With intestinal dolichosigma, treatment in adults may have different approaches. Everything determines the degree of the disease. This disease is a congenital anomaly of the large intestine (sigmoid colon), when its length is slightly increased. As a result, the intestine begins to twist and wrap, and this leads to problems with emptying, or rather, constipation.
Until now, modern medicine has not come to a consensus regarding the danger of dolichosigma. Some experts consider this pathology dangerous, others are inclined to believe that it is quite compatible with life if the patient does not complain about it. The main symptom is constant constipation, which over time begins to greatly disturb the patient.
Dolichosigma of the intestine - why it is dangerous
This disease means abnormal elongation of the sigmoid colon (this is one of the sections of the intestine). The result of increased size may be large bowel diameter or bowel torsion. The result of such changes is the appearance of persistent constipation and impaired bowel movements.
In some cases, there may be no symptoms. Then dolichosigma is defined as an individual characteristic of the body, which is considered the norm.
The essence of the disease
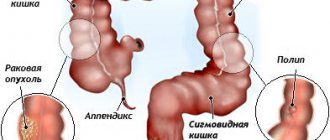
Dolichosigma is the abnormal structure of the sigmoid part.
This is the last section of the intestine that ends in the large intestine. An anomaly is defined as an elongation or increase in the diameter of the intestinal lumen. In a normal adult, the length of this section is approximately 24 to 46 cm. With dolichosigma, there are 2 or 3 additional loops. They can twist, fold in layers, and bend. By doing this, they interfere with the full passage of feces and intestinal gases. According to medical statistics, every fourth person has such deviations in the structure of the intestines. Although the indicators should be higher, the difficulty of detecting the disease does not make it possible to accurately determine the disease in all cases. In children, the disease is registered in 40% of cases with problems with constipation.
Forms of the disease
Elongation of the sigmoid colon can have 3 forms, which make sense to consider as stages of the development of the disease. This means that one stage is capable of transitioning to another. So, the forms themselves:
- Compensated. In this case, constipation occurs with noticeable interruptions and lasts for a maximum of 5 days. There is also noticeable pain in the abdomen. Otherwise the patient feels fine. In order to empty the intestines, the patient must use enemas and laxatives.
- Subcompensated. Dolichosigma of the intestine at this stage leads to noticeable pain, constant constipation and bloating. Laxatives are no longer able to provide the required level of patency.
- Decompensated. This form is the final stage. There may be a disturbance in the movement of feces and food through the intestines. The abdominal pain does not go away, and the constipation lasts all week. The intestine itself increases in size and swells due to the accumulation of gases and feces in it. Against the background of this condition, intoxication may develop (toxic substances poison the body). All this is accompanied by purulent skin rashes, nausea, vomiting and lack of appetite.
Causes and consequences of the disease
In the 1st trimester of pregnancy, the embryos of the intestine and its functional parts are formed in the fetus. If the pregnancy proceeds unfavorably, if the expectant mother is forced to take potent medications, there is a high probability of failure in the development of the fetal systems and organs.
There are other possible causes of exacerbation of congenital anomalies of intestinal development.
If a patient with dolichosigma avoids treatment and ignores the diet, negative consequences of the congenital pathology will soon occur:
- Intestinal fibrosis.
- Replacement of normal tissues of the intestinal walls with connective tissue. The muscle fibers grow too much, which leads to the saturation of the walls of the colon with tissue fluid.
- Swelling.
- Acquired dysfunction of intestinal innervation.
- Disturbance in the movement of feces through the colon.
- Cramping pain in the abdominal area, which is accompanied by constipation.
- The disease can develop into cancer.
Why do additional sigmoid loops appear?
Dolichosigma of the intestine can be either an acquired or a congenital disorder. Doctors cannot fully determine the cause of the appearance of extra loops of the sigmoid colon during fetal formation. But some factors that can affect the condition of this part of the intestine have been identified: These include:
— Viral, bacterial, and infectious diseases suffered by a woman during pregnancy.
— Use of medications during pregnancy that can negatively affect the condition of the unborn child.
— Heredity. We are talking about anomalies and pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract in the anamnesis of the parents.
— Preservatives in food products, dangerous additives and pesticides can also have a negative impact on the fetus.
In addition to hereditary factors, the cause of elongation of the sigmoid colon can be various disorders of the digestive processes, which result in gradual fermentation of the intestinal contents and its subsequent putrefaction. This condition is most often recorded in people over 50 years of age, or in ordinary people who lead a sedentary lifestyle, are addicted to fatty junk foods and have no desire to undergo any physical activity.
Reasons for increasing dolichosigma
Dolichosigma can be a congenital or acquired condition.
The exact causes of dolichosigma are unclear. It is believed that impaired growth of the sigmoid colon has a direct connection with heredity, the influence on the fetus developing in the womb, unfavorable factors (environmental, chemical, physical), infectious diseases of the pregnant woman and her use of certain types of medications.
Acquired dolichosigma (rarely found in children) may appear due to malfunctions of the digestive organs associated with prolonged fermentation and rotting of undigested food in the intestines. This often affects people after 45-50 years of age who move little, abuse meat products and carbohydrates, and often experience stress.
In proctology, it has not yet been decided whether dolichosigma is considered a developmental pathology or is it an individual variant of the norm. Due to the fact that dolichosigma is diagnosed in almost 15% of healthy children, there is reason to classify this anomaly as a normal variant. At the same time, the elongation of the sigmoid colon may be accompanied by organic and functional disorders of the distal colon. In fact, dolichosigma can be a kind of background for the formation of clinical pathology.
Dolichosigma does not have its own ICD 10 code, it is considered a congenital anomaly and has a common code with other diseases (colon diverticulum, dolichocolon, megaloappendix, megaloduodenum, microcolon, prolapse (coloptosis) of the transverse colon, left-sided dolichocolon, dolichotransversum and others) code Q 43.8 .
