The gallbladder is removed after the formation of many solid particles that clog the bile duct - common bile duct. Surgery does not always cure concomitant diseases. The operation saves a person’s life in severe and emergency cases. After the bladder is removed, the symptoms of the disease disappear, but the pathological condition and improper functioning of the organs remain. We have to resort to drug treatment. Only a doctor can tell you what medications to take after gallbladder removal. Self-medication will only complicate the situation.
Taking medications after gallbladder removal
Indications for use
Taking choleretic herbs is included in the treatment of many diseases. Among them:
- foci of inflammation of the gallbladder,
- pancreatitis,
- biliary tract dysfunction,
- cholecystectomy,
- cholestasis,
- the presence of parasites in the intestines.
Cholecystitis of the gallbladder is treated by collecting herbs with a choleretic effect. This disease is associated with the occurrence of foci of inflammation of the gallbladder. As a result, its work malfunctions, bile stagnation occurs and a pathogenic environment is formed. In addition to drug therapy, the specialist prescribes choleretic herbs for stagnation of bile.
When treating biliary dysfunction, herbs with a choleretic effect are also prescribed. This disease is associated with a disruption in the motor activity of the gallbladder and bile ducts, as a result of which bile ceases to be excreted normally. Herbs for liquefying bile can help the body free itself from bile stagnation.
Pancreatitis provokes inflammation of the pancreas. The substances it produces are not excreted into the intestines, but accumulate in the gland, gradually destroying it. Often this process is triggered by the entry of bile into the pancreatic duct. In this case, the use of phytohepatol is indicated to improve digestion processes and facilitate the functioning of the pancreas.
Before expelling bile stagnation from the ducts and expelling excess bile from the duodenum, it is necessary to coordinate treatment with a specialist who knows which medicinal herb effectively expels bile. After the cholecystectomy procedure, the functioning of the digestive organs is disrupted, which provokes stagnant bile flow in the liver. It stops working correctly. When the gallbladder is removed, normal functioning of the liver is ensured by herbs with a choleretic effect.
Valerian, coltsfoot, calendula, immortelle are choleretic herbs that are indicated in the absence of the gallbladder. They do not replace drug therapy, but are a good help in treatment, in addition to a special diet and taking antispasmodic drugs. After removal of the gallbladder, herbal infusions are taken in courses; the attending physician, based on the patient’s condition, determines which herbs can be drunk and the duration of their use.
With cholestasis, the liver is primarily affected, and its main function of producing bile is disrupted. It accumulates, resulting in the body being poisoned by toxins. Choleretic herbs for stagnation of bile in the gallbladder caused by cholestasis are aimed at activating the processes of cleansing the body of toxic substances.
When the intestines are colonized by parasites, bile stagnation is common. At the initial stage of treatment, bile ducts are used. You can use folk remedies to drive stagnant bile through the channels and expel parasites from the body. For this purpose, special fees are used, which are prescribed by the attending physician.
Among the contraindications to the use of choleretic preparations are stones, colic, inflammatory processes in the gallbladder, hepatitis, and pregnancy.
Antispasmodics
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P8ZDMezif4U
To relax the smooth muscles in the intestinal tract, doctors prescribe antispasmodics - No-shpa, Drotaverine, Meverberine, Duspalatin.
Such medications help get rid of spasms, colic, eliminate discomfort in the stomach and intestinal disorders.
No-spa is a strong antispasmodic agent that relaxes smooth muscles. Often, pain in the right hypochondrium after removal of the bladder occurs as a result of spasm of the bile ducts during the release of liquid secretions into the intestines. No-spa also relaxes the biliary sphincter, helping the release of fluid into the intestines.
Mebeverine or Duspatalin are drugs with myotropic action. Relaxes the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract. Completely disintegrate in the body. It relieves spasms and colic well, relieves abdominal discomfort and intestinal upset. They begin to act 20 minutes after taking the tablet. Reviews about the drugs are very positive. Adverse reactions occur extremely rarely.
Alternative choleretic agents
Herbs that our ancestors used even before the advent of special tablets can also be used as choleretic agents.
Corn silk
It is one of the most valuable herbal remedies for its effectiveness, helping to increase the flow of bile. At the same time, if stones have already formed in the body, then using decoctions based on corn silk is prohibited.
The product is prepared as follows:
- Pour boiling water over 3 teaspoons of stigmas;
- put the dish into which boiling water has been poured into a larger pan and turn on low heat on the stove, making sure that the liquid does not boil;
- wait 30 minutes;
- remove from heat, add boiled water in a 1 to 1 ratio.
