Peritoneal carcinomatosis is one of the variants of metastases that usually affects the pleura and peritoneum. If there is a diagnosis of cancer, regardless of the location of the tumor, metastasis may occur, and if the patient has secondary lesions, his chances of cure are significantly reduced.
Carcinomatosis is not a separate disease, but is a serious complication of other malignant cancers, such as pancreatic, liver or uterine cancer, with a very poor prognosis.
Carcinomatosis of the abdominal cavity. What it is?
According to ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases), carcinomatosis is a secondary oncological pathology, a consequence of the spread of cancer cells from the primary focus.
Such transfer is usually carried out using the lymphatic system (lymphogenous disease), less often the pathology is caused by germination of the primary tumor into the peritoneum.
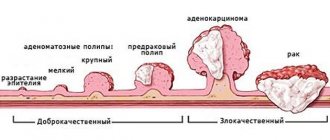
Cancer cells that find themselves in the serous cavities are fixed there and form formations resembling the shape of millet grains. These tumors gradually expand, occupy new areas, and as a result merge, creating an impressive tumor.
The difference between a metastatic tumor and a primary one
In terms of their structural structure, the maternal and daughter tumors are practically no different from each other, since they have a common origin. What distinguishes them is the nature of their development and progression: if the primary malignant focus grows slowly and spreads to neighboring tissues (with rare exceptions), then metastases behave much more actively.
As a complication of oncology, metastatic tumor cells divide faster and lose signs of differentiation. Therefore, upon histological examination, it is not difficult to distinguish them from the maternal neoplasm.
Leading clinics in Israel
Assuta
Israel, Tel Aviv
Ikhilov
Israel, Tel Aviv
Hadassah
Israel, Jerusalem
This malignant process disrupts the exudative and resorptive functions of the serous membrane. This change causes excess fluid to accumulate, causing ascites.
An examination of patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis revealed that most often this complication occurs in patients with oncology of the gastrointestinal tract - pancreas, stomach.
The second most common cause of pathology is ovarian cancer, and since the development of peritoneal carcinomatosis is possible with ovarian cancer, this means that women are susceptible to this complication much more often than men.
Regardless of the type of cancer, damage to the peritoneum is considered a very unfavorable sign. And since with such a diagnosis it is impossible to use many treatment methods, this can affect the likelihood of a successful recovery of the patient and his life span.
The formation of carcinomatosis of the pleural cavity is also possible. It is typical for lung cancer, breast cancer, and pleural mesothelioma. However, this condition can be caused by any tumor that can metastasize to the pleura and lungs. Such metastases in the pleura increase the permeability of its vessels and disrupt the outflow of lymph, which can lead to the accumulation of fluid and the appearance of carcinomatous pleurisy.
Treatment prognosis
The lifespan of a patient depends on the degree of damage to the body by the oncological process. The doctor cannot say for sure how long a person will live. This depends on the physical indicators and psychological mood of the patient.
Damage to a small area of the peritoneum - the survival rate is higher in patients. Life expectancy is up to 3 years or more. If the primary lesion is treatable, the chances increase.
If a larger area of the organ is affected, the prognosis for the patient is unfavorable. Death is diagnosed after a few months. Palliative therapy is used to relieve pain and psychological discomfort.
With this disease, everything depends on the timing of detection and the psychological mood of the patient. Scientists have proven that a positive attitude towards recovery significantly increases the chances of recovery and a long life.
Causes
The main cause of peritoneal carcinomatosis is an existing cancer focus.
As a result of development, tumor cells inevitably acquire mobility, as a result of which they are able to separate and move. The spread of cancer cells occurs:
- Through the bloodstream or with the lymph flow;
- Through germination of the primary neoplasm into the peritoneal area;
- During surgical intervention to remove the primary tumor.
The area of the serous membrane and the entire peritoneum can reach 2 square meters. Such dimensions determine the location of the peritoneum itself in the abdominal cavity, that is, it has adjacent folds. This structure contributes to the damage to a large area of the peritoneum during a malignant process.
