FCC
In order for fibrocolonoscopy to be carried out successfully, the patient must undergo a number of preparatory procedures before undergoing it. Preparation for the FCS procedure begins at least 3 days before it and includes taking special medications that have a laxative effect, as well as following a diet.
Dietary nutrition involves the patient eating only the following foods:
- all kinds of porridges cooked in water without adding milk or butter;
- baked goods containing small amounts of glucose (sugar);
- lean meats or fish, steamed or boiled;
- all kinds of low-fat broths, both meat-based and vegetable-based;
- Eating boiled eggs is allowed, but only 1 per day;
- various dairy products.
In this case, the patient must exclude from the daily diet:
- eating raw vegetables and fruits, especially those with many small seeds;
- fatty fish and meats;
- legumes and dishes prepared on their basis;
- fried, smoked and sour dishes;
- food seasoned with any spicy food additives;
- consumption of various alcoholic beverages.
To cleanse the intestinal tract of feces, a drug such as Fortrans is used. The action of this drug is based on fluid retention in the intestines, softening of formed feces and their further comfortable removal from the human body. The use of such a medication may cause nausea in a person. Therefore, in order to eliminate this unpleasant phenomenon, after taking the drug it is recommended to put a piece of lemon or sour apple in your mouth. Fortrans should be taken 1 day before the start of the FCS and no less than 3 hours before the procedure itself. The dosage of such a drug is determined by the doctor individually for each patient and depends on his body weight.
Conducting the FCC
How is FCC done? Before the actual fibrocolonoscopy, the person being examined may be given general anesthesia. This is done if the person being examined is in serious condition or cannot keep his or her body from moving for a long period of time. When carrying out diagnostics, the following manipulations are carried out:
- Before general anesthesia is administered, the patient will be undressed and placed on his left side on the couch, after which he will need to pull his knees closer to his chest.
- Then the subject is given anesthesia, and the appropriate specialist palpates the anus.
- A colonoscope is gradually inserted into the anus, the flexible part of which is pre-lubricated with Vaseline, ensuring comfortable insertion and further passage of the medical device into the cavity of the large intestine. If fibrocolonoscopy is performed without the use of general anesthesia, then the person being examined may experience discomfort and a false urge to defecate at the initial stages of supplying air through the colonoscope. After a certain period of time, the intestinal muscles gradually get used to this effect, and the discomfort becomes less intense.
- The slow movement of the optical probe allows you to examine and evaluate the condition in which one or another part of the large intestine is located. At the same time, in order to be able to clearly visually observe all areas of the mucous membrane through the colonoscope, a stream of air is supplied, which ensures straightening of the intestinal cavity.
Resection of any small tumors is carried out immediately upon detection, which is the main advantage of such a diagnostic study. A biopsy is performed in cases where such a manipulation was previously prescribed to the patient or the doctor has discovered any questionable tissues that require additional laboratory testing to determine their structural characteristics. The maximum duration of intestinal fibrocolonoscopy can be 40 minutes.
This method makes it possible to assess the condition of the tissues and mucous membrane of a given internal organ with maximum accuracy, which allows the specialist to make the correct diagnosis. In addition, if necessary, during such a diagnostic procedure, resection of a particular neoplasm can be performed.
After research
The doctor tells the patient about the procedure in advance. This allows you to remove most of the fears, and a smooth emotional background is very important for a successful examination. The patient, prepared and naked to the waist (special panties for colonoscopy can also be used), is laid on his left side, with his legs pulled up to his chest.
Since the procedure does not cause severe pain, it often does not require prior anesthesia. In some cases (severe fear, children), gels with anesthetic can be used, sedation is used less often, and general anesthesia is even less common. The doctor slowly inserts the colonoscope into the intestines.
Avoiding sudden movements, he advances it, simultaneously inspecting its walls. Unpleasant sensations can occur in places where the intestines have physiological bends, as well as when the intestines are filled with air - this is necessary to straighten the folds. Upon completion of the examination, it is pumped out with a colonoscope without causing further discomfort.
Instrumental diagnostics includes a number of studies carried out using special devices for the purpose of early detection of serious diseases of any part of the intestine. The most common of them are magnetic resonance therapy, ultrasound, irrigoscopy, computed tomography of the intestine, anoscopy and sigmoidoscopy.
Many of them are similar to each other, are alternative, but at the same time differ in some nuances and capabilities.
Let us compare the main diagnostic methods with colonoscopy and find out how they differ from it.
- MRI of the intestine is more modern, comfortable and painless. It also has another name – virtual colonoscopy. It is carried out using a scanner that takes pictures of the organ from the front and back, and then forms a 3D image from the captured frames. But it is still inferior to traditional colonoscopy, since it cannot detect formations whose diameter is less than 10 mm and is prescribed if colonoscopy is contraindicated or if the small part of the intestine should be examined, where the colonoscope cannot reach. We can say that MRI is a preliminary method, after which the proctologist still prescribes a colonoscopy.
- Colonoscopy and irrigoscopy, or simply an X-ray of the intestines using a contrast agent, what is the difference between them? The image shows defects in the large intestine, but, unlike colonoscopy, is not capable of identifying neoplasms in the early stages.
- CT scan of the intestines is also a painless and informative method, but does not show tumors in the early stages. And again, the doctor will prescribe a colonoscopy and biopsy procedure for a more detailed study of the condition of the intestinal mucosa.
- Intestinal ultrasound and colonoscopy - in this case it is impossible to say so simply which is better and more informative, since these are two completely different methods used for different indications. Ultrasound examination has advantages due to its availability, low cost, safety and complete painlessness. But still, if there is a suspicion of pathology of the large intestine, after an ultrasound, the doctor again prescribes a colonoscopy.
- Capsule colonoscopy is performed using a special endocapsule with a built-in camera, which passes through the entire gastrointestinal tract and is excreted with feces through the anus. The method is expensive and not always informative.
What are the differences between colonoscopy and fibrocolonoscopy?
So: this is the same thing, including video colonoscopy.
Clearly, this diagnostic method has many advantages. But the exact answer to the question: which is better and more informative - MRI, ultrasound, CT, intestinal irrigoscopy or colonoscopy, can only be given by a coloproctologist, depending on the individual characteristics and indicators of the patient, his medical history and the results of previous studies.