Home / Parasites
Back
Published: 10/09/2019
Reading time: 13 min
4
13770
A person may develop parasites in the intestines, the symptoms of which manifest themselves in the form of diarrhea, abdominal pain and other unpleasant phenomena. Parasites in the intestine can colonize any part of it: small, thick, cecum, rectum. The article presents photos of common intestinal parasites and recommendations for the treatment of parasitic diseases.
Parasites belonging to various biological species, classes and even types can live inside the human body: protozoa, helminths, bacteria, microscopic fungi.
Some of them are useful for humans. These are lactobacilli and similar microorganisms that make up the normal microflora of the intestines and genitourinary tract.
Others simply live on the surface of the human body and in internal organs, without causing harm to human health - this is a mutually harmless cohabitation.
Parasites are another matter. Unlike beneficial “tenants” and harmless, albeit useless, “cohabitants,” parasites cause direct harm to humans - they poison a person with secretions, feed on organs and tissues, and sometimes directly kill in order to make the host’s body food for predators in which the parasite can continue the life cycle.
Parasites are able to live in tissues, fluids, bones and any internal organs of the host, including the spinal cord and eyeballs.
The habitat of many parasites is the human intestine. The “freeloaders” who have settled in it feed on chyme (a mixture of semi-digested food, bile and gastric juice entering the small intestine), feces or blood.
Parasites from the following biological groups can live in the human intestine:
Author:
Mironova Elena
Didn't understand the article or need help? Ask a question now and get an answer.
auto RU
- protozoa;
- helminths (worms).
Parasitic protozoa and helminths cause life-threatening diseases: amoebic dysentery, toxoplasmosis and many others. It is important to prevent parasites from entering the intestines, and to do this you need to know the ways they enter the body. In addition, it is useful for any person to know the symptoms by which one can determine that parasites live in the intestines.
Worms
Worms or helminths are parasitic multicellular organisms. Unlike protozoa, worms have tissues and organs. The size of the worms does not allow them to settle inside cells, as parasitic protozoa do.
Experts divide helminthiases into three types:
- Geo-helminthiases - a person becomes infected with worms through elements of the external environment on which eggs or larvae of the parasite are located: soil, food, water.
- Bio-helminthiases - the parasite enters the human body from the tissues of intermediate hosts: vertebrate and invertebrate animals.
- Contagious - parasites are transmitted directly from person to person; their development does not require intermediate hosts or environmental elements.
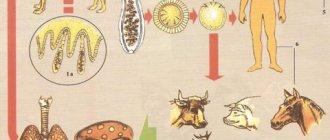
Helminths have a complex development cycle.
Most worms go through the following stages:
- Egg.
- Larva.
- Adult.
The larvae of worms develop in the intermediate host, and then enter the final host, where they transform into sexually mature individuals capable of laying eggs.
How does infection occur?
It is important to understand that infection with worms always occurs only through the fecal-oral route. That is, the infection mechanism looks something like this:
- A person or animal infected with worms defecates.
- Feces contaminated with worm eggs are found in the external environment. This is where pets, garden herbs, vegetables, fruits and people can come into contact with it.
- On the hands, parasite eggs are transferred to the mouth with food if hand washing is poor.
- Or helminth eggs can enter the human stomach with food (poorly washed vegetables, fruits, herbs, undercooked meat or fish).
In addition, worms can enter the human body in the following ways:
- Through insects (fleas, flies, cockroaches), which carry parasite eggs on their paws;
- Through swimming in polluted waters;
- When walking barefoot on contaminated soil.
Important: in any case, the worms first appear in the stomach and only then reach the intestines. It is there that they grow and develop into sexually mature individuals capable of laying eggs.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing parasitic infections in the human body is quite difficult, since intestinal helminths manifest themselves in different ways. Therefore, to find out whether there are worms, a person is prescribed a series of examinations. Refusal of research methods is fraught with inaccurate diagnosis, which means it leads to difficulties in choosing treatment tactics. Diagnosis of intestinal parasites in humans using laboratory and instrumental methods is as follows:
- stool analysis for worm eggs;
- blood test for helminth antibodies;
- general blood analysis;
- serological methods;
- coprogram;
- blood test “liver tests”;
- X-ray;
- computed and magnetic resonance imaging;
- radionuclide method;
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound);
- histological analysis (if it is necessary to determine the origin of the tumor, for example, with alveococcosis).
