Introduction
The abdominal cavity
is a space located in the body below the diaphragm and is entirely filled with abdominal organs. It is divided into the abdominal cavity itself and the pelvic cavity. The cavity is lined with a serous membrane - the peritoneum, which separates the peritoneal cavity (the abdominal cavity in the narrow sense) from the retroperitoneal space.
| Anatomical diagram of the location of the abdominal organs | MRI image of the abdominal cavity |
At the present stage of medicine, MRI is the most effective and informative method for studying the abdominal organs. Magnetic resonance scanning allows you to establish an accurate diagnosis and prevent further development of the pathology.
Indications for MRI of the abdominal cavity
MRI is a safe diagnostic method, since during its implementation a person is not exposed to radiation or ionizing radiation. That is, the procedure is harmless for patients of different age categories. MR imaging is based on the phenomenon of nuclear magnetic resonance.
To understand what MRI is, you need to understand how this method works. The essence of the study is that the nuclei of some atoms, which are placed in a magnetic field, are able to absorb electromagnetic pulses. They convert energy into radio signals and emit them at the end of the pulse. These vibrations are recorded on special instruments.
Tomographs work on the nuclei of hydrogen atoms, which are part of water molecules (70% of the human body consists of water molecules). The volume of fluid in different organs is different, and therefore the intensity of the signal is different. Thus, MRI allows you to obtain a picture of internal organs, identify violations of their functionality, and distinguish healthy cells from pathological ones.
The study is carried out if pathologies in tissues or neoplasms are suspected. With the help of MRI, it is possible to carry out a differentiated diagnosis of neoplasms and distinguish a benign tumor from a malignant one. MRI can detect bleeding in the pelvis, stones in the gall bladder or bile ducts. This diagnostic method allows you to monitor the abdominal organs and blood vessels when planning surgery or organ transplantation.
Using MRI of the abdominal cavity, the following diseases are diagnosed:
- Purulent tissue inflammation.
- Tubular necrosis of the kidneys with an acute course.
- Oncological formations on the abdominal organs.
- Hypertrophy of the spleen or liver.
- Diseases of the gallbladder and ducts.
- Benign tumor.
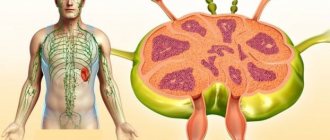
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Superior vena cava syndrome.
- Malignant tumor of the pancreas, gall bladder.
- Compression in the portal vein.
- Immune response during transplant rejection.
- Enlargement of the abdominal aorta.
- Insulin-producing tumor.
The decision to prescribe an MRI is made by the attending physician.
Classification of tomographs
MRI scanning is carried out using a special installation - a tomograph. To understand which equipment is best for performing MRI, it is worth studying the design features and technical characteristics of the devices.
According to their design, the devices are divided into:
Closed tomograph
– capsule type device with a retractable table. Working magnets are located around the entire perimeter of the chamber, allowing for a three-dimensional projection of the body.
Advantages of a closed type tomograph:
- Generates a high voltage magnetic field.
- Provides higher inspection speed.
- Provides informative diagnostics due to high resolution images.
Weaknesses of the equipment:
- A long tunnel causes psychological discomfort in an anxious personality type.
- The pull-out table has weight restrictions.
- The diameter of the tunnel is not provided for people with the 3rd degree of obesity, patients with non-standard fixation of broken limbs.
Increasingly, closed-type tomographs with a shortened scanning capsule are found in clinics. This allows scanning with high magnetic field strength, creating a favorable environment for a person with claustrophobia.
Open tomograph
– a device equipped with a magnetic installation at the top and bottom, leaving the space around the table open.
Advantages of the device:
- Suitable for assessing patients with claustrophobia and anxiety disorders.
- The retractable table has a greater load capacity.
- Allows for MRI scanning of overweight patients with difficult fixation of fractures.
- Recommended for examining young children.
Flaws:
- Generates a low intensity magnetic field.
- Produces images with low resolution.
- Unable to detect pathology at an early stage of formation.
| Open MR tomograph | Closed-type MR tomograph |
From the variety of technical characteristics of tomographs, the patient must take into account the magnetic field strength. Measured in Tesla - Tl.
Based on the voltage strength of the working magnetic field, the devices are divided into:
Low-floor installations with voltages from 0.1 to 0.5 Tesla.
Advantages of tomographs:
- The magnetic field is not aggressive, which allows scanning of patients with metal implants.
- Cheaper cost of research.
Weak sides:
- As a rule, these are old-made devices, so they have limited functionality.
- The pictures have low resolution and detail.
- Not suitable for examining abdominal organs, blood vessels, and mammary glands.
Mid-field devices with magnetic field strength from 0.5 to 1 Tesla.
Advantages of the equipment:
- Lower price for examination.
- Suitable for preliminary diagnosis.
Flaws:
- Poor image resolution.
- Determines pathologies of moderate severity.
High-field tomographs with an intensity of 1.5 Tesla.
Installation benefits:
- High resolution images.
- Greater information content of soft tissue research.
- Determines pathologies at an early stage, metastases and other small structural disorders.
Weak sides:
- To generate a high voltage magnetic field, a closed space is required; being in a scanning capsule causes discomfort and a state of panic.
- The diameter of the tunnel is limited in volume.
- The retractable table has limitations on load capacity.
- A ban on examining patients with pacemakers, defibrillators, hearing aids, and metal implants.
Ultra-high-field tomographs with an intensity of 3 Tesla.
They have the same disadvantages as high-field devices.
Advantages:
- High scanning speed compared to other MRI scanners.
- Determines functional disorders.
- Detects neoplasms at an early stage, when the nucleus has not yet formed.
To conduct a high-quality examination, a tomograph with a magnetic field voltage of 1.5 Tesla is sufficient.
| Image quality depending on equipment power |
Indications
The diagnostic capabilities of MRI make it possible to identify a wide range of pathologies with an accuracy of up to 95%; the procedure is indispensable in preparation for surgery, therefore, both a therapist and a surgeon, oncologist, and nephrologist can refer for MRI of the peritoneum. You can also undergo examination using an MRI scanner on your own initiative if you have the following conditions:
- abdominal injuries, road accident, bad fall
- frequent pain in the peritoneal area of unknown origin
- nausea, vomiting for no apparent reason
- ascites
- congenital anomalies and/or malformation of one of the organs
- Ultrasound revealed an enlarged liver or spleen, congestion and intestinal obstruction
- tests indicate the presence of inflammatory processes in the peritoneum
- suspicion of neoplasms and metastasis.
An MRI of the abdominal cavity is also necessary in the following situations:
- preparation for surgery
- analysis of the dynamics of the disease
- assessment of the quality of therapy and surgical intervention.
Nutritional considerations in preparation for scanning
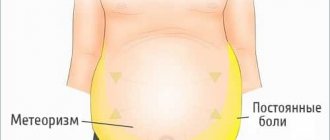
A diet several days before an MRI of the abdominal cavity is prescribed on the recommendation of a doctor. In preparation for the study, it is mandatory to limit foods that cause bloating during the day. Such food products include flour products, sweets, carbonated drinks, cabbage, beans, meat, milk, apples.
Foods that cause bloating
According to the doctor's indications, a limit on sweets, fruits, onions, beans, fried meat, milk and carbonated drinks is prescribed for two days. The day before the scan, exclude bread, cabbage and juices.
When diagnosing the pancreas and liver, a carbohydrate-free diet is prescribed for two days. This is necessary to exclude false results due to the load on the organs being examined. A low-carbohydrate diet consists of completely abstaining from flour products, cereals, some fruits, such as bananas, sweets, sweet carbonated drinks, and potatoes. Green vegetables, nuts, buckwheat, kefir are what you can eat before an MRI of the abdominal cavity.
Attention! The article is not a guide to action; for detailed information, contact a specialist.
Contraindications
Before prescribing an MRI scan, the doctor conducts a survey to find out possible contraindications to the procedure. Their range is quite wide, so experts divided them into two groups:
Absolute contraindications
– a special condition of the patient’s body in which MRI is strictly contraindicated.
Absolute contraindications include:
- presence of a built-in defibrillator
- presence of a pacemaker
- decompensated heart failure
- built-in insulin pump
- connection of bone tissue using the Ilizarov apparatus
- hearing implants
- presence of metal hemostatic clips
- the presence of foreign metal objects (bullets, fragments) in the body.
Relative contraindications
– conditional restrictions, overcoming which the patient can undergo examination on an MRI machine.
Relative contraindications include:
- first trimester of pregnancy
- tattoos made with metallic ink
- claustrophobia
- presence of bleeding
- state of alcoholic intoxication.
Preparation
An MRI scan of the abdominal organs is performed on an empty stomach, 8 hours after the last meal. The intestines also need to be emptied.
- For greater diagnostic efficiency, experts recommend following a diet for several days before the procedure: reduce the consumption of flour, sweets, eliminate foods that impede intestinal motility and cause bloating - kefir, legumes, cabbage, meat, seeds, carbonated drinks.
- Patients taking insulin can eat 3 hours before the MRI.
- Before the examination, it is necessary to reduce gas formation in the intestines. To do this, you can take Espumisan. 2 tablets of No-shpa will help relieve muscle spasms.
Preparation for the procedure
For emergency indications, no preparation is required, however, during routine diagnostics, to improve quality and efficiency, it is necessary to prepare for MRI.
The main preparation is diet:
- exclude for 2-3 days foods that contribute to increased gas formation (legumes, cabbage, alcohol);
- when examining the pancreas, it is not recommended to eat carbohydrate foods for 2-3 days;
- perform a cleansing enema the day before if necessary;
- test for allergies to a contrast agent;
- 4 hours before the diagnosis, do not drink any liquid;
- 30-40 minutes before the patient is recommended to take an antispasmodic drug (“Spazmalgon”, “No-Shpa”, “Drotaverine”);
- remove metal objects: jewelry, piercings, belts, metal dentures.
How does the procedure work?
Carrying out MRI diagnostics of the abdominal cavity is conventionally divided into 3 stages: organizational issues, scanning and obtaining results.
Organizational part.
The patient must arrive at the clinic an hour before the start of the examination to arrange the following points:
- Provide a referral from a doctor indicating the purpose of the examination. If the diagnosis is carried out on one’s own initiative, then it is necessary to clearly define the tasks of the specialist conducting the research.
- Verification of documents confirming the free procedure within the framework of VHI or compulsory medical insurance.
- In case of a paid examination, sign an agreement for the provision of medical services and make payment.
- A questionnaire or interview to determine possible contraindications for the patient.
- If it is necessary to conduct contrast-enhanced MRI, the specialist selects the drug and calculates the dose.
- Before starting the procedure, you must remove jewelry and items containing ferromagnetic alloys. Some clinics provide the patient with a loose disposable shirt to change into.
Carrying out a scan.
- The patient is placed on the retractable tomograph table and secured with soft straps.
- Headphones are provided to reduce discomfort caused by noise in the capsule.
- The table slides into the tomograph, the machine starts up, and the scanning procedure begins.
Delivery of results.
The speed of processing and decoding information depends on the radiologist’s workload.
The minimum waiting time is half an hour. But it may happen that the results will be ready the next day. The patient receives:
- description (decoding)
- a printed photograph and/or a disk with images.
The final diagnosis based on the examination results will be made by the attending physician. However, in some medical institutions it is not forbidden to ask questions to a radiologist.
How is MRI performed?
Diagnostics is carried out in a horizontal position. In this case, the hands must be fixed. To do this, soft belts are fastened, which are also located in the chest and head area. While the patient is lying down, he is pushed into the tomograph ring.
During scanning, the ring of the device rotates around the patient. The received data is sent to a computer and processed by special software.
The patient must remain motionless throughout the examination.
If necessary, someone close to you can be with the patient. In addition, you should take a sedative. The patient will need to hold their breath while taking pictures.
The doctor is nearby and monitors everything from the next room
The doctor gives all recommendations through two-way communication. This way you can also tell your doctor about any negative symptoms. At the end of the diagnosis, medical workers will decipher the results obtained. A diagnosis is made and effective treatment is selected.
Upon completion of the diagnosis, the patient can return home. There is no need to reduce physical activity.
Duration of the procedure
An examination using an MRI scan of the abdominal cavity on a closed tomograph takes from 20 to 40 minutes, depending on the strength of the magnetic field.
Thus, a 3 Tesla installation will diagnose the condition of all organs located in the abdominal cavity in no more than 20 minutes. A similar device with an operating magnetic field voltage of 1.5 Tesla will spend up to 40 minutes for research.
If, to improve the effectiveness of the examination, the doctor orders an MRI with contrast enhancement, then the scanning time will take 2 times longer. First, the specialist carries out the procedure as usual, after which contrast is introduced and the examination is restarted.
Features of this diagnostic: advantages and risks
The main advantages of MRI of the retroperitoneal space are its versatility and diagnostic accuracy. This procedure is completely safe, but only if you follow the rules and pay attention to established contraindications. When following the doctor's recommendations, any risks are completely excluded, regardless of how long the MRI lasts.
How often can an MRI be done? The frequency is dictated by the detected pathologies and the time frame of the prescribed therapy. In other words, magnetic resonance imaging of the abdominal cavity can be performed as many times as required, without the harmful radiation of x-rays.
What does it show
In the absence of pathologies, the homogeneous structure of all organs, their correct location, size, contours, and unobstructed blood flow will be visible. Otherwise, MRI will detect the following diseases and disorders:
- Change in the homogeneity of liver tissue, indicating hepatitis.
- An increase in the size of the liver, the appearance of nodes and seals confirming cirrhosis, hemangioma, malignant or benign tumors, metastases.
- Accumulation of fluids (abscess, cyst).
- Compaction of the walls and increase in the size of the gallbladder, congestion, deformation of the ducts, cholelithiasis.
- Pancreatitis, neoplasms in the pancreas.
- The presence of hidden bleeding in the spleen, hematoma, rupture of the membrane.
- Impaired intestinal patency, thickening of the walls, neoplasms and metastases.
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm, narrowing of the lumen, thrombosis. Sclerotic plaques.
- Enlargement and deformation of lymph nodes.
- The accumulation of fluid in the cavity is ascites.
Timely identification of pathologies and degenerative processes allows us to select the most effective therapy, plan surgical intervention, and increase the chances of defeating the disease.
What disorders can be detected using MRI?
The purpose of magnetic resonance imaging allows us to identify even very complex disorders and pathologies that have appeared in the patient’s body. In particular, we are talking about such types of diseases and disorders as:
- benign and malignant neoplasms, including cysts and metastases;
- pathological disorders in the development of internal organs that are congenital in nature;
- the presence of foreign bodies in the body, in particular stones in the bile ducts;
- deformation of organs as a result of injury, scar formation;
- suspected internal bleeding;
- accumulation of fluid, swelling;
- pathological disorders in the functioning of blood vessels, thrombosis and aneurysm;
- ischemia;
- pancreatitis, liver cirrhosis, fatty degeneration.
All types of disorders cannot be identified during a routine examination, or the results obtained will not be accurate enough to make a diagnosis.
MRI results are transmitted to the patient in the form of a report on paper and in the form of photographs.
What's the difference with and without contrast?
To obtain the most informative clinical picture of the condition of the abdominal organs, the doctor may prescribe a contrast-enhanced MRI scan. When diagnosing pathologies of the digestive tract, the contrast agent is administered orally, in other cases - intravenously.
Advantages of MR imaging with contrast:
- The components of the substance are independently transported throughout the body thanks to the circulatory system and reach maximum concentration at the site of pathology.
- Under the influence of a magnetic field and a contrast agent, the affected tissues appear highlighted in the image. This allows you to determine the location, size and shape of the tumor, the presence of metastases and the vector of their spread.
The paramagnetic components of the intensifying solution are non-toxic; they do not contain iodine, so they extremely rarely provoke an allergic reaction. However, there are contraindications for their use:
- Acute and/or chronic renal failure.
- Predisposition to allergic reactions.
- Increased sensitivity of the body to contrast components.
- Liver failure.
- Pregnancy.
- Breast-feeding.
The MRI imaging enhancement drug is excreted from the body through the kidneys, placing increased stress on the organ. If the patient has kidney problems, contrast should be used with caution and in small doses.
Decoding the results
The decryption process usually lasts several hours, but in complex cases it can take 2-3 days.
The following indicators are considered normal:
- no signs of inflammation or infection;
- the abdominal organs are located correctly and are of normal size;
- blood vessels function clearly and have no abnormalities;
- no tumor formations were detected;
- the ureters and internal ducts are free from plugs and blockages;
- there are no aneurysms, abnormal fluid collections or bleeding;
When studying with contrast, the duration of the study will be longer.
Deviations occur when the decoding can show:
- the size or location of the organ being examined is abnormal;
- traces of scars or injuries were found;
- tumor formations are present - regardless of their nature;
- infectious processes are present;
- excess fluid is detected - a sign of internal bleeding or infection;
- the walls of the vessels are affected by the aneurysm;
- there is blockage or narrowing of blood vessels;
- plugs in the bile ducts, blockages in the ureters, indicating the presence of neoplasms, or inflammatory and infectious manifestations.
CT or MRI, which is better?
CT and MR scanning are based on different diagnostic processes. For a more correct comparison of methods, the following factors must be taken into account:
1. Device capabilities.
A computed tomograph is best at visualizing bone tissue, while the strength of a magnetic resonance imaging machine is the construction of accurate projections of soft tissue. However, some experts recommend examining the lungs using a CT scan, since the organ has great mobility and may appear blurry on the MR image.
In some situations, it is optimal to use both methods to compile a complete clinical picture of the pathology.
2. Comfort.
The CT machine does not limit space, while examination with a closed-type tomograph is carried out in a special capsule. For patients with claustrophobia and other anxiety disorders, an MRI is more difficult to undergo than a CT scan.
3. Duration of the procedure.
For a CT examination, the installation requires 1-2 minutes. MRI diagnostics requires the patient to remain motionless for 15 to 60 minutes. The exact time depends on the complexity and purpose of the examination, and the power of the tomograph.
4. Harmfulness
. The magnetic resonance effect used in the operation of an MRI scanner does not have a harsh effect on the body, so MRI is not limited by the number of procedures. Excessive exposure to X-ray radiation, which is used to create CT projections, leads to adverse consequences for the body. If we consider that once a year a person undergoes basic fluorography and/or mammography, then computed tomography is recommended to be used for diagnosing pathologies no more than once a year.
| MRI image of the abdominal cavity | CT image of the abdomen |
| Three-dimensional visualization of the abdominal cavity |
What does an abdominal MRI show?
A traditional closed-type tomograph looks like a large cylindrical tube surrounded by a magnet. During the procedure, the patient lies on a table that moves towards the magnet. In open-type devices, the magnet is open on the sides.
Diagnostics using open tomographs (they are mostly low-field) are carried out for patients with claustrophobia or obesity. There are more modern open-type machines with a high field (1 Tesla or more), with which you can get high-quality images, while open MRI models with a low magnetic field produce lower-quality images.
For abdominal MRI, the coil is placed on the patient's abdomen. If necessary, the doctor prescribes glucagon to reduce motility. The patient should lie on his back and not move for 30 to 45 minutes. When diagnosing with a contrast agent, the duration of the procedure increases.
Magnetic resonance imaging does not cause pain, but some patients feel warmth in the abdomen (this is how tissue reacts to the magnetic field). During the procedure, the patient is alone in the machine, but the radiologist maintains an audio connection with him.
A qualified specialist interprets the research results. The patient receives a medical report printed on paper and photographs. If the client wishes, images can be recorded on a flash card or disk, sent by email or to a personal account on the diagnostic center website.
Testing can detect the following pathologies:
- Congenital defects of organ structure;
- Diseases that are accompanied by an inflammatory process, obstruction (obstruction), the appearance of a cyst;
- Benign and malignant tumors (with identification of the stage of disease development), metastases (secondary tumor foci);
- Circulatory disorders.
After an MRI, the patient does not need time to adapt.
X-ray or MRI, which is better?
X-ray and MRI are two completely different diagnostic methods. Each of them has its own advantages and weaknesses. To make an objective comparison, the following aspects must be taken into account:
1. The principle of operation of the devices.
The MRI device performs layer-by-layer scanning of body tissues using the magnetic resonance effect. An x-ray machine uses x-rays to scan the body at once.
2. Visualization quality.
On an MRI image, you can see clear structures of soft and bone tissues, lymph nodes and blood flow; the high resolution of the image allows you to determine the slightest abnormalities. The x-ray shows the densest bone tissue. A survey radiograph is not advisable to use to search for pathologies of the abdominal organs, since it can display signs of a fully formed disorder.
3. Availability of the procedure
. X-rays can be taken at the clinic at the place of registration or attachment, and MRI is available only to patients in hospitals and commercial clinics.
4. Price
. X-ray examination is included in the general health insurance program and is available for free diagnosis. Prices for x-rays in commercial medical institutions are 3 times lower than for MRI scans.
