You are here: Blood test -
Basophils -
Basophils are increased
- Etiology
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention
An increase in basophils in the blood is a process of excessive production of these components, which may be caused by a certain disease or exposure to external factors negative for health. The reasons that basophils are elevated can only be determined through laboratory and instrumental research methods.
Elevated basophils in the blood do not have a specific clinical manifestation - the nature of the symptoms will depend on the underlying factor. That is why, if you feel unwell, you should consult a doctor, and not carry out treatment yourself.
Therapeutic measures are selected on an individual basis, depending on what led to the increased number of basophils in the blood. The same can be said about forecasts.
Methods for normalizing the level of these cells
When diagnosing basophilia, doctors often prescribe the use of animal products (eggs, dairy and meat dishes).
The reason lies in the vitamin B12 content of such foods. It is able to normalize hematopoiesis and, accordingly, the level of leukocytes.
If the consumption of the above products is not enough, then you may need to introduce vitamin B12 into the body in the form of injections.
Taking iron-containing medications and foods high in this substance will help get rid of anemia, which is often the cause of basophilia.
Fish, seafood, buckwheat, liver and red meat will not only replenish iron reserves, but will also improve the functioning of other systems in the body. Vegetables and fruits will also not be superfluous in this process.
If an increase in the level of basophils is a consequence of the use of hormonal drugs or other medications, then it is necessary to discuss with your doctor their further use or replacement with analogues that do not cause side effects.
In some cases, you may need to follow a diet and adjust your daily routine.
Basopenia in most cases does not require special treatment. If diagnostics do not reveal pathological conditions or inflammatory processes in the body, then restoring the body will help increase the level of basophils.
It’s enough to learn to alternate between stress and rest, eat the food your body needs in the right quantities, and get enough sleep.
Video:
Try to avoid stressful situations and lead an active lifestyle. This approach will help bring leukocytes back to normal without the use of drugs.
Of course, changes in the level of granular leukocytes in the blood cannot be ignored
It's important to be aware of what this means for your health. Seeing a doctor and following his instructions is mandatory.
Basophils are involved in many vital processes of the human body. Their number in percentage comparison with other cells is insignificant, but the decisive role is played by the content of these cells within normal limits.
Even minor deviations in the ratio of basophils can indicate the presence of serious inflammation or infection of the body.
It is not without reason that the diagnosis of any pathological condition begins with a general blood test. The correct ratio of all its components is an indicator of a healthy body.
What functions do basophils perform in the body?
Like other leukocytes, they participate in the inflammatory process, primarily in immediate allergic reactions, in which basophils are released into the tissues and their concentration in the blood decreases. Basophils are also capable of participating in delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions, but not directly, but indirectly through lymphocytes. During the development of the inflammatory process, numerous granules contained in basophils are released. During this process, a large number of biologically active compounds are released, causing clinical manifestations such as itching, burning, redness and swelling of tissues. With a prolonged inflammatory reaction (more than 72 hours), increased formation of new cells occurs in the bone marrow and a condition called basophilocytosis occurs.
Another function of basophils is to ensure blood flow in small blood vessels and the efficient growth of new capillaries. Cells of this type take part in the process of regulating blood clotting due to the presence of heparin granules. Basophils do not play any significant role in maintaining the body's defenses, although they have the ability to phagocytose.
What to do if basophil levels are elevated
Most often, an increase in the level of basophils in the blood does not require any specific treatment. Moreover, there is no therapy for basophilia. After all, this condition is not an independent pathology, but only a consequence of some kind of disorder in the body. Therefore, treatment should be aimed at eliminating it. After the inflammatory or other reaction is stopped, the level of basophils will return to normal.
Treatment of an allergic reaction involves eliminating the allergen, taking antihistamines, and using glucocorticoids. In case of anaphylactic shock, the patient needs emergency administration of adrenaline.
Rheumatoid arthritis is treated with anti-inflammatory drugs and immunosuppressants.
Bacterial infections require antibiotics. In case of helminthic infestation, it is necessary to take anthelmintic drugs.
If basophilia is a consequence of iron deficiency anemia, then a person needs to reconsider his diet, including more red meat, liver, and eggs. You may need to take iron supplements to increase your hemoglobin levels.
In rare cases, basophilia is a sign of blood cancer. However, in addition to basophils, a blood test will reveal a decrease or increase in the level of leukocytes, platelets and red blood cells. Suspicion of blood cancer requires consultation with an oncologist and hematologist with a comprehensive diagnosis. Treatment involves stem cell transplantation and chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
As for the prognosis, with a mild infection, basophils return to normal fairly quickly. You just have to wait for the body to recover. You definitely need to relax more and spend time outdoors.
Allergies and inflammation of internal organs often become chronic and recur periodically. At the same time, the level of basophils in the blood will increase.
Severe cancer diseases require an individual approach and long-term treatment.
So, basophilia is not a disease, but a symptom of a disease. Therefore, efforts should be aimed at treating the cause that led to an increase in the level of basophils in the blood.
Author of the article:
Education: Moscow Medical Institute named after. I. M. Sechenov, specialty - “General Medicine” in 1991, in 1993 “Occupational diseases”, in 1996 “Therapy”.
‹
25 products for memory and intelligence
15 substances that speed up brain function and improve memory
›
Basophils are reduced, reasons
The lower limits of basophils are too low to correctly assess the true degree of basopenia.
Therefore, as a rule, the very fact of their reduction is assessed. This condition is observed when:
- severe acute infections;
- hyperthyroidism;
- severe pneumonia;
- hyperthyroidism;
- long-term corticosteroid therapy;
- disease and Cushing's syndrome.
Also, basopenia can be diagnosed in patients during the period of recovery from infectious diseases.
Important. A decrease in basophils in pregnant women is an absolute norm. The minimum number of basophils is detected in the third trimester.
Normal for adults and children
You can determine the concentration of basophils and find out whether they are elevated or not using a detailed general blood test with a leukocyte formula. There are few mature basophilic cells in the peripheral bloodstream; their number normally does not depend on the gender of the person. The only thing is that basophils may increase slightly in women during menstruation and pregnancy.
Since basophils are leukocyte cells, their number is measured in relation to the total number of other leukocytes. Absolute content is indicated less frequently.
- The norm in adults is 0.5-1%.
- The norm in children is 0.4-0.9%.
On the forms of medical institutions you can see that the indicators of these components in the blood are as follows:
- VA% is a relative indicator,
- BA (basophils abs.) – absolute indicator.
The number of basophils in the blood indicates that an inflammatory process or an allergic reaction is occurring in the body
This value does not have any decisive diagnostic value, but in some cases it is important for specialists to find out about the general activity of leukocytes
What do deviations from the norm indicate?
The level of basophils in the blood is a kind of indicator of the presence of allergic or inflammatory processes in the human body. This indicator is not decisive in making a diagnosis, but in most situations it is necessary for the doctor to understand the complete picture that determines the functional activity of leukocytes. With its help, it is possible to track the reaction of white blood cells in response to the action of various pathogens.