Diseases that accompany dolichosigma
Often, elongation of the sigmoid colon occurs in childhood, and over many years of stable progress, the disease can lead to serious complications:
- Immunodeficiency. This pathology causes inflammatory changes in the intestinal walls and causes an increase in the number of diseases throughout the year, affects the occurrence of various infections and the occurrence of skin manifestations due to intestinal disorders.
- Gastroduodenitis, esophagitis and gastritis. Dolichosigma of the intestine influences the development of these diseases by disrupting the passage of feces, which, in turn, leads to an imbalance in the functioning of various organs of the digestive tract, chronic dysbiosis and the accumulation of gases.
- Chronic stress. Heartburn, constant pain and bloating lead to this condition in a person. Stress itself, which is a consequence of decreased tone (due to pain and discomfort), can cause the development of gastritis and other complications.
Symptoms of dolichosigma
Clinical manifestations of dolichosigma are determined by transformations in the colon, as well as chronic fecal intoxication.
The main symptoms of dolichosigma are constipation, which develops in most cases in children from six months to one year. This is due to the beginning of the introduction of complementary foods or the transfer of the newborn to mixed feeding. In 30-40% of children, constipation may occur at 3-6 years of age. At first they are episodic in nature - lasting 2-3 days, later - long-term constipation occurs. Long-term constipation is fraught with intestinal dilatation and a decrease in the reflex to emptying. Some children may experience encopresis.
The consistency of the stool in patients is dense, it is large in diameter, sometimes looks like a “fir cone”, often with a fetid odor. When passing such feces, blood impurities appear due to a violation of the integrity of the rectal mucosa.
Characteristic signs include recurring pain in the left iliac or periumbilical region and bloating. These phenomena are aggravated after eating, physical activity and decrease after the intestines are emptied.
Most patients are diagnosed with malfunctions in other parts of the gastrointestinal tract: biliary dyskinesia, hypomotor dyskinesia, dysbacteriosis, colitis, diverticular disease and others. Frequent concomitant diseases of dolichosigma in adults can be hemorrhoids and varicose veins. If patients fight the disease with an enema, then there is a loss of the emptying reflex.
Due to prolonged absence of bowel movements, fecal stones may accumulate, causing irritable bowel syndrome. One of the dangerous complications is considered to be intestinal obstruction - this is a consequence of nodulation, volvulus, and bends.
Diagnostic methods
One of the first signs by which problems with the sigmoid colon can be identified is the patient’s pale skin and lack of body weight. With the help of palpating the abdomen, which is carried out by a gastroenterologist, it is not difficult to identify intestinal loops filled with feces. A digital rectal examination, in turn, can reveal emptiness in the rectum.
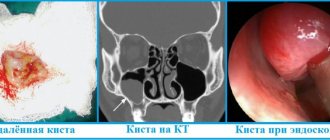
The key method for diagnosing the sigmoid colon is irrigography. As for instrumental techniques, the best of them can be called computed tomography of such a part of the digestive system as the large intestine. Dolichosigma can be detected without endoscopic examination; for this it is worth using virtual CT colonography. This technology makes it possible to qualitatively assess the condition of the colon mucosa and determine space-occupying formations.
It is also necessary to analyze stool for hidden blood, worm eggs and dysbacteriosis. Blood tests will also have to be taken (determining the level of hemoglobin, leukocytes and ESR value).
Diagnostics
When going to the hospital, the doctor performs a rectal examination of the patient and palpates the abdomen to identify stagnation of feces in the intestine. A blood test is performed to check for infections. A general stool analysis is prescribed. Additionally, it is examined for worm eggs and the presence of hidden blood. Diagnostics includes hardware methods:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity - helps to see the presence of dolichosigma, expansion of the large intestine.
- X-ray examination reveals loops in the sigmoid region.
To make an accurate diagnosis, doctors prescribe:
- Endoscopic examination of the inner surface of the intestinal mucosa - colonoscopy. With this method, it is possible to take tissue for a biopsy to exclude oncology.
- Irrigoscopy is an X-ray examination using the injection of a contrast agent. The method reveals the lengthening of the section, the presence and number of loops.
Dolichosigma intestines: treatment
Regardless of the stage of development of the disease, the treatment process should begin with complex conservative therapy. Its goal is to normalize the functioning of the digestive system through dietary nutrition.
For a disease such as intestinal dolichosigma, the diet should include the following elements:
- black bread, honey;
- fractional meals;
- consumption of fermented milk products;
- foods rich in fiber (greens, bran, berries, fruits and vegetables).
It is advisable to replace flour dishes with potato ones and switch to drinking medicinal sulfur-containing mineral waters (warm). The use of pasta, meat dishes, wheat cereals, rice, semolina, bread and crackers in the diet when lengthening the sigmoid colon is prohibited.
In some cases, patients are prescribed microenemas and laxatives to improve their condition. If intestinal dolichosigma has been diagnosed in adults, then it is possible to use antispasmodics to relieve pain syndromes. In case of intestinal hypotension, Proserin and massage of the anterior abdominal wall are prescribed. Treatment in a sanatorium and vitamin therapy courses are very effective.
As for alternative methods, folk remedies can also have a noticeable effect on a disease such as intestinal dolichosigma. The following popular recipes can be distinguished:
- an infusion of yarrow herb, nettle leaves and buckthorn bark (effective for constipation);
- daily consumption of cabbage juice, squeezed from fresh leaves (half a glass per day);
- A decoction of buckthorn berries is also an effective method of neutralizing constipation.
But it is worth remembering that any folk remedies can be used only after consulting a doctor.
Treatment
The pathology is treated by a gastroenterologist. Based on the results of the analysis, the specialist determines the stage of the disease and prescribes therapy.