The following factors contribute to the accelerated development of peritoneal carcinomatosis:
- Constant contact of the folds of the peritoneum;
- Contact of the peritoneum with the digestive organs;
- The presence in the organ of an extensive network of blood and lymphatic vessels.
Once in the peritoneum, cancer cells tend to gain a foothold in the place where it is least exposed to intestinal peristalsis. Also, the risk of carcinomatosis depends on the volume of the primary malignant tumor and the degree of penetration deep into the organ.
In the case of undifferentiated gastric cancer, damage to the peritoneum by tumor cells is observed in the majority of patients.
At what stage do they appear?
Having first formed, a malignant tumor is small in size and remains within the parietal boundaries of the affected organ, that is, there is no metastasis in the early stages of cancer. But this stage cannot last forever - in the absence of treatment, the neoplasm expands beyond the serous membrane of the anatomical structure and begins to spread cancer cells. As a rule, in this case we are talking about the third and fourth stages of high-grade oncology.
If in the early stages the tumor practically did not make itself felt and the symptoms of the oncological process could be confused with concomitant somatic ailments without proper laboratory and instrumental diagnostics, then with the development of metastases the clinical picture of the disease worsens significantly.
Classification and signs of carcinomatosis
Since peritoneal carcinomatosis is a secondary lesion, the symptoms that appear with the primary tumor first appear.
However, sometimes it is the clinical picture of damage to the serous membrane that makes it possible to make a diagnosis of cancer. The main symptoms that indicate damage to the peritoneum include:
1) Enlargement of the abdomen with a sharp decrease in body weight. An increase in the size of the abdomen occurs due to the accumulation of fluid - this pathology is called “ascites”;
2) The appearance of aching, dull pain. The pain may be constant or disturbing to the patient for periods of up to several days;
3) Digestive disorders. They are manifested by nausea, colic and abdominal pain, and vomiting is also possible. It is difficult to empty the intestines, sometimes constipation can be replaced by diarrhea;
4) Symptoms of intoxication. Heavy sweats, severe weakness, fever, chills, pain in the head and muscles - these symptoms characterize developing carcinomatosis.
Would you like to receive an estimate for treatment?
*Only upon receipt of data on the patient’s disease, a representative of the clinic will be able to calculate an accurate estimate for treatment.
The patient has a serious general condition; such patients often end up in gastroenterology or surgery with diagnosed ascites, the cause of which is revealed later.
Peritoneal carcinomatosis has a classification based on the number and location of metastases:
- P1 – local damage to the peritoneum, limited to just one area;
- P2 – several foci of caceromatosis are detected. Between these lesions there are areas of healthy peritoneum;
- P3 – numerous, merging malignant foci of caceromatosis are observed.
Main symptoms
Since carcinomatosis is a secondary lesion, its clinical picture primarily depends on the original cancer tumor. In the case of peritoneal carcinomatosis, symptoms may be as follows:
- the occurrence of aching pain syndrome;
- a sharp decrease in body weight with an increase in the abdomen;
- impaired functioning of the digestive system, in particular the intestines;
- intoxication.
A characteristic sign of peritoneal carcinomatosis is the formation of ascites, and therefore patients are initially admitted to the gastroenterology department, where doctors determine the cause of the ascites.
Diagnostic measures
First of all, an oncologist may suspect carcinomatosis in people who already have a history of cancer.
However, in case of weight loss, abdominal pain and other signs of cancer, the doctor must, in order to exclude or confirm the diagnosis, send the patient for diagnostic procedures.
Appointed:
- CT scan. Layer-by-layer examination of the abdominal region, identification of all foci of pathology, their location, structure;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs. This method allows us to identify the primary tumor, its size and location, changes in the peritoneum;
- MSCT is used to assess the extent of the tumor and to identify lesions of the lymph nodes;
- A blood test accurately determines the location of the primary lesion;
- Laparoscopy allows both to examine the peritoneum and to collect altered tissues for the purpose of biopsy.