Basophil levels are increased
The absolute content of these cells is not a constant value. It can be influenced by many endogenous and exogenous factors. At the same time, a significant increase in basophils (over 0.2 * 109 g/l) is observed extremely rarely, but a less pronounced increase is a common phenomenon. In adults, the most common causes of increased basophils in the blood are the following:
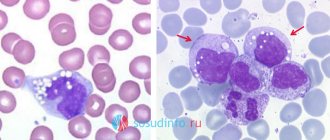
Normoblasts in the blood
- diseases of the hematopoietic organs (hemolytic anemia);
- diabetes mellitus, intoxications of various etiologies, chicken pox;
- myxedema – insufficiency of pancreatic function;
- acute and chronic diseases of the digestive system (gastritis, ulcerative colitis, gastric and duodenal ulcers);
- allergic reactions: damage to the respiratory organs, itching, urticaria, dermatitis, eczema and others;
- neoplasms in the lungs and bronchi in the initial stages.
Also, the cause of increased basophils can be the use of corticosteroid drugs, estrogens or hormones prescribed for thyroid dysfunction. Allergic reactions and blood pathologies are a group of the most common conditions when an excess of these cells is noted in the blood test of adults. In a child, such manifestations are caused by similar reasons, but to them it is also worth adding poisoning with toxic substances and helminthic infestations.
Blood pathologies leading to basophilocytosis include a list of diseases such as acute and chronic leukemia (malignant pathology of the hematopoietic system), Hodgkin's disease or lymphogranulomatosis (pathology of the lymphatic system, which is malignant), polycythemia vera (benign damage to the hematopoietic system). Each of the listed pathologies can cause an increase in the number of any leukocyte groups, not excluding basophilic granulocytes.
Important! Slightly elevated basophils may be evidence of the development of an acute or chronic inflammatory process in both adults and children.
Processes that perform the body’s protective function from adverse influences can occur in the respiratory, urinary, and digestive systems. The negative influence of factors gives a signal to trigger an immune response, as a result of which hormones and enzymes that are found in basophil granules become necessary.
The process of releasing basophil cell granules into tissue
The breakdown of basophilic granulocytes leads to the release of prostaglandin, histamine and other elements, which is the impetus for launching a protective tissue reaction to the antigen that has entered the body. In addition, there are several more non-pathological situations in which basophils can also be elevated. Such reasons in women include the condition preceding the onset of the menstrual cycle and the period of ovulation, but, as a rule, with them the increase in level is observed to be low.
It is also worth mentioning that iron deficiency in the body often leads to an increase in the number of basophils. From all of the above, it follows that if a general blood test indicates an increase in the content of these cells, then what such an increase means can only be understood by a specialist. Self-diagnosis in such situations will not bring the desired result, and delaying a visit to the doctor will only worsen the development of the disease.
Approach to eliminating basophilocytosis
In most cases, when choosing the right treatment strategy to rid the patient of the underlying disease, and its timely administration, the number of basophils returns to normal. If the cause of basophilocytosis lies in prolonged use of hormonal drugs, then medications are canceled or analogues are selected that do not cause such side effects.
To normalize the blood count after treatment for infectious and inflammatory diseases, patients are prescribed an additional course of vitamins, as well as a diet that includes foods that contain a lot of B12. This approach has a beneficial effect on hematopoietic function, which affects the general condition of a person. A constantly observed increase in basophil levels is a high probability of a chronic disease that needs to be diagnosed and eliminated.
What are basophils, their norms
Basophils are one of the smallest types of leukocytes, white blood cells. They are produced by human bone marrow.
After birth, basophilic leukocytes move into the blood for several hours, after which they live in the body tissue.
The lifespan of basophils is short - only twelve days, but all this time white blood cells try to fulfill their purpose: to protect a person from harmful organisms.
Basophils consist of biologically active substances - serotonin, histamine, heparin, which have the form of granules.
The protective function of cells is to detect harmful organisms (usually various allergens) and neutralize uninvited guests through degranulation.
This means that during contact with foreign cells, basophils disintegrate, releasing biologically active granular substances, thereby binding pests.
As a result of degranulation, an inflammatory focus is formed, which attracts other groups of leukocytes that can destroy harmful organisms or remove them from the human body.
This increases blood flow, allowing white blood cells to reach the affected area faster.
We can say that basophils are the first line of defense of the human body in defense against harmful organisms. Their main function is to detect allergens, stop their further advance and call for help.
Some laboratories determine the basophil level in absolute terms. In men, as in women, over 12 years of age, values from 0.5 to 1 percent, or 10 - 65 * 1012 cells per liter of blood, are considered healthy.
For a newborn child, the norm is 0.75%; when the baby is one month old, it is 0.5%. Per year, the normal value is 0.6%, up to twelve years - 0.7%.
It should be noted that the percentage of basophils in leukocytes is not always informative.
For example, in women in the last trimester of pregnancy, the total number of white blood cells increases significantly, which somewhat distorts the overall picture. During the onset of the menstrual cycle and during ovulation, the total number of basophils increases.
Video:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=hOugDDzX-sg
After surgery to remove the spleen, the patient’s basophilic leukocyte count will be higher than that of a healthy person.
As a rule, the number of basophils in the human body is constant. Only in some ailments, which are quite rare, temporary deviations from the norm are observed, so a detailed blood test is very important.
If the number of basophils increases relative to the norm, doctors diagnose basophilia; if the number decreases, they diagnose basopenia.
What are basophils responsible for?
Like other cells of the leukocyte group, basophils control inflammatory processes in the body.
Due to their mobility and ability to migrate outside the bloodstream, they provide the manifestation of allergic reactions.
Thus, they are the same supporting cells of the immune system as platelets and mast cells.
When entering the affected area, basophils release inflammatory mediators, which lead to itching, swelling or redness. Also, leukocytes of this type are responsible for the movement of blood flow, ensuring the process of blood clotting in case of vascular damage.
Thus, basophils perform the following functions:
- Preventing the effects of allergens on the body,
- Maintaining the tone of blood vessels and capillaries,
- Mobilization of defensive forces,
- Ensuring blood clotting and the process of phagocytosis,
- Control of skin metabolism
- Block the spread of poisons and toxins.
What is "baso"?
In laboratory analysis, the level of basophils is designated by the term “baso” - the number of cells per liter of blood. The norm is considered to be an indicator not exceeding 1%, which is typical for white cells in a calm state.
How to return basophils to normal
It is important to understand that basophilia is not a separate disease, therefore, in order to normalize the number of basophils in the blood, it is necessary to establish the cause of their increase and prescribe treatment for the underlying disease that provoked changes in the tests. Considering the role of basophils in the development of immediate hypersensitivity reactions, every person should be able to recognize anaphylactic shock and competently provide first aid at the prehospital stage
Considering the role of basophils in the development of immediate hypersensitivity reactions, every person should be able to recognize anaphylactic shock and competently provide first aid at the prehospital stage.