First, it is necessary to normalize the functioning of the digestive tract. For this, the patient is prescribed a special diet.
Dietary components:
- black bread;
- dairy products;
- fresh fruits and vegetables;
- honey;
- oatmeal, potato dishes, salads with olive oil;
- warm mineral water containing sulfur;
- fine wheat bran.
Meals must be fractional . What does it mean? The number of meals throughout the day is 4-5 times. Portions should be small. You can't overeat.
In the morning, it is advisable to take 15 ml of some oil - castor or olive - on an empty stomach.
It is prohibited to consume alcoholic beverages, fatty meat dishes, pasta, rice, semolina, buckwheat, wheat, white bread, baked goods, cakes, coffee, carbonated drinks.
To improve bowel movements, laxatives ( Lactulose syrup ) and enemas are prescribed. But you need to use enemas as little as possible, it is important to form a reflex to defecation. You must go to the toilet calmly, without suppressing the urge to defecate.
In order to break up hardened feces, an abdominal massage is prescribed. It is necessary to do therapeutic exercises. By doing simple exercises you can ensure blood flow to the intestines and strengthen the abdominal muscles.
To normalize intestinal function, physiotherapy is prescribed: electrical stimulation, acupuncture, laser therapy.
Drug treatment
If the disease is not complicated by the formation of nodes or the formation of loops, then medications are prescribed.
Medical treatment is aimed at facilitating bowel movements, relieving pain, and suppressing attacks of flatulence.
Antispasmodics ( Platiphylline, Drotaverine, No-shpa ) are used to relieve pain. For intestinal hypotension, Proserin . The body is saturated with vitamins B, C, E.
For this, the Polyzyme or vitamin injections . If muscle tone decreases, Proserin or Reglan .
The patient is prescribed drugs to reduce the volume of feces, prokinetics, and laxatives. Prebiotics are used to normalize microflora.
Improvement in intestinal function occurs with the use of Motilium . Duration of treatment – 2 weeks.
Folk remedies
A variety of folk remedies are used to treat pathology. For this purpose, a tincture is prepared from yarrow, buckthorn bark and nettle.
A decoction of prunes and rose hips stimulates the intestines. Squeeze juice from cabbage leaves and drink half a glass a day.
Prepare an infusion based on celandine. For this purpose, celandine and sugar are placed on a gauze bandage.
The mixture is tied into a knot and immersed in whey for two weeks. After the expiration date, drink 100 grams of infusion per day.
Surgical intervention
Unfortunately, conservative treatment methods do not always help overcome difficulties with the sigmoid colon. And if the symptoms indicating a disease such as intestinal dolichosigma do not subside, surgery becomes the only effective solution to the problem. The most compelling argument in this case can be considered non-expanding loops of the sigmoid colon. If nothing is done in such a situation, then, most likely, you will have to deal with intestinal obstruction.
The purpose of surgery is to remove excess intestinal rings in which the innervation and blood supply are impaired. For this operation, an inferomedian approach is used. It is possible to use endoscopic techniques to eliminate excess loops. But the disadvantage of this treatment is the excessive duration of the operation and the high risk of complications.
For a disease such as intestinal dolichosigma, surgical treatment involves the use of general anesthesia. The operation lasts on average 1.5 hours. If surgical treatment is timely, then there is every chance to forget about problems with the sigmoid colon.
Carrying out the operation
In some cases, surgical intervention is indicated. It is usually performed in adult patients.
Reasons for the operation:
- additional loops cannot be straightened;
- ruptures of the intestinal walls appeared;
- poisoning of the body increases due to rotting of feces;
- Conservative treatment methods did not bring positive results.
During the operation, additional loops are removed, blood supply and normal motility of other parts are restored. Surgery is performed under general anesthesia. Medical technology and modern devices make it possible to avoid complications.
If all the recommendations of the attending physician are followed, the person leaves the hospital healthy, with a stable intestine. For 4 months you must adhere to a diet and do not lift weights.
Period after surgery
When surgery is successfully completed, the patient is usually admitted to the intensive care unit. After 24 hours, the patient, provided he feels normal, is transferred to a regular ward. Already on the third day you are allowed to get up, and after the drains are removed, you can walk. According to the indications, a particular patient may be prescribed antibacterial and hemostatic drugs. Infusion of solutions can also be carried out, the purpose of which is to improve blood clotting and detoxification.
Sutures are removed 10 days from the date of surgery (approximately). But before this is done, dressings are done daily. A month after visiting the surgery, the patient can be considered able to work.
What symptoms indicate dolichosigma?
Symptoms of dolichosigma are caused by stagnation of waste substances in the intestine, their fermentation and transformation into toxic poisons, with gradual poisoning of the body, intestinal bloating in the sigma zone, and the development of partial or complete obstruction.
Patients consult a doctor with complaints of the following:
- Constipation - at first, bowel movements are delayed for 3-4 days, then this period reaches up to a month. The symptom is caused not only by lengthening the path of feces, but also by careless treatment with addiction to laxatives and enemas. A person’s reflex mechanism for cleansing the intestines disappears.
- Pain syndrome - caused by a distended, overcrowded sigmoid colon, associated with inflammation. Localized in the navel or left half of the abdomen. It is persistent and sometimes turns into spasms (when feces move). Feces hardened to a stone-like state damage the intestinal mucosa and “open the gate” for the introduction of pathological flora and intestinal inflammation (colitis).
An admixture of blood is found in the stool after defecation, which confirms vascular injury. Increased symptoms are provoked by eating, walking, and physical activity. Improvement occurs only after stool is removed.
Development of the disease in children
Dolichosigma of the intestine in a child is a problem that occurs in 25% of all children. The reason for this diagnosis may be various unfavorable factors that occurred during pregnancy.
