Colonoscopy. How often can I do it?
If there is a need for a medical examination of the colon, doctors use a special probe. Today, colonoscopy is considered the safest and most informative diagnostic method, identifying polyps, Crohn's disease, cancer, etc. Most patients are prescribed a procedure such as Colonoscopy. How often can the procedure be done is a question that concerns all patients. Doctors at our medical center in Moscow carry out a whole range of procedures that are necessary for the study of proctological diseases. Thanks to modern equipment and the skills of doctors, all manipulations are carried out at the highest level. Based on the results of the examination, doctors prescribe the correct therapy and monitor its progress.
List of contraindications
Absolute indications for intestinal colonoscopy:
- suspicion of a malignant tumor (colonoscopy allows you to take a sample for a biopsy);
- diagnosis of polyps (in the process you can excise them and do a biopsy for cancer cells);
- an admixture of blood in the stool (most likely, there is open bleeding);
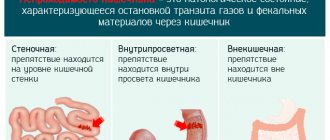
- frequent cases of complete disruption of the passage of contents through the intestines;
- suspected Crohn's disease;
- the presence of symptoms of nonspecific ulcerative colitis.
In addition, the following may serve as relative indications for examination of the colon:
- bowel dysfunction (persistent constipation or frequent diarrhea);
- low-grade fever, which appears several times a day for a long time without objective reasons;
- rapid weight loss with normal diet;
- a sharp decrease in hemoglobin;
- systematic abdominal pain.
Colonoscopy is performed to monitor the condition of the intestinal mucosa during the treatment of narrowing of the lumen, ulcerative colitis and intestinal obstruction due to the penetration of one part of the intestine into another.
First of all, colonoscopy is not performed against the will of the patient. He must voluntarily undergo such an examination, having familiarized himself with all possible risks. If the patient is categorically against such a diagnosis, then his opinion is taken into account and an attempt is made to find some alternative. All medical contraindications to colonoscopy are divided into absolute and relative.
Some conditions after colonoscopy can worsen so much that it will greatly affect the patient’s health, so they are considered absolute contraindications: purulent inflammation of the abdominal region (peritonitis), necrosis of the heart muscle against the background of an extensive infarction, a state of shock in which blood pressure is greatly reduced, rapid the increase and intensity of symptoms of colitis, perforation of the intestinal wall, in which its contents exit into the abdominal cavity.
Among the relative contraindications for colonoscopy are the following:
- intestinal bleeding (accumulation of blood in both the abdominal cavity and large intestine);
- recent abdominal surgery (risk of suture dehiscence);
- saccular protrusion of the wall of the large intestine (it is impossible to conduct an adequate examination);
- a hernia in the groin or navel, into which a loop of intestine may prolapse.
If the patient has ignored all the recommendations for preparation, then on the day of the scheduled procedure, the proctologist-diagnostician may refuse to perform it.
Colonoscopy can be prescribed in the postoperative period after removal of neoplasms of various nature and excision of adhesions.
The most serious and quite common complications after the colonoscopy procedure can be perforation of the intestinal wall or bleeding after excision of the polyp.
If the procedures are performed by a specialist who lacks experience and qualifications or the patient behaves inappropriately during the procedure, then perforation of the intestinal wall may occur. This involves the appearance of an opening through which intestinal contents leak into the abdominal cavity, which can lead to purulent peritonitis.
How can you check your intestines other than a colonoscopy?
If a patient encounters such a complication, he will experience the following symptoms:
- pain in the peritoneum, which becomes more intense during movement;
- the abdomen is swollen and upon visual examination its asymmetry is observed;
- nausea and vomiting;
- the heartbeat quickens, sticky cold sweat appears on the forehead;
- a febrile state appears.
Such a patient needs urgent hospitalization and emergency measures, since this condition can be fatal.