Important! First of all, you need to stop contact with the allergen that caused the reaction and call an ambulance.
Next, the patient must be placed on his back and his legs elevated. The head is turned to the side, the mouth is opened slightly and the lower jaw is extended. If there are leftover food, sweets, etc. in the oral cavity. they need to be removed.
An important step is to limit the spread of the allergen that has entered the body. That is, when an insect bites, the sting is pulled out, the poison is squeezed out, the bite site is washed with water, a tourniquet is applied above (the time of its application must be indicated, every ten minutes, the tourniquet is loosened for a couple of minutes). The maximum time for which the tourniquet is left is 25 minutes.
Cold (ice pack) is applied for 10-15 minutes.
If a reaction develops after taking an allergen with:
- food, tablet medications, etc., it is necessary to rinse the stomach and give sorbents (activated carbon);
- drops, nasal or eye - the mucous membranes are washed with water, then, if possible, 0.1% solution of adrenaline.
It is also necessary to provide access to fresh air, calm the victim, and free him from constrictive clothing.
If possible, a 2% solution of Suprastin or a 1% solution of Diphenhydramine is injected intramuscularly. And at the site of the bite (or injection of the medicine that caused the reaction) and above the tourniquet (at five to six points), a 0.1% solution of adrenaline (0.2-0.3 milliliters, diluted in four to five milliliters of 0.9% saline solution) is injected subcutaneously.
People prone to allergic reactions and those who go on vacation with children need to have medications with them to provide first aid.
In what cases are basophils elevated in a child?
Just like in adults, in children basophils perform a protective function and participate in the body's immune responses. The basophil content indicator is detected using a clinical blood test, during which the leukocyte formula is necessarily determined. In newborn children, the level of basophils in the blood is high and amounts to 0.75*109/l. As the year progresses, this figure decreases and remains at the level of 0.7*109/l for a long time.
The level of basophils in children increases with a variety of chronic and acute diseases, allergic reactions with a pronounced clinical picture, and with malignant blood diseases.
Sometimes children experience basopenia, the opposite condition in which the level of basophils in the child’s blood plasma decreases. In this case, it is necessary to carry out a number of additional tests, since a low level of basophils may indicate severe functional disorders in the child’s bone marrow and endocrine diseases.
In adults, a decrease in basophil levels is not assessed.
There are a number of pathological conditions in which basophils can be elevated. The reasons for the increased level of basophils can only be determined by a specialist. To make a correct diagnosis, studying the leukocyte formula alone is not enough. A number of additional studies are often required to identify allergic, endocrine, infectious and oncological diseases. If necessary, appropriate treatment or a special diet is prescribed if a high level of basophils is associated with a lack of iron in the body.
Basophils are the smallest group of leukocytes, granulocytes. Basophils make up 0-1% of all leukocytes. Basophils are born in the granulocytic region of the bone marrow. The young enter the bloodstream and circulate in the human circulatory system and only then enter the tissues where they exist for about a week.
The cell contains a lot of histamine, prostaglandins, leukotrienes and serotonin. An “army” of basophils, together with other leukocytes, react to inflammatory phenomena in the body. In the place where there is inflammation, basafil releases substances histamine, heparin, and serotonin. These substances determine the function of these cells in the inflammatory process.
They manifest themselves most acutely during allergic reactions to the presence of an allergen in the body. By releasing numerous granules with substances contained in basophils, the body fights against unfavorable factors, which leads to an increase in basophils in the tissues and a decrease in them in the blood.
Increased basophils in tissues lead to a biological response, in particular redness, swelling of the tissue, and patients complain of itching.
The granularity of basophils is well stained with alkaline, or basic, paints. Alkalies are also called bases. And base in Latin is “basis,” which is why these cells are called basophils.
Indications for analysis
Attention! The results of the study should be interpreted in conjunction with clinical symptoms and other studies.
The role of basophils in the development of anaphylactic reactions
Upon contact with an allergen, basophils actively migrate to the site of its greatest accumulation and secrete chemotaxis factors, heparin, histamine, leukotrienes, etc. This ensures a spasm of smooth muscles, a sharp increase in vascular permeability, vasodilation, and, consequently, a drop in blood pressure, the development of edema and an inflammatory response.
The first reactions to the entry of an allergen into the body appear from the respiratory system, skin and intestines, which explains the main symptoms of anaphylactic reactions.
Functions of basophils
Basophils include granules of histamine, heparin and serotonin, which act as biologically active substances. When they come into contact with allergens, degranulation occurs. This allows allergens to be associated. Inflammatory foci are formed, which attract other groups of leukocytes, which have the ability to destroy foreign and, in addition, uninvited guests.
Basophils are prone to chemotaxis, namely, to move freely throughout the tissue. A similar movement occurs under the influence of special chemical components. They also have a predisposition to phagocytosis, that is, the process of absorption of harmful bacteria and organisms. But this is not the main or natural function for basophils.
Moderately elevated basophils in adults physiological factors
Slight deviations in white blood cell counts can occur with various external or internal changes.
Since basophils suppress and block not only allergens, but also other foreign bodies, and also take part in regulating the permeability and tone of capillaries, any disturbances slightly increase the values. Increased levels are observed when exposed to the following physiological factors:
- Recovery after an infectious disease;
- Taking hormonal drugs with estrogen;
- Radiation in small doses (found in doctors’ x-ray rooms);
- Iron deficiency;
- Increased production of estrogen in a woman (menstrual cycle, ovulation);
- Poor nutrition.
In any case, even a moderate increase in indicators should alert the patient. It is necessary to undergo an examination to prevent the development of a serious disease. If the increase in BAS is temporary and is not associated with pathologies, then there is no need to worry about your health.
High basophilic cells in an adult facing periodic relapses of a chronic disease indicate an exacerbation of the process and an increased fight of the body against foreign particles and the inflammatory process.
General characteristics of basophils
Basophils, like the rest of the blood components, are formed in the bone marrow.
The maturation scheme for such substances includes several stages:
- stage 1 – stem blood particle;
- stage 2 - myelopoiesis precursor cell - is common to erythrocytes, leukocytes (all except lymphocytes) and red blood cells;
- stage 3 – myeloblast or the so-called ancestor of all leukocytes, except lymphocytes;
- stage 4 – basophilic promyelocyte;
- stage 5 – basophilic myelocyte;
- stage 6 – basophilic metamyelocyte;
- stage 7 – band basophil;
- stage 8 – segmented.
The formed component circulates through the bloodstream from several hours to several days.
Their main task is to search for a pathological agent, suppress it and prevent its spread throughout the body.
In addition, basophils have the following functions:
- increased sensitivity to immunoglobulins of category E - they take part in the development of an allergic reaction of both delayed and immediate type;
- activation of the release of serotonin, heparin and histamine in areas of the inflammatory process;
- regulation of vascular permeability;
- normalization of the blood clotting process - the granules of each basophil contain platelet adhesion factor.
