About pathology
The standard dimensions of the ovary for a woman of childbearing age are (according to ultrasound): length up to 3.5 centimeters, width up to 2.5 centimeters, thickness up to 15 millimeters.
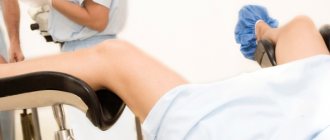
During an internal examination, the gynecologist should not palpate the ovary.
An enlarged ovary is considered to be an excess of more than 10% of the normal size or an ovary detected during vaginal examination.
This can be typical for both the left and right organs; the reasons for the increase are also the same.
Enlargement is possible at any age. In 40% of women, after undergoing an examination by a gynecologist and performing an ultrasound examination, it is discovered that one ovary is larger than the other.
The average size of the ovaries in a woman of childbearing age
Normal ovarian size in women
In a healthy young woman who is of reproductive age, the size of the ovaries may vary slightly depending on the level of hormones and the condition of the body. The size of the right and left ovaries may not be the same, but the difference is usually no more than a few millimeters. A sharp and disproportionate change in their dimensions may indicate the presence of a tumor or an inflammatory process.
The size of these gonads depends on many factors that can affect fluctuations in the size of a woman’s ovaries during different phases of the menstrual cycle.
In order to most accurately analyze this data and take correct measurements, ultrasound examination is usually performed from the fifth to the seventh day of the menstrual cycle. The main indicator is not the length or width of the ovary, but its volume, since it is this that can indicate the presence of tumors, cysts and inflammation.
If you measure the size of a woman’s ovaries normally, then these indicators can be as follows:
- Volume – from 4 to 10 cubic centimeters.
- Length – from 20 to 37 mm.
- Width – from 18 to 30 mm.
- Thickness – from 16 to 22 mm.
As you can see, the “scatter” of indicators is quite large, so measuring the size of the ovaries is not the only type of research on the basis of which a diagnosis can be immediately made. Many indicators must be taken into account.
Symptoms and diagnosis
As a rule, an increase can only be detected when a woman visits a gynecologist. In exceptional cases, it can be so strong that it is visible to the naked eye. Symptoms of enlargement may include the following:
- Lower abdominal pain;
- Uncharacteristic discharge;
- Discomfort when walking and playing sports;
- Mood changes.
During a two-handed (vaginal and through the abdominal wall) examination, the gynecologist palpates the uterine appendages, including the ovaries. Normally, the ovaries are not available for examination. If the doctor finds an ovary, he may suspect it is enlarged and refer it for an ultrasound examination. An ultrasound will determine the exact dimensions, then the gynecologist will make a diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
What does the diagnosis of “polyxitosis” mean when the ovaries are enlarged?
Polycystic disease can occur as an independent disease or against the background of other pathologies.
It is spoken of in the following cases:
- Confirmation by ultrasound results;
- Scanty, irregular periods or their absence for six months;
- Increased concentration of androgens in the blood plasma, clinical signs of hyperandrogenism (eg male pattern hair).
The disease is accompanied by a decrease in the production of follicle-stimulating hormone. As a result, the follicles produced by the gonads do not form into mature eggs. Since the latter are absent, ovulation does not occur, and therefore pregnancy does not occur. Even if the follicle is allowed to fully mature, it will still not be able to come out and ovulate, because the ovaries increase in size and become covered with a dense capsule.
When the ovary is enlarged due to polycystic disease, treatment can be conservative and surgical for an enlarged ovary. In the first case, hormonal drugs are used that promote the development of follicles and ovulation. Conservative techniques are mainly aimed at reducing clinical manifestations (excessive hair growth, acne).
Taking oral contraceptives for several months in half of the cases of the disease allows you to restore ovarian function, ovulation occurs and pregnancy becomes possible. Hormone therapy is also used when a woman is not yet planning a pregnancy. Otherwise, when her goal is to give birth to a child, ovulation stimulation is carried out over several months.
In case of obesity, efforts are directed towards weight loss. It happens that such a measure is enough to restore reproductive function.
Surgery involves removing the enlarged ovary or destroying the part that synthesizes androgens. The effect of the operations is short-term, so if you want to get pregnant, this is done in the next couple of months. It is recommended to perform laparoscopy, since after it the risk of formation of adhesions and other complications is significantly reduced than after laparotomy.