Bleeding
During the process of polypectomy (removal of a polyp), bleeding may occur. Pediatric and geriatric patients are at particular risk for this complication because they have the thinnest intestinal walls. This complication occurs, as a rule, against the background of incorrect manipulation - the loop electrode captures too deep layers of the intestinal wall.
Bleeding can begin either immediately after polyp removal or within 7–10 days after a therapeutic colonoscopy. To eliminate this complication the following measures can be taken:
- hemostatic drugs are used - tablets, suppositories, cold enemas (water temperature should be 3–4 °C);
- in severe cases, after bleeding has stopped, a blood transfusion may be performed;
- cleansing enemas to remove blood clots in the large intestine.
However, most often they resort to laparotomy, during which the peritoneum is cut and the resulting defect is sutured.
Other complications
There are other serious complications that occur extremely rarely: disorders of the respiratory system after using an incorrectly selected anesthesia, infection with syphilis, hepatitis B, C or HIV infection, rupture of the spleen.
Complications are eliminated with open surgery
Other unwanted side effects may also occur:
- flatulence after manipulation of forcing air into the intestines;
- inaccurate insertion of the colonoscope can cause mechanical trauma to the mucous membrane and associated pain (you can take analgesics orally, and lubricate the anal area with gel or ointment with an anesthetic);
- secondary diarrhea after the preparatory period for colonoscopy;
- spasms and aching pain in the intestines after polypectomy;
- low-grade fever.
If you undergo a colonoscopy in a trusted medical institution, then problems, as a rule, do not arise. If the patient worries too much about possible complications, then his pessimistic attitude will only worsen the picture. Most often, adverse consequences arise due to unscrupulous preparation of the patient himself. And if there are no serious contraindications for the procedure, then the patient will receive significantly more benefit from it than harm.
The controversial question “What is the best way to undergo a colonoscopy with or without anesthesia?” remains relevant, pain frightens many patients, they must make a decision and choose the type of anesthesia. After studying many sources, our journalists found that the majority choose colonoscopy through sedatives.
The option is very suitable for three reasons: it does not cause pain, intoxication and complications. As a result, this option is considered by a medical council, which takes into account the patient’s sensitivity to the drug, concomitant diseases of systems and organs (cardiovascular, endocrine, diabetes mellitus, tumors, central nervous system diseases) and the degree of gastrointestinal damage.
Colonoscopy is performed when:
- constant complaints of pain in the epigastric region of the abdomen; pain along the perimeter of segments of the large intestine;
- complaints of dyspeptic processes with the presence of pus and blood streaks in the stool;
- chronic constipation;
- the presence of fresh blood during bowel movements;
- specific stool for internal bleeding;
- constant urge to defecate;
- hemorrhoids;
- chronic anemia;
- poisoning;
- increased gas formation with dyspeptic symptoms;
- suspected malignant or benign tumors;
- sudden weight loss of unknown etiology;
- Crohn's disease;
- confirmation of the diagnosis and for the purpose of collecting histological materials;
- to exclude relapse of the disease.
After surgery to remove a colon tumor, it is recommended to perform a colonoscopy to rule out recurrence. If there have been incidents of intestinal cancer in the family, there is a need to be examined and undergo a hardware examination of the digestive organ to exclude pathology.
The procedure for examining segments of the colon through an endoscope has become the number one tool in making the correct diagnosis. But despite the positive side of the diagnostic method, there are contraindications for its implementation.
Colonoscopy is not recommended if:
- increased reactivity of the body to anesthetics;
- pathologies of the central nervous system;
- epilepsy;
- pernicious anemia;
- cardiovascular failure;
- suffered a heart attack or stroke;
- mitral valve insufficiency;
- urolithiasis;
- peritonitis;
- pregnancy.