Types of intestinal parasites in the body
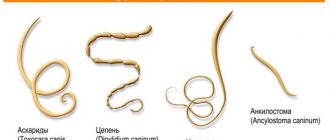
There are more than a hundred types of helminthic infections. However, the most common parasites in the human intestine are no more than 10 species. Below is a list of commonly encountered worms in Central and Central Europe:
- Pinworms. The most common “guest” in the body of children aged 3 to 14 years. The maximum length of the parasite is about 1 cm. The helminth is localized mainly in the small and large intestines. It lays its eggs in the folds of the skin of the anus. In this case, the egg matures within 5 hours after the female lays it. As a result of scratching the anus during itching, re-infection with a parasitic infection occurs through the hands and subsequently through the mouth.
- Ascaris. The maximum size of the parasite can reach 40 cm. The shape of the worm is spindle-shaped. The helminth is localized mainly in the intestines. But at the same time, it is able to migrate throughout the body with the bloodstream and stop in the lungs, liver, heart and even in the brain. The worm feeds on human blood, which sooner or later leads to persistent anemia. It is noteworthy that roundworm eggs can survive in the soil for up to 3-5 years.
- Giardia. These are protozoa that choose the human intestines, liver or gall bladder as their habitat. The carriers of such parasites in the intestines are cats, dogs and rodents. Insects can also carry protozoan eggs. Giardiasis, if treated poorly and untimely, can lead to serious intoxication of the human body and damage to the central nervous system.
- Wide tape. The maximum size of the parasite can reach 10 meters. And its life cycle in the human body is up to 25 years. The main cause of infection is the consumption of fish and its derivatives that have not undergone sufficient heat treatment.
- Toxocara. It is dangerous because it parasitizes in the human body without being released. It can live in the stomach, rectum, bronchi and even in the eyes. The maximum length of Toxocara reaches 30 cm. Toxocariasis can cause serious harm to the human body.
- Bovine and pork tapeworm. Such helminths enter the human body through cow or pig meat that has not undergone sufficient heat treatment. The body length of an individual can reach 2-7 meters. The life cycle of the parasite is up to 20 years. The main danger of tapeworms is that they feed on the resources of the human body. At the same time, they can remain undetected for a long time.
- Echinococci and alveococci. This type of helminth also enters the body through dirty hands and mouth. That is, parasites first appear in the human stomach, and then in the intestines.
- Whipworm. This parasite causes a disease called trichocephalosis. Such worms live in the human stomach (photos below) and in the large intestine. If not detected and treated in a timely manner, they lead to appendicitis and anemia.
- Hookworm. This worm has a round shape and a light pink pigment. Its length can reach 14 mm. The helminth feeds on human blood, sucking about 0.35 ml of blood per day. That is why the main sign of such helminthic infestation is anemia and anemia.
Toxocara
TOXOCAROSIS is a helminthic disease caused by a parasite unusual for humans - Toxocara, very similar to the human roundworm - a nematode of the Anisakidae family of the Tohosaga genus. The diameter of its larva is 0.02 mm.
Two types of Toxocara are known:
- Tocsocara canis is a helminth that affects representatives of the canine family (dogs, wolves, foxes, arctic foxes),
- Toxocara mystax (cati) is a helminth of the cat family.
However, toxocariasis caused by Tocsocara canis also affects humans. The entry of Toxocara larvae into the human body is a “mistake of address” and is death for the parasite.
According to some authors, in Russia the number of children infected with toxocariasis is 40-50%. In the United States, the Center for Disease Control reports 700-1000 cases of toxocariasis annually.
Consequences of toxocariasis for the body
Migrating in the human body, the larvae of toxocariasis pathogens injure tissues, leaving hemorrhages, necrosis, and inflammatory changes. The parasite dies, having managed to harm a person.
Damage to the optic nerve by Toxocara larva can lead to one-sided blindness.
With visceral toxocariasis, there are known cases of the development of severe pneumonia, which occurred with complications and ended in death.
Cases of toxocariasis associated with the migration of larvae into the myocardium and functionally important areas of the central nervous system have been described.
With toxocariasis, numerous granulomas often form in any organ and tissue (liver, lungs, pancreas, myocardium, lymph nodes, brain), in the center of which a zone of necrosis appears, destroying this organ.
Prevention of toxocariasis
Washing hands after contact with soil or animals; Thorough processing of greens, vegetables and other foods that may contain soil particles.
