Characteristics of the disease
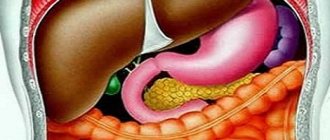
The causative agent of opisthorchiasis is the cat fluke, which lives in the liver, bile ducts and gall bladder. Helminths of this species infect both animals and humans.
The life cycle of the fluke is quite complex: the eggs of the parasite fall from the feces into fresh water bodies, where they penetrate the body of the snail. There, the larvae hatch from them - opisthorchis. These creatures return to the water and enter the body of the fish.
Parasites infect a child’s body when eating poorly cooked fish. Carriers of this type of helminths are different types of carp:
- chebak;
- bream;
- rudd;
- carp;
- ide.
An infected person spreads helminths.
Opisthorchises negatively affect the mucous membranes of the bile ducts, disrupting the normal flow of bile. Thanks to their activity, cystic formations begin to form in the liver. Helminths poison the entire body with toxins. The size of adult parasites is about 1 cm.
In Russia, the largest number of sick children is observed in Western and Eastern Siberia. Fish that is found in the Ob, Volga, Irtysh, Dnieper and their tributaries carries a risk of infection.
What is opisthorchiasis
Opisthorchiasis is a difficult parasitic disease (a group of helminthiases) that affects the liver and pancreas. In the complicated form, almost all important organs of the body are affected. Trematodes (opisthorchid) are small worms up to 2 cm long and up to 0.2 cm wide, which have spines and suckers on their body, which are very harmful to internal organs. Opisthorchiasis – symptoms in a person may reappear, but then the disease is difficult to treat, and the patient’s recovery is much longer and more difficult.
Path of infection with opisthorchiasis
Often, people living in a certain region who have traditions associated with eating raw, poorly fried or salted fish become infected. The path of infection with opisthorchiasis is a vicious circle, which consists of 4 stages. From the human body, opisthorchis eggs, along with feces, end up in the water, then are eaten by mollusks, which feed fish. The last stage is the acquisition of a new owner (it can be a person, a dog, a cat). Essentially, the helminth chooses shellfish and fish as a means of transportation.
Life cycle of the cat fluke
Cat fluke is a parasite that is found in cats, but humans cannot become infected from a pet, only from fish or crayfish. The life cycle of the cat fluke begins with the release of the egg from the host's body (in the feces). These eggs are swallowed by mollusks, become larvae and within 2 months turn into a cercaria (active larva). This form of larval development helps the fish enter the body, where it forms cysts in the subcutaneous layer of fat and muscles.
What fish have opisthorchiasis?
Even before the human body or other mammal, the worms change two temporary (intermediate) hosts - a mollusk and a fish (bream, roach, carp). The peculiarities of the physiological structure and processes in the organisms of fish of the carp family allow opisthorchiasis larvae to gain a foothold, therefore fish from freshwater rivers of Siberia and other regions can be a source of infection with helminthic infestation (opisthorchiasis disease). Opisthorchiasis occurs in fish passing through freshwater bodies of water, stopping there only for the spawning period.
Which fish does not have opisthorchiasis?
According to the latest data from laboratory tests of freshwater fish, almost every species is a carrier of helminths. Opisthorchiasis does not occur in sea fish: too salty an environment does not allow the fluke larvae to survive. There is an opinion that there is no opisthorchis in predatory fish, but in practice, helminth eggs can be found in pike perch, perch and pike. To protect yourself from infection with such a parasite, you need to monitor high-quality heat treatment and timely prevent the disease.
Symptoms of the disease in children
In children infected with opisthorchiasis, the disease at the initial stage occurs with mild symptoms. The acute form of the disease begins to manifest itself more clearly. Doctors distinguish several variants of opisthorchiasis:
- cholangitis (bile ducts are infected);
- hepatocholangitic (liver is affected);
- typhus-like (pathological changes occur in the myocardium);
- bronchopulmonary (respiratory disorder).
Opisthorchiasis in a child occurs in the following forms:
- chronic can proceed sluggishly for several years;
- the acute form has pronounced symptoms and lasts from one week to a couple of months.
The disease manifests itself most clearly in children of primary school age. Symptoms of opisthorchiasis in children are as follows:
- pain under the right rib;
- diarrhea;
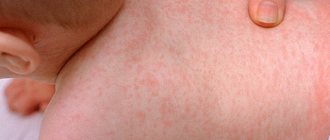
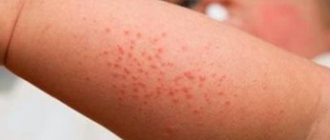
- skin rash;
- catarrh of the respiratory tract;
- temperature increase;
- increase in liver mass.
Opisthorchiasis in children occurs at a slow pace. If the disease is not treated, it will negatively affect the development of the baby.