Even with such contraindications, if there is a critical need, this procedure is performed. All stages are discussed in advance, and when it is performed, in addition to the endoscopist, several doctors are present (anesthesiologist, resuscitator, oncologist, surgeon). Considering the risks of the procedure, doctors are ready to provide specialized assistance in case of unforeseen circumstances such as bleeding, respiratory arrest, heart rhythm disturbances, perforation of the intestine due to ulcers, polyps or tumors.
How is the procedure carried out?
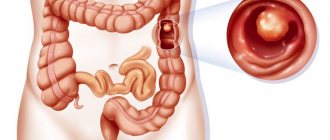
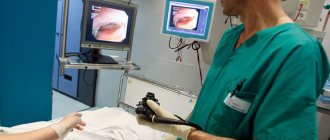
Colonoscopy is performed in clinics and diagnostic centers. Before the procedure begins, the person lies sideways on the couch. Then the doctor administers anesthesia, after which the patient quickly falls asleep and comes to his senses at the end of the process. To visualize the inner lining of the intestine, specialists use a probe. A colonoscope is a thin and elastic tube with a video camera at the end that transmits an image to a monitor. The device is inserted into the intestine through the anus and begins to move it to the junction of the large intestine and the small intestine. In general, the manipulation can take up to half an hour.
Prevention procedure
So, we told you what a Colonoscopy is. How often can this manipulation be done for preventive purposes? Every person is required to undergo examination once every five years. Bowel cancer kills a large percentage of people every year. Unlike other cancers, this disease develops quite slowly and is highly treatable at the initial stage. The risk of colon cancer increases markedly in those people whose immediate relatives also suffered from this disease.
How to prepare your body for a colonoscopy?
A special diet and cleansing manipulations for the intestines will help to properly prepare the intestines. Dietary nutrition involves completely abstaining from food about half a day before the procedure, as well as drinking large amounts of water. For the procedure to give maximum results, the intestines must be completely cleared of feces. For this purpose, a special solution is used that helps to liquefy the stool. In addition, abdominal pain and bloating occur.
Contraindications for the procedure
Despite the safety and low traumatic nature of the procedure, in some situations, colonoscopy is associated with a high risk of complications. The procedure is usually not prescribed to pregnant women, and is only permitted in cases where open bowel surgery is considered an alternative. Preventive colonoscopy is unacceptable during exacerbation of Crohn's disease or colitis, as well as in the situation of an attack of diverticulitis.
Is a colonoscopy painful and what are its complications?
Today, the procedure in most situations involves the use of a short-term procedure due to which the patient does not experience pain or discomfort. Even if no anesthesia is used, patients report a minimal feeling of discomfort. Colonoscopy extremely rarely provokes any complications, but these include:
• Intestinal puncture (less than 1% of situations), for the treatment of which emergency surgery is used. During the manipulation, the affected area of the organ is restored.
Signs of bowel cancer: tests and studies
Colon cancer is not a pimple, it never pops up right away! Its growth, for example from potentially dangerous polyps, usually takes about 10 years. Therefore, modern clinical practice is logically completely justified: regular colonoscopy, starting from the age of 50 years with a 5-year interval.
We look, if we find a suspicious polyp, we remove it. If we don’t find it, that’s good, we’ll see you in 5 years! This approach can reduce the risk of dying from colon cancer by almost 90%.
But we are afraid! “And you want to put this pipe in me?”, “What?! What 4 liters of laxative the day before?!” And the immortal: “What if they find something?!” Well, why are we doing this - to admire your intestines from the inside?!
Regarding “it hurts” and other things: today in many clinics you can undergo this procedure under anesthesia. An injection into a vein, the person falls asleep, after the procedure they wake him up, he opens his eyes and the usual question: “When will they start?!” And joyful surprise when he realizes that everything is already behind him.
Well, finally there is “virtual” computed tomography. There, no probe is inserted anymore, although no one has canceled the need for a large volume of laxative for thorough bowel preparation.
Pros: the opportunity not only to see the intestine from the inside, but also the tissues surrounding it (although this sometimes turns into a minus - the chance of findings of “unclear clinical significance” increases, entailing a cascade of other studies without a definite result).