Building features include:
- volumes – vary from 8 to 10 microns;
- large core, consisting of either 2 lobes - S and C forms;
- light blue cytoplasm;
- a small number of organelles;
- large granules - 0.5-1 microns, with a blue, bright blue and violet tint (they cover the core and easily dissolve in water and contain serotonin, histamine and heparin).
Basophil
Go to the doctor on time
When a child’s blood test determines an increased level of basophils, you must contact a qualified pediatrician so that he can conduct an examination and, if necessary, prescribe an additional diagnostic examination. A complete examination allows you to find out the reasons for the increase in basophils and eosinophils in a child. Based on the results of the entire examination, the pediatrician determines the disease and makes a diagnosis.
If a child has elevated basophils in a blood test, the doctor can send the child for a consultation with a hematologist in order to, together with specialized specialists, find out the causes of this condition and establish an accurate diagnosis. The decrease in basophil levels in the child’s blood can be monitored during treatment of the underlying disease.
The fact that these granulocytes are involved in the fight against inflammatory processes and the consequences of allergies especially helps doctors recognize anaphylactic shock, which occurs with insect bites and the rapid spread of poisons.
Doctors know the mechanisms of action of basophils, so they do not recommend lowering their levels with medications; they are more advised to review the list of products in baby food.
Different contents of basophils in children of different ages, as a percentage of the number of leukocyte cells:
- Children under 1 month: 0.75%;
- Children under 1 year: 0.5%;
- Children over 1 year: 0.7%.
How and what functions they perform
Determining the location of a foreign agent occurs as follows. In the area of inflammation, basophils release histamine, serotonin and heparin from the granules. They bind the allergen.
As a result, the concentration of these protective cells in the blood decreases, and in tissues, accordingly, increases. This change provokes biological processes: blood flow increases, the permeability of nearby vessels increases, redness, tissue swelling, and itching occur.
A focus of inflammation is created, a point of recruitment of cells capable of coping with the foreign agent. The body begins to react to the pathogen and activates protective functions, and also devotes strength to eliminating the negative factor. Basophils are a kind of “scouts” that find the source of inflammation and give a signal about its location.
DETAILS: Rapid heartbeat after eating
In addition to the function of accelerating the process of suppressing allergens and preventing their spread, basophils also tend to perform additional tasks, such as:
- Stabilization of blood flow in capillaries.
- Transport of other groups of leukocytes to the location of the foreign agent.
- Ensuring the growth of new capillaries.
- Promoting tissue nutrition.
- Active fight against helminths and protection from their effects on the skin, intestines and mucous membranes.
- Preventing the spread of insect poisons.
- Participation in the development of an allergic reaction.
Despite their small numbers, basophils have a versatile effect on the body and are involved in many protective processes.
Treatment
Basophils are not specifically normalized. This indicator returns to normal after the cause is eliminated. In case of diabetes mellitus, reactive inflammatory processes provoked by arthritis, absence of the spleen, hypofunction or atrophy of the thyroid gland, pregnancy or for other reasons associated with hormonal dysfunction in women, the indicators will be normal only with an artificial decrease in the content of basophilic bodies, and this is not advisable.
If there are no pathologies, the indicator is normalized as follows:
- Enrichment of the body with iron: medications – Actovegin, hematogen; food - seafood or liver (veal and chicken, to a lesser extent pork); additional recommendations - walks in the fresh air at least 2-3 hours a day.
- Allergies: medications – suprastin, tavegil; diet – more baked foods and less vegetable fats; Recommendations – avoid hypothermia and sudden temperature changes.
- Lack of vitamin B12 - taking vitamin complexes, and eating more eggs, dairy products, and yeast products.
Basophils in women
Specific causes of basophilia in women are mainly associated with hormonal imbalance.
- During pregnancy due to intense release of progesterone.
- During sexual desire, estrogen levels increase.
- During emotional upheavals, the level of basophils in the blood can be either high or low. To make sure that there are no pathologies, it is necessary to conduct a general blood test for 3-5 days, several times a day.
- If female hormones decrease, basophils can also be high - the body perceives hormonal deficiency as an allergy.
Important! An increased level of basophils signals the initial stages of carcinomas, prostate and ovarian diseases, while other diagnostic methods are not yet able to detect these pathologies.
What are basophils, content norm
As a result of a laboratory blood test, one often encounters an inscription about zero absolute basophil content. Some clients begin to panic in advance, while others ignore this phenomenon.
Both options are wrong. Let's take a closer look at what basophils are, what their role is in the body, and what a change in their content may indicate.
Briefly about basophils
Blood cells are divided into leukocytes and platelets. The former provide comprehensive protection of the body, the latter help heal external and internal wounds. Basophils are a type of granular white blood cell.
The cell itself is quite large, equal to 10-12 micrometers. It holds the core and granules. The latter contain substances that provoke inflammation. Granules are used only if the cell is affected by an allergen. Mainly, the granules include histamine and heparin.
The main role of heparin is to slow down the formation of blood clots when the skin is damaged. Its function is opposite to that of platelets.
Thus, the indicator of the absolute content of basophils reflects the specific functioning of internal organs and their ability to resist penetrating harmful bodies.
What are the functions of basophils?
- They provoke allergic processes - red spots, swelling, and itching appear on the skin.
- The entry of foreign bodies can provoke phagocytosis of basophils. In this case, the cell captures, completely envelops the foreign part and absorbs it.
- Basophils form immune resistance. If a “stranger” is detected, histamine is released, which is an alarm signal for leukocytes.
- Heparin helps the blood maintain the necessary condition. And histamine dilates capillaries, which reduces the risk of blood clots.
- Cells transport nutrients. This promotes tissue growth and renewal.
The basophil content is normal
Basically, when doing a laboratory blood test, doctors look not at the number of basophils itself, but at their ratio to the level of white blood cells, i.e. leukocytes. Normally, this ratio for an adult ranges from 0 to 1%. Up to 10-11 years of age, the limits of normal proportions are 0.4 – 0.9%.
There are frequent cases of an increase in the absolute value of basophils as a result of insect bites. In the fair sex, an increase may occur during ovulation. Common causes of childhood basophilia:
- formation of parasitic worms in the body (helminthiasis);
- the appearance of chronic pathologies;
- food poisoning.
If the absolute content of basophils ranges from 0 to 0.2%, we can talk about a reduced level. Sometimes this manifestation is diagnosed as basopenia, but there is no such concept in medical dictionaries.
Often the absolute value is zero during the first three months of pregnancy. But this is more likely caused by a general increase in fluid levels in the body. Accordingly, there are fewer basophils in one unit of liquid.
The absolute content of basophils decreases due to ionizing radiation or when chronic infectious diseases appear.
It is worth adding that diseases cannot be diagnosed based on basophil levels alone. Their content is constantly changing, so this change simply cannot be a sign of pathology. If the doctor notices an increase or decrease in the corresponding level, he simply prescribes a course of therapy.
In most cases of diagnosis, the content of basophils decreases with prolonged hard work, depression, and the presence of negative psychological influences. Therefore, full-fledged therapy is not limited to drug treatment.
