Parasites can enter the human body along with food, causing diseases of internal organs. One of these diseases is opisthorchiasis, a type of helminthiasis. The worm that causes the disease is called the Siberian or cat fluke from the class of flukes.
This worm parasitizes organs such as the gallbladder, pancreas and liver ducts. Often the cause of infection is the consumption of fish that have not been properly processed. In the early stages, symptoms of opisthorchiasis do not appear.
Although opisthorchiasis is contagious, it is not spread from person to person or from pet to owner, as it requires waste from an infected cat fluke to enter the digestive tract of a healthy person.
The causative agent of opisthorchiasis and its life cycle
Life cycle of the cat fluke
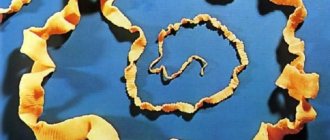
Cat flukes or Siberian flukes (Opisthorhis felineus) are also called opisthorchid flukes. They look like a small parasite, 8-15 mm in length and no more than 2 mm in width. The parasite is yellow-brown in color, flat with suction cups at the base, with which it clings to the host’s body. The worm is a hermaphrodite, like others from the class of flukes, which allows it to lay eggs in the body of the final host without special conditions.
Going through a full life cycle, opisthorchia changes more than one host. Feces infected with parasite eggs end up in the reservoir. There is a settlement of freshwater snails. And for the next couple of months, development takes place inside this mollusk. The eggs will then hatch into cercariae, which wait to be swallowed by the fish. Mostly cyprinids are infected. But the most interesting thing is that the exception is the carp itself.
Predatory fish can become infected if they swallow fish with opisthorchiasis. From unprocessed, thermally contaminated fish, the cat fluke ends up in the final host - a person or a piscivorous animal. Then the cycle begins again.
This worm has a rather long development period. First, time passes until the larvae form special suckers while still inside the fish, with which they later cling to the mucous membrane of the internal organs. It is the suckers that lead to damage to the walls of organs and the development of bacterial infection. Sometimes a rash appears on the patient's skin as an allergic reaction.
In just one month, helminths mature inside the human body and begin to reproduce. In one week, 5000-10000 eggs are produced by just one individual. Eggs accumulate in the body, which leads to stagnation of bile.
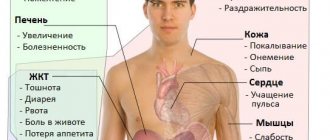
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of opisthorchiasis
It is important to know how opisthorchiasis manifests itself so that you can consult a doctor at the first sign. The incubation period lasts 2-4 weeks. During this time, the disease is asymptomatic. The disease can initially occur in a chronic form, then a person can live for several years without symptoms until the internal organs are damaged so much that it becomes extremely difficult to recover.
However, even this form can be determined by the stagnation of bile in the body. The acute form of opisthorchiasis appears immediately after the end of the incubation period. First, the body temperature rises. At first it is insignificant, however, over time it can exceed 39 degrees and not subside for half a month.
Important! Do not wait for the fever to go away on its own. You should consult a doctor or call an ambulance!
Symptoms of acute opisthorchiasis:
- elevated temperature;
- pain and aches in the joints;
- pain in the right hypochondrium or under the sternum;
- liver enlargement;
- stomach upset;
- vomit;
- bloating;
- general weakness;
- insomnia;
- shortness of breath or cough;
- migraine and nervousness;
- allergic skin reaction.
Some patients complain of poor appetite and bitterness in the mouth. And if opisthorchiasis is not identified in time and proper treatment is not started, the disease progresses from acute to chronic form. And this leads to serious complications.
Often the symptoms of the disease are mistaken for a cold or flu. In this case, treatment does not give results, and the infected person only gets worse. Therefore, it is important to see a doctor and get examined.
Diagnostics
Only stool analysis can accurately determine opisthorchiasis
The diagnosis of “opisthorchiasis” is made only after special parasitological studies, otherwise it is impossible to identify the disease with simple tests. The presence of pathogens can be determined by special blood tests.
Feces should be collected at least three times, with a break of at least one month between the first and last times. Because the incubation period is up to a month, and cat flukes lay eggs in different numbers on different days.
Ultrasound, CT and MRI do not make it possible to accurately diagnose or exclude the diagnosis of opisotrchiasis. With the help of these types of diagnostics, you can only notice an increase in internal organs and suspect a disease. Bile can be examined using probing. Its stagnation can also help suggest the presence of parasites in the body.