Cons: if a polyp is discovered, there is no way to immediately remove it or take a biopsy; you still need to do a real colonoscopy. Therefore, this method is not for high-risk patients or those who have previously been diagnosed with polyps. But for most people, experts consider it quite acceptable to have a real colonoscopy initially at age 50 and then repeat a computer colonoscopy every 5 years. Well, then let’s look at the results.
For those who fly abroad for examination (our favorite destinations are Israel, Germany, Turkey, Switzerland): if you had a real colonoscopy and a polyp was removed, you should not take a return ticket earlier than 2 days later. The point is: that at the altitude at which passenger planes fly, there is rarefied air and pressure in the cabin (that’s why ink from fountain pens once spilled out in flight, staining your shirt - whoever is older remembers that flight attendants carried special plastic bags for pens).
The air that is pumped into the colon during a colonoscopy in order to straighten all the folds for better visibility partially remains inside for some time. It is he who inflates the intestine in flight. And the place where the polyp was removed the day before is a “weak link”, hence the possibility of intestinal rupture. So postpone your flight for a couple of days!
But the most common screening method is not a colonoscopy, but an annual stool occult blood test. Yes, the test is very nonspecific, its result can be influenced by many things, but it helps to identify that small amount of blood that accompanies the growth of a polyp or tumor. Since 2014, stool analysis to determine tumor DNA has also been introduced into practice (pure forensics!).
A common practice in America is for a patient to purchase a stool occult blood test strip, apply a piece of stool to it, seal it, and mail it to the laboratory. Very comfortably! By the way, you can also get tested for HIV: you run a test strip along the inside of your cheek, seal it and send it.
Anesthesia for intestinal colonoscopy: reviews
Today, the method of examining the intestines using a colonoscope is the most popular and widespread throughout the country, since it is this procedure that makes it possible to identify minor pathologies formed in the patient’s rectum. Before performing the procedure, the doctor should tell the patient about any risks and also prescribe medications to prepare the intestines for this process.
Both children and adults are allowed to undergo this examination, since the examination process itself is in most cases painless; in our country, painkillers are used extremely rarely, but there are also clinics that offer different methods of eliminating unpleasant sensations.
Anesthesia in our country is not used as often as in Western clinics, where doctors try to offer patients the most comfortable examination possible, because although colonoscopy is a simple procedure, it is very unpleasant, and in some situations even painful.
Many doctors believe that for the patient’s convenience, it is best to do a colonoscopy under special painkillers. But it is worth considering in what case anesthesia can be performed, and when this procedure is prohibited for a patient, and the patient should also know what risks are associated with anesthesia.
Preparation with the drug "Duphalac"
The purpose of colonoscopy is determined by the symptoms that the patient complains about, as well as to determine the results of therapy in people suffering from chronic diseases of the large intestine and rectum. Appointment cases may be as follows:
- painful sensations in the intestines of unknown etiology;
- lack of regular bowel movements and pain during bowel movements;
- suspected neoplasms in the colon or rectum;
- pouch-like protrusions of the walls of the colon (diverticulosis);
- inflammation of hemorrhoids;
- causeless change in stool (presence of pus, blood, black stool);
- benign growths or polyps in the rectum (rectal polyposis);
- Gregersen's reaction (stool test for occult blood) is positive.
Contraindications include:
- violation of the blood clotting process (hemophilia);
- low blood pressure (hypotension);
- acute period of chronic inflammation of the colon (colitis, enterocolitis);
- blood clots in the veins of the rectum (thrombosis);
- pathologies of the respiratory system.
You cannot undergo examination at elevated temperatures.
For the procedure to be successful, preliminary two-stage preparation is necessary. The first step is diet, the second is taking laxatives or enemas. 3-4 days before a colonoscopy, it is imperative to change your diet to the so-called slag-free diet. Products such as raw vegetables, fresh fruits, brown bread, sausages, nuts and chocolate, pickles and marinades are subject to exclusion.