The body needs more rest to restore resources; a healthy diet and pleasant experiences will not hurt.
Basophils in the blood
Sometimes we are faced with a situation where a doctor orders a laboratory blood test, and within a group of leukocytes, an abnormality in basophil levels is detected. Let's figure out what the fact that basophils are increased or decreased may indicate.
What are basophils
Basophils belong to a subtype of granulocytic leukocytes. Leukocyte granules of this type contain large quantities of histamine, heparin, serotonin, leukotriene and other mediators of inflammation and allergy.
Basophils are one of the smallest populations of leukocytes. They account for no more than 1% of white blood cells. They originate in the granulocytic section of the bone marrow; these cells enter the bloodstream in a mature form.
The lifespan of this cell ranges from 8 to 12 days.
Their main purpose is:
- Reaction to allergic reactions related to immediate type reactions - anaphylactic shock. At times when the immune system is exposed to increased exposure to antigens, basophil granules release histamine, which promotes the production of antibodies, namely immunoglobulin. Reaching a critical level of these white blood cells entails anaphylactic shock.
- The heparin contained in them is needed by the body to thin the blood and prevent its premature clotting, which is important for maintaining blood flow in small capillaries and vessels.
- They are responsible for fighting toxins that enter the victim’s body.
- Fight against parasites.
- Supporting the migration of the desired types of leukocytes.
When considering the role of basophils, it is extremely important to understand that they do not fight pathogens in the body, but by releasing certain substances in the affected area, they only seem to call upon the blood cells needed for the fight. It happens approximately as follows. These cells are the first to respond to the penetration of an aggressive agent.
They rush to the site of penetration and release the substances contained in the granules, thereby binding the allergen and slowing down its spread. As a result of this process, there are fewer basophil cells in the blood, and there are more of their constituent substances in the affected tissues - a focus of inflammation appears.
This becomes a place of attraction for other types of leukocytes.
As noted earlier, basophil cells in the blood are contained in very small quantities, and as a result, it is quite difficult to detect their content in a smear. Such a calculation is usually performed only for the analysis of the leukocyte component in a detailed analysis.
In medical practice, these cells are usually counted in two ways:
- VA% – quantity in relation to other types of leukocytes;
- BA# – absolute content of basophils 0.01 – 0.065 * 109 grams/liter.
Standards for adults
The generally accepted norms of basophils in men throughout their lives are approximately the same - 0.5 - 1%. The same norms apply to women, but here it is necessary to take into account certain periods of life during which a number of deviations are acceptable:
- the period of menstruation and ovulation is characterized by an increase in estrogen, and therefore a slight increase in this type of leukocytes;
- pregnancy during the first trimester is characterized by a decrease relative to accepted norms.
Norms for children
The performance of scout cells usually stabilizes only by the age of twelve. During the first years of life, changes will occur in parallel with the process of growing up:
- newborn child – 0.75%;
- 1 month – 0.5%;
- 2 months – 1 year – 0.4 – 0.9%;
- up to 12 years – 0.7%;
- from 12 to 21 years – 0.6 – 1%.
The highest rate will be in a newborn baby as a result of the fact that his immune system is just undergoing the process of formation. After this process is completed, basophil levels gradually return to normal.
Deviations from the norm
Sometimes, during a detailed blood test for basophils, a deviation from the accepted norms is noted in the leukocyte component. There are two options here:
- basophilia – increased content of these white cells;
- basopenia – reduced content.
DETAILS: How to remove congestion in the pelvis in women
Increased level
Faced with such a result, you should not immediately panic. It is advisable to wait a few days and take this test one more time.
If the situation repeats, you should seek help from a doctor as soon as possible. This is especially true for an increase or decrease in leukocytes of this type in a child.
An indicator when basophils are higher than normal usually indicates the development of pathological processes in the body, and these can be:
- hepatitis;
- infection;
- disorders of the thyroid gland;
- allergic reaction;
- benign or malignant tumor;
- blood diseases;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- various types of intoxication.
When conducting an analysis, it is imperative to take into account what medications the patient has previously taken. In a child, an increase in this type of leukocytes in the blood can develop as a result of long-term or chronic allergies.
If a blood test shows a decrease in basophils, then it is worth considering the following nuances:
- stressful situation;
- hyperthyroidism;
- increased thyroid function;
- pneumonia;
- Cushing's disease;
- disruption of the adrenal glands.
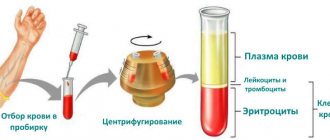
Blood sampling is carried out in specialized laboratories. Blood is most often taken from a finger - probably everyone is familiar with this procedure, but in order to get correct results, it is best to prepare a little before taking the tests:
- the test is taken on an empty stomach - the last meal should not be earlier than 8 hours before;
- increased physical activity should be postponed for about a day;
- do not drink alcohol for at least 24 hours;
- Before taking the exam, you should try not to be nervous;
- The doctor must be warned in advance about taking any medications, and he will advise which medications should be temporarily interrupted.
If changes in the composition of the blood are the result of any disease, then, naturally, in order to bring the indicators back to normal, it will be necessary to cure this disease. At the end of treatment, the patient is usually prescribed a second blood test and a comparative analysis of the situation is carried out.
If the change in indicators is not associated with disease, then the person needs to pay attention to the diet. One of the vitamins needed to produce these white cells is B12.
Thus, it is important to include enough meat, eggs, milk, liver, etc. in your diet. It is also important to eat fish and other seafood.
You can activate the process of iron absorption by adding dry white wine or orange juice to your diet.
Despite the small number of basophils compared to other blood cells, it is by no means impossible to say that they are less important for the body. Like all leukocytes, basophils perform a protective function, being the first to respond to an allergen or infection. Their reaction leads to the mobilization of other cells of this type - granulocytes - to the lesion.
Like other blood cells, basophils can change their concentration, which is often a sign of a disease, sometimes quite serious. Therefore, if during the test it turns out that basophils in the blood are low or high, then you should go to a specialist as soon as possible for a consultation and a comprehensive examination.
Basophils are a subtype of granulocytes, along with blood cells such as neutrophils and eosinophils, and are a type of white blood cell that also includes lymphocytes and monocytes. Basophilic granulocytes have an S-shaped nucleus, which is quite difficult to see even with powerful microscopes due to histamine granules and other allergic mediators blocking the cytoplasm.
These cells are the largest of all granulocytes. They contain a large number of mediators of allergic and inflammatory processes: histamine, prostaglandins, serotonin, leukotrienes, etc. Basophils act as mediators in the formation of allergic reactions of the immediate type (anaphylactic shock).
Thanks to these blood cells, poisons are blocked, which prevents them from spreading throughout the body. In addition, basophils are responsible for the regulation of coagulation produced by heparin. They carry immunoglobulin E on their surface and have the ability to undergo cell lysis (dissolution) or degranulation (give off granules) upon contact with an allergen.