Physiological reasons
What does it mean?
Physiological is considered an increase during:
- ovulation – the release of an egg from the ovary;
- pregnancy;
- breastfeeding a newborn;
- puberty;
- taking hormones;
- sudden weight loss.
Physiological enlargement most often reflects a certain condition in a woman’s life and does not require correction.
Taking hormones
Important. Uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs to protect against unwanted pregnancy or as a method of self-treatment for gynecological diseases can lead to an enlarged ovary.
The thing is that the hormones included in the drugs replace one of the main functions of the ovaries - the production of female sex hormones. After stopping the medication, the ovaries, having rested from work, begin to function intensively in order to maintain hormonal levels at the same level. Hypertrophy develops and, as a result, they increase.
Causes of ovarian enlargement
Hormonal drugs, stress, and worries can cause the appendages to increase in size. Often the reasons for ovarian enlargement in women lie at the beginning of pathological processes. Such problems are observed due to rapid weight gain, age-related, and physiological changes.
Hormonal drugs
As a result of hormonal therapy, disturbances in the functioning of the female genitourinary system are often observed. In this case, there is a failure of the reproductive cycle, pain appears in the lower abdomen.
During an ultrasound, it is revealed that one ovary is enlarged or changes are noted in two organs at once. As a rule, when the hormonal balance is restored, the condition returns to normal.
Lactation period
Ovarian enlargement during the postpartum period is due to increased concentrations of prolactin. The condition is regarded as a variant of the norm. Over time, the size of the appendages becomes the same.
You need to regularly visit your gynecologist and have an ultrasound scan. In this way, it will be possible to exclude the development of possible pathologies.
Depression, stress
The cause of an enlarged ovary in a woman is often nervous overstrain. Stress and chronic depression lead to changes in the size of the appendages. Before starting treatment for a disease caused by psycho-emotional stress, you should calm down. Only then will the treatment give the desired result.
Sudden weight change
A rapid decrease in body weight and enlargement of the ovaries is observed for the following reasons:
- following a strict diet;
- therapeutic fasting;
- development of serious pathologies;
- stress.
At the same time, a negative reaction of the body to such changes is noted. There are problems with the thyroid gland and strong hormonal fluctuations.
Excess weight also negatively affects the condition of the pelvic organs. It is extremely important to identify the reason that provoked rapid weight gain. This often requires consultation with a gynecologist and a number of specialists.
Endocrine diseases
Enlarged ovaries are often observed in acute and chronic pathologies of the thyroid gland. This is due to the close connection between the endocrine and reproductive systems. The pathological process leads to changes in hormonal levels. Therefore, you should seek help from an endocrinologist. With timely initiation of therapy, the size of the organs, as a rule, becomes normal.
Neoplasms
Neoplasms of a benign or malignant nature can provoke a change in the size of the appendages. An ultrasound reveals that the left or right ovary is enlarged. In fact, one or several tumors grow along its perimeter.
An ovarian cyst is a benign formation. When present, the organ visually looks larger. These can be single or multiple growths that differ in size.
The formation of a cyst is dangerous because there is a risk of its rupture and damage to nearby tissues, especially if the capsule is large.
Malignant processes pose a serious threat to life. Therefore, it is extremely important to identify them in a timely manner and begin therapy.
Adolescence
During puberty, when the first menstruation appears (menarche in girls), the ovaries are often enlarged. The condition in this case does not cause concern, is considered normal and does not require treatment. It should also be taken into account that in the first few years the regulations are unstable.
If a child begins to complain about the regular occurrence of pain in the hips, lower back, or abdomen, then you should consult a gynecologist. There is a risk of developing serious diseases at any age.
Pathogenic flora
The vaginal microflora is often disrupted due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms that provoke inflammation of the organs of the reproductive system. Pathogenic microflora include:
Therefore, if an enlargement of the right, left ovary or two appendages at once is detected, additional laboratory tests (smear for microflora, blood test) are prescribed. Pathogenic microorganisms provoke the appearance of adhesions and infiltrates that can lead to changes in the size of paired organs.