There is a device called Optisalt IridoScreen, which can detect worm infestation using the iris of the eye and determine the toxic load on the organs. However, not every clinic or hospital has it.
Watch a video about the IridoScreen device:
https://youtu.be/rtfpyEQfnZ8
Complications
If treatment is not started on time, the disease becomes chronic and leads to consequences. Parasites feed on the mucus of internal organs and blood. Also, the life process of the larvae cannot do without their decay, which poisons the body with toxins.
The consequences of opisthorchiasis are very serious:
- liver damage by types of cirrhosis;
- abscesses may occur on the liver;
- the occurrence of peritonitis or pancreatitis;
- the gallbladder may become inflamed;
- the pancreas becomes inflamed;
- liver cancer;
- pancreas cancer;
- anemia;
- chronic hepatitis;
- development of asthma;
- general allergic reactions of the whole body;
- heart problems;
- risk of gastritis and stomach ulcers;
- epileptic seizures.
Features of infection
When the larvae are in the body of the fish, their development has already begun. Suckers grow on their body. When these suckers penetrate the human body, they attach to the mucous membranes of various organs, damaging them. The result is ideal conditions for the development of bacteria. The patient also develops allergies.
About 3-4 weeks will pass, after which the larvae develop into an adult, which is capable of reproducing. This causes the females to lay eggs. This has a detrimental effect on health, as the body becomes clogged.
There are two stages of the disease:
In the first case, an unexpected manifestation of the disease occurs. The patient may experience an immediate increase in temperature. However, it does not decrease for several weeks. Allergies often appear. A person feels discomfort in the muscles, his liver becomes enlarged, he feels nauseous and has a fever.
In the chronic form, the patient experiences periods of exacerbation. When he is very tired, nervous, changes his previous diet, then opisthorchiasis can worsen. In this case, there is often pain on the right side in the hypochondrium and heart, the person does not want to eat, he has a headache, and excessive sweating occurs.
How is the disease transmitted? Can you get infected from a person or a pet?
Wash vegetables with baking soda
When to be wary of infection and when not to:
- Fish eaten with opisthorchiasis that has not been properly processed is contagious.
- Infection does not occur in everyday life, through airborne droplets or through intimate contacts.
- Also, a sick animal is not contagious. However, opisthorchid larvae may remain on the hands or nails after contact with a pet. And from there it gets into the digestive tract. So always wash your hands thoroughly before eating anything.
- The larvae may end up on vegetables from soil that has contained feces from infected animals. If food is not processed before consumption, you can get opisthorchiasis.
- Also, parasites can end up in the body in accidentally swallowed water when swimming in ponds, lakes, and rivers.
To summarize, we can say that by adhering to basic hygiene rules, infection from a person or animal is excluded.
Prevention
Watch a video on how to protect the liver from opisthorchiasis:
To avoid infection, you should remember a few simple rules:
- Do not buy fish from private individuals who do not check the product for parasites.
- Cook the fish for 20 minutes after boiling.
- To ensure that the fish is cooked well, it needs to be fried in small pieces rather than whole.
- Fry the fish only under a tightly closed lid for at least 20 minutes.
- Bake fish in the oven for at least one hour.
- It takes 2-5 weeks to salt the fish, depending on its size.
- For drying, you first need to salt the fish, and only then dry it for at least three weeks.
- The larvae die at a temperature of -40 in just a few hours. Or when frozen at 30 degrees below zero for more than two days.
- It is dangerous to eat raw and lightly salted fish.
- It is not recommended to eat prepared fish dishes in dubious catering establishments.
- Knives and cutting boards should be thoroughly disinfected after fishing.
- Before eating, you should wash your hands well for at least 30 seconds.
- Vegetables from the garden beds also need to be processed well.
Treatment for opisthorchiasis can only be prescribed by a specialist. Do not try to remove parasites yourself. This is not a simple disease that requires competent reduction of the level of intoxication and prevention of possible complications.
Immunity to opisthorchiasis is not developed, so you can become infected again. So be sure to follow the rules given above.
How is opisthorchiasis transmitted? Who are carriers of opisthorchiasis? Is it transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person? And from pets? How to protect yourself from opisthorchiasis? You will find out in this article.