The main task of these cells is rapid degranulation, causing an increase in blood supply, vascular permeability, as well as the influx of fluid and other granulocytes. That is, the primary goal of basophils is to attract other cells of this type to the source of inflammation.
Reference! With a prolonged inflammatory reaction (over 3 days), the production of new blood cells of this subtype increases in the bone marrow, leading to basophilocytosis or basophilia (increased level of basophils).
Brief information about the functions of basophilic granulocytes
Since basophilic granulocytes are a type of leukocyte, their number is determined as a percentage of the total number of these blood cells. In some cases, absolute values are indicated in analysis forms. The norm of basophils in the blood of adults, that is, the specific gravity, is 0–1 percent and the absolute value is 0–0.065*109 g/l.
Normal levels of basophilic granulocytes in children are almost no different from those of an adult and are equal to 0.4–0.9%. In medical test forms, information about these cells is as follows: VA% (basophils) is a relative indicator and BA (basophils abs.) is the absolute content of basophils. You can read more about basophils in a child’s blood in this article.
The level of basophils in the blood is a kind of indicator of the presence of allergic or inflammatory processes in the human body.
This indicator is not decisive in making a diagnosis, but in most situations it is necessary for the doctor to understand the complete picture that determines the functional activity of leukocytes.
Why do basophilic cells increase?
Basophils in the blood may be elevated in an adult for the following reasons.
Common reasons:
- Inflammation, mainly in rheumatoid arthritis. ESR and leukocytes are also elevated.
- For autoimmune diseases. With high basophils and ESR, leukocytes are within normal limits or low.
- For immune diseases - rubella, chickenpox, HIV. Low leukocytes, ESR within the normal range.
- Iron deficiency. Also low hemoglobin.
- Helminthiasis - high eosinophils. If helminths or their metabolic products have damaged liver cells - high red blood cells and AST above 25 in biochemical analysis; gastrointestinal mucosa – rods increase no more than 10.
- Crohn's disease, gastrointestinal ulcers - ESR increases to 12-15, rods above 15; with spastic colitis - ESR above 18.
- Allergies – may occur if other indicators are normal. And if a lot of histamine is released, the ESR is 20 or more.
- Diabetes – due to high sugar levels. In many modern clinics, a general blood test and a sugar test are performed as part of one sample collection.
- With cancer, leukocytes and red blood cells increase, platelets are present, and hemoglobin drops sharply.
- If basophilia occurs due to taking medications, other indicators may be normal, additional examinations need to be carried out.
- Enlarged thyroid gland - additionally, biochemical analysis for iodine, histamine.
- With an enlarged spleen or after its removal - against the background of low red blood cells.
The norm of basophils in the blood, causes and diagnosis of abnormalities
The results of the examination may be influenced by prolonged use of estrogen or the patient’s lack of preparation for the procedure. Therefore, it is very important not to donate blood without appropriate preparation and to warn your doctor about medications that are taken during the month.
An increased result indicates:
- An increase in estrogen in the blood.
- Taking hormonal medications.
- Past infectious disease.
- Malfunction of the pancreas.
- Benign or malignant tumor.
- Presence of hepatitis.
- Minor radiation exposure during medical examinations.
- Blood disease.
- Allergic reaction.
- Failure in the endocrine system.
- Surgical removal of the spleen.
- For gastrointestinal diseases.
- Intoxication after insect bites.
In adults, the number of “scout cells” may be reduced due to:
- Infectious disease.
- Exposure to stress.
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Cushing's disease.
- Active activity of the thyroid gland.
- In case of abnormalities in the functioning of the adrenal glands.
- Pneumonia.
What are basophils
Symptoms of basophilia
It is quite difficult to determine the increase in basophils based on clinical signs, since everything depends on the reason that provoked this phenomenon. For example, if they are elevated due to a malfunction of the thyroid gland, the patient may experience:
- swelling of the face;
- hair fragility;
- hoarse voice;
- keratinization of the skin;
- causeless weight gain;
- disruption of bowel function;
- significant drop in temperature.
But if we talk about general features, we can highlight the following:
- weakness;
- increase or decrease in temperature;
- redness and itching of the skin;
- swelling and tearing;
- pain in the joints;
- bowel dysfunction;
- weight fluctuations;
- liver problems;
- increase in the size of the spleen.
As a rule, when the level of basophils rises above normal, clinical signs appear; in very rare cases, nothing indicates basophilia. However, the absence of symptoms may be due to a physiological increase in the number of basophils - ovulation, pregnancy, menstruation.
Signs of basophilia
Basophilia is a complex disease that involves the manifestation of the body’s defensive reaction to external or internal stimuli. Basophilia is diagnosed in the presence of an increased content of basophils in the blood for at least 3 days, if the analysis was carried out 3 or more times a day and there are no concomitant diseases in which basophils necessarily increase.
With concomitant diseases, symptoms of pathologies appear. If there are none, symptoms of basophilia appear if the concentration of basophilic bodies in the blood plasma is 3 or more times higher than the upper normal value.
- A rash is a protective allergic reaction; pimples are accompanied by redness or become inflamed.
- Itching - constantly changes location, of varying intensity, may be accompanied by low-grade fever.
- Dry mouth as a result of iron deficiency.
- Dizziness, possible short-term fainting. With these symptoms, hemoglobin does not exceed 50.
- If the spleen is removed, increased sweating, low blood clotting, frequent inflammation without other pathologies.
- Brittle nails, hair loss, frequent bleeding in the absence of vitamin B12.
How to prepare for research?
Everyone has ever taken a general clinical blood test and knows that it requires blood from a vein or capillary blood from a finger.
It is also important to prepare for the study, especially since there is nothing difficult in preparation.
- Blood must be donated in the morning on an empty stomach. This way, nothing will interfere with determining the parameters on the hematology analyzer.
- It is recommended not to smoke for several hours before the test.
- Physical and emotional peace before blood sampling will only be beneficial.
It was previously mentioned that when taking estrogen-containing drugs, the number of basophils may increase. Therefore, it is worth warning the doctor about this so that he can make allowances for this when decoding.
What are basophils?
Basophilic leukocytes are a group of the largest and most numerous cells from granulocytes. Their synthesis occurs in the bone marrow from myeloblasts, after which they penetrate into the human blood, where they linger for only a few hours. Then they migrate into tissues, where they continue their functional activity for up to 12 days.
Basophils have many functions, one of them is to help fight infections.
The functions of basophils also include:
Participation in inflammatory processes and allergic phenomena.
Removal of toxic decay products after insect and animal bites, as well as other injuries of mechanical origin.
Stimulation of normal blood flow in small vascular branches.
Activation of capillary growth.
Regulation of blood clotting
Since these cells contain heparin, they have a beneficial effect on blood thinning and are responsible for preventing the development of thrombosis in the vascular network. Other components of basophils: serotonin, histamine and prostaglandin, having detected the presence of an allergen in the human body, envelop it, provoking signal reactions in the form of burning, swelling, and itching (allergic manifestations).