Cervical erosion
The erosive process in the area of the cervix of the reproductive organ leads to the proliferation of pathogenic microflora and infection. There is a high probability that at the beginning there will be an enlarged ovary. The cervical tissue is affected. Ulceration occurs due to exposure to chemicals, infections and damage to the epithelium.
Inflamed appendix
It is extremely rare that the cause of an enlarged ovary is an inflammatory process in the appendix. Such changes are due to the fact that the right appendage is in close proximity to this organ. Nearby lymph nodes can also change in size.
Ovulation
Enlarged ovaries in women during ovulation are considered quite normal. Such changes do not cause concern closer to the arrival of the regula, as well as with successful fertilization. Soon the size of the appendages becomes the same. However, you should undergo a comprehensive examination to exclude possible pathological changes.
We recommend reading more about pain in the ovary after ovulation in a separate article on our website.
Does anything need to be done?
If the ovary is enlarged due to pregnancy, breastfeeding, ovulation, or during adolescence, nothing needs to be done.
This is the norm.
If growth occurs against the background of weight loss, then it is necessary to adjust the diet, making nutrition complete.
Hormonal medications should be taken only under the supervision of a doctor, ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs and hormone levels. If the ovary is enlarged due to constant stress, you need to either reduce your worries and rest, or consult a psychologist.
Why do women have enlarged ovaries: reasons
During a routine ultrasound, every representative of the fairer sex can hear the diagnosis - the right ovary is enlarged. What provoked this pathology? The ovaries enlarge if disturbances occur in the body or a disease occurs. Each woman is interested in what reasons can cause pathology.
Let's look at the most common reasons:
- if a woman has been continuously taking hormonal medications for a long time;
- breastfeeding when prolactin levels are elevated;
- stress, depression, psycho-emotional tension;
- sudden loss of body weight;
- adolescence;
- obesity of different feet;
- if there are disturbances in the endocrine system.
Pathological causes
Not in all cases, the enlargement of the female reproductive glands is physiological. This can be a manifestation of various diseases from appendicitis to malignant tumors.
Inflammatory diseases
Inflammation of the ovary is called oophoritis, and inflammation of the appendages is called adnexitis . Diseases can be caused by both nonspecific (streptococcus, E. coli) and specific (chlamydia, trichomonas) microorganisms. Inflammation is accompanied by an increase in general and rectal temperature, chills, pain in the lower abdomen, and deterioration in health.
Enlargement of the appendages is due to the fact that during inflammation, blood flow to the organ increases and vascular permeability increases. Swelling of the organ develops, which is manifested by an increase in its size. The consequence of the disease can be the formation of adhesions in the pelvis, which are very difficult to treat.
Polycystic
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) occurs in approximately 20% of women . Polycystic disease manifests itself:
- an increase in the size of the ovaries;
- menstrual cycle disorders (shortening or lengthening);
- chronic anovulation (in almost all cycles the egg does not mature);
- infertility due to anovulation;
- manifestations of androgen excess.
An increase in the size of the gonads occurs due to the formation of cystic cavities.
Reference. With PCOS, the content of male sex hormones (androgens) in a woman’s body is increased.
Endocrine diseases
Most often, the ovaries are affected by pathology of the thyroid gland. Insufficient or excessive production of thyroid hormones can lead to an increase in the size of the ovary. Other endocrine disorders also lead to hormonal imbalance in a woman’s body and affect the size of the gonads.
Neoplasms
New growths may appear in the female reproductive glands. They are both benign and malignant. These can be various cystic formations, nodes, tumors. The size of the ovaries with a neoplasm may be slightly increased or gigantic.
Expert opinion
Olga Matveeva
Gynecologist-obstetrician Experience 6 years
Often tumor processes in the pelvis have close relatives , that is, the disease is hereditary. Therefore, women who have had such pathologies in their family should monitor their health more carefully and visit a gynecologist more often.
The neoplasm can appear at any age, including in children. There are congenital tumors (teratomas) that increase in size as the patient ages.
Cervical erosions
Erosions, as a rule, appear in mature women, often after termination of pregnancy (abortion) or after childbirth.
They are localized on the mucous membrane of the cervix.
They represent defects of the mucous membrane, i.e. are open wounds.
When microorganisms come into contact with erosion, local inflammation develops. Under certain circumstances (decreased immunity), inflammation can spread to the ovaries. The increase in size due to inflammatory diseases was described earlier.