Opisthorchiasis is a parasitic disease (biohelminthiasis) that has natural foci. The development of the disease begins after eating infected fish. In this case, individual organs of the digestive system are affected - the liver, bile ducts and pancreas.
How opisthorchiasis is not transmitted
Here you can debunk several myths and finally determine that the disease is not transmitted:
- through kisses;
- when drinking drinking water;
- through dishes from a sick person;
- from mother to child during pregnancy and by inheritance;
- You cannot get infected through red fish, as well as predatory fish and sturgeon;
- by airborne droplets;
- sexually.
It is impossible to transmit opisthorchiasis through any household contacts and from person to person, so there is nothing to be afraid of. However, this does not reduce the danger of this disease, which can hardly be detected by symptoms, so only a doctor after a course of diagnostics will be able to determine the type of disease, its stage and spread.
Pathogens of opisthorchiasis
These are about 30 species of parasites - flatworms of the genus Opisthrchis.
The causative agents of opisthorchiasis in humans:
- Opisthrchis felineus (cat fluke or Siberian fluke) - common in Russia, Kazakhstan and Ukraine. The outbreaks are located in the coastal strip of rivers. These are the Volga, Don, Kama, Ob, Irtysh, Northern Dvina, Biryusa, Ural. The most contaminated area is the Ob and Irtysh river basins in the middle and lower reaches.
- felineus arvicola - territory of the Shiderty River in Kazakhstan;
- O.viverrini is native to South and Southeast Asia (Thailand, Cambodia, Laos, Vietnam).
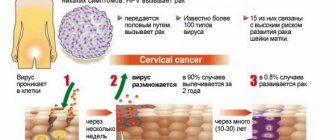
Life cycle
The cat or Siberian fluke goes through several stages of transformation of life forms. At the same time, a change of hosts (carriers of opisthorchiasis) occurs. A carrier is a living organism in which the parasite develops into one of its forms.
Intermediate hosts:
Freshwater mollusks of the Bithynia species, living in floodplains, oxbow lakes, lakes, shallow, drying up reservoirs.
Additional:
Cypriniformes (lat. Cyprinidae) are fish of the order Cypriniformes.
Basic:
Humans and carnivores, omnivores: cat, dog, arctic fox, sable, fox, otter, wolverine, lion, pig, rat, rabbit, ferret, mink.
Biohelminthiasis throughout its development undergoes metamorphosis (deep transformation of the structure of the body) of various forms of life:
- Eggs - enter the water from sewage and flood waters contaminated with the excrement of their carriers. Water is an ideal environment for eggs to live; they can survive in rivers for more than a year. They live in feces for up to seven and a half months. In the ground - more than 11 days, up to a maximum of 34 days. At temperatures down to -8 °C on snow - 72 hours. The eggs are swallowed by a Bithyneedae snail from the family of freshwater gastropods, which feeds by filtering water, scraping algae and organic debris at the bottom of shallow, stagnant reservoirs.
- In the acidic environment of the snail's gastric juice, the egg shell dissolves and the miracidium hatches. Miracidia is a fluke larva covered with cilia and capable of swimming.
- Miracidia move from the stomach into the body tissues of the mollusk and turn into sporocysts. Sporocyst (sporo + Greek kystis bladder) is another larval form of the fluke; it is a stationary closed sac containing embryos.
- When the sporocyst bursts and dies, it gives life to more than 100 redia. Rediae are the third stage of larval development and have the structure of a sac, a large pharynx and an intestine.
- Each redia gives birth to tens of thousands of cercariae. The cercaria is the fourth stage of larval development. The cercariae develop and after about 60-70 days they emerge from the snail into the water. With the help of the tail they actively move, using the shadow of the fish they determine its location, become active and attach to it. Invasion (infection) of fish occurs.
- Inside the fish, the cercariae lose their tails and become metacercariae. A metacercaria is a resting cyst of a fluke. Metacicariae are invasive (infectious) to humans when they eat fish with them. When infected fish are eaten by the definitive host, the metacercariae enter the stomach, where they emerge from the cyst, move along the bile ducts to the liver and gallbladder and turn into opisthorchids. Opisthorchis felineus is a cat or Siberian fluke that can lay up to 1000 eggs per day. After three or four weeks, opisthorchiasis reaches sexual maturity, and eggs appear in the stool of an infected person or animal. By parasitizing the digestive system of humans or animals, the fluke causes pathological changes in the body - the disease opisthorchiasis. The entire cycle (from eggs entering the water to infecting people or animals) takes approximately four months. Opisthorchis can remain in the animal body for up to three years, and in the human body from 15 to 30 years. An increase in invasion occurs when infested fish enter the stomach again.
