A standard examination of the rectum allows us to identify many diseases and pathological processes in the early stages of their development. Modern medicine has many ways to check the condition of the intestines. The most common techniques are colonoscopy, anoscopy and sigmoidoscopy. The method is selected according to the patient’s complaints and the results of the preliminary examination.
An intestinal examination should be carried out systematically, at least once a year. This will make it possible to recognize pathological processes in the early stages of their appearance and begin comprehensive elimination. Otherwise, the development of serious diseases, in particular oncology, is possible.
How to check the intestines in the hospital
A detailed examination is prescribed after identifying the main symptom, namely occult blood in the stool.
Analyzes
Laboratory diagnostics include:
- General analysis of capillary blood taken on an empty stomach. Allows you to detect an inflammatory process in the intestine, a violation of its absorption function, disorders, helminthiasis, bleeding, and neoplasms. These diseases are characterized by low hemoglobin levels and high ESR levels.
- Biochemical analysis requires venous blood. With its help, urea, C-reactive and total protein are detected, which are used to determine helminthic infestations, acute infections, cancer, and bleeding.
- A study on tumor markers, which are judged by the decay particles of degenerated cells. Exceeding the norm does not always indicate a malignant neoplasm. The preliminary diagnosis is confirmed or refuted by additional research.
- A general urine test reveals dehydration and impaired absorption. The biomaterial is collected in the morning.
- Coprogram. This is the name for examining stool for intestinal diseases and the presence of parasites. 2 days before analysis, exclude tomatoes, beets and other foods containing pigments from the diet.
- Hidden blood is determined by its traces in the stool, for example, using a fecal immunochemical test performed at home.
- Determination of pathological microbes for suspected acute or chronic infections. Using a special loop, the doctor takes a smear from the rectum for further cultivation of bacteria. Microscopic examination allows us to identify the type of pathogenic microorganisms and their sensitivity to various antibiotics in order to select the most effective therapy.
- Analysis for dysbiosis is carried out using stool culture for flora and counting the number of coli-, lacto- and bifidobacteria, as well as hydrogen and other tests.
Palpation
A method for checking the condition of the abdominal organs, the presence of seals, and the degree of pain.
Initially, indicative palpation is performed to determine body temperature and muscle tone. The norm is considered to be a condition when there is no pain when palpated, the organs are mobile, and the abdominal cavity is soft. Muscle tension shows the location of the disease.
The method is used to study the anal canal. It is carried out with the index finger using an anesthetic ointment according to strictly prescribed rules and examination procedures. In 90% of cases, an accurate diagnosis can be made.
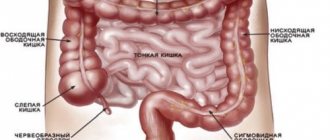
Colonoscopy
An instrumental diagnostic method that can be used to check any part of the large intestine. For this purpose, a device equipped with a miniature video camera is used, which is inserted through the anus. When examining the internal walls of the lower parts of the digestive canal up to the appendix, inflammation, ulcerations, tumors or polyposis are revealed.
New models of endoscopes provide sampling of a tissue fragment for more thorough examination and removal of small formations. Previously, such actions were performed only during the operation.
Preparation for a colonoscopy includes a 3-day diet and taking laxatives on the eve of the procedure. Sometimes it is performed under anesthesia. The pain depends on the level of medical equipment and the qualifications of doctors.
Irrigoscopy
The intestines can be examined without a colonoscopy using a number of techniques, including a non-traumatic X-ray method using barium sulfate. Compared to CT (computed tomography), it is more gentle in terms of radiation exposure. Contrast is administered by enema or orally. On the monitor you can see the nature of the folds of the intestinal wall, study cicatricial narrowings and congenital defects in the development of the digestive canal.
The darkened areas reveal:
- polyps;
- neoplasms;
- diverticula;
- foreign bodies.
The method is indicated if colonoscopy is impossible or its results are in doubt.