The key symptoms include constipation, the frequency of which is increasing, pain during bowel movements, or severe pain in the abdomen. As for the stages of development of the disease, they follow the same algorithm as in the case of adults. During the period of compensated form, mild laxatives and a well-chosen diet are used for treatment. The subcompensated stage involves the use of cleansing enemas.
If the dolichosigma of the intestine in a child has turned into a decompensated form, then it makes sense to pay attention to a siphon enema. In order for children to be able to overcome this disease relatively easily, parents should ensure that they visit a doctor at the first stage of development of the pathology.
Relationship between symptoms and stage
Treatment of dolichosigma in adults begins with the doctor determining the degree of development of the disease. At each stage, the disease manifests itself differently:
At this stage, most patients are not even aware of their illness, since there are no complaints about their health. But when palpating, the specialist feels that the intestine is filled with solid contents. This stage is the easiest to treat; you just need to choose the right diet for the patient and take mild laxatives. In this case, the gastrointestinal tract will begin to function normally.
At this stage, constipation becomes longer lasting, so the use of laxatives does not have the desired effect unless additional cleansing enemas are used. Here the first signs of intoxication may be observed.
This degree occurs quite quickly, and the patient’s condition quickly deteriorates. The desire to eat disappears, while the patient suffers from a feeling of nausea and even vomiting. Constant headache, lethargy and weakness are observed, which may be signs of developing anemia. To cleanse the intestines, you have to use only siphon enemas.
Against the background of all the symptoms, the doctor prescribes a diagnosis, which includes several measures:
Even visually, a patient with dolichosigma is distinguished by low weight and pale skin. Also at the initial visit, the specialist performs palpation of the abdomen and a rectal examination. At the last examination it will be seen that, despite complaints of constipation, the rectum remains empty.
- The patient must undergo irrigography, which allows one to detect the number and degree of intestinal curls.
- Computed tomography provides very accurate results, allowing you to examine the mucous membrane of the large intestine. Using CT colonography, the doctor sees the presence or absence of space-occupying formations.
- With dolichosigma, it is important to determine the state of intestinal motility. For such purposes, electromyography and sphincterometry are performed.
And of course, feces must be submitted for testing. This allows you to identify the presence of bloody inclusions, dysbacteriosis and worms. At the same time, blood is also donated.
Based on the results of all the tests performed, the doctor draws up an overall picture and can already select a course of treatment for the disease.
Prevention
To prevent dolichosigma from reminding itself again, you should pay attention to the following preventive measures:
— vitamin therapy;
- drink plenty of water on a regular basis;
- use cellulose preparations;
- massage the abdomen (helps improve the passage of stool);
- diet.
You should also be attentive to the instructions drawn up by your doctor.
What is dolichosigma
This is a defect of the large intestine that causes its excessive mobility, as a result of which serious problems arise with the formation and passage of feces. The incidence of pathology in the adult population is quite high and amounts to 25%, although the real numbers are much higher. Reasons: difficulties in diagnosis and erased symptoms. In childhood, dolichosigma is found in 40% of cases associated with constipation.
Bottom line
Dolichosigma of the intestine, the symptoms of which are not so difficult to identify, is a disease to which you need to respond quickly. If the patient goes to the doctor without delay and undergoes treatment at the first stage, then the disease will not be difficult to overcome. In addition, you will not have to deal with dangerous complications.
The symptoms of dolichosigmoid intestines should not be taken lightly. This disease, if left untreated, can cause significant damage to health. Therefore, at the first signs of problems with the sigmoid colon, it is worth undergoing diagnostics and determining a treatment strategy (with the help of a specialist, of course). These measures, combined with proper nutrition, will help you forget about intestinal problems.
Forecast
If you follow the recommendations of a gastroenterologist, follow a diet and take medications prescribed by him, then at the initial stage of the disease you can achieve regular bowel movements. The prognosis in this case is favorable. It is important to follow a daily routine, eat right, and exercise.
The disease is not always a pathology leading to constipation. Many people live with this feature and do not have any problems with bowel movements. If alarming symptoms appear, it is important to consult a doctor immediately.
If the disease is ignored and no measures are taken, complications may develop. The patient develops constant constipation, which develops into intestinal obstruction. The stool hardens and fecal stones form.
These masses cannot leave the body on their own. Fermentation occurs in the intestines, and this in turn leads to the formation of toxic substances and intoxication of the body.
Advanced stages cannot be cured with medications. What does it mean? This means that the person needs surgery.
Surgical method of treatment
If everything goes according to the “knurled” rut, constipation progresses, complications increase and conservative methods do not bring results - the patient is prescribed surgical methods of treatment. One of the final arguments in favor of surgery is non-expanding loops of the sigmoid colon, which are a direct harbinger of intestinal obstruction.
Removal of part of the sigmoid colon
During the operation, excess loops and loops with impaired blood supply and innervation are removed. As a rule, the classic lower-median surgical approach is used. There are also endoscopic methods for removing dolichosigma loops, but this method has not shown significant advantages, since the operation is delayed and the likelihood of complications increases. This can be especially uncomfortable when dolichosigma is combined with adhesive disease in the pelvis in women.
Surgical methods for dolichosigma are performed under general anesthesia. Both spinal anesthesia and endotracheal or intravenous anesthesia are used. The duration of the operation usually does not exceed one and a half hours. The pathologically changed part of the intestine is removed, the abdominal wall is sutured. With modern materials and techniques, in most cases there is no cosmetic defect.
If the operation is not delayed, then the subsequent prognosis for patients with dolichosigma is quite favorable. If the instructions are followed during the postoperative period, the patient leaves the clinic healthy, with normal stools.
Drug treatment
Clinical guidelines for dolichosigma in children include:
- Herbal enemas, laxatives (increase stool volume), prokinetics, stool reducers.