Opisthorchis
Opisthorchis are helminths related to liver flukes. The most common type of opisthorchid is the Siberian fluke. This is a tapeworm, the length of which can reach 1.8 cm and the width is 1.2-2 mm.
The life of opisthorchis is divided into 2 cycles: the 1st takes place in mollusks and fish (usually the carp family), which are thus the intermediate hosts of this parasitic worm, and the 2nd cycle takes place in the human body - that is, man serves as the final the owner.
When these parasites enter the human digestive organs, metacercariae (infective larvae) are separated from the cysts, which invade human organs - through the bile ducts into the gallbladder, and then from there further along the bile ducts into the liver.
After 10-12 days, these larvae become sexually mature and begin to lay their eggs. If eggs enter the external environment, they can live up to 10 days, but then inevitably die.
These parasites do not live long in the body of an intermediate host, but in humans opisthorchids are able to reproduce and parasitize for up to 20 years.
Routes of infection and prevention
I have been detecting and treating parasites for many years. I can say with confidence that almost everyone is infected with parasites. It's just that most of them are extremely difficult to detect. They can be anywhere - in the blood, intestines, lungs, heart, brain. Parasites literally devour you from the inside, at the same time poisoning your body. As a result, numerous health problems appear, shortening life by 15-25 years.
The main mistake is delaying! The sooner you start removing parasites, the better. If we talk about medications, then everything is problematic. Today there is only one truly effective anti-parasitic complex, this is Toximin. It destroys and sweeps out all known parasites from the body - from the brain and heart to the liver and intestines. None of the drugs existing today is capable of this.
Within the framework of the Federal program, when submitting an application before October 12. (inclusive) every resident of the Russian Federation and the CIS can receive one package of Toximin for FREE!
- Eating raw and semi-raw fish
In a household refrigerator, metacercariae remain viable for a month. They tolerate low temperatures well. In small fish they can be stored for up to 4 days, in large fish up to 20 days. Temperature in the fish body required for disinfection:
- -40 °C - 7 hours;
- -35 °C - 14 hours;
- -28 °C - 32 hours.
This temperature can only be created in industrial refrigerators. The following dishes should not be consumed: stroganina, patanka, “heh” dish, “super cheese”, fish with “blood”, “steam” fish. Due to the possibility of infection, it is better to avoid this. Do not try raw minced fish.
- Eating boiled and fried fish without sufficient heat treatment
Treatment
Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. Hospitalization is necessary for children under 3 years of age or over 3 years of age with complications.
Praziquantel is used as an antiparasitic agent. The drug is taken in recommended doses 3 times a day immediately after meals with an interval of 4-6 hours. The course of treatment is 1 day.
The mechanism of action is based on the permeability of the parasite's cell membranes to calcium ions. This causes paralysis of the worm's muscles.
On the day of taking the drug and for 2-3 days after taking it, choleretic drugs are recommended.
If you are prone to allergic reactions, antihistamines are necessary.
The effectiveness of treatment is 95-98% in children, 86-90% in adults.
Fish not susceptible to infection
These are the following types:
- Carnivorous animals - perch, pike, ruffe, pike perch, burbot and whitefish (muksun, peled, whitefish, whitefish) do not get opisthorchiasis, parasites cannot take root in their muscles.
- Sturgeon (sterlet, sturgeon) and red fish (chum salmon, char, salmon) do not become a source of infection. Sterlet comes from fish farms, where the quality of the fish is analyzed before sale. There is an opinion that you can become infected with opisthorchiasis from predatory fish, in particular from pike. There is evidence that this is not the case. Cat fluke larvae do not survive in these fish. Theoretically, this could happen if a predator swallows the fish, and a person eats the raw insides of the pike along with the swallowed fish. But in practice no one will do this.
Quite a few helminthic diseases are now known, and one of the most intractable of them is opisthorchiasis. The insidiousness of this disease lies in the difficulty of its timely detection due to the diversity and nonspecificity of manifestations. Moreover, the described illness leads to serious and sometimes irreversible consequences.
Is opisthorchiasis contagious or not? The disease is very well camouflaged, which is why people sometimes spend years being treated for various other diseases by doctors of different specializations, without even suspecting that they actually have opisthorchiasis.