The duration of the procedure is 15-45 minutes. Correct execution eliminates complications. Carrying out irrigoscopy is possible both in a specialized center, clinic, and in a hospital, equipped with appropriate equipment and supported by the skill of a radiologist.
Sigmoidoscopy
A painless diagnostic method that allows you to check a section of the large intestine 30 cm long from the anus. Before the manipulation, a digital examination of the anus is performed to identify contraindications, which include:
- acute form of hemorrhoids;
- anal fissures;
- inflammation in the lower parts of the digestive canal.
Checking the intestines begins with assessing the condition of the mucous membrane, its color, the presence of erosions and ulcerations, swelling, the severity of folds in the walls of the anus and rectum.
A safe diagnostic measure that allows you to examine the intestines for diseases, including in pregnant women and children. It is carried out through the abdominal wall or rectally using a catheter inserted into the rectum.
The second method helps in diagnosing complex neoplasms on the outer layer of the anal canal, “invisible” during colonoscopy. It is performed with a full bladder, which pushes back the loops of the small intestine.
A special diet, enemas, and taking the drug “Fortrans” cleanse the intestines, including gases that interfere with the study. A special liquid is used as a contrast.
The study requires a capsule with a video camera, which is swallowed by the patient. Information is recorded on a special medium. After analyzing it, the doctor selects a treatment regimen. Preparation consists of following a diet and fasting on the eve of the procedure. The price of the procedure can reach 30,000 rubles.
A diagnostic method used in various fields of medicine, including gastroenterology. When examining the digestive canal, MRI is an auxiliary procedure, since problems arise with visualizing the layered loops of the large intestine. The test is painless and does not require special preparation.
Detection of an inflammatory or malignant process using MRI is not a basis for making a diagnosis. A colonoscopy will be required to examine every centimeter of the mucous membrane with the possibility of biopsy and therapeutic measures:
- Cauterization of damaged vessels.
- Elimination of intestinal volvulus.
- Removal of polyps.
The method is not very informative at the initial stage of the disease. But when examining seriously ill patients and pregnant women, it is the only one available.
The abbreviated name is FGDS. It is a progressive and highly informative method of instrumental diagnostics. Provides visualization of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum, performing pH measurements, administering medications, stopping bleeding, removing polyps, collecting biomaterial for microscopic examination and detection of Helicobacter pillory.
On the eve of the procedure, which lasts 5-10 minutes, careful preparation is carried out. It can be done under local anesthesia with lidocaine, which relieves discomfort in the pharynx area.
FGDS is indicated for all adults after 40 years of age in order to be checked at an early stage for oncological degeneration of the digestive canal organs.
The arsenal of intestinal research methods is wide. Accurate, timely diagnosis is a condition for successful recovery.
Rectoscopy
Rectoscopy (rectaromanoscopy) allows you to assess the condition of the rectum and sigmoid colon. The depth of the examination is 15–20 cm. The examination is carried out in the knee-elbow position. The patient is introduced into the rectoscope into the anus and moves along the lumen to 5-7 cm in depth. The end of the rectoscope has a light that allows you to examine the tissue and surface of the intestine. Indications for rectoscopy are suspicions of tumors, painful urge to defecate, blood in the stool and identifying the causes of stool disorders.
Bowel sigmoidoscopy procedure
https://youtu.be/-v14SKwFzqU
Alternative bowel examination methods
To diagnose pathologies of the large intestine, laboratory and instrumental research methods can be used:
- computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- plain radiography using contrast agents;
- Ultrasound of the intestines and abdominal organs;
- rectosigmoidoscopy;
- coprocytogram;
- bacteriological examination of stool.
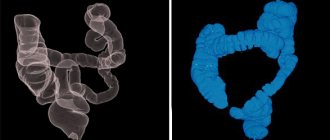
CT and MRI
With CT or MRI, layer-by-layer images of the entire intestine are obtained; tumors, diverticula or places of narrowing of the intestine are perfectly detected. In both cases, the patient is placed in a special device that scans the required organ or system. Sometimes, to obtain more information, the subject is given intravenous contrast.