Appendicitis
In rare cases, the appendix may be located in an atypical location, more precisely, in the pelvis. When an inflammatory process develops in the appendix, it increases in size due to swelling. An inflamed appendix can push the ovary upward, so during the examination the gynecologist can feel it. With acute appendicitis, the lower abdomen hurts and the body temperature rises.
Normal sizes of the uterus and ovaries according to ultrasound
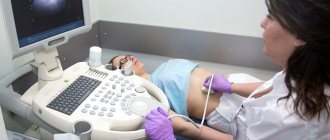
Ultrasound diagnostics (ultrasound) is a fast, safe and most informative examination method in medicine. Recently, various gynecological pathologies have become increasingly common, so it is important to know the normal sizes of the uterus and ovaries by ultrasound.
When is ultrasound diagnostics prescribed?
There are different conditions under which a doctor may order an ultrasound examination. Common ones:
- severe pain during menstruation;
- regular cycle disorders;
- frequent pain in the area of the ovaries or uterus;
- to establish a possible pregnancy and exclude the formation of an ectopic pregnancy;
- when strange vaginal discharge appears that is not associated with menstruation.
Thanks to ultrasound diagnostics, it is possible to promptly identify various pathologies of a woman’s internal organs and prevent the formation of serious complications.
How is an ultrasound performed?
The following methods are used for ultrasound examination:
- Transabdominal
- Transvaginal.
Let's take a brief look at each of the methods.
Transabdominal ultrasound diagnostics
This research method is carried out through the abdomen. For better glide of the device over the skin, a special gel is applied to the diagnosed area by the doctor. For free penetration of ultrasonic waves, an important requirement of this method is a filled bladder.
Transvaginal ultrasound diagnostics
The study is carried out with a special device through the vagina. To avoid infection, put a condom on the device. With such an examination, the bladder, on the contrary, should be empty. This method is more accurate than the first.
The diagnostic procedure does not cause any discomfort or pain, and does not have a negative effect on the female body. However, it is important to know what sizes of the ovaries and uterus are normal according to ultrasound.
Norm for ultrasound diagnostics of ovaries
If ovulation is painful, constant pain in the lower abdomen, discomfort during sexual intercourse, it is recommended to undergo an ultrasound of the ovaries.
During the procedure, the doctor checks the following indicators.
Organ location
The ovaries are located on both sides of the body of the uterus. However, their location may be asymmetrical.
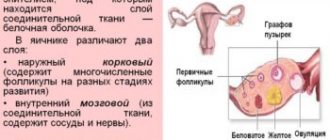
Ovarian shape
Healthy ovaries are oval in shape with a clearly defined follicular apparatus. If the procedure is performed on days 8-9 of the cycle, then the size of the dominant follicle can be determined. It will fluctuate in the range of 15-25 mm. An increased parameter can usually indicate the formation of a follicular cyst.
Ovarian sizes
The normal sizes of ovaries in women are:
- width – 25 mm;
- length – approximately 30 mm;
- thickness – 15 mm;
- the volume of each ovary should not exceed 80 mm³.
If the size of the ovaries increases, inflammation or serious pathology of these organs may be present.
Structure of the ovaries
Correct structure of the ovaries: capsule and follicles. The number of the latter may not be the same in both the right and left organs.
Echogenicity and external contours of the ovaries
Ovaries without pathologies should have a clear and lumpy outer shell, as well as uniform echogenicity. Fuzzy contours indicate the development of inflammatory processes (for example, oophoritis).
Ultrasound examination of the uterus
Having felt alarming symptoms, the woman is sent for examination. If the reproductive organs are functioning correctly, all studied indicators should be normal.
To assess the general condition of the uterus, the doctor examines the following indicators using an ultrasound.
Body position
The uterus is located between the upper part of the rectum and the bladder. It is considered correct when the organ is tilted forward towards the rectum or urinary tract. The doctor carefully examines the location of the uterus and indicates everything in the protocol.
Organ outlines
Normally, an organ is considered to have a flat and smooth surface. There should be no scar changes, neoplasms, or thinning on the body of the uterus. An uneven contour may indicate the presence of inflammation.