Parasites in the intestines. The eggs of toxocariasis pathogens are covered with a sticky substance that prevents them from being torn off from the surfaces on which they find themselves. Therefore, you can remove them from your hands, as well as from vegetables, herbs, fruits, household items and shoes only with the help of special detergents.
It is necessary to protect playgrounds, parks, and public gardens from animal visits; use of natural soil remediation factors (open sunlight).
Symptoms of parasites in the intestines
It is important to understand that the symptoms of parasites in the intestines can be either common to any helminthic infestation or manifest themselves in the form of signs specific to each type of parasite. So, the general symptoms for a parasitic infection look like this:
- Soreness in muscles and joints. This is caused by the accumulation of toxins that the helminth releases into the human blood during its life activity. That is, intoxication occurs.
- Stool disorders. Moreover, there can be both diarrhea and constipation.
- Inflammatory processes in the intestines. They occur due to a violation of the integrity of the intestinal walls by helminths. As a result, all nutrients are absorbed with less effect. The presence of intestinal parasites is indicated by a symptom - a high level of fat during a coprogram (stool analysis).
- Low hemoglobin level. However, its level is not corrected by iron supplements.
- Allergic rashes. They are a response of the immune system to the introduction of helminthic invasion.
- Weight loss for no apparent reason. Occurs due to a systemic lack of nutrients and substances beneficial to the human body.
- General fatigue and nervousness. They are the results of intoxication.
- Formation of benign and malignant formations. Especially in the gastrointestinal tract.
There are also a number of characteristic signs of helminthic infections inherent in certain types of parasites in the human body.
Pinworms (enterobiasis):
Herb Troychatka Evolar: reviews of parasitologists about the medicine
- Unbearable night itching in the anus;
- Mucus in stool;
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
Ascariasis:
- Night dry cough and shortness of breath;
- Increased body temperature;
- Increased sweating;
- Pain in the lungs and heart;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Bloating;
- Yellowing of the skin and sclera of the eyes.
Giardiasis:
- Decreased appetite;
- Eczema and urticaria;
- Sharp intestinal pain;
- Headache;
- Heart rhythm disturbance.
Wide tape:
- Constant nausea and dizziness;
- Enlarged spleen and/or liver;
- Increased heart rate;
- Numbness of the legs and their paralysis;
- Memory impairment and a sharp decrease in concentration;
- Malfunctions of the vestibular apparatus;
- Pale skin.
Toxocara:
- Sleep disorders;
- Periodic attacks of suffocation;
- Enlarged lymph nodes;
- Increased body temperature;
- Tearfulness and purulent inflammation of the eyes;
- Decreased vision;
- Vomiting and nausea;
- Bronchitis type cough.
Bovine and pork tapeworms (teniarinhoz and cysticercosis):
- Discomfort in the anus;
- Detection of proglotids under the skin and in feces;
- Fainting conditions;
- Anemia;
- Decreased sensitivity and subsequent paralysis;
- Decreased vision and increased reaction to light;
- Irritability;
- The appearance of hallucinations;
- Formation of tumors.
Alveococci and echinococci:
- Red spots all over the body;
- Weight loss;
- Dizziness;
- Pain in the chest and right hypochondrium;
- Diarrhea and vomiting.
Hookworm:
- Weakness and headache;
- Increased salivation;
- Heart pain and shortness of breath;
- Inflammatory processes on the organs of vision;
- Disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- Infertility;
- Soreness in the stomach;
- Belching with an unpleasant aftertaste.
Important: if symptoms of a parasite appear in a person’s stomach or intestines, you should immediately consult an infectious disease doctor or parasitologist. Delay can cost your life.
Diagnostic measures
It is impossible to make a reliable diagnosis on your own. Therefore, at the first alarming symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. Among the diagnostic measures used in such a situation are:
- Stool analysis. If infection occurs, parasite eggs will be found in the sample. But a negative result does not guarantee the absence of a problem, so other examination methods are also used.
- Biochemical and general blood test. The study determines the level of eosinophils, hemoglobin and ESR. Exceeding standard values indicates invasion.
- Analysis of urine.
- Examination of a smear from the anus.
Such simple examination techniques will help the specialist accurately determine the diagnosis. Only after this will he be able to develop the correct treatment strategy.
Drug therapy
Drugs for the treatment of tapeworms in humans
To completely neutralize worms in the intestines and stomach, it is necessary to select competent drug therapy. In this case, antiparasitic drugs are used against helminths. Some of the most potent drugs of the latest generation include the following tablets and suspensions:
- Pyrantel and Piperazine;
- Levamisole and Praziquantel;
- Naftamon and Zentel;
- Mebendazole and Difezil.
In this case, it is better to give drugs in suspensions to children from one year to 6 years old. It is important to understand that all anthelmintic drugs are quite toxic. Therefore, not all of them are acceptable for use during pregnancy, kidney and liver pathologies, or during lactation.
Important: only the attending physician should evaluate all symptoms and prescribe treatment according to the type of drug (select its dosage).
Signs of infestation
Symptoms of worms in the human intestine can vary depending on the type of parasite. A number of common features can be identified:
- An increase in body temperature up to 38 degrees, which lasts for a long time.
- Pain that is localized in the navel or right hypochondrium.
- Attacks of vomiting.
- Changing the stool.
- Loss of appetite.
- Pallor of the skin.
- Weight loss.
- Skin rashes.
- Increased fatigue, drowsiness.
- Dry cough.
- Sleep disturbance.
If you notice the above symptoms, you should consult your doctor. Delay in such a situation is fraught with dire consequences for health.
If worms parasitize the body for a long time, other symptoms may develop:
- Alopecia (hair loss).
- Destruction of tooth enamel, bleeding gums.
- Bad breath.
- Critical loss of body weight.
- Development of an apathetic state, depression.
If the worms have spread to the liver, jaundice appears. When the lungs are affected, severe shortness of breath and cough are observed. It is possible that blood may appear in the sputum.
Colon worms can lead to the development of obstruction. This is accompanied by severe pain, fever, and impaired bowel function. In severe cases, the problem can only be solved surgically.
Folk remedies
If taking medications against worms is impossible for any reason, folk remedies can be used to treat helminthic infestations. In particular, the following anti-parasite agents are used:
- Ledum and celandine - from Giardia;
- Pumpkin seeds - from pinworms;
- Pomegranate peels are from roundworms.
In addition, you can include the following antiparasitic foods in your diet:
- Garlic;
- Hot black and red pepper;
- Cinnamon and ginger;
- Cloves and cardamom.
You can drink the following herbal decoctions against worms:
- Tansy;
- Sagebrush;
- Elecampane.
Enemas with garlic or soda are carried out as cleansing measures for the body. You can cleanse your body with cognac and castor oil once a year. To do this, drink 50-100 ml of cognac at night, and after 15 minutes - 50 ml of castor oil heated to 40 degrees. The next morning, diarrhea should occur, along with which all existing parasites will come out.
It is also worth considering that, along with folk remedies or drug treatment, it is very important to create an unfavorable environment for helminths. And for this you need to reconsider your diet. All sweets and meat, fatty and smoked foods should be excluded from the menu. The diet should contain simple cereals, vegetables, berries and fruits, as well as fermented milk products, nuts, legumes, strawberries, currants, and cream.
Treatment methods
It is almost impossible to cleanse the intestines of worms without the use of medications. Traditional medicine methods can only be used as a complement to conservative therapy. The entire treatment process can be divided into several stages:
- Preparatory. You should completely reconsider your diet. You will have to avoid fatty and fried foods, smoked foods and sweets. Preference is given to foods high in fiber. In this case, you need to drink at least two liters of clean water per day.
- Taking medications. Specific drugs and their dosage are selected by the doctor on an individual basis. The most commonly used are: Nemozol, Dekaris, Helmintox, Vermox, Albendazole and others. The duration of treatment is also determined by the doctor.
- Restorative. After the main course of treatment, it is necessary to cleanse the body of formed toxins. To do this, it is better to use energy sorbents, for example, Filtrum, Enterosgel, Smecta or simple activated carbon. You can give a cleansing enema.
After an invasion, the immune system will also need to be restored. To do this, you need to introduce more vegetables and fruits into your diet, and take vitamin and mineral complexes recommended by your doctor.
Prevention measures
In order to avoid possible infection with worms, you should adhere to basic preventive measures. These are:
- Thorough hand washing before eating, after using the toilet, after contact with animals or working in the garden;
- Regular and timely deworming of pets;
- Limiting contact with street animals and birds;
- Thorough washing of vegetables, fruits and herbs before consumption;
- Boiling water or using only purified water for food;
- Regular house cleaning and insect control.
Remember, it is always easier to prevent a parasitic disease in the stomach in an adult and a child than to later reap the benefits of a helminthic infestation and fight it for a long time. Keep your hands clean and stay healthy!