Contrast radiography of the intestine allows you to “see” tumors, intestinal obstruction, diverticula, ulcers and structural abnormalities. To carry it out, the patient is asked to drink a special solution (barium suspension), after which, at certain intervals, photographs of the intestines are taken in a direct projection.
Ultrasound of the intestines
Ultrasound is an absolutely painless and harmless way to diagnose intestinal diseases such as diverticulitis, acute appendicitis, mesadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes) or intussusception. The study is carried out with an ultrasound sensor, which is applied to the abdomen, while the patient lies on his back.
We recommend reading:
Irrigoscopy and colonoscopy: which test is better?
The disadvantages of ultrasound in this area include relatively low information content and subjectivity.
Stool culture tank
Bacteriological examination of stool helps to detect the source of infection, if any, and the sensitivity of the isolated bacteria to antibiotics.
Coprocytogram
A coprocytogram shows the number of leukocytes, neutral fats, fiber and other dietary fibers in the stool. Based on the results of this analysis, one can judge the presence of inflammation in the intestines and pathology of the pancreas. A stool occult blood test is prescribed if internal bleeding emanating from the gastrointestinal tract is suspected.
Most analogues are harmless and painless for humans, do not require special preparation and are carried out in a hospital setting.
The following are distinguished:
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging);
- CT (computed tomography);
- Ultrasound;
- irrigoscopy;
- capsule examination;
- anoscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- PET positron emission tomography;
Replacing the procedure helps not only to facilitate the inspection process itself, but also to identify more serious lesions and obtain detailed inspection results.
MRI is a full-fledged alternative to colonoscopy, but the cost is several times higher. This option is used in isolated cases; more often it is prescribed as an auxiliary examination of the sigmoid colon.
Doctors include MR colonography here, during which about two liters of liquid with a contrast agent are injected into the rectum. The doctor then uses a special machine that examines the organs in three dimensions.
The process lasts about an hour.
Can be compared to an x-ray examination. Only in this case, the tomograph takes several pictures in a row, which allows you to painlessly check the lesion. Doctors say that this technique does not always help to detect cancer at the very early stages of development.
The procedure is used infrequently, since it can only determine the stage of appearance of tumors or a large tumor. Intestinal ultrasound is most often performed in patients with suspected diseases of the abdominal organs, mainly of an inflammatory nature.
Indications for ultrasound:
- pancreatitis;
- cholecystitis;
- hepatitis;
- tumors.
It can become an analogue of a colonoscopy only if a person is unable to undergo the standard procedure due to individual anatomical features. The patient swallows a small enterocapsule, which, when it enters the gastric tract, begins to take photographs. This method is considered minimally invasive and allows you to examine every part of the digestive system.
Photos can be taken from 4 to 35 pictures per second, it all depends on the speed of movement of the capsule itself. The device is removed naturally. The examination may take from 4 to 8 hours. The procedure is indicated for hidden bleeding, suspected neoplasms and pathologies. Enterocapsule examination helps to detect stomach or intestinal cancer with probable accuracy.
Pros and cons of capsule diagnostics. Video provided by the program “Live Healthy”!
Irrigoscopy
Irrigoscopy is one of the safest methods and helps to identify the following diseases:
- bowel cancer;
- polyps;
- ulcerative colitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- diverticula.
The patient is given a barium enema and then x-rayed. Irrigoscopy should be performed when it is not possible to examine a person with a colonoscope, or when these results do not provide a complete picture. Experts strongly recommend irrigoscopy if cancer is suspected, since this examination most accurately finds tumors in the intestinal lumen.
Anoscopy
Allows you to painlessly examine the rectal cavity to a depth of 10-15 cm. A proctologist can independently carry out this procedure in his office by inserting an anoscope through the anus.
Using anoscopy, doctors visually evaluate the inner surface of the anus and distal intestine.
In addition, at the very initial stage it is possible to identify any pathologies of the lower intestine.
More detailed information about anoscopy is presented in the video. Photographed by Maryana Abritsova.