A general blood test of basophils makes it clear their number, which helps determine whether the body’s condition is normal or not.
Treatment of eosinophilia
After identifying the true cause of the change in the blood formula, treatment is carried out by a specialist doctor. In case of blood pathology, this is a hematologist; if the prerequisite for the development of the condition was parasites - an infectious disease specialist; allergies will be cured by an allergist; lungs - pulmonologist and so on. There is no single way to get rid of eosinophilia; the doctor takes into account the patient’s age, concomitant diseases, general health, medications taken and many other factors on an individual basis.
You should also not be upset if eosinophils are moderately elevated; this may indicate the beginning of recovery and the formation of a healthy immune system response to the infection. Let the doctor do his job and strictly follow his recommendations.
Each person's body naturally produces several types of leukocytes (white blood cells formed in the bone marrow, from where they travel through the circulatory system to various organs).
We need leukocytes to keep us healthy; they destroy various infectious agents, viruses, bacteria, parasites and fungal infections that invade the body.
There are 5 types of leukocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, basophils).
Basophils are a type of white blood cell. They are part of the immune system and play a role in protecting the body.
If basophils are elevated in an adult, this indicates a problem with the thyroid gland, certain types of blood cancer (leukemia, leukemia), various inflammatory processes, and much more.
Abnormal changes in the number of these small groups of white blood cells have a variety of causes, from “minor” to “usually fatal.” What this means is that the search for the true cause is carried out by eliminating or confirming each possibility - in other words, diagnosis.
What are basophils?
Basophils are a type of granule containing leukocytes (white blood cells) in the bone marrow: it also produces red blood cells and platelets. They are few in number and make up only 0.01-0.3% of the total number of leukocytes. Although present in small quantities, basophils play an important role in keeping the human body safe - protecting the body from bacteria and parasites. However, their excess production is a cause for concern that cannot be ignored.
Where is the analysis performed?
This blood test is free if you have a compulsory health insurance policy. That is, when contacting a budgetary medical organization, the patient should undergo a general clinical blood test without any problems.
There are also no problems in conducting this study in any other medical institution, especially for money. A separate cell count in a private medical center can cost between 200 and 300 rubles. If we conduct a complete study of all indicators included in the UAC, then the price increases to 500 rubles.
Photo: https://pixabay.com/photos/medicine-withdrawals-nurses-3493688/
Please note that the determination price is indicated for one specific region. Therefore, the exact cost must be clarified in your locality.
Keep in mind that the medical center may charge a fee for the blood draw procedure. On average it is 200 rubles.
Decreased basophils (basopenia)
With basopenia, the number of basophils is pathologically reduced (less than 0.01*10 9 /l).
The number of basophils can be reduced in a number of pathologies:
A decrease in the number of white cells in children can occur due to dysfunction of the endocrine system, lack of iron and vitamin B-12 in the diet.
Only a qualified specialist can decipher the leukocyte form for the number of basophils: a therapist, an infectious disease specialist, a hematologist or a functional diagnostician.
Basophils - act as the smallest cells belonging to the category of leukocytes. However, they contain large granules that include substances such as histamine and heparin - they are released during allergic reactions. Increases and decreases in such substances develop extremely rarely, since there are very few of them in the blood.
In the vast majority of cases, deviations from the norm are facilitated by pathological processes. However, the provocateurs of low and high basophils will be different.
Basophils in the blood are determined during a general clinical examination of human biological fluid. However, this will not help to establish the main factor that provoked the deviation from the norm: this requires a comprehensive examination of the body.
Normalization of such substances in children and adults occurs simultaneously with the elimination of the provoking disease, which can be accomplished by conservative or surgical techniques.
Treatment of basophilia
Therapy consists of treating the underlying condition that has caused an excessive increase in these white blood cells in the bone marrow.
Basophilia associated with infections, allergies, or thyroid disease is usually not a cause for concern.
However, if basophilia occurs as a result of bone marrow cancer, then it is a serious problem and requires immediate treatment.
- Bone marrow transplant - transplant surgery is performed in severe cases such as leukemia.
- Antiallergic drugs - they are prescribed for basophilia caused by allergic reactions that lead to respiratory diseases.
- In cases of hypothyroidism, taking hormonal drugs and medications such as L-thyroxine and L-Thyroxine 50 Berlin-Chemie (levothyroxine sodium) leads to normalization of basophil levels (be sure to consult a doctor before purchasing and taking drugs).
- If iron deficiency anemia is the cause of basophilia, then treatment is carried out by taking iron supplements (Actiferrin, Tardiferon, Sorbifer Durules).
- Bacterial infections causing the phenomenon are treated with antibiotics.
Vitamin B12, which is administered by injection, can play an important role in normalizing the level of these leukocytes; it is also recommended to eat meat, eggs and milk, these products contain a sufficient amount of vitamin B12.
This vitamin helps normalize the formation of new blood cells and improves the functioning of the bone marrow.
Now you will find out what this means if, as a result of a blood test, basophils are elevated in an adult. The leukocyte formula is a study to decipher the number of each subpopulation of leukocytes. The results are presented as a percentage of each cell type or their absolute number.
Normally, basophils are the smallest population of leukocyte cells. Their number determines the presence or absence of an allergic reaction in the patient. However, their value may change against the background of other pathologies: oncology, infection or inflammatory lesions of intestinal tissue, some types of anemia, kidney damage, etc.
The price of the “Leukocyte formula” analysis in private laboratory departments is from 150 rubles. The lead time depends on the workload of the laboratory, maximum – 1 day.
What is the cause of elevated basophils in an adult?
Basophilia, which forms independently, is rare, but is a sign of chronic myeloid leukemia. An increase in the number of these cells is also associated with a wide range of diseases.
Myeloproliferative neoplasms (MES)
Because basophils are produced in the bone marrow, their increased production is associated with myeloproliferative neoplasms, a group of diseases in which an excess number of blood cells (platelet, white blood cell and red blood cell) are produced. This phenomenon is especially common in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), a cancer that causes excessive production of a certain type of white blood cell called granulocytes. Their main types are basophils, eosinophils and neutrophils. The process can only be identified in a laboratory way. The concentration of basophils increases significantly - it accounts for at least 20% of the total number of white cells circulating in the bloodstream.
Oncology
Carcinoma is a cancerous tumor formed from cells that form epithelial tissue: this type of lining lines the internal surfaces of various organs. The process also involves external surfaces, involving blood vessels. This form of malignant neoplasm leads to the development of basophilia, which can only be detected in a laboratory way.
Lymphoma
Elevated levels of basophils in the blood are also associated with Hodgkin lymphoma, a form of cancer that causes an abnormal increase in the number of lymphocytes (white blood cells). The neoplasm affects the lymphatic system, increasing tissue production. Since they form lymph nodes - natural reservoirs of lymphocytes, along with an increase in the volume of immune cells, there is often an increase in other types of white blood cells, including basophils.