In approximately 5-6% of cases, difficulties arise when identifying a cancerous tumor; sometimes it is so small that it cannot be detected intravitally.
Diagnosis of the disease
A doctor can detect a disease without conducting an examination in a patient at an oncology center undergoing cancer therapy. In other cases, an extensive examination of the patient’s body is required. Diagnostics includes the following procedures:
- An ultrasound scan examines the organs of the peritoneum and the small pelvis. Here the primary focus is revealed with signs of internal changes in the organ tissue. The doctor determines the size, shape and exact location of the formation.
- Using computed tomography, the organ is studied structurally. CT scan identifies all malignant areas, structure and localization.
- MRI and MSCT are performed using contrast - this makes it possible to detect distant metastases and the extent of damage to the lymph nodes.
- Laparoscopy is required to internally examine the affected peritoneal walls and obtain a biological sample. The sample is examined in the laboratory using a biopsy method.
- The blood is studied by RT-PCR analysis. Based on this analysis, doctors accurately determine the location of the primary focus of the disease.
Sometimes it is not possible to determine the primary site of development of the pathology. In other cases, diagnostic methods provide detailed information about the disease. The examination allows you to determine the degree of damage to the body and prescribe adequate treatment.
How to treat peritoneal carcinomatosis?
Treatment of patients with carcinomatosis is quite complex, and it is not always quite effective.
If possible, surgery is prescribed in combination with chemotherapy. Also, many other innovative treatment methods are constantly being used, so it cannot be said with certainty that an effective method of treating this pathology will not become available in the near future. However, folk remedies cannot cure the disease.
Surgery
Surgical intervention (peritonectomy) primarily involves removing the primary cancer focus, affected lymph nodes, and foci of insemination by cancer cells. Often the operation is combined with the removal of part of the small or large intestine, sigmoid colon, gallbladder, uterus and appendages.
Chemotherapy for carcinomatosis
When treating patients with carcinomatosis, one of the most modern methods is used - hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy.
This method involves injecting chemotherapy drugs using hot air directly into the peritoneum, which can be achieved during surgery.
The injected solution containing chemotherapy drugs continues to remain in the peritoneum for about an hour, continuously circulating and destroying cancer cells. The effectiveness of treatment increases several times with hyperthermic chemotherapy.
Treatment of the primary lesion
In the case of peritoneal carcinomatosis, the primary focus should be identified, as well as its location, stage and extent of metastases assessed.
The decision on the necessary treatment is made only after all studies have been completed. If the stage of cancer and the localization of the tumor allow it, surgery is performed to remove the formation (for example, at grade 4 the prognosis is unfavorable). Additionally, sessions of radiation and chemotherapy are prescribed.
Symptomatic therapy
This is a treatment aimed at reducing or eliminating the main symptoms of the disease. For carcinomatosis, as a rule, the following is carried out:
- Anesthesia. In very advanced cases, pain can be relieved only with the help of a narcotic analgesic;
- Treatment of ascites. It involves removing fluid through a puncture in the abdominal wall;
- Improving the functioning of the digestive organs. It is required to improve the digestibility of food and digestion, strengthen peristalsis;
- Infusion of solutions. Intravenous infusion has a detoxification effect, such treatment normalizes blood composition;
- The use of diuretics helps remove excess fluid.
If necessary, patients are prescribed drugs that improve the functioning of the heart and blood vessels, antispasmodics, and enzymes. The patient must remain under observation and undergo periodic re-examination.
Metastases in the abdominal region indicate the presence of a primary tumor in which organs and systems?