Sigmoidoscopy
Rectomanoscopy is not an analogue of colonoscopy; it is not performed unless absolutely necessary. During the procedure, it is possible to examine about 30 cm of the large intestine.
If there is a tumor, a piece is plucked off from it for analysis. The technique does not give a broad picture of whether a person has a disease or not, and at what stage it is.
Proctologists recommend being examined in other ways.
The procedure is done according to the principle of ultrasound, but the sensor is inserted into the patient’s rectum. Ultrasound allows you to reveal the source of damage to the organ itself. The main advantages are simplicity and safety, absence of contraindications. The sensor technique can be used during pregnancy and for examining children.
Positron emission tomography (PET) in proctology is used to diagnose malignant tumors of the colon at the initial stage.
PET is combined with CT to obtain reliable data on the exact localization of the detected tumor. During the session, radioactive sugar is injected into the patient through a vein.
The process lasts about an hour and a half, the drug itself spreads throughout the body within an hour.
Hydrogen test
The patient should breathe into a special tube for two to three hours. Using a hydrogen test, the doctor determines disturbances in the microflora of the small intestine, as well as intolerance to a number of substances (fructose, lactulose, etc.).
Photo gallery
Ultrasound of the intestine Hydrogen breath test Irrigoscopy Enterocapsule for capsule study MRI of the intestine Sigmoidoscopy Loading...
This video from the Capsule Diagnostics channel describes in detail the main methods of diagnosing the large intestine.
Colonoscopy is an examination that no one likes, and patients very often ask, how can you check the intestines without a colonoscopy? What is there besides colonoscopy? What can replace this unpleasant procedure?
Of course, there is an alternative to colonoscopy; the intestines can be checked in different ways, however, the information content of all studies is inferior to this most unpopular colonoscopy. Sigmoidoscopy - the grandmother of colonoscopy - is also not loved by patients, so this article will talk about other, more pleasant studies.
Let's touch on colonoscopy a little, even though no one wants to hear about it. For details of this procedure, read the article “Colonoscopy - what is it.”
Why is an unpleasant colonoscopy prescribed? For the sake of early diagnosis of cancer. This is the most informative study, because the doctor personally, so to speak, examines the intestinal mucosa, can take a piece of tissue for examination, if something bad is found, and immediately during diagnosis can remove almost everything, for example, polyps.
Colonoscopy - endoscopic examination of the colon allows you to establish the correct diagnosis of polyps in the intestines or intestinal cancer, rectal cancer, rectal polyps in 80-90% of cases.
But there are those 10-20% when even a very sensitive colonoscope device misses the problem. The study fails most often due to poor bowel preparation.
There are also cases where the patient's intestines are so long or so narrow that the colonoscope is not able to pass through the entire intestine. And some patients have contraindications to colonoscopy.
It is in such cases that
- virtual colonoscopy;
- computed tomography - CT;
- magnetic resonance imaging – MRI;
- And even capsule endoscopy;
- Ultrasound (rare);
- Irrigoscopy with barium;
- PAT
Their main difference from colonoscopy is that they only diagnose the tumor, and then to take a biopsy, you still have to do a colonoscopy.
Those who have already encountered this procedure are looking for a way to check the intestines without a colonoscopy, since not only the procedure itself is quite unpleasant, but also the preparatory stage before it takes a lot of time and effort.
No one denies its effectiveness and efficiency, its indispensability in terms of obtaining information, but it is common for a person to want to do without unpleasant sensations, especially if he knows about the availability of alternative methods.
Modern research methods indeed offer other options for obtaining the necessary information, which in some cases allows them to replace colonoscopy.
Colonoscopy is performed by inserting a flexible tube with instruments and a camera at the end into the colon. During examination, noticed polyps and fecal stones may be removed from the intestinal walls.
Lab tests
When patients are admitted to the inpatient department, a series of standard laboratory tests are performed to give a general idea of the state of the body.
Many intestinal diseases are accompanied by chronic blood loss. Even small but prolonged bleeding can significantly worsen the well-being of patients. Blood loss will be expressed as a decrease in the total number of hemoglobin and red blood cells. Most inflammatory bowel diseases are accompanied by leukocytosis. Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are manifested by an increase in the level of leukocytes and a decrease in red blood cells against the background of chronic blood loss.
Stool analysis is of particular importance in the diagnosis of intestinal diseases. The consistency, color and smell of stool can suggest the nature and involvement of certain parts of the digestive tract. For example, if the feces are black and foul-smelling, this indicates bleeding from the upper intestine. Light streaks of blood are characteristic of bleeding from the sigmoid or rectum. In case of infectious diseases, additional impurities such as bloody discharge or mucus are observed in the stool.
Modern and popular methods of intestinal examination
There are several methods for diagnosing the intestines without the use of colonoscopy. The simplest of them is digital examination or palpation. Obviously, in this way it is possible to tactilely assess the condition and diagnose diseases only in a small area of the intestine, namely in the rectum at a distance of 10-12 cm.
A not much larger area of the intestine can be examined by sigmoidoscopy. Using a special device - a sigmoidoscope, the doctor is able to visually assess the condition of the internal walls of the rectum to a depth of approximately 30 cm. This is a more informative method compared to palpation, but is also limited in scope.
Studies that allow you to “see” the condition of the entire intestine require sophisticated equipment. Thus, irrigoscopy is based on X-ray examination with contrast, ultrasound and magnetic resonance examinations are based on the penetrating action of sound waves and excitation of hydrogen atoms by a magnetic field. All these procedures can be used for certain narrow purposes as preliminary and complementary to each other.
From the first moments, when a person begins to choose what he wants to eat, he gives preference to food that is not so healthy, but rather more tasty.
Of course, everyone knows that nowadays, in order to make food taste more attractive and have a distinct spicy aroma, many substances and additives are added that affect our human taste buds. They are the ones who lead us astray.
After eating such food for a long time, some of the first signs of problems with the stomach and pain inside the organ begin to be felt. In this article, you can learn more about indigestion, different types of stomach diseases, as well as how to check your intestines, and which specialists can help you in a given situation.
PET – positron emission tomography
The procedure lasts 1.5 hours. The patient waits one hour for the results. Radioactive sugar is used in the examination method. Administered intravenously. With its help it is possible to diagnose oncological diseases and tumors. Pathological cells absorb the substance - it is easy to see their location.
This is from the field of nuclear medicine, created by using a special type of scanner and atoms to establish an assessment of the functioning of organs. The effectiveness of the method depends on the drug used.
The method is prescribed together with CT. The combination of PET results with CT images allows one to acquire detailed information about the location of radioactive elements. Determine the stages of oncology, checking the function of blood flow or organ function.
Such an examination without a colonoscopy makes it possible to detect cancer at an early stage.
For tumors, the method will help:
- reveal distant metastases;
- assess the process of tumor spread;
- diagnose relapses
- detect stages of cancer
- monitor the condition of the organ after surgery.
What is intestinal colonoscopy and why patients prefer to replace it
Colonoscopy helps examine the large intestine. To carry it out, various models of endoscopes are used, with the help of which the examinee examines the inner wall of the intestine, and, if necessary, polyps are immediately removed or a biopsy is performed.
Patients do not like this procedure and want to conduct an intestinal examination without a colonoscopy for the following reasons:
- This is an unpleasant and painful method that requires anesthesia.
- Discomfortable preparation period (dietary nutrition and emptying the intestines of feces).
- Serious mistakes made during a colonoscopy can lead to abdominal surgery.
Many people understand that when a tumor is detected, a biopsy should be taken to determine its nature, however, they are interested in whether it is possible to check the intestines for the presence of cancer without a colonoscopy. Patients also want to know how to examine the small intestine.
Irrigoscopy
Intestinal irrigoscopy is a method of examining the intestines using X-rays and preliminary administration of contrast agents. It allows you to evaluate not only the structural features of the large intestine, but also its functionality. Irrigoscopy has a number of advantages. Allows you to determine the presence of morphological abnormal changes, assesses the size, length and degree of patency of the intestinal lumen.
The method detects the presence of tumor processes and allows one to evaluate the folding and motility of the intestine with minimal doses of radioactive exposure. The procedure is painless and does not require anesthesia. To prescribe an irrigoscopic examination, the presence of a number of specific symptoms is necessary:
Indications are diarrhea for a long time, disruption of bowel movements (frequent constipation), discharge of mucous or purulent impurities from the anus, bursting and cutting pain in the lower abdomen, frequent or chronic flatulence.
Irrigoscopy allows you to check the intestines for oncology only partially without colonoscopy. With the X-ray method of examination, the neoplasm itself is detected, but it is impossible to examine its structure or take a sample of biomaterial for histological examination.
Irrigoscopy is a more gentle diagnostic method compared to colonoscopy
How to check the intestines without colonoscopy: alternative research methods
The appearance of pathological symptoms from the gastrointestinal tract requires clarification of the cause of its malfunction. An intestinal examination is not a very pleasant procedure, which is accompanied by lengthy preparation and pain. Therefore, let's figure out how to check the intestines without a colonoscopy to avoid unpleasant moments of the procedure.
Data from an objective examination and laboratory tests are auxiliary methods that confirm the presence of a pathological process. But confirmation of the disease and its form is determined only by instrumental examination methods.
Invasive and non-invasive manipulations make it possible to accurately determine the type of pathological process. Colonoscopy is the most informative examination. But there are other instrumental manipulations that make it possible to determine the development of the pathological process in the intestine.
Often, invasive examination of the intestine is hampered not only by the fear of patients, but also by a number of contraindications to the procedure. Therefore, a specialist may prescribe an alternative examination.
Non-invasive diagnostic methods can reveal:
- erosion;
- ulcers;
- benign or malignant tumor formations;
- cracks and polyps of the mucous membrane;
- rectal diverticula.
These diagnostic procedures have their advantages. First of all, these are painless manipulations that are well tolerated by patients and give a clear picture of intestinal damage.
- However, non-invasive examination methods do not make it possible to take biopsy material for histological examination.
- When small tumor-like formations are detected, the malignancy or benignity of the pathological process is not always determined.
- The final diagnosis in complex cases of intestinal disease and suspected malignancy is always confirmed by histology. Sometimes the patient has to undergo the examination procedure twice, since only invasive examination methods allow for visual examination and taking material for biopsy from problem areas of the organ.
Preparation for gastroscopy of the stomach and diet rules
Preparing for a rectal examination
Before undergoing an examination, the patient must prepare properly. For the initial examination, only the rectum can be cleaned with an enema. If, in addition to palpation, a rectal examination involves examining the entire colon, then the cleansing procedure must be carried out more carefully. There are several ways to prepare for the examination:
- Give an enema. 1 day before the examination, you need to give up vegetables, fruits, flour and sweets and switch to light plant foods. In the evening before the procedure you need to give 1 enema, and in the morning you need to do another one. It is important that cleaning occurs at least 2 hours before the examination.
- Take a laxative. You need to cleanse your intestines with laxatives in courses. Cleaning must be carried out at least 12 hours before inspection. The medications must be taken according to the instructions.
The cleaning method must be selected together with the proctologist who will conduct the examination, since a specific cleaning method is suitable for each diagnostic method.
Anamnesis
Initially, the doctor should familiarize himself with the medical history.
Taking a medical history is the basis for diagnosis. To begin to put forward versions of a possible pathology, the doctor must become familiar with the symptoms and other factors that may indicate a particular pathology. Anamnesis may include collecting information about the following facts:
- presence of taste in the mouth and its character;
- possible painful sensations and information about them;
- data on appetite, thirst;
- fatigue, drowsiness;
- analysis of other symptoms;
- information about intestinal diseases of close relatives;
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract of which the patient is aware;
- other diseases, etc.