It is important that the intestines are properly prepared
Alcohol and carbonated drinks are strictly contraindicated, as well as dishes that cause flatulence (pea soup, pearl barley porridge, etc.). The menu should consist of stewed vegetables, thin, non-rich soups, and fermented milk products. Boiled fish and lean meat are allowed. On the day of the procedure, you should refuse to eat.
On the eve of the colonoscopy, it is necessary to completely empty the intestines with the help of medications. When choosing a drug, you should consult a doctor, since all medications have contraindications. An alternative option may be a rectal cleansing enema. If you are prone to constipation, you need to combine both methods.
The examination consists of assessing the internal state of the final part of the digestive tract and large intestine. For more comfortable tolerance, local anesthetics are used or general anesthesia is injected.
Diet before colonoscopy
An endoscope (a long flexible tube) equipped with a video camera is inserted into the anus and slowly advanced down the rectum. During the process, air is supplied to expand the intestines.
The time range of the procedure is from 15 minutes to half an hour. If you experience discomfort after the procedure, you should take a sorbent agent and follow your previous diet for 2-3 days. Based on the results of the study, the patient is diagnosed and appropriate therapy is prescribed. Complications after the procedure are a tiny percentage. The most severe may be perforation (through disruption) of the intestinal wall.
Other undesirable consequences may include:
- excessively increased gas formation;
- pain in the anus;
- loose stool.
These symptoms are usually self-limited by the patient. If this cannot be done, you must seek medical help.
It is not the diagnostician who deciphers the results of the study, but the treating specialist.
How often an intestinal colonoscopy can be done depends on the stage of the disease. For people with chronic forms of disease, preventive examinations are prescribed every 3 years or every 5 years.
As a preventive measure, the doctor may prescribe the procedure for those who are at risk for the possible formation of cancerous tumors in the rectum. This group includes people with a family history of unfavorable cancer.
At the same time, a colonoscopy is prescribed once every 10 years if a relative was diagnosed with cancer at the age of 60. If the person was younger, the examination is carried out once at 5–6 years of age. As part of a set of diagnostic measures, the procedure is carried out once. In the absence of serious indications, colonoscopy is not prescribed.
There are many ways to cleanse the intestines. Although until recently there was only one - an enema. Many people still use this method to this day. How to prepare for an intestinal colonoscopy using an enema? To do this you need:
- On the eve of the examination at 19:00, give an enema using 1.5 liters of water.
- At 20 o'clock repeat the steps. Rinse until clear water comes out.
- On the day of the examination, at 7 o’clock, do a bowel cleansing with an enema. The volume of water, as in the evening, is one and a half liters.
- At 8 o'clock, repeat the procedure.
Before the evening cleansing enema, it is recommended to take 50 g of castor oil or 100 ml of a 25% solution of magnesium sulfate as a laxative at 16:00. However, such preparation for intestinal colonoscopy has significant disadvantages:
- An assistant is needed to hold a container of water and control its supply;
- the rectal mucosa may be damaged by the enema tip if the patient suffers from hemorrhoids or has cracks in the anus.
The only advantage of such cleansing is that it is cheap, the procedure costs nothing.
This gentle and effective laxative makes bowel movements easy. How to prepare for an intestinal colonoscopy using Duphalac? To do this, you must purchase a 200 ml bottle of the drug in advance. The medication should be taken before the day of the procedure, two hours after lunch.
To do this, the medicine is dissolved in two liters of plain water. The resulting solution is drunk in small sips over two or three hours. Colon cleansing begins 60 minutes after taking the medication and ends three hours after consuming the last portion. For the patient, this procedure is very comfortable.