- "Motilium". It speeds up the evacuation of the food bolus. It is prescribed for 2 weeks.
- If there is no effect from the diet, laxatives are used, and they start with minimal doses.
- Abdominal pain and gas formation are relieved with Dibazol and Prozerin injections. “Proserin” also increases the tone of the intestinal walls. The effect increases significantly if it is combined with electrical stimulation of the large intestine.
- Antispasmodics are ineffective, since pain is caused not by spasm, but by intestinal atony.
- An important step is to improve the intestinal microflora, for which pre- and probiotics are prescribed: Bifidumbacterin, Lactobacterin, Narine, Linex, etc.
- For drug treatment of intestinal dolichosigma in children, to improve well-being, the doctor prescribes Duphalac, Psyllium, Mucofalk (these preparations are made from the shell of plantain seeds), Duspatalin, and Festal. Their effect is multifaceted: increasing the tone of the intestinal wall, diluting stool, increasing intestinal motility.
The effect of treatment can be enhanced with herbal decoctions and infusions, but only after consultation with a doctor. Drugs are also used to reduce flatulence and reduce the smell of feces.
Stages of the disease, their manifestations
Gastroenterologists distinguish between forms of the disease or stages of the disease, since one form/stage can progress to another, more severe one. Each is characterized by symptoms of a certain intensity.
Compressed or initial (hidden) - usually patients are not aware of the existing intestinal pathology and do not feel any unusual manifestations. The only complaint is a tendency to constipation (no bowel movement for up to five days). During the examination, the doctor pays attention to the palpable solid intestine in the left iliac region. Switching to a diet and using mild laxatives helps normalize bowel movements.
Subcompensated - expressed in longer-term constipation, abdominal pain, bloating, lack of effect from laxatives, mandatory use of cleansing enemas. Patients develop signs of intoxication (weakness, headaches, irritability, insomnia, nausea).
Decompensated - the condition worsens, periodic vomiting is added to nausea and loss of appetite. Headaches become frequent, weakness is caused by the development of anemia. Skin manifestations in the form of increased pallor and the spread of pustules are added. Siphon enemas are used to cleanse the intestines. You can read about the characteristics of the disease in childhood in this article.
What complications does dolichosigma cause?
Stretching of the intestinal wall contributes to its thinning; rupture is possible with the release of feces into the abdominal cavity and peritonitis. Then the pains after sharp “dagger” pains develop into constant ones, spread throughout the entire abdomen, the temperature rises, blood pressure drops to the point of shock, and intoxication increases.
Dysbacteriosis causes irritable bowel syndrome and vitamin deficiencies. Anemia (anemia) develops in the absence of synthesis of essential vitamins in the intestines. Chronic colitis and acute intestinal obstruction appear - caused by fecal stones, kinks, and torsions of the elongated intestine.
Causes
Dolichosigma in adults and children can be congenital or acquired. Experts have not fully studied the factors behind the appearance of additional loops of the sigmoid colon during fetal development. However, there are some causes of the disease that affect the condition of this area of the intestine.
- bacterial, viral, infectious pathologies that befell women during pregnancy;
- unfavorable ecological environment where the pregnant woman lived;
- a woman’s use of certain medications that have a negative impact on the condition of the fetus;
- heredity.
- low physical activity, sedentary lifestyle;
- chronic gastrointestinal pathologies;
- increased nervousness, constant stress, depression;
- bad habits;
- age over 40 years and associated anomalies in the body;
- poor nutrition, increased consumption of carbohydrate foods.
The development of dolichosigma is not caused by an inflammatory process or infection. The initial signal may be long-term rotting, fermentation in the intestines.
Acquired dolichosigma rarely occurs in children. It often appears in patients over 45 years of age with a sedentary lifestyle. But dolichosigma and pregnancy are closely interrelated.
Symptoms and signs of dolichocolon
ICD-10 code-Q43.8
There may be no specific clinical manifestations of dolichocolon; some patients complain of the absence of bowel movements for up to three days. Constipation is an indirect sign of dolichocolon.
In this case, the accompanying symptoms are typical for stool retention:
• bloating; • increased gas formation; • pain and discomfort; • weakness; • loss of the normal reflex to spontaneous defecation.
When the intestinal mucosa is traumatized by solid feces, bloody discharge and mucus may appear.
The foul odor of stool may indicate an inflammatory process and dysbacteriosis. As with any disorder in the gastrointestinal tract, the condition of the skin, hair and nails worsens, bad breath and seizures appear. If left untreated, a variety of skin reactions occur, including allergic ones.
Many patients note an improvement in their well-being if they adhere to proper nutrition, regularly take laxatives, including for local treatment, and use cleansing enemas.
Constipation with dolichocolon is permanent and is sometimes diagnosed from early childhood. Some patients consult a doctor only after chronic constipation gives way to diarrhea and/or unstable stools, and there are complaints about deterioration in health associated with increased flatulence, bloating, and gas retention. When collecting anamnesis, the doctor always pays attention to the duration of the pathological process: a short history of the disease may indicate a tumor process in the intestine or a stricture of inflammatory origin. There are a number of predisposing factors:
• taking certain medications: anesthetics, antidepressants, muscle relaxants, narcotics; • injuries and operations on the intestines; • organic lesions of the central nervous system; • endocrinological pathology; • parasitic diseases (American trypanosomiasis); • abuse of cleansing enemas; • “hard” vegetarianism; • burdened heredity; • sedentary lifestyle; • concomitant pathology: hemorrhoids, varicose veins of the small pelvis, biliary dyskinesia, pancreatitis.
Diseases with which differential diagnosis is often carried out: megacolon, tumor, Hirschsprung's disease, ulcerative or pseudomembranous colitis.