You need to take ¼ cup before meals.
Attention! The decoction has contraindications, for example varicose veins or pregnancy. It is better to consult a doctor before use
Dandelion
Dandelion roots have a good choleretic effect. To prepare the decoction you need:
- prepare the roots of a dandelion that has not yet bloomed;
- chop them well;
- pour one tablespoon of roots with one glass of boiling water;
- keep the mixture on low heat for 15 minutes;
- remove from heat and cool for 45 minutes;
- strain.
Take half a glass of decoction 15 minutes before meals. You can drink the drink up to three times a day.
Immortelle
This plant is also widely used in folk medicine for problems with bile stagnation. In addition to the choleretic effect, immortelle has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects.
To prepare the decoction you need:
- pour one tablespoon of immortelle leaves with two hot water boiling water;
- boil for 10 minutes.
The infusion is taken half or ¼ glass three times a day. In this case, you need to drink it warm.
If you have hypertension or impaired gastric acidity, then the use of this folk remedy is contraindicated for you. Consult a doctor before using immortelle infusion.
Diet for gallbladder cholesterosis
The main condition of this diet is to limit the consumption of animal fats as much as possible and replace them with vegetable fats, which are necessary to stimulate metabolism in liver cells and reduce the risk of stone formation in the gall bladder.
During the postoperative period, patients can drink only non-carbonated mineral waters - Luzhanskaya, Morshchinskaya, Naftusya, Polyana Kvasova and Berezovskaya.
A large selection of plant-based preparations, as well as herbal remedies - pumpkin seeds, types of pectins in plant fiber, help make dietary nutrition much more effective.
The main condition of the diet is five warm meals a day every day in small doses.
Requirements for cooking: soups must be vegetarian, meat, fish, and poultry must be steamed. All products that have a choleretic effect should be strictly limited. This applies to black bread, vegetable oils, white cabbage, and eggs. In the postoperative period, under no circumstances can it be transmitted.
The main principle of such a diet is fractional nutrition. In other words, you need to eat little by little, but every three hours. Alcohol, fatty foods, fried foods, hot spices and carbonated drinks should be completely excluded from the diet. Also prohibited are: fresh baked goods, sorrel, spinach, ice cream, processed foods, fast food and black coffee.
The basis of the diet is porridge, boiled or steamed lean meat or fish, vegetable soups, non-acidic types of fruits and vegetables with a high fiber content. Taking recommended multivitamin complexes is also useful with such a diet.
This diet is called “Healing Table No. 5.” Its observance is recommended not only for elevated cholesterol levels in the gallbladder, but also for any pathologies of the biliary system, which is formed by internal organs such as the liver and gallbladder.
Preparations – enzymes
Preparations that contain enzymes that help break down substances in food. Patients who have undergone cholecystectomy are prescribed Festal and Mezim-Forte to compensate for insufficient bile production. The composition of these medications includes proteins, fats, enzymes and carbohydrates. When the biliary system functions properly, bile is released into the duodenum, which stimulates the synthesis of gastric juice.
The absence of a storage device has a bad effect on the secretion of bile by the hepatic system - synthesis occurs in insufficient quantities. In this case, enzyme therapy is necessary to compensate. One of the popular medicines is Creon, the unique composition of which distributes the active substances throughout the small intestine. Fats begin to be broken down more intensively, and proteins, carbohydrates and beneficial elements with vitamins from food are actively absorbed from food, the intestines begin to function correctly.
What medications to take
After removal of the affected gallbladder, a condition called postcholicystectomy syndrome develops. The first clinical sign of the condition is intense pain. To relieve it, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Antispasmodics with additional effects to improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, for example, Pirenzepine, Drotaverine, Pinaveria Bromide, Mebeverine.
- Anti-inflammatory medications for the relief of severe, acute pain. To improve digestive function and get rid of diarrhea, you will need to prescribe medications containing bile, bile acids, and digestive enzymes:
- "Allohol";
- "Ursofalk";
- "Liobil";
- "Omez";
- "Holenzym."
Tablets should be alternated with taking yoghurts and kefir enriched with bifidobacteria.
Certain cases require appointment:
- lactulose disaccharide – for the treatment of constipation;
- antidiarrheal and antimicrobial drugs for hologenic diarrhea;
- drugs "Simethicone", "Dimethicone" - for the treatment of flatulence;
- drugs "Domperidone" - to eliminate reverse peristalsis, associated nausea and vomiting;
- enterosorbent with lignin, activated carbon - for the treatment of severe intoxication;
- aluminum-containing and acid-neutralizing agents - for the treatment of heartburn and the elimination of pain syndromes, in particular after overeating.