Children over 7 years of age experience the disease more severely . It is accompanied by a fever and a skin rash. Exacerbations in the form of pneumonia, heart disease, and hepatitis may occur. A child suffering from opisthorchiasis begins to develop poorly physically, has poor appetite, and often develops an apathetic state.
In older children, the immune system is more developed, and antigens against parasites are produced more actively. Therefore, adolescents over 15 years of age tolerate the disease more easily. But this does not mean that the disease does not require treatment - even without a clear clinical manifestation, opisthorchiasis is dangerous. If left untreated, it leads to liver cirrhosis, peritonitis, and in rare cases can cause pancreatic cancer.
Pathogenesis
Opisthorchis felineus
Pathogenesis is based on the mechanical and toxic effects of parasites on the host body.
Opisthorchids cause great damage to the walls of the bile ducts during fixation and movement. Using suction cups, they draw the mucous membrane into the cavity and pinch it, which leads to impaired blood circulation and sometimes the integrity of the tissue. Young parasites cause additional damage with cuticular spines. In addition, large accumulations of parasites, their eggs and desquamated epithelium create obstacles to the flow of bile and pancreatic secretions, which leads to a slowdown and cessation of fluid flow. This may cause cystic dilatation of the bile ducts. Stagnation of bile provoked by the parasite is a favorable condition for the development of infection. Infectious agents can penetrate the bile ducts from the intestine, which is facilitated by the colonization of its upper sections by bacteria as a result of achylia, which often develops with opisthorchiasis. In addition, with repeated infections with opisthorchiasis, young opisthorchiasis, penetrating through the common bile duct into the bile ducts, introduce infection into them. Finally, the infectious agent can enter the bile ducts through the hematogenous route. As a result of the described processes, purulent cholangitis is sometimes observed in opisthorchiasis.
Metabolic products of parasites, released directly into the host’s body, cause its sensitization and the development of allergies, for example, with opisthorchiasis, skin dermatitis may periodically appear, affecting the face. If left untreated, long-term opisthorchiasis can lead to the development of cholangiocarcinoma, which is associated with the mutagenic effect of the pathogen and its ability to cause proliferation of the epithelium of the bile ducts and oval cells (see liver). O. viverrini
included in the IARC category 1 carcinogen list.
The course of the disease is significantly influenced by genetic factors. For example, in people with the third blood group, diffuse liver damage is often detected, and in people with the first, erosive and ulcerative gastroduodenitis.
Diagnostics
The childhood variant of opisthorchiasis is difficult to diagnose at the initial stage. With opisthorchiasis in children, symptoms at the initial stage are mild. Only a month after infection, signs of the disease become more noticeable. During this period, the worms reach their full development and begin to lay eggs.
The most informative method for diagnosing the disease is duodenal intubation, which will need to be done twice at an early stage of infection. Gastric juice, pancreatic secretions, and duodenum are taken for testing.
In addition, X-ray results, cholecystography, gastroscopy and ultrasound will be required to determine the exact location where the parasites have settled. A stool analysis will be informative only if opisthorchiasis has sufficiently developed in the human body and the parasites have begun to lay eggs.
A blood test includes several types of examination:
- general analysis;
- sugar test;
- examination of liver and enzyme insufficiency.
Opisthorchiasis should be distinguished from diseases such as:
- acute respiratory infections;
- viral hepatitis;
- pneumonia;
- other helminthic infestations of the liver.
After confirming the diagnosis, it is necessary to proceed to treatment.
Treatment
Opisthorchiasis is the cause of the development of diseases that disrupt the activity of the pancreas and liver. To avoid complications, it is necessary to treat the disease in a timely manner. To do this, you need to see a doctor - only a specialist will tell you how to treat opisthorchiasis.
Treatment of opisthorchiasis in children includes drugs of different spectrum of action. Doctors prescribe the following medications:
- anthelmintics;
- choleretic;
- antihistamines;
- immunomodulatory;
- regenerating liver cells.
Medicines should be taken according to a schedule drawn up by a specialist, which depends on the complexity of the disease. The duration of treatment is from two to four months.
The basic treatment regimen is as follows.
- In the acute stage of childhood opisthorchiasis, the main actions are aimed at eliminating the fever. First of all, it is necessary to relieve the allergic reaction. For this purpose, the child is prescribed anti-allergy drugs.
- The next step is to eliminate worms - the child is prescribed antihelminthic drugs.
- During treatment you need to follow a special diet. Spicy, sweet, fatty foods are removed from the diet. To restore the body, children are prescribed vitamins.
Throughout the entire therapeutic course, doctors monitor its progress and effectiveness, so children undergo regular tests. Even after treatment is completed, clinical observation will be required for another three years to prevent the infection from reoccurring.