For some diseases associated with the presence of blood in urine or chronic diarrhea, constipation, an intestinal colonoscopy is performed to make an accurate diagnosis. "Fortrans" is used to prepare for research. This laxative works only in the intestines and is excreted unchanged from the body. The package contains four fruit-flavored powders. To carry out cleansing you need:
- Calculate the required amount of medicine, taking into account that one powder is taken per 15–20 kg of weight and dissolved in a liter of water, which means that for a person weighing 80 kg, 4 liters of water and a package of powder will be required.
- Purchase the required amount of the drug from the pharmacy.
- Dissolve the powder in water.
- It is recommended to take the solution the day before the examination, it is recommended to start at 15:00. To do this, drink one glass of liquid every hour, or divide the solution equally into two parts. The first one should be drunk the day before, and the second one in the morning. The last portion must be consumed four hours before the examination.
Bowel movement occurs one and a half hours after taking the first portion, and the final one - in the form of clean water - two hours after the last dose. In this case, we can assume that the preparation for intestinal colonoscopy was successful. The advantages of the drug "Fortrans" are as follows:
- not absorbed into the intestinal and gastric mucosa;
- a large volume of liquid helps maintain water-salt balance;
- there is no need to resort to the help of strangers.
Flaws:
- not everyone likes the specific fruity taste;
- Nausea and vomiting are possible;
- you need to drink a lot of fluid, not every patient can do this;
- applies to persons over 15 years of age.
This drug, like the previous ones, is successfully used to cleanse the intestines. How to prepare for intestinal colonoscopy with Flit? It is consumed the day before the scheduled procedure, immediately after breakfast - 45 ml is diluted in 0.5 glasses of water and in the evening after meals in the same dose. When examined during the daytime, take another identical portion up to 8 hours. When using the drug, the following conditions must be met:
- breakfast and dinner should consist of water, of which you should drink at least a glass;
- for lunch - 750 ml of liquid in the form of broth, tea, water;
- After each dose of the drug, drink one to three glasses of water. The volume of liquid is not limited.
After starting to take the medicine, bowel movement occurs at the earliest after half an hour, and at the latest after six hours. Proper bowel cleansing for colonoscopy depends on following the instructions exactly.
All drugs containing macrogol act equally. Taste is very important for the patient in order to drink the right amount of solution when cleaning the intestines. This depends on the special qualities of the medicine, which are influenced by the amount of salts and flavorings. Endofalk does not contain bitter sodium sulfate, but it does contain a pleasant additive with the taste of passion fruit and orange.
How to prepare for an intestinal colonoscopy using this laxative? For normal bowel movements, it is enough to drink three, but for irregular bowel movements, four liters of solution will be required. For ease of use, the drug is available in several dosage forms. To prepare one liter of liquid, you will need to dissolve two sachets of Endofalk. The balanced and pleasant taste of this product will not cause any unpleasant moments.
There are several methods for making the correct diagnosis for gastrointestinal diseases, but colonoscopy and MRI are accurate and provide reliable information. Patients are often concerned about what to choose: MRI of the intestine or colonoscopy? The essence of the first method is to obtain detailed images as a result of passing magnetic fields through the organs being studied.
They allow you to identify areas of bleeding, inflammation, polyps, tumors. MRI is most often performed on the small intestine. The manipulation is completely painless and comfortable. Before scanning, do not eat for 11 hours before the procedure, empty your bladder and do not drink water 4 hours before the procedure.
The second method is carried out using a special device - a colonoscope, which consists of a tube with a video camera. It requires careful preparation - following a certain diet for a week and thoroughly cleansing the intestines with an enema or using laxatives. After completing the preparation for the procedure, intestinal colonoscopy is carried out not only with an examination of the intestinal mucosa, but also the polyps encountered are removed, and biomaterial is taken for microscopic examination.
Indications for the use of painkillers
Many patients would like to have a colonoscopy under anesthesia; reviews from patients who have already undergone this procedure vary greatly, so it is important to consider in what case there are indications for the use of anesthesia, as well as who is better off avoiding the use of painkillers altogether. To begin with, the indication for the use of drugs of this nature is the immediate desire of the patient, but not every clinic has special drugs for putting the patient under anesthesia. Still, there are certain rules when the doctor must perform the procedure only under anesthesia.