Endometrial size
The endometrium is the mucous lining of the uterus. In patients of reproductive age, its thickness may vary depending on the period of the cycle. If the diagnosis was carried out immediately after the end of menstruation, this value is approximately 1-2 mm; after ovulation, its width reaches 10-15 mm.
In women during menopause, the thickness of the endometrium does not change throughout the month. Over the years, after the cessation of its functions, the endometrium gradually becomes thinner. At the beginning of menopause, its thickness is about 8.5 mm, and after 10 years it may become smaller - 1.32 mm.
Uterus size
If the uterus is normal, then its size depends on age, number of pregnancies and is approximately 45-70 mm. The anterior-posterior size of the uterine body varies from 34 mm to 44 mm, width - 45-60 mm.
If the size of the uterus is smaller than normal, underdevelopment of the organ can be suspected. When these indicators are increased, this indicates the presence of pregnancy or neoplasms.
The nulliparous uterus has the following dimensions:
- length – 4.5 cm;
- thickness – 2 cm;
- width – 2.5 cm.
During pregnancy, the uterus increases in length to 40 cm and becomes heavier.
Cervical parameters
The cervix, which has no pathologies, is homogeneous. Its correct size is on average 35-40 mm. The cervical canal should contain a homogeneous fluid (mucus) and be approximately 2-3 mm in diameter.
An enlargement of the cervical canal or the cervix itself may indicate the development of various pathologies.
Echogenicity
This parameter indicates the density of the fabrics. The norm is homogeneous echogenicity. In the presence of any other indicators, the development of a neoplasm or fibroids is possible.
Presence of free fluid
After ovulation, fluid in small quantities may be observed in the retrouterine area. But during other periods of the menstrual cycle, the presence of this fluid indicates possible pathologies caused by sexually transmitted infections.
Cavity structure
In a healthy body, the uterine cavity is homogeneous. A blurred structure indicates endometrial disease or the presence of neoplasms.
The doctor records all examination data in the protocol. Having assessed the above indicators, he can make an accurate diagnosis.
Ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries is rightfully considered a fairly informative diagnostic method, which is prescribed for violations of the functioning of the organs of the woman’s reproductive system. If an ultrasound examination does not help establish an accurate diagnosis or the doctor has any doubts, the patient is recommended to donate blood for hormones, bacterial culture and other tests.
oyaichnikah.ru
Diagnosis of pathology
Among the main symptoms of ovarian enlargement are the following:
- Pain of varying intensity, intensifying before menstruation. The appearance of severe cutting pain in the ovarian area is a reason to immediately seek medical help. A similar condition is observed with ectopic pregnancy or cyst rupture. It poses a real danger to life. In some cases (with certain diseases) there is no pain syndrome.
- Visual enlargement of the abdominal cavity. Occurs when a large cyst or tumor appears in the ovary. It is not the ovary itself that increases, but the contents of the tumors. Sometimes a temporary increase is observed before menstruation.
- The appearance of unnatural vaginal discharge. A change in their color, smell, or consistency indicates the addition of pathogenic flora. The developing inflammatory process causes the ovary to enlarge due to swelling. With bilateral damage, clinical symptoms are more pronounced.
- Change in body temperature. Low-grade fever accompanies a sluggish inflammatory process. A high temperature (above 39 degrees) indicates a serious pathology and requires immediate hospitalization in an inpatient department.
Timely detection of the disease increases the chances of successful treatment. Why the ovaries could have enlarged and what to do in each specific case is determined by the doctor based on the test results obtained during laboratory and instrumental examination methods.
The set of diagnostic measures includes the following procedures:
- General blood analysis. The data obtained contains valuable information for the doctor, allowing him to assess the general condition of the body and identify signs of the inflammatory process.
- Blood test for hormones (testosterone, luteinizing hormone, cortisol, thyroxine, follicle-stimulating hormone, progesterone).
- Cytology smear (PAP test). Cytological examination of the material makes it possible to determine pathological processes on the surface of the cervix and identify serious diseases.
- PCR and other methods for detecting STIs.
- Hysterosalpingoscopy is a method of x-ray examination of the pelvic organs in order to determine adhesive processes in the organs of the reproductive system, the presence of benign and malignant neoplasms, and congenital anomalies.
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs can identify structural abnormalities in the ovaries.