Possible complications
Opisthorchiasis in a child is dangerous because it provokes the development of serious complications. Among them are:
- pathologies of the liver and other organs of the digestive system (hepatitis, peritonitis);
- abscess;
- allergic reactions, among which a high risk is Quincke's edema, which inhibits the functioning of the central nervous system;
- bronchial asthma.
If a parasitic infection is detected in a timely manner, the prognosis for the disease is favorable. Therefore, attention to changing the child’s behavior and condition is important. If your health worsens, you should call a doctor at home.
Traditional medicine
Traditional medicine methods can be included in the treatment plan for opisthorchiasis, but only as an additional treatment.
An effective anthelmintic agent is prepared from aspen bark:
- aspen bark is crushed;
- take 9 tbsp. spoons of raw materials and pour a liter of boiling water;
- the resulting liquid is put on fire and boiled for half an hour;
- Remove the broth from the heat and leave for another 30 minutes.
A decoction of aspen bark is taken one tablespoon three times a day.
Diet
Diet is a prerequisite for the treatment of opisthorchiasis in children. Meals should not be plentiful; it is advisable to feed the child little by little, but more often.
Fried and fatty foods are completely eliminated from the children's menu. It is better to bake or boil food, preferably steamed. It is undesirable to consume mushrooms, legumes, garlic, and radishes. The daily norm should not exceed 2900 kcal.
List of products that must be included in the diet:
- vegetable dishes;
- milk soups;
- lean meat;
- Rye bread;
- porridge (oatmeal, rice, buckwheat);
- lean fish;
- fruits.
Signs of the chronic stage
The chronic stage of the disease is different:
- incessant, paroxysmal pain from the right hypochondrium;
- dyspepsia, characterized by frequent constipation or, on the contrary, loose stools;
- painful sensations in the gallbladder area;
- constant fatigue, the child cannot run and jump for a long time;
- poor sleep;
- tremor of the limbs;
- signs of food allergies;
- rashes on the skin accompanied by itching.
Treatment of opisthorchiasis should begin immediately after the first symptoms of opisthorchiasis (also called Siberian fluke) appear in children . Delay in this matter is fraught with the most serious consequences for the child’s health.
Disease prognosis
If you notice that your child has suspicious symptoms, you should consult a doctor. Many parents are concerned about which doctors treat worms. In any case, you should first contact your pediatrician. Next, you will need to visit specialized specialists - a parasitologist and gastroenterologist.
Timely consultation with a doctor improves the prognosis of the disease. The earlier it is started, the less damage the liver will suffer.
Severe stages of the disease will need to be treated in a hospital, but mild forms of the disease can be treated at home. It is important to avoid self-medication - only an experienced doctor, based on diagnostic indicators, will be able to prescribe a course of therapy for the child.
Prevention
To prevent the development of the disease, you need to follow a few simple rules, the main one of which is thorough heat treatment of the fish. This means that it must be thoroughly boiled and fried before use. It is unacceptable to eat half-raw fish.
You should not give your child poorly salted fish. In large salted fish, parasite larvae can exist for two weeks, in small salted fish - 5 days. These data should be taken into account when salting fish and keep it in brine for at least the prescribed period. Cold smoked fish is also dangerous - the cold smoking method does not kill worm larvae. And the greatest danger is stroganina. It is necessary not to forget about the rules of culinary processing of fish - this is the only way to avoid infection.
Kitchen utensils used to cut fish must be carefully cleaned after use.
There is no need to cut bread, vegetables and fruits with a fish knife. The same goes for cutting boards. Hands should be washed well with soap after raw fish.
To prevent a child from becoming infected, it is necessary to follow preventive measures and know what the symptoms and treatment are for opisthorchiasis in children. You cannot let the disease progress and self-medicate.
Causes and routes of infection
Opisthorchiasis is not transmitted by contact with an infected person or animal; the disease is spread in the following ways:
- When eating sick fish. Residents of Russia become infected with worms from representatives of the carp family: bream, roach, ide, carp, crucian carp. Infection occurs due to eating raw or insufficiently cooked fish.
- There is a widespread belief that there is a danger of infection while cleaning fish if the rather hard scales injure the skin. This version remains unproven.
Some ordinary people believe that infection can occur in utero from mother to child, but is this true? The answer is clear: no. On the contrary, it is not the worms themselves that are transmitted from a sick mother to the fetus, but antigens that develop immunity to parasites. In addition to the intrauterine method, a mother can pass on immunity to her baby through breast milk.
A sick mother has a risk of harming her child. Due to the impossibility of treatment during pregnancy and lactation, the fetus may develop hypoxia, which threatens the future baby with many complications after birth. Opisthorchiasis reduces labor, so hypoxia may begin during childbirth.
READ ALSO: treatment of hypoxia in newborns: effective means