How to treat bacterial overgrowth syndrome?
Almost half of patients with a removed bile organ experience aching pain. Other symptoms that are caused by laparoscopic manipulation may also occur. This is a bitter, bile taste in the mouth, bloating and severe flatulence, manifestations of dyspepsia and belching. The patient suffers from prolonged nausea.
This occurs due to the loss of bile's bactericidal effect. In the cavity of the duodenum, pathogenic microorganisms actively multiply, exceeding all normal indicators. In clinical practice, such conditions are called small intestinal bacterial overgrowth syndrome.
Read also: Is it possible to live without a gallbladder?
Treatment involves a course of Furazolidone or the antimicrobial Biseptol. Any antibiotics should be taken in combination with drugs that restore the microflora of the intestinal tract. It is forbidden to choose a drug on your own; there are specifics of use that only a doctor can tell you about. After a week's course of anti-microbial medications, Linex, Bifidobacterin or Bifidum are needed. You will also need complex vitamins.
Contraindications
As with any other medications, choleretic drugs may not be used by everyone. In some cases, they can only cause harm to the body. This occurs in the following diseases:
- acute pancreatitis and exacerbation of a chronic disease;
- cirrhosis, hepatitis and other diseases that damage the liver;
- gastritis and ulcers of the stomach, duodenum.
In these cases, the doctor must try other methods to improve the patient's condition after cholecystectomy, which are applied strictly individually based on test results and medical history.
Attention! Information about drugs and folk remedies is presented for informational purposes only. Under no circumstances should you use the medicine or give it to your loved ones without medical advice! Self-medication and uncontrolled use of drugs are dangerous for the development of complications and side effects! At the first signs of liver disease, you should consult a doctor
The use of site materials is permitted only with prior approval from the editor.
Duspatalin should not be taken if you are hypersensitive to mebeverine, the active substance. It is also not recommended for use by patients with allergies to components of the drug.
Pregnant women and during lactation should take the drug very carefully.
Like any other medicine, Odeston has its contraindications. This drug is not prescribed in the following cases:
- individual intolerance to its constituent components;
- obstruction of the bile ducts;
- in case of severe pathologies of the liver and kidneys, causing disruption of their functioning;
- stomach ulcer;
- duodenal ulcer;
- ulcerative colitis;
- if you have Crohn's disease;
- with hemophilia (disorder of normal blood clotting);
- during breastfeeding;
- if the patient is under 18 years of age.
- Acute renal and hepatic dysfunction.
- Blockage of the bile ducts.
- Cholelithiasis (formation of gallstones).
- Severe disturbances in the functioning of the liver and gall bladder.
- Individual intolerance to individual components.
You should avoid drinking alcoholic beverages during treatment with Hofitol.
The drug should be prescribed with caution to patients who have:
- alcohol addiction,
- epileptic disease,
- there is a TBI due to the presence of alcohol in the drug.
In the early stages of pregnancy, the medicine is prescribed to eliminate the symptoms of early hystosis. During late toxicosis, the drug is taken in combination with other medications. The dosage of the medicine is similar to that of an adult patient.
Surgery
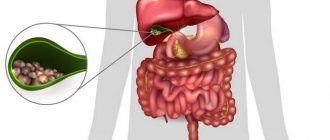
Gallstone disease is a common pathology of the digestive secretion organs. Gallstones are deposited for various reasons:
- genetic predisposition;
- stagnation of bile due to dyskinesia;
- bending of the main bile duct;
- errors in diet;
- obesity;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- toxic lesions.
In a patient with a tendency to form sediment in the gallbladder, it may gradually thicken, resulting in the formation of a gallstone. The chemical composition of stones depends on the salts that form them. The determining factors are the patient’s diet and the individual characteristics of his body.
The consistency of formations resembling stones can be dense or medium density. The softer the calculus, the easier it is to respond to cholelitic (stone-dissolving) drugs. You can drink these drugs only on the recommendation of a doctor and after establishing the density and composition of the stone-like formations that the gallbladder contains.
The doctor can make a decision to remove the gallbladder based on clinical indications, simultaneously comparing the patient’s individual data: age, degree of the process, concomitant diseases, lifestyle and range of professional activities of the person.
Removal of the bladder (cholecystectomy) is indicated for the development of the following conditions:
- inflammatory processes in the wall or excretory duct of the organ;
- gangrene;
- signs indicating compression of the main bile duct.
Surgery is performed in two ways: laparoscopic or conventional. The scale of the manipulation depends on the technical capabilities of the clinic, the condition and age of the patient, the neglect of the process, prospects for future life and the choice of the desired operation.
Laparoscopy involves removing the gallbladder through small punctures in the anterior abdominal wall without making an incision or damaging the muscles. This is a low-traumatic operation, which has a short rehabilitation period, is gentle on the patient and is as physiological as possible.
A conventional cholecystectomy involves removal of the organ with a full-scale incision in the abdominal wall and transverse dissection of the abdominal muscles in the area of the gallbladder. This operation is performed if laparoscopic equipment is not available, in emergency cases, when it is necessary to ensure the absence of peritonitis or complications from other organs.
The bladder removed during the operation is sent for histological examination in order to establish the condition of the wall, the etiology of inflammation, and confirm or refute tumor processes.
Contraindications for use
Choleretic drugs after removal of the gallbladder are a way to improve digestive processes and avoid dangerous complications. However, the instructions for use will necessarily contain a list of contraindications, including age-related ones. Herbal remedies are more gentle on the body, but before taking them you should also consult a specialist.
The most common contraindications with the use of choleretic agents:
- acute inflammation of the pancreas;
- severe liver pathologies;
- inflammatory and ulcerative processes in the stomach or intestines.
Recovery after cholecystectomy lasts at least 1-1.5 months
During this period, it is important to normalize the processes of digestion, production and outflow of bile. There is a huge selection of choleretic agents for different age groups on sale.
They are taken according to the instructions, observing the indicated dosages. However, treatment will be effective only in combination with a therapeutic diet and complete abstinence from prohibited foods.
For a person who has undergone cholecystectomy, life is divided into two stages. The first refers to the preoperative period, the second - after it. An operation is not prescribed out of nowhere; therefore, the final stage of the first period of life represented a certain kind of physical and psychological suffering associated with periodic pain, regular visits to the attending physician, doubts and worries about the upcoming surgical intervention. The postoperative period begins with the fact that “everything is already behind us,” and ahead is a rehabilitation period filled with some uncertainties. However, life after removal continues. The main task at this stage that worries the patient is the question of changes in the digestive process.
The gallbladder, as an organ, is endowed with certain functions. In it, like in a reservoir, bile accumulates and concentrates. It tends to maintain optimal pressure in the bile ducts. But with the diagnosis of calculous cholecystitis, or cholelithiasis, the functions of the gallbladder are already limited, and it practically does not take part in the digestive process.
Throughout the course of the disease, the body independently removes the gallbladder from the digestive processes. Using compensatory mechanisms, it fully adapts to new conditions under which the function of the gallbladder is already disabled. The function of secreting bile is performed by other organs. Therefore, removing an organ that has already been removed from its life cycle does not cause a serious blow to the body, since adaptation has already occurred. Through the operation, the organ that promotes the spread of infection and generates the inflammatory process is removed. In this case, the patient can only experience relief.
Prompt decision-making on the part of the patient about the upcoming operation largely contributes to the successful outcome of the surgical intervention and a short period of rehabilitation. By making a timely decision, the patient protects himself from complications that may occur as a result of delaying the timing of surgical intervention, calling into question the satisfactory condition of the patient in the postoperative period.
True, there are exceptions when the patient does not agree to undergo surgery for a long time, allowing the disease to affect the body for a long time. The inflammatory process spreading from the walls of the gallbladder can affect neighboring organs, causing complications that develop into concomitant diseases. As a rule, problems arise in the background in the form of peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, inflammation of the head of the pancreas, gastritis or colitis.
Patients with complications after gallbladder removal surgery require additional treatment after discharge from the hospital. The nature of the treatment and the duration of the procedures are prescribed by the patient’s doctor. The main issue facing both the group of operated patients without obvious signs of complications and the patients with complications is the nutrition process. The diet during the postoperative period is not strict, but excludes animal fats, which are difficult to digest by the body:
- lard
- fried lamb
- brisket.
Subject to a strict diet in the preoperative period, patients are allowed to gradually introduce new foods into the diet, excluding spicy canned food, strong tea, coffee, and the consumption of alcoholic beverages is strictly prohibited.
Herbs to stimulate bile release
These plants have a pronounced choleretic effect, which is actively used in traditional medicine. The effect of stimulating the movement of bile is achieved by increasing its production, relieving spasms, and increasing peristalsis of the common bile duct. For example, the herb milk thistle has a pronounced and confirmed effect; its use alleviates the condition of the patient after cholecystectomy. An excellent cleansing and choleretic result is obtained by taking remedies from this plant to prevent bile stagnation and the formation of stones.
The above herbal remedies are indicated both individually and in collections recommended for the treatment or prevention of pathologies of the biliary system. It is necessary to observe the correct proportions when preparing products such as decoctions and infusions from medicinal raw materials. More preferable for treatment and rehabilitation in the postoperative period are herbal mixtures, which consist of several choleretic herbs.
Experts recommend medicinal herbs to achieve a choleretic effect after removal of the gallbladder to almost all patients.
Choleretic fees
To achieve the best effect in herbal treatment, infusions are used. This is a mixture of plants whose action is aimed at achieving specific results. Can be used for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes. Available in bulk and as herbal tea. Choleretic preparations help to enhance the production of secretions, remove them into the intestines, disinfect the mucous membranes of the biliary apparatus, and relieve inflammation. They have an antitoxic, disinfecting effect. There are three different herbal mixtures. When choosing, it is necessary to take into account the individual tolerance of the components, purpose of use, contraindications. In pharmaceutical herbal preparations, the components are selected in such a way as not to harm the liver.
What should the diet be like?
After a person has his gallbladder removed, he will have to stick to a diet for the rest of his life. Now there is no reservoir for the accumulation of bile, and it collects only in the bile ducts. Therefore, it cannot be stored in large quantities and must be emptied more often. The first months after surgery are especially difficult. Then it becomes easier - the person gets used to his new diet.
Bile unloading occurs after every meal. Therefore, you need to eat small meals, at least 5 times a day. The more often the patient eats food, the less likely it is that bile will stagnate. If these recommendations are not followed, then stagnant bile will cause inflammatory processes in the bile ducts. And in the future this can lead to the formation of stones and surgical operations.
In addition, removal of the gallbladder leads to a decrease in the production of enzymes that help digest fats.
Therefore, it is important for patients to exclude from their diet foods containing animal fats. After removal of the gallbladder, it is not easy for a person to stick to a diet - he changes his previous lifestyle
Preparing food for patients with gallbladder removal
It is best to steam food. You can also boil the food and lightly bake it in the oven (without a hard crust). Frying food is strictly prohibited.
You should eat food 5–7 times a day, in small portions (200–400g). It's good if you train yourself to eat at the same time. It is better to eat warm food.
What foods can you eat?
After surgery, you should give preference to products that have a choleretic effect. Fermented milk products are perfect for light snacks and breakfasts. Low-fat cottage cheese, kefir, and yogurt are well absorbed and do not cause bile stagnation. As main dishes, you can have porridge cooked in water, vegetable soups.
You should not include soups with mushroom or fatty meat broth in your diet. Meat and fish should be chosen of low-fat varieties. It is better to eat meat dishes no more than one serving per day.
Sometimes you can do fasting days, giving up meat products and sweets. Hot spices, sauces, and various marinades are also prohibited. For dessert, it is useful to eat cottage cheese with the addition of sweet fruits and berries. It is allowed to eat marshmallows, marmalade, and jelly in small quantities.
It is better to quench your thirst with special herbal teas. It is also beneficial for the body to drink compotes made from fresh fruits. In the summer, you should eat melons and watermelons more often. The juice they contain has a beneficial effect on the flow of bile into the intestines. The daily diet should be varied and filled with vitamins and beneficial microelements.
What can't you eat?
First of all, you will have to remove foods containing refractory fats from your diet. Because they overload the liver.
In addition, after surgery you should not eat food that irritates the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract:
- Pickled, salted, pickled vegetables.
- Onion garlic.
- Parsley.
- Radish, radish.
- Spicy dishes.
- Sour berries and fruits.
- Canned food.
- Smoked products.
- Mushrooms.
- Sausages (sausages, wieners).
- Fatty meats (lamb, pork), lard.
In addition to junk food, you will have to give up some “healthy” foods.
Products containing large quantities of coarse fiber are also prohibited during the diet:
- Brown and wild rice.
- Bread with bran.
- Sprouted grain.
- Legumes (peas, beans, soybeans, lentils).
- Cabbage.
- Wholemeal baked goods
It should be remembered that drinks containing caffeine and alcohol are prohibited.