Characteristic features of constipation:
• bowel movements less often than once every 3 days; • the need to strain; • hard stools or stools that resemble hard balls; • feeling of a foreign object in the rectum; • the need for additional measures for the act of defecation.
These signs must be present for 3 months out of 12, sequence and continuity are not taken into account. If the patient has two or more symptoms, it is reasonable to conduct an examination to exclude or confirm intestinal dolichocolon. An elongated colon and at least one confirmed episode of volvulus, intussusception or nodulation is assessed as complicated dolichocolon.
How to be treated without surgery?
At the stage of compensation and subcompensation, therapy involves a strict diet, massage, exercise therapy, and the use of folk recommendations.
Diet
Nutrition of a patient with intestinal dolichosigma requires:
- mandatory transition to frequent (fractional) meals in small portions (5–6 times a day);
- reduction in the diet of light carbohydrates (sweets, baked goods, wheat bread, pasta);
- increasing the proportion of fiber;
- limited meat consumption;
- refusal of millet and rice porridges that are difficult to digest in the intestines;
- daily provision of fluid of at least 1.5–2 liters, drinking warm mineral waters containing sulfur;
- prepare dishes only boiled or steamed; fried, smoked and spicy foods irritate the intestines, inhibit intestinal motility, and are poorly digested.
Disease in adults
Many experts believe that dolichosigma is a congenital defect, and digestive disorders can provoke the manifestation of clinical manifestations with existing anatomical prerequisites.
However, there is another opinion - that dolichosigma can be acquired. Most often, it is caused by fermentation and rotting processes in the intestines.
It occurs in people after 45-50 years of age in the presence of the following factors:
- lack of physical activity;
- sedentary work;
- an abundance of meat and carbohydrates in the diet;
- psycho-emotional tension, stress.
With dolichosigma (ICD-10 - Q43.8), dense feces of large diameter are formed. During its passage, the intestinal mucosa is injured, which causes pain and bleeding.
This causes a negative attitude towards defecation, which greatly complicates the clinical picture of the disease.
Typically, in adult patients, diet and drug therapy are ineffective due to intestinal insensitivity. In these cases, radical treatment is indicated - surgery.
✔ Algorithm for complex step-by-step conservative treatment of constipation in the Consilium System
Download the document now
Symptoms
Basically, the disease is noticed in early childhood; parents discover that the child has abnormal bowel movements, constipation, and hardening of the stool.
There are also some symptoms of intestinal dolichosigma in children and adults:
- periodic pain, cramps, flatulence in the abdomen;
- some stool particles are completely dry;
- bloating, rumbling;
- increased gas formation, distension;
- brittle nails and hair loss are noted;
- feces with a foul odor, sometimes with blood;
- nausea, vomiting;
- disorder of absorption processes, intestinal obstruction, resulting in poisoning;
- decreased appetite.
If the disease is not treated, the skin becomes pale, health worsens, drowsiness and lethargy appear. The tongue is covered with a white coating.
Complication
Under no circumstances should pathology be ignored, as it can cause unpleasant complications:
- intoxication of the body;
- Difficulties with emptying lead to stagnation of feces, rectal fissures;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- formation of fecal stones;
- weight loss;
- anemia of various forms;
- inflammatory, purulent rash on the skin;
- perforation;
- peritonitis.
The functioning of the intestines is disrupted, leading to discomfort and pain. Signs disappear when emptying occurs.
Causes of exacerbation
The main reasons for the formation of an elongated sigmoid colon in a patient include:
- Chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Lack of physical activity.
- Physiological changes of an age-related nature (occur after 40 years of age).
- Experienced neuroses and stress.
- Long-term use of pharmaceutical drugs that can change the structure or structure of a person's insides.
- Alcohol and nicotine abuse.
- Excessive consumption of carbohydrates against the background of a deficiency of other nutrients.
Cigarette abuse
Prevention and prognosis
You can avoid pathological elongation of the sigmoid colon by following these simple preventive recommendations:
- control over the course of pregnancy;
- rejection of bad habits;
- good nutrition;
- avoiding physical and emotional exhaustion;
- taking medications as prescribed by a doctor;
- strengthening the immune system;
- abdominal massage for children;
- maintaining an active lifestyle;
- body weight control;
- Regular visits to all clinicians for a complete preventive examination.
Symptoms and treatment dictate the outcome of the disease. The prognosis of dolichosigma is often favorable: with both conservative and surgical treatment, it is possible to achieve independent stool passage and a significant improvement in the quality of life.
In some situations, lifelong adherence to gentle nutrition is necessary for dolichosigma. The development of complications is not uncommon, but the consequences are easily eliminated with the help of medical intervention and do not pose a threat to human life.
Dolichosigma is a disease in which there is an increase in the size of the sigmoid colon and its mesentery. This is a fairly common pathology, occurring among both adults and children.
The condition can be either primary or secondary - the causes may differ slightly. The most common triggers are poor nutrition, sedentary lifestyle and stress.
In some cases, intestinal dolichosigma in a child or adult is completely asymptomatic, but more often causes unpleasant symptoms. The clinical picture is based on chronic defecation disorder, flatulence and recurrent abdominal pain.
Only instrumental examinations can confirm the presence of pathology, but the diagnostic process also includes laboratory tests and physical examination.
Treatment of dolichosigma in adults and children in most situations is performed using conservative methods. If the pathology leads to the development of complications, surgical intervention is necessary.
In the international classification of diseases, tenth revision, such a deviation in the structure of the intestine has a separate code. The ICD-10 code is Q43.8.
How are intestinal diseases diagnosed?
Diagnosis begins with an examination by a doctor. The doctor pays attention to the patient’s pale skin, nervousness, and bloating. Palpation reveals a painful compaction in the area of the sigmoid colon. It could be a fecal impaction or a tumor.