What is opisthorchiasis?
Opisthorchiasis is an infectious disease that occurs due to parasitism of the trematode species Opisthorchis felineus in the liver and pancreas. This disease is very common in Russia, primarily in Siberia.
The causative agent of opisthorchiasis is the Siberian fluke, whose vital activity takes place in the human body, but this parasite can also live in the body of a dog or cat. The fluke attacks the pancreas, liver, bile ducts and gallbladder.
Diagram of the spread of opisthorchiasis
After the excrement of a person or animal infected with opisthorchiasis gets into the water, their eggs are swallowed by aquatic snails, in which the larvae then multiply and develop. These larvae later emerge from the snail's body and into the water. The hatched larvae have the form of cercariae.
Cercariae settle in the bodies of carp fish: crucian carp, roach, ide, dace, bream, roach, rudd, carp. In fish, these parasites live in the subcutaneous tissue and muscle tissue, turning there into metacercariae.
When a person consumes raw, contaminated fish, or fish that has undergone insufficient heat treatment during cooking, or insufficiently salted fish, metacercariae enter human internal organs.
How to prevent infection
To prevent infection with opisthorchiasis and many other diseases associated with helminths, it is worth taking preventive measures. Among them:
- Observe the technique of preparing and cutting fish. For example, she must have her own knife and board. And in establishments where they prepare fish, there is a whole separate table for working with fish and seafood.
- Properly salt and heat-treat fish.
- Do not feed raw fish or minced fish to people or animals.
- Freeze fish at 28°C for at least a day and a half.
- Dry the fish for at least 21 days (subject to an additional three days before salting).
- Follow sanitary rules in the kitchen or food preparation area.
- Observe the rules of personal hygiene, do not neglect hand washing.
- Take care of pets and wash them, especially dogs after a walk. Also, do not allow them to eat outside or interact with wild and stray animals. This can lead primarily to infection of pets that do not easily tolerate parasitic diseases.
In addition to these rules, there are more global methods. For example, checking and cleaning reservoirs of helminth eggs and infected animals. This should be handled by special services. It is equally important to inform the population about the contamination of the reservoir and the possibility of infection by parasites. Thus, opisthorchiasis is widespread in many regions where they do not care about ecology and sanitary conditions. However, it can appear anywhere in the world where the rule remains - the presence of carp fish in the reservoir.
Understanding the transmission routes of opisthorchiasis is very simple. But it’s worth doing this after consulting a doctor, who should conduct tests and prescribe treatment as soon as possible. After all, the disease can progress to a severe stage, then the methods of transmission of helminths will no longer be so important. It is better to inform about them in advance, as preventive measures. Then the disease will definitely bypass friends and loved ones.
Opisthorchiasis is a pathology caused by parasitic microorganisms. They affect the pancreas, liver, and gallbladder. In rare cases, the disease is fatal, but it has a significant impact on quality of life and is difficult to treat. In addition, the disease can become chronic, and in this case it will be difficult for the patient to get rid of it. How is opisthorchiasis transmitted?
Symptoms of the disease
You should contact your doctor immediately if you have the following symptoms::
- temperature increase;
- muscle and/or joint pain;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- increase in liver size;
- pain in the right side;
- change in the size of the spleen;
- allergic rashes;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- sleep disorders;
- frequent mood swings and irritability without obvious external reasons.
How the disease is transmitted: routes of transmission
This disease is transmitted to a healthy person from an infected person only if somehow waste from the patient’s body enters the healthy body. This is the only option in which you can become infected from a sick person. Opisthorchus is a parasitic worm that, when it penetrates the human body, can poison it for years. Another name for opisthorchiasis is “cat fluke.”
The exact lifespan of opisthorchids today remains unclear. Some biologists and doctors are of the opinion that these worms are capable of living in a person throughout his entire life, although the majority is inclined to believe that no more than 20 years. However, even within 20 years the parasite will have time to lay eggs, the number of which will be in the millions.
The main sources of infection are infected animals and people. In their bodies, opisthorchids lay eggs, which come out with feces, after which the larvae of the parasites penetrate the bodies of other animals and people.
The most dangerous thing is to eat infected carp fish . This is a dangerous food product if the processing of such fish during cooking was insufficient or if it is consumed raw. When eating such fish, both people and animