Impaired digestion is a common occurrence in humans. The disease occurs due to the frantic pace of life, poor nutrition and lack of exercise. Most often, people complain of heartburn, a feeling of heaviness, bloating, and increased gas formation. If symptoms are present, the specialist will prescribe an ultrasound examination of the gallbladder. The visual inspection of the bladder on the device depends on how well the patient prepares for the procedure. Even a specialist with extensive experience will have difficulty examining the bubble due to excess gas formation. Therefore, it is important to know how to prepare for an ultrasound of the gallbladder. Preparation measures should begin 7 days before the specified time.
It is necessary to properly prepare for an ultrasound scan of the gallbladder.
Anatomy
The gallbladder consists of a fundus, body and neck. In adults it is usually pear-shaped, and in children it is often spindle-shaped. The wall consists of several layers:
- Mucous. Thanks to it, the inner surface of the organ is folded.
- Muscular. The layer is formed by spirally arranged smooth muscle cells.
- Serous. It is a thin connective tissue membrane covering the abdominal organs.
The cervix passes into the cystic duct, which goes into the common bile duct. It flows into the duodenum. The role of the muscular “valve” that regulates the flow of bile into the intestine is played by the sphincter of Oddi. During eating, the gallbladder contracts and the sphincter of Oddi relaxes. Thanks to this, bile enters the duodenum. During an ultrasound, you can evaluate the structure of the gallbladder and its functional ability.
What pathologies can be identified during an ultrasound examination?
With high-quality preparation of the organ, ultrasound diagnostics will provide the specialist with almost all the necessary materials for making a diagnosis and prescribing appropriate therapy. So, the examination reveals:
- cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) – acute and chronic form;
- cholelithiasis (formation of stones and sand);
- dyskinesia (impaired motor-evacuation function);
- neoplasms (polyps, cysts, tumors);
- congenital developmental anomalies.
The high information content of the method will save patients from the need to undergo other methods of examination. In addition, the absolute harmlessness of the procedure allows you to resort to it to monitor the prescribed therapy and the postoperative period as many times as necessary, without worrying about side effects.
Scientific editor: M. Merkusheva, PSPbSMU named after. acad. Pavlova, medical practice. August, 2020.
Ultrasound examination of the gallbladder is a non-invasive diagnostic method that allows you to obtain accurate information about the condition of both the organ itself and its ducts. Typically, ultrasound of the gallbladder is performed as part of a comprehensive examination of the abdominal organs and is most often combined with ultrasound of the liver.
When is it held?
There are several groups of indications for ultrasound examination. The first is a diagnostic search for the suspected disease, the second is dynamic observation of the detected deviation during treatment. As a rule, the gallbladder is not examined separately, but together with other parts of the biliary system, for example, the liver. The reasons for performing an ultrasound are:
- Pain in the stomach, right hypochondrium. Especially if the complaint is related to the consumption of fried, fatty, spicy foods.
- Signs of bile metabolism disorders. Yellowness of the sclera, skin, itching, increased bilirubin levels.
- Acute/chronic cholecystitis, cholelithiasis. Confirmation of the diagnosis, evaluation of the results of treatment. Search for complications.
- Tumor diseases. Including benign neoplasms of the gallbladder, ducts, pancreas, and duodenal papilla.
- Study of gallbladder motility. If biliary dyskinesia is suspected.
- Developmental defects. For example, abnormalities in the shape of the gallbladder.
The indicated list of indications is general. The individual reasons for performing an ultrasound of the gallbladder are determined by the attending physician.
What diseases does ultrasound detect?
What does the examination show? Ultrasound detects diseases:
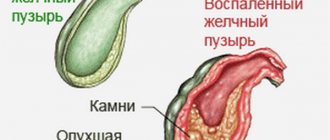
- The most common pathology is cholecystitis. The scan reveals an enlarged bladder with thickened walls. The cavity contains bubble inclusions and partitions. The contours of the light-colored walls are not clearly visible on the monitor screen. In a chronic process, the organ decreases in size and becomes deformed.
- Cholelithiasis is a gallstone disease. Ultrasound identifies stones in the bladder and ducts. When the body position changes, they shift. The walls of the organ are thickened with uneven edges. A sign of small stones on ultrasound is an expansion of the duct above the blockage. Stones are more often found in women than in men.
Cholelithiasis
- Dyskinesia of the biliary tract is manifested during scanning by increased tone and thickening of the walls of the bladder. A bend in the neck is detected.
- The tumor is visualized as a mass. The walls of the deformed bladder are thickened.
- Polyps appear on the monitor as round formations. A size greater than 1 cm requires dynamic monitoring, as there is a risk of a malignant process.
- Congenital pathology – double gallbladder or diverticulum.
The study of this part of the liver is carried out at the gastroenterology center. It is better to combine the procedure in combination with all digestive organs.
Before the study
Preparation for an ultrasound of the gallbladder is based on several principles. Namely:
- The study is performed on an empty stomach. You should refrain from eating for 8-10 hours. Infants undergo an ultrasound scan before the next feeding.
- 2-3 days before the ultrasound, limit foods containing large amounts of fiber. Exclude from the diet: raw vegetables and fruits, black bread, and any dairy products. Dishes from legumes and alcoholic drinks are prohibited. This is necessary to reduce gas formation in the intestinal loops, which worsens the echo signal.
- Pre-medication if necessary. If the diet fails to reduce gas formation on your own, 3 days before the ultrasound, carminative drugs (Espumizan) and sorbents (activated carbon) are prescribed. Additionally, enzyme preparations are used that improve food digestion (for example, Mezim).
Sometimes a cleansing enema is additionally required. In emergency situations, for example, with biliary colic, ultrasound is performed without these preliminary measures.
Important! How to prepare for an ultrasound scan of the gallbladder for insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus? Such patients are prone to hypoglycemia, so they are allowed to eat unsweetened tea and dried white bread.
Can I eat and drink on the day of the procedure?
Ultrasound is done on an empty stomach. If the diagnostic test is carried out after 15:00, health workers allow a light breakfast. Doctors allow people with diabetes to drink sweetened tea with crackers. Your appointment should be no later than 6-8 hours before the start of the ultrasound.
If diagnostic tests have already been carried out the day before, for example, a colonoscopy or other procedures on the organs of the digestive system, you must inform your doctor about this. If these diagnostic methods are used one after another, the ultrasound results may be unreliable.
How is an ultrasound of the gallbladder done?
The study is carried out in several positions: lying on the back, then on the left side. If necessary, ultrasound is performed while sitting or standing. The sensor is installed under the right costal arch along the midclavicular line. To improve sound conductivity, a special gel is applied. The resulting ECHO image is projected onto the monitor.
Norms for adults
The structure of the gallbladder and ducts is assessed. Indicators that are recorded normally when examining the gallbladder:
- Form. Usually it is pear-shaped, ovoid (ovoid), cylindrical.
- Magnitude. In an adult, the size of the gallbladder varies from 6 to 9.5 cm in length. The average width of the organ is 3-3.5 cm.
- Wall thickness. Does not exceed 2 mm. With age, it thickens due to the proliferation of connective tissue in the mucous and muscle layers. This is most clearly observed in patients over 60 years of age.
- Location. It must be intrahepatic. Only the bottom of the gallbladder protrudes beyond the liver (1-1.5 cm).
- Circuit. Smooth, clear.
- Content. A healthy bladder should contain only homogeneous bile. Like any liquid, it does not reflect ultrasound, that is, it is anechoic. Therefore, the anechoic contents of the gallbladder are a sign of normality.
Norms for children
The size and shape of the gallbladder directly depend on the age of growth of the child. In young children, the organ resembles a spindle. Starting from six months, the gallbladder begins to take on a pear-shaped shape, close to that of an adult. The smallest size of the organ is observed in children 2-5 years old: the length is approximately 50.5+/-1.5 mm and the width is 17 mm.
Functional tests
They are used to determine the motor-evacuation activity of the organ. To assess contractility, an ultrasound of the gallbladder is performed under load. This is the main way to diagnose biliary dyskinesia.
First, an ultrasound scan of the gallbladder is performed on an empty stomach. After this, the patient is given 2 egg yolks. Every 5-10 minutes, ultrasound is repeated, observing the characteristics of emptying and relaxation of the gallbladder. If dyskinesia is absent, the organ contracts by 50-70% by the 45th minute of the study. To assess the entire cycle, 1.5-2 hours are required, but more often they are limited to assessing the diameter of the gallbladder by the 45th minute.
Decoding the results
The sonologist evaluates the following parameters of the object under study:
- location, mobility;
- shape, dimensions, wall thickness;
- diametric characteristics of the lumen of the bile ducts;
- the presence of stones, pathological formations;
- contractile functionality.
Based on a comparison of the obtained figures with the normative ones, a diagnosis is made. Here are the signs of common diseases of the biliary system:
- acute cholecystitis - enlargement of the object, thickening of the walls (delta - more than 4 cm), multiple partitions, intensified blood flow;
- chronic cholecystitis - compression and blurring of the outlines of the organ, deformation, thickening of the walls, numerous inclusions;
- dyskinesia – bending, thickening and tightness of the walls;
- cholelithiasis (cholelithiasis) – visualization of stones (they look like light structures with echo shadows), bilirubin crystals, thickened walls, uneven outlines;
- polyp - atypical formations on the walls; differentiated diagnosis is necessary to exclude the malignant nature of the cells;
- tumor - a deformed contour of the gallbladder, significant thickening of the walls, a formation measuring 1 centimeter or more.
An ultrasound machine detects a double gallbladder, agenesis (its absence), diverticula (bulging of the walls) and the ectopic position of the organ (at the junction of the right lobe of the liver with the diaphragm).
Table of normal values for adults
Normally, in adults, the format of the gallbladder corresponds to the following parameters.
| Index | Meaning |
| Length | 70-95 mm |
| Width | 35-55 mm |
| Cross section | 30-35 mm |
| Volume | 40-70 cm3 |
| Wall thickness | less than 4 mm |
| Diametrical section of the common duct | 6-8 mm |
| Diametrical section of the lobar ducts | less than 3 mm |
| Form | oval or pear-shaped |
| Outlines | clear |
| Protrusion of the fundus beyond the lower edge of the liver | 10-15 mm |
If a patient, due to his health condition, is prescribed an ultrasound to determine the function, then the length, volume and other parameters of the studied object are compared without applying a load and with it. If all is well, after taking choleretic products, the volume of the organ decreases by approximately 40-60%.
Possible deviations
Indicators that differ from the standard ones help to suspect the presence of pathology. The shape and size of the gallbladder may change. If there are deviations during a functional test, the type of biliary dyskinesia is determined.
Increase in size
This is often observed with cholecystitis. The bladder may be enlarged due to thickening of its walls against the background of inflammatory edema. A change in size is observed when there is a violation of the excretion of bile: the organ cannot empty itself normally, so it begins to stretch (due to impaired contractility, the presence of a mechanical obstacle).
Enlargement of the gallbladder is possible with tumor diseases, when the tumor grows into the wall of the organ. A rare but dangerous pathology is gallbladder carcinoma. More often it is diagnosed in women. In 75% of cases it is combined with cholelithiasis. The greatest risk of occurrence is in patients with a “porcelain” (calcified) gallbladder.
Downsizing
A change in this indicator does not always indicate pathology. In a healthy person, the size of the gallbladder will be reduced if he has eaten before the test. In this case, ultrasound loses its information content.
A rare cause of size anomaly is hypoplasia (underdevelopment) of the gallbladder. Such an organ can function, but its shadow on the echogram is sharply reduced.
Gallstone disease can lead to a shrinkage of the gallbladder. This happens in severe cases, when stones interfere with the normal functioning of the organ so strongly and for a long time that it gradually atrophies.
Echoic inclusions
They often mean gallstones. They look like dense hyperechoic formations (white on the monitor) with an ultrasound shadow. Sensors can detect stones ranging in size from 1-2 mm. The size of the stones on ultrasound does not correspond to reality: on the screen they look somewhat larger.
Gallbladder polyps will also appear as echogenic lesions. To distinguish them from stones, the patient is asked to change his body position. The polyps will remain in place, but the stones will move.
Changing shape
Configuration changes can be congenital or acquired. For example, ultrasound often reveals an S-shaped gallbladder. When inflected between the bottom and the body, the organ takes the shape of a Phrygian cap.
Kinks of the gallbladder are common in young children. For them, this is not always an indicator of pathology. The kinks can be temporary, functional in nature and often disappear with age without a trace, without causing complications.
Indications for liver ultrasound
Indications for prescribing such an examination are the patient’s complaints:
- pain in the right abdomen;
- feeling of fullness in the stomach;
- unhealthy complexion – yellowness of the skin;
- bitterness in the mouth.
The specialist also recommends an ultrasound scan after collecting the patient’s medical history. So, ultrasound is indicated if:
- a person eats incorrectly: abuses fatty, spicy, smoked, fried foods;
- the patient is addicted to low-calorie diets;
- does not follow the eating schedule (eats 1-2 times a day);
- the patient takes certain medications for a long time;
- the person has injuries in the abdominal cavity;
- the patient has general intoxication of the body with drugs, alcohol, etc.;
- it is necessary to monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
Lab tests
A long-established practice involves initial mandatory studies of biological material, which are not very informative in certain areas of therapy and surgery, but give an idea of the condition of the patient’s body and the presence of pathological changes in the body. This is the first signal received in the form of indicators about the need for medical intervention.
- A CBC (complete blood count) can be taken from a finger or from a vein. Sometimes this is done in parallel to compare the contents of capillary and venous vessels. In them, ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) and leukocyte level are important, indicating the presence of inflammation, but not the reason for its development. The biomaterial is collected by a laboratory assistant or nurse, and the analysis is interpreted by the attending physician.
- Blood biochemistry is a more informative study, during which you can obtain data on the functioning of the liver, the main neighbor of the gallbladder. The activity of the natural reservoir for collecting produced bile largely depends on well-being. In gallbladder diseases, the presence of bilirubin, cholesterol and the level of liver transaminases are important. Data may indicate cholestasis, inflammation, destruction of hepatocytes and disruption of the synthesis of bile secretions, disruption of bile outflow or blockage of passages for its excretion into the digestive system.
- The liver test consists of a diagnostic triad - a coagulogram, indicators of the level of blood clotting, a general urine test to detect protein and LHC. A patient without a medical education will not be able to independently decipher liver test parameters - this requires special knowledge, the ability to draw conclusions from reference values and those present in the patient’s analysis, as well as practical experience. For example, an increase in aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels means an inflammatory process in the bladder or a disruption of the liver parenchyma. In this case, the basis for the conclusions is found in the results obtained by other methods of diagnosing the gallbladder.
- Analysis of feces and urine allows us to identify the fact of a violation of bilirubin metabolism and inflammatory processes. Stool is examined under a microscope to determine the presence of bleeding in the digestive system or to confirm the presence of parasitic infestation.
- Analysis of bile secretion is carried out using the collection of duodenal contents. It also contains secretions of the liver and pancreas, gastric juice and particles of the contents of the duodenum. Any of the components can be examined if necessary.
A laboratory technician has a limited period of time to study bile, because it contains fractions that quickly dissolve under the influence of aggressive gastric enzymes. Hence the need to use several methods. Bile analysis is an important and informative part of laboratory methods for diagnosing the ducts and the gallbladder itself, giving an idea of its functioning in a physiological or pathological state.
Ultrasound diagnostics of the biliary tract with identification of function
Another name for the diagnostic method is ultrasound with a choleretic breakfast or dynamic cholescintigraphy.
This procedure allows you to determine what the contractile function of the gallbladder is in real time.
After the first procedure for diagnosing the biliary tract on an empty stomach, the patient must take a test breakfast of two boiled (or raw) yolks and 250 g of cottage cheese (or sour cream). You can also use a sorbitol solution as a choleretic breakfast.
After this, the ultrasound examination must be repeated at intervals of 5, 10 and 15 minutes.
Contraindications
Today, ultrasound of the liver and gallbladder has no absolute contraindications. In numerous studies, ultrasound has proven its safety for human health. Ultrasound of the gallbladder is not performed if there are open lesions on the skin in the area of the anterior abdominal wall, where the sensor must be placed.
Also, the method is not recommended in acute conditions when urgent medical attention is required.
Preparation for the procedure
It is very important for the patient to prepare for the scan in a certain way so that the resulting picture is more accurate for the doctor. During the procedure, there should be no gases in the patient’s abdominal cavity; they impede the passage of the ultrasound signal, cause its distortion, and then the results of the examination may give an unreliable picture. During preparation, it is very important to exclude from consumption foods that can cause flatulence. It is also recommended to take medications - enzymes (festal, mezim) and absorbents (charcoal, motilium) to reduce the formation of gases.
Preparations should begin a few days (3) before the scheduled ultrasound. Food that increases the formation of gases is excluded from the diet, light food is allowed to be eaten, not in large portions, but often, it is preferable to cook food in a double boiler or boiled, you should drink at least 1.5 liters of clean water without gas, but do not wash down the food. Alcohol is strictly prohibited, otherwise the results of the study may be unreliable.
On the day before the procedure, you do not need to eat meat/fish. The food should not be heavy, it is better to have dinner no later than 20:00, but fasting the day before is also contraindicated. The day before you need to cleanse the intestines, if this does not happen naturally, then drink a mild laxative, but no later than 16:00, you can also do an enema.
If the examination takes place in the morning, you will have to skip breakfast and drinking is also undesirable. If the examination is carried out in the second part of the day, then a small breakfast is possible, for example, tea plus a cracker, after which there should be an interval of at least 6 hours. In a couple of hours you can take charcoal or its equivalent.
Attention! Before the ultrasound procedure, it is forbidden to drink antispasmodics, smoke, chew gum or suck hard candies.
Permitted and desirable products include:
- lean beef, fish, chicken, turkey;
- porridge - oatmeal or buckwheat in water without oil;
- soft-boiled or hard-boiled eggs, maximum 1 piece per day;
- low-fat cheese and low-fat cottage cheese.
Undesirable products include:
- all legumes;
- fermented milk products;
- sweet;
- yeast bread products;
- raw vegetables/fruits;
- non-lean meat/fish;
- caffeinated drinks;
- any soda.
Children under 15 years of age do not need to follow the diet. Infants under one year of age may be fed once before the scan. Children under 3 years old should not be fed 4 hours before an ultrasound, and older children can wait 6-8 hours.
Important! An hour before the procedure, you should not drink anything, then the gallbladder will be completely filled with bile and will take on the desired size, and if you drink even a little liquid, the bladder will shrink, which will complicate the diagnosis.