Oncologists have determined what the pattern of spread of tumor cells from cancer foci of various locations looks like:
- melanoma metastasizes to the liver and pancreas;
- cancer, most often adenocarcinoma, of the lung - in the esophagus, stomach and ovaries;
- malignant tumors of the ovaries, uterus and cervix - kidneys and bladder, large intestine;
- breast cancer, kidney and prostate cancer - spleen, liver, small and large intestine;
- Pancreatic carcinoma - any organs of the abdominal cavity.
Psychological help
When a person first hears about an oncological diagnosis, he experiences a serious shock. His life is divided into two segments - before and after; many questions arise in the patient’s soul, from treatment to prognosis for death. And the patient cannot figure all this out on his own; he simply needs the help of qualified specialists.
It’s good if a person is supported by family and friends in difficult times. Communication during this period of time is vital for him, but if there is no psychologist in the patient’s environment, it can be complicated by such issues as depression, failure to accept one’s own diagnosis, outbursts of anger and other problems. To avoid all this, it is important to understand the value of psychological support for a cancer patient.
Working with a patient, a psychologist strives to stabilize his emotional background, help establish contact with medical staff and others, and set him up for effective treatment. The specialist tries to answer all the questions that concern the person, trying to relieve the level of anxiety and fear. Such assistance gives noticeable results, including in the later stages of cancer.
Getting a disability
Every person diagnosed with cancer has the right to contact the ITU office at their place of residence to determine their disability group. In case of metastases and relapses, the prognosis for recovery is questionable and unfavorable, therefore, in this clinical case, the patient is assigned an indefinite disability group, which guarantees receipt of a pension and social support from the state.
To apply to ITU, you need to collect a package of documents. It may include information about laboratory and instrumental studies, an extract from the medical history, a conclusion from the attending physician, characteristics from the last place of work, data on radical and auxiliary therapy. The commission reviews the application for a medical examination within 5 days, after which a date is set for its completion. If, due to complications of the disease, a person cannot independently visit the medical examination, representatives of the medical group can go to his home or hospital, or carry out the procedure in absentia in the presence of a legal person representing the interests of the patient.
Diet
Human nutrition plays a key role in the treatment of any disease, and oncology is no exception. There are certain recommendations that are important to follow when preparing food, creating a daily menu and combining products. Since it takes a lot of strength and energy to fight metastatic cancer, it is imperative that the selected diet specifically strengthens a person's health, especially his immune system.
The nutritional principles will be as follows:
- A fractional diet consisting of 6 meals, which are served in small portions.
- Cooking all dishes by steaming, boiling and stewing.
- Dishes should be warm, the food temperature should be close to the patient’s body temperature.
- Replacing salt with lemon and cranberry juice.
- Compliance with the drinking regime to eliminate and prevent cancer intoxication of the body.
The list of permitted products includes dietary meats and poultry, sea fish and seafood, fermented milk products, sprouted grains, cereals, vegetables, fruits, nuts, herbs, eggs, and wholemeal bread.
The list of prohibited products includes alcohol, carbonated drinks, processed foods, fatty and spicy foods, confectionery, and marinades.
In addition to proper nutrition, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, moderate physical activity, and a positive psychological attitude are encouraged, which will make it possible to more effectively resist the disease both during treatment and after its completion.
Prevention
In oncology, there are no specific preventive measures that could prevent the development of a malignant process in the body. Experts recommend adhering to general rules that help maintain overall health. These include:
- rejection of bad habits;
- timely treatment of infectious, inflammatory and other somatic ailments;
- balanced diet;
- taking multivitamin complexes;
- moderate physical activity to eliminate stagnant processes in the body;
- living in an area with satisfactory environmental conditions;
- avoidance of stress factors.
Malignant tumors are extremely dangerous pathologies that are not always amenable to treatment and can kill a person literally in a matter of weeks and months. It is important not to neglect timely preventive medical examinations and not to refuse additional examination if suspicious symptoms and signs of an oncological process arise.
Are you interested in modern treatment in Israel? Thank you for taking the time to complete the survey. Everyone's opinion is important to us.