As the ovary enlarges, a woman’s general well-being and health may deteriorate. This disease manifests itself as:
- bleeding after menstruation;
- pain during sexual intercourse and in the process of emptying the bladder;
- purulent vaginal discharge.
If the right ovary is enlarged and your health has worsened, self-medication is prohibited. Only after examining the patient can the doctor identify the disease that provoked the active enlargement of the appendage. Based on the diagnostic results obtained, the gynecologist will prescribe medications. The duration of therapy is determined strictly by a specialist. Self-medication can do a lot of harm and only make the problem worse.
As a rule, for correct diagnosis, a specialist prescribes an ultrasound at the beginning and middle of the cycle. It is generally accepted that the ovary is enlarged when a woman has more than 12 follicles, which are of different sizes.
In addition, you need to pass the following tests:
- for testosterone;
- thyrotropin;
- luteinizing;
- insulin;
- follicle-stimulating hormone;
- cortisol;
- thyroxine.
Before making a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to exclude pathologies such as:
- increased cortisol levels;
- decreased thyroid function;
- excess of the hormone prolactin;
- increased amount of testosterone.
Each woman must clearly understand that she will not be able to cure the disease on her own. If the disease is allowed to progress to a severe state, the consequences may be irreversible. For example, if an increase is a sign of amenorrhea, then with the help of infusions and herbal decoctions you can restore hormonal levels. Amenorrhea should only be treated under close medical supervision.
If your ovaries are enlarged and this is a sign of polycystic ovaries, you need to pay attention to yoga. This is the most gentle method for improving the functioning of the pelvic organs. Remember that yoga is only an additional therapy; the main treatment is prescribed by a specialist.
Effective folk methods are considered to be:
- use of medicinal tampons;
- the use of healing compresses;
- taking infusions, decoctions, herbal teas, as well as herbal remedies.
Representatives of the fair sex should remember preventive measures and know the reasons why the ovary is enlarged, which can become a catalyst. You need to visit a gynecologist or endocrinologist every six months, monitor your weight, eat right, exercise, listen to your body, it will always tell you if something is wrong.
A serious symptom indicating the presence of gynecological diseases is an enlarged ovary in women, the causes of which may vary, but it will definitely bring discomfort to the woman. Moreover, it can occur both in women of childbearing age and those who are in menopause.
According to doctors, the right ovary is most often enlarged. Why is this happening? The answer to this question lies in the fact that the appendix is on the right side. Inflammatory processes in it can also provoke an enlargement of the ovary.
What are the other reasons that cause this phenomenon? They may be as follows:
- Inflammatory diseases of the female reproductive system. This can be inflammation of the uterus, tubes, including inflammation of the ovary itself, which is called oophoritis. Sometimes these diseases are practically asymptomatic. Their cause can be hypothermia, as well as STDs.
- Erosion. Such a pathology of the cervix, even a small one, can cause an enlargement of this organ. Any violation of the integrity of the epithelium can lead to inflammatory processes and enlargement of the ovaries.
- Cyst. Most often women of childbearing age encounter it. Cysts form regularly, but their size does not exceed 3 cm. If the cyst is larger, then it can cause the organ to enlarge.
- Polycystic. A condition in which numerous cysts form. The reason is a hormone imbalance.
- Oncological diseases of the pelvic organs. A symptom such as enlarged ovaries can also indicate a serious illness. That is why you should be very careful about your women's health.
- Ovulation. A slight enlargement of the ovary in women, caused by the release of an egg, can be observed on certain days of the cycle. However, this is normal and should not be a cause for concern.
This condition may be asymptomatic. It depends on the reason that caused it. However, most often the increase is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- nagging pain in the right or left side;
- temperature increase;
- weakness;
- headache.
Some symptoms may tell a woman that she has an enlarged left ovary or an enlarged right one. Such signals are:
- frequent malaise and fatigue;
- opening of bleeding in the middle of the cycle;
- aching pain in the area of the female appendages;
- pain in the back;
- pain during intimacy;
- heavy discharge every day.
The acute form of the disease may be accompanied by a sharp increase in temperature (up to 39 °C). Such alarming symptoms require immediate intervention by a qualified specialist. The acute form of the disease is treated only in a medical hospital under the supervision of doctors.