Allergy
Individual intolerance to certain medications, foods or other environmental factors leads to a high concentration of basophils. When the body is exposed to allergens, cells are activated and histamine is released. This reaction causes a wide range of symptoms, including runny nose and watery eyes.
Inflammatory processes
Chronic inflammatory processes are also responsible for increasing basophil levels. These cells play an important role in initiating the inflammatory response by releasing irritating chemicals histamine and serotonin. This leads to dilation of the blood vessels and muscles of the bronchial wall (asthma), thereby causing breathing problems.
Infection
Regardless of the origin - be it a viral or bacterial disease, it awakens the body to increase the production of white blood cells to fight the pathogen. This most often occurs with influenza, chickenpox, tuberculosis, and chickenpox.
Iron deficiency
Iron deficiency, which leads to anemia, can also cause an increase in basophils. With anemia, there is a sharp drop in the number of healthy red blood cells. The body's health primarily depends on dietary iron to produce hemoglobin (a red, iron-rich protein). It is present in red blood cells (erythrocytes). The ability of red blood cells to carry oxygen to various parts of the body is due to hemoglobin. However, imperfect iron in the diet leads to a deficiency of this substance, which reduces the number of healthy red blood cells. People with iron deficiency anemia tend to show high levels of basophils in the blood. Also, deviations from the norm can be observed in people suffering from hemolytic anemia.
Endocrinopathy
Endocrinopathy is defined as a disorder of the endocrine system in which the glands produce hormones and function with severe impairment. There are 8 endocrine glands, one of the most important is the thyroid. An increase in basophils occurs in people diagnosed with hypothyroidism, a condition in which the thyroid gland experiences hypofunction, producing insufficient amounts of hormones.
Diabetes
When endocrinopathy occurs, the functioning of the pancreas (another endocrine gland) is markedly impaired, causing diabetes mellitus, a condition in which blood sugar levels are abnormally high. The pancreas is involved in the production of insulin, a hormone that keeps glucose levels under control. An unfavorable condition of the pancreas reduces the secretion of insulin, which causes chronically elevated blood sugar levels. Diabetes mellitus is accompanied by an increase in the concentration of basophils, worsening their resistance to fighting infections. Despite the increased volume of immune cells, diabetics are susceptible to various infections.
Signs of elevated basophils
Symptoms of pathologies in which the concentration of basophils increases in an adult will vary depending on the nature and course of the underlying cause. For example, myeloproliferative neoplasms often become the basis for an enlarged spleen, which leads to abdominal discomfort and a feeling of fullness. An anemic state is characterized by weakness, constant fatigue and headache. While thyroid problems cause constipation, muscle pain, unexplained weight gain and joint stiffness.
Level reduction
The condition when basophils are low is called basopenia. This disease indicates depletion of leukocyte reserves in the hematopoietic organs.
The following factors can cause low cell levels:
disturbance of psycho-emotional balance, exhausting physical activity, hyperactivity of the adrenal cortex (Cushing's syndrome), pronounced activity of thyroid hormones, exhaustion of the body (after serious illness or long-term use of antibiotics), acute course of diseases of infectious origin.
Any causes of low levels of leukocytes require surgical therapeutic intervention so that the situation does not worsen. After all, if basophils are reduced, this means that the functional ability of the body and its protective functions is impaired.
Treatment of the condition
Basophilia due to an allergic reaction, infection or thyroid problems should not be a cause for concern as the issue can be resolved by taking appropriate medications. It is important to promptly seek medical help and undergo examination. The therapeutic approach will involve hormone therapy, the introduction of antibiotics, and general restoratives. A more complex situation relates to the appearance of basophilia, which develops against the background of bone marrow cancer. This problem requires systemic treatment by an oncologist. The specialist will suggest the option of bone marrow transplantation.
7 minutes Author: Lyubov Dobretsova 3008
Despite the small number of basophils compared to other blood cells, it is by no means impossible to say that they are less important for the body. Like all leukocytes, basophils perform a protective function, being the first to respond to an allergen or infection. Their reaction leads to the mobilization of other cells of this type - granulocytes - to the lesion.
Like other blood cells, basophils can change their concentration, which is often a sign of a disease, sometimes quite serious. Therefore, if during the test it turns out that basophils in the blood are low or high, then you should go to a specialist as soon as possible for a consultation and a comprehensive examination.
Causes of pathology
If eosinophils are elevated, it is necessary to identify the cause, since the pathology is a symptom of a disease, and not a separate disease. An increase in the number of these blood cells indicates intensive work of the immune system, and does not always require treatment.
There are several prerequisites for the development of eosinophilia:
- Parasitic infections;
- Allergic reactions;
- Diseases of internal organs;
- Blood diseases;
- Dermatological pathologies;
- Autoimmune diseases;
- Infections;
- Formations of a malignant nature.
Parasites
A blood test reveals eosinophilia when a person is infected with helminth infections. The following diseases may be the cause:
- Toxocariasis;
- Opisthorchiasis;
- Giardiasis;
- Ascariasis;
- Filariasis;
- Strongyloidiasis;
- Malaria;
- Paragonimiasis;
- Echinococcosis;
- Trichinosis;
- Amoebiasis.
Allergy
An allergic reaction occupies a leading place among the causes of increased eosinophils. The condition develops when:
- Hay fever;
- Quincke's edema;
- Bronchial asthma;
- Allergic reaction to medications;
- Hay fever;
- Serum sickness;
- Rhinitis of an allergic nature;
- Hives;
- Fasciitis;
- Myositis, etc.
Diseases of internal organs
Eosinophilia manifests itself in diseases of the following organs:
| Lungs | Gastrointestinal tract | Heart | Liver |
| alveolitis | gastritis | myocardial infarction | cirrhosis |
| pleurisy | colitis | birth defects | |
| Loeffler's disease | ulcer | ||
| sarcoidosis | gastroenteritis | ||
| histiocytosis | |||
| aspergillosis | |||
| pneumonia | |||
| presence of infiltrates | |||
Blood diseases
An increase in eosinophils is observed in erythremia, myeloid leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis, polycythemia, pernicious anemia, Sezary syndrome.
Dermatological pathologies
Almost any skin disease leads to elevated eosinophils:
- Lichen;
- Pemphigus vulgaris;
- Contact or atopic dermatitis;
- Pemphigus;
- Eczema;
- Fungal disease.
Autoimmune conditions
Often, a blood test reveals an increase in eosinophils in scleroderma, SLE (systemic lupus erythematosus), and a large number of these cells are formed when the transplant is rejected.
Infections
Infection in the body always causes eosinophilia. The condition can be provoked by both the acute phase and exacerbation of chronic diseases:
- Scarlet fever;
- Tuberculosis;
- Gonorrhea;
- Mononucleosis;
- Syphilis, etc.
Malignant tumors
Various forms of malignancies, including lymphomas and lymphogranulomatosis, cause an increase in eosinophil cells in the blood. Tumors can be localized in various organs: genital or internal organs, thyroid gland, skin, stomach, etc., the condition worsens with the appearance of metastases.