The patient is also indicated for anesthesia for adhesive disease; in this case, the patient is immersed in a short sleep during the procedure, so the procedure will be painless.
Adhesions do not allow the colonoscope to move normally through the intestine, which causes severe pain, but if the patient is under anesthesia, then his intestines relax, this allows the examination to be carried out faster and easier. A person necessarily falls asleep if he has mental illness, as well as with a low pain threshold.
WHAT TIME SHOULD I START A COLONOSCOPE FOR PREVENTIVE PURPOSES?
Even for prevention, different frequency of colonoscopy is allowed. It all depends on what health group a person is in for a given medical profile. So, someone who is hypothetically healthy, has no symptoms, no complaints, no heredity, will be able to visit a colonoproctologist every 5 years, upon reaching fifty years of age. If the person being examined has reason to be concerned, and there are blood relatives in the family with any problems in the form of intestinal cancer, then colonoscopy is performed not only annually, but even twice every year, with an interval of 6 months. The same applies to those people who have already encountered the formation of polyps or other difficulties in their own intestines.
Colonoscopy is not considered harmful, but its information content is invaluable in medical practice.
Rules for preparing for the administration of anesthesia
In fact, a good doctor will perform the procedure correctly and without anesthesia, but if the patient needs to receive pain relief, then he should know about some of the nuances of preparing his body for the administration of the drug; usually it will be enough that the patient has prepared his body for the examination.
But it is still recommended to consult an anesthesiologist so that he can assess the consequences and possible risks of this method of pain relief. During the conversation, the anesthesiologist must clarify the height and weight of his patient, find out about any types of concomitant diseases that have already been identified in the person. It is also important for the specialist to know about any types of allergic reactions to medications or household chemicals, and the number of types of anesthesia the patient has suffered throughout his life. Already before the procedure the day before, the doctor must measure the patient’s blood pressure, the number of heart beats per minute, as well as the patient’s breathing rate.
To begin with, the patient needs to take certain types of medications to help the patient calm down faster; children are simply given tablets with water, while adults are given injections that are given thirty minutes before the administration of anesthesia. The calmer the patient is before the anesthesia is administered, the less medicine will be needed to put the person into a state of anesthesia.
What types of anesthesia can be used during a colonoscopy?
The doctor will choose which anesthesia is best to use; the anesthesiologist must rely on clinical information about the patient, as well as his immediate health condition. There are several types of pain relief, which will be discussed in more detail in this article below.
The first thing worth talking about is superficial anesthesia (sedation), for this the doctor simply injects special drugs into the blood that help slow down the functioning of the human nervous system, which allows the procedure to be carried out painlessly. In most cases, such drugs do not make the patient fall asleep, but due to the relief of nervous tension, the muscles relax, making the examination process almost painless. This method of pain relief is good because the doctor can add a dose of medication, thus transforming superficial anesthesia into full anesthesia, then the patient falls asleep and wakes up some time after the procedure.
There is another method of pain relief, in this case the doctor uses intravenous anesthesia, the anesthesiologist administers drugs such as propofol or diprivan, which help the patient fall into a sound sleep. If the patient’s pain threshold is too low, then drugs containing narcotic substances are added to these medications.
Well, the last method of anesthesia is called inhalation; doctors consider this method of pain relief to be the safest for human health, but most often they use it to induce anesthesia in a child. The baby needs to breathe air from the mask for a few seconds; only six breaths are enough for the patient to fall asleep soundly.
WHO NEEDS ADDITIONAL INVESTIGATION?
When diagnosing a number of diseases, it is necessary to visit the endoscopic diagnostic room even more often than once every six months. Although this option is considered optimal, some people, regardless of age, have to prepare regularly every 60 to 90 days. This is possible, for example, during the initial diagnosis of ulcerative colitis. However, the decision is made solely by the doctor treating a particular patient.