5. Harmfulness.
MRI has no restrictions on the frequency of procedures. X-rays are recommended to be taken no more than once a year.
| Abdominal MRI | X-ray |
MRI with contrast
In some cases, the gastroenterologist prescribes an MRI scan of the abdominal cavity with contrast. This is necessary when serious illnesses are suspected, when an accurate diagnosis is simply indispensable. A similar study is prescribed for neoplasms of internal organs to determine the type of tumor. MRI with contrast can detect metastases in the abdomen in order to perform surgery or simply for diagnosis.
Tomography with contrast costs 2 times more than a standard study. The duration of the procedure also increases. This is due to the fact that first a normal image is taken for 30 minutes, then a contrast solution is injected into the venous vessel. After some time, magnetic resonance imaging with contrast is performed, which lasts from 20 to 30 minutes.
After receiving the second image, the doctor compares the data and gives the patient a report. In general, the study lasts from 60 to 90 minutes.
Contrast agents are iodine- or bromine-based drugs that are administered intravenously before magnetic resonance imaging. They are not toxic.
Most often, MRI with contrast is performed to diagnose neoplasms, namely tumors. This can be explained by the fact that they absorb contrast well. With the help of such a study, it is possible to accurately determine the location, size, clear boundaries, and composition of tumor cells.
Contrasting makes it possible to determine the structure of pathological tissues. Contrast is also necessary for vascular pathologies. For example, it is often done for cerebral strokes and aneurysms. Since it is possible to accurately determine the site of hemorrhage.
Areas where there are many blood vessels are especially visible, since the contrast enters the tissue through the blood.
There are two ways to undergo an examination of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space using a tomograph: with or without contrast. In a conventional MRI procedure, magnetic waves of different lengths are used, which, when reacting with hydrogen atoms, provide transillumination of the body. To carry it out, a tomograph is required - a device where the subject is placed. The result is a three-dimensional picture of organs, tissues and individual structures with their location.
MRI of the abdominal cavity is a safe examination technique that is painless. Also, its advantage over similar examinations such as CT OB or fluorography is the absence of radiation exposure.
If it is necessary to study a particular organ in more detail and obtain a high-quality image, contrast is used. It is based on the use of intravenous jet injection of contrast, which is an iodine solution, for example, the drugs Visipak, Omnipaque, or a medical solution of the heavy metal gadolinium.
Ultrasound or MRI, which is better?
Ultrasound diagnostics and magnetic resonance imaging are the safest and most informative examination methods. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages. To understand which method is most suitable for you, you need to analyze the following factors:
1. Operating principle of the equipment
. The ultrasound machine receives information by processing the reflected signals of ultrasonic waves; it is able to display the formed pathologies. The MRI scanner examines the body layer by layer, converting hydrogen vibrations under the influence of a magnetic field, and builds an image of soft and bone tissues; the processor is able to detect disorders at an early stage.
2. Image quality and technical capabilities of the devices.
To construct an MR projection of the abdominal organs, the signals are processed by a processor, after which the specialist draws up a research protocol. The information content and reliability of an ultrasound examination depends on the experience and skills of the doctor, since a person is responsible for interpreting the data. MRI images have high resolution and detail, which reduces errors in interpretation.
3. Duration of the procedure.
An ultrasound scan takes no more than 5 minutes, but for a full MRI scan the patient needs to lie still for 15 minutes or more.
4. Availability.
MR equipment is currently the privilege of large regional medical institutions and commercial clinics, while an ultrasound machine is available in every clinic. Therefore, getting an ultrasound examination is much easier.
5. Price.
Ultrasound diagnostics is included in the list of services provided free of charge under the compulsory medical insurance or voluntary medical insurance program. Free MRI is provided for patients in hospitals and surgical departments. If you need to undergo examination through paid services, ultrasound will be 2-3 times cheaper than tomography.
| Abdominal MRI | Ultrasound |
How research is done
The opportunity to undergo an MRI examination is available in any modern clinic in the metropolis. This is an accessible but relatively expensive procedure. The device itself is an almost completely closed cylindrical chamber, which consists of a movable table of the diagnostic capsule itself. People with various forms of claustrophobia may be examined in an open MRI capsule; in some clinics it is allowed to invite a loved one with them.
At the beginning of the examination, you need to lie down on the table, after which the specialist will fix your arms and head so that involuntary actions do not occur. This is necessary because after starting the device you need to lie still. During operation, the device takes a large number of pictures, which are then combined into one whole 3D image using a special program.
From time to time you may have to hold your breath for a short time. How long does an MRI take? It depends on the goal set for the medical staff. If one organ is checked, it takes 5-10 minutes; if the abdominal cavity is examined completely, you need to prepare for a procedure lasting 30 minutes or more.
After the examination, with or without a contrast agent, the result takes approximately two to three hours to prepare. With a more serious and extensive examination, if an MRI of the abdominal cavity is performed with contrast, the conclusion will be ready only the next day. The results obtained will need to be shown to the attending physician, who will prescribe subsequent treatment with medications.
MRI of the abdomen with contrast agent
If the doctor has prescribed an MRI of the abdominal cavity with contrast, before the examination begins, a special medication will be injected into the vein, acting as a dye. It accumulates in the cavity of the organ being examined and provides detailed information about the disease.
To kid
MRI of the abdominal cavity is a safe and informative examination method, and therefore has no age restrictions. However, one should take into account the fact that it is very difficult for a child to remain motionless for a long time. The doctor may suggest testing under anesthesia.
The second unpleasant factor for a child is being in a closed capsule for scanning. In this case, it is worth looking for a clinic with an open-type tomograph. The parent can be in the baby's field of vision and even hold his hand.
Contraindications for MRI
In some cases, an MRI procedure is contraindicated. In particular, it is not carried out if:
- the patient’s body contains foreign bodies (bullets, fragments, ferroalloy metals), as well as electronic systems, for example, a pacemaker;
- in the first two trimesters of pregnancy and lactation;
- if the patient is claustrophobic. Although the problem can be solved with the help of sedative medications or painkillers. By the way, today some clinics are equipped with open-type tomographs and the problem disappears by itself;
- when the patient’s body weight exceeds 130 kg;
- when it is necessary to use a contrast agent - with high sensitivity to it;
- the patient suffers from mental disorders.
As a rule, MRI is not prescribed for children under 6 years of age, since at this age it is difficult to remain motionless for a long time. An exception is made in cases where MRI remains the only option to clarify the clinical picture. In this case, the procedure is carried out after the child has been given anesthesia, and the use of a contrast agent is strictly prohibited.
Although a strong magnetic field is not harmful in itself, implanted medical devices that contain metal may become damaged or malfunction.
Photo
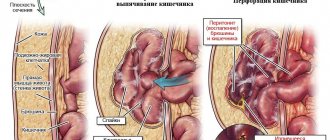
| Bowel tumor on MRI |
| Right-sided nephroptosis |
| Pancreatic head cancer |
| Colon carcinoid cancer |
| Adhesive obstruction of the small intestine |
Price
Most of the clinics in our catalog indicate the cost of MRI of the abdominal organs, so site users have the opportunity to choose a medical institution according to their capabilities.
To view prices, you need to go to the list of medical institutions in your city.
- Open the website section Clinic Addresses.
- Select your locality.
- We get into the directory of clinics in your city.
- We indicate the name of the procedure in the search filter in the Study area field.
- The program automatically sorts the list of diagnostic centers in ascending order of price.
| List of clinics filtered by MRI of the brain using the example of the city of Moscow |
You should take a little time and call clinics that do not have a price list published on their page. It may happen that in one of them the cost of abdominal examination will be an order of magnitude lower. When communicating with the administrator, do not hesitate to ask the administrator for information about current promotions and discounts. To attract clients, some clinics hold promotions for comprehensive examinations or discounts on MRIs at night.
Every person has the right to undergo a free MRI once a year. To do this, you need to check with your insurance company which medical institution has an agreement with them to provide MRI under the compulsory medical insurance or voluntary medical insurance policy. After which you need to issue a referral from your local doctor or specialized specialist.
Reviews
To simplify the choice of a clinic for abdominal MRI, we publish patient comments about the quality of the services provided by the medical institution.
To access reviews, you need to go to the list of diagnostic centers in your city.
In the window of brief information about the clinic there is a button to go to reviews and their number is indicated.
| Reviews button |
If there are no comments, the button will be called Your Review. To publish your opinion about the clinic, staff, and the quality of the examination, follow this button and fill out the comment field.
| Your review button |