A rectal examination reveals an empty rectal ampulla. This means that there are reasons above that impede the passage of feces. X-ray examination is carried out by preliminary ingestion of a barium suspension or by direct injection of a contrast agent into the intestine with an enema (irrigoscopy).
Upon admission with a drink, the doctor on the first day has the opportunity to examine the esophagus, duodenum and stomach condition. On the second day, the contrast should fill the loops of the colon. Fluoroscopy reveals: intestinal prolapse (colonoptosis), contrast retention in the area of the descending and sigmoid intestines, additional loops and elongation of the sigmoid.
The doctor makes a differential diagnosis with another congenital anomaly - megacolon. The disease is accompanied by an enlargement of the entire large intestine with thickening of individual areas, which causes a narrowing of the passage.
Computed tomography makes it possible to determine not only the size and patency of the sigmoid colon, but also the condition of the mucous membrane, to distinguish dolichosigma from neoplasms and polyps that often affect this area. Ultrasound of the intestines reveals dense fecal stones, the method is not of great importance, since the picture is blurred due to a significant amount of gases.
For diagnosis, the following tests are important: blood - leukocytosis and ESR indicate inflammation, a decrease in red blood cells and hemoglobin - anemia, in a stool analysis it is important to identify hidden bleeding (Gregersen reaction), signs of parasites in the intestines, dysbiosis. Electromyography and sphincterometry are used to determine motor activity and the possibility of intestinal motility.
Diagnostic measures
The diagnosis of dolichosigma in children is made after a comprehensive examination of blood, stool, and instrumental research methods. First, a visual examination reveals the child’s underweight and pallor, peeling of the skin on the fingers due to vitamin deficiency.
On palpation it is felt that the abdomen is full in the loops. Digital examination shows that the rectum is empty.
Irrigography will help to identify the degree and number of loop curls and the sigma value. Additional loops can be in the form of a figure eight, snail, or knot.
CT is used for diagnosis in older children. This technique allows you to determine space-occupying formations. CT scans cannot be performed on young children due to their mobility.
Ultrasound, X-ray, irrigoscopy, colonoscopy, general and biochemical blood tests, stool analysis for worm eggs and the presence of hidden bleeding are also prescribed. On ultrasound, the intestine is clogged with dense feces. What do reviews say about the examination of dolichosigma in a child? Many parents worry that this procedure causes discomfort and pain to the baby. Many mothers categorically do not go for examination precisely because the child is simply unable to tolerate the procedures and is afraid. Others believe that the barium used for barium enema will cause infertility in the girl in the future. Some people consider taking barium disgusting; even an adult wouldn’t drink it.
All these fears are unfounded. Many people tolerate the procedure easily. Moreover, during a colonoscopy, for example, children are given a short anesthesia.
Dolichosigma
Dolichosigma is a congenital anomaly of the sigmoid colon, which is most often detected at an early age. The pathology leads to impaired motor activity and, as a result, constipation. Sometimes the symptoms of the disease do not appear even throughout life. The disease can begin to develop during fetal development.
The reason for this is genetic failures, taking certain medications, and maternal infections. Acquired dolisigma often occurs as a result of problems with the gastrointestinal tract. These may be putrefactive or fermentation processes. Stressful situations, a sedentary lifestyle, age-related changes, addiction to meat and carbohydrates - all this is fraught with the occurrence of dolichosigma. Abnormal development of sigma can sometimes be a variant of the norm.
Experts say that the anomaly may be neurogenic in nature. For example, if a person suppresses the reflex to defecate due to the inability to comfortably empty the intestines. This may occur among drivers or children who are afraid to ask to go to the toilet after class.
Important! Most patients are diagnosed with an asymptomatic form, so some experts regard the anomaly as a variant of the norm, and not a defect.
At the compensated stage of development, stool disturbances are not observed. Patients may suffer from vomiting, bloating and colicky pain. Subcompensation manifests itself in the form of constipation, which persists for several days. Painful attacks become more intense. With decompensation, disturbances in the motor function of the intestinal tract increase.
Patients experience the following symptoms:
Dolichosigma in children
- long-term constipation (the intestines are filled with a large amount of hard feces, which is visible during irrigoscopy);
- flatulence;
- spastic pain;
- against the background of coprostasis, loose stools may appear;
- painful act of defecation;
- the appearance of blood impurities in the stool;
- dry, coated tongue;
- irritability, insomnia;
- weakness, fatigue.
The first complaint of a child with dolichosigma is that it is difficult for them to go to the toilet. The problem can also arise in children under one year of age during the introduction of the first complementary foods. The baby cannot explain his symptoms, so it is difficult to get an accurate clinical picture. Parents should pay attention to how often their child has problems with bowel movements.
Severe forms of the disease can provoke retardation of the child’s growth, as well as physical and mental development. If constipation first bothers you from time to time, and then persists for a long period of time, this is a serious reason to contact a specialist and undergo a comprehensive examination.
Dolichosigma may be complicated by intestinal obstruction, volvulus, intussusception, or nodule formation. With the development of strangulation intestinal obstruction, the following symptoms occur: colicky abdominal pain, bloating, shock, lack of peristalsis.
The main diagnostic method of examination is radiography with contrast. The specialist conducts a differential analysis with diseases such as helminthiases, ulcerative colitis, neoplasms, and Crohn's disease. To exclude other pathologies, sigmoidoscopy, ultrasound, biopsy, and tomography may be required.
The basis of treatment is conservative treatment and diet. If an asymptomatic form is accidentally detected, preventive measures are prescribed to prevent constipation. If the disease causes clinical symptoms, drug treatment and physical therapy will be required. The selection of a therapeutic regimen is carried out based on the stage of the pathological process. In critical situations, surgical intervention is inevitable.
Dolichosigma affects the sigmoid colon
Drug therapy is aimed at timely bowel movements, as well as the elimination of flatulence and pain. In addition to laxatives, patients may be prescribed antispasmodics, analgesics, defoamers, and antidepressants. Physiotherapeutic procedures, such as acupuncture, electrical stimulation and laser therapy, will help improve peristalsis.
Surgical intervention is indicated in the following cases:
- ineffectiveness of conservative methods in the development of strangulation CI;
- recurrent complications leading to obstruction;
- transit disruption due to lack of results from drug therapy.
Patients are advised to eat fractional meals in small portions. It should be balanced in proteins, fats and carbohydrates. You should limit simple carbohydrates in your diet, these include sugar, rice, potatoes, and confectionery. It is better to replace them with complex carbohydrates, such as cereals, fruits and vegetables.
Do gymnastics, do exercises in the morning. Take more walks in the fresh air. Do not suppress the urge to defecate. If possible, avoid medications that can cause constipation. Get rid of bad habits, in particular smoking and addiction to alcohol.
Causes of occurrence and development of dolichosigma
Dolichosigma can be either congenital or acquired. What specifically affects the enlargement of the sigmoid colon is still unknown. There is an assumption that dolichosigma is transmitted from parents to children at the genetic level. There is also a theory that dolichosigma in children develops in the womb under the influence of infectious diseases that a pregnant woman suffers from, or under the influence of drugs that she took. Dolichosigma in children is usually congenital.
Acquired dolichosigma occurs in middle-aged people - from 45 to 55 years. This is due to the fact that by this age people begin to lead a sedentary lifestyle and often abuse meat products and foods rich in fast carbohydrates. These factors promote fermentation and putrefaction in the colon, which leads to enlargement of the sigmoid segment. Although there are experts who believe that in these cases, dolichosigma was congenital in the patient, but manifested itself only under the influence of age and these factors.
Currently, there is no clear answer to the question of the origin of dolichosigma or whether it should be recognized as an anomaly at all. It is known that more than 15% of children with dolichosigma live without experiencing any problems with the colon and its functionality. On the other hand, prolonged occurrence of dolichosigma causes inflammation on the inside of the intestine, which affects the entire functioning of the digestive system.
Special diet
It is necessary to ensure water and drinking regime. You should drink at least 10 glasses of water per day. Meals should be fractional - 5-6 times a day, in small portions, strict in time. Lemon water helps a lot as it loosens the stool. Meat is prohibited; a glass of 1% kefir is required.
Menu for a child with dolichosigma: more foods with fiber (berries, greens, fruits). They require heat treatment - boiling or steaming. Anything that is covered with an appetizing crust, as well as fried, smoked, and spicy, is excluded. Also contraindicated are dishes that slow down the movement of feces through the intestines - rice, semolina, millet, pasta, white bread, baked goods, cookies and cakes, coffee, cocoa, strong tea. Animal fats increase fermentation and are poorly digestible. Regarding chocolate: it can be given rarely, not an hour before or after meals.
You can give your child fish, cottage cheese, fermented milk products, buckwheat porridge, salads, and vegetarian soups. Bran is recommended; vegetables and fruits include beets, prunes, carrots, figs, pumpkin, baked apples, apricots, plums, dried apricots. Sweets include compotes, limited honey, marmalade (contains pectins).
Bananas, grapes and pears are excluded. Due to the limited choice of products, the diet for dolichosigma in children is supplemented with multivitamins containing C, A, E, group B, D. They will support the immune system.
Symptoms
The most specific symptom is that the elongated colon takes on an S-shape or forms several, less often, one loop. The specificity of the disease is that the symptom can only be detected during instrumental diagnostic examinations.
Symptoms of dolichocolon
As for external manifestations, the degree of the disease is dictated by several factors:
- length of elongation of the sigmoid colon or mesentery;
- level of disturbance of tone and peristalsis of the affected organ;
- adaptive reactions of the body.
The main symptom is problems with bowel movements (recurrent or prolonged constipation). The more severe the pathology, the longer the period of absence of spontaneous passage of feces will be.
Associated symptoms of dolichocolon-dolichosigma:
- pain in the abdominal area - the focus is located on the lower left side of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity or in the peri-umbilical area, in some cases the localization of pain remains uncertain;
- excessive gas formation and sweating;
- painful appearance - puffiness of the face and the appearance of dark “bags” under the eyes;
- rashes on the skin of unknown etiology of a purulent nature;
- bloating;
- attacks of nausea ending in vomiting that does not bring relief;
- loss of appetite or complete aversion to food;
- lethargy and weakness of the body;
- pale skin;
- decreased performance;
- dry tongue and white coating;
- increased fragility of nail plates and hair loss;
- bad breath;
- weight loss;
- formation of hemorrhoids of external or internal localization;
- Varicose veins;
- rumbling and seething in the stomach;
- anal fissures;
- the presence of pathological impurities in feces.
All symptoms of the disease are observed in both children and adults.
What is dolichocolon
Dolichocolon is a disease that is characterized by elongation of the entire large intestine or certain parts of it. It is diagnosed in both adults and children. The most characteristic symptom of the disease is prolonged constipation, but patients often do not pay attention to it and try to solve the problem on their own.
Dolichocolon is characterized by an increase in the length of the large intestine
When dolichocolon develops, medical attention is necessary, as the disease can lead to intestinal obstruction and even death.
As a rule, the pathology is considered congenital - approximately 30% of cases are diagnosed during the newborn period. However, there are hypotheses about the possible acquired nature of dolichocolon. Sometimes the disease is detected even in old age.
The clinical picture of this disease is due to the elongation of the large intestine, since due to the increase in the number of bends and loops, the passage of feces becomes difficult, resulting in constipation. As for the structure of intestinal tissues, with dolichocolon it remains unchanged.