In the presence of diverticulosis on the intestinal walls, colonoscopy is carried out with strict regularity. This should be observed because food deposits accumulate in the resulting intestinal pocket, which can cause an inflammatory process.
What are the benefits of anesthesia during an examination?
Many doctors say that it is much easier to perform a colonoscopy under anesthesia, especially for children, because anesthesia makes it possible to completely eliminate the pain of the procedure, the patient will not have to experience discomfort, and after the procedure the person will not feel any pain.
Also, putting the patient into deep sleep makes it possible to shorten the examination time, since the doctor does not need to persuade the patient to be patient a little longer; the doctor can calmly examine any pathologies in the intestines. In childhood, a fear of doctors often develops, since pediatric procedures are often performed without anesthesia, which means that the baby may feel pain. If the child is given anesthesia, then he will not experience pain, which will help avoid fear of doctors in the future. In addition, pain relief makes it possible to do the procedure more than once, if necessary. And the risks after such an examination are significantly reduced, because the intestines are relaxed, which means it will be easier for the device to pass through the rectum, which makes it possible to reduce the number of injuries and complications.
Typical consequences and complications
Complex endoscopic examination, in some cases, does not pass without consequences, which include:
- bloating due to residual air forced into the intestines;
- pain and spasmodic contractions after removal of growths and tumors;
- headache;
- an unpleasant feeling of discomfort in the epigastrium;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- temperature increase;
- painful sensations due to minor damage to the mucous membrane as a result of inaccurate insertion of the endoscope.
In addition, a colonoscopy examination can cause serious complications:
- Violation of the integrity of the intestinal walls (perforation). The contents of the intestine leak into the abdominal cavity and can lead to purulent inflammation. Deterioration of the condition after the examination is a signal for immediate consultation with a doctor.
- The appearance of bleeding. After a therapeutic colonoscopy to remove growths and tumors, the patient may bleed. Children and the elderly are primarily at risk due to thin intestinal walls. Bleeding may begin immediately or 5–7 days after the procedure.
In very rare cases it is possible:
- dysfunction of the respiratory system due to improper anesthesia;
- infection with various diseases (HIV, hepatitis);
- splenic rupture.
To avoid complications during colonoscopy, you must follow your doctor’s instructions and choose a trusted medical facility.
What are the possible complications after anesthesia?
Many patients are very concerned about whether any complications may occur after or during anesthesia, and whether the anesthesia may have dangerous consequences for their health. In fact, fears are not in vain, since anesthesia, like any other type of medical procedure, can lead to certain complications. Still, if the patient contacts an anesthesiologist and tells him the most detailed information about his health, then the risk of complications will be minimized. It is very important to prepare for the procedure as advised by the doctor; also, you should not hide from the specialist chronic or acute diseases that the patient has at this time.
Some patients are very wary of this type of pain relief, as they have read that drugs can affect a person’s psyche and memory, but in fact this is not true, since modern drugs do not cause harm to health. All these stories are related to old drugs that were used a few years ago, they were indeed quite dangerous, but today modern medicine has improved the drugs.
Still, it is worth saying that there is a resuscitation kit in every office for a reason; in some cases, patients do not mention heart or lung diseases, and this leads to disastrous consequences.
Colonoscopy does NOT prevent cancer
Data from the American Cancer Society through 2009 states: “…there are no randomized controlled trials examining the effect of screening colonoscopy in reducing colorectal cancer incidence or deaths.”
Quoting from a 2006 New York Times article: “In all studies, patients had at least one adenoma detected during colonoscopy, but they did not have cancer. However, these people developed cancer within a few years, at the same rate as the average statistics dictate, and without screening colonoscopy.”
Another study published in 2006 found that patients in the study who were scanned developed colorectal cancer over the next few years without screening, “in line with the population average as shown by statistics.” , despite the fact that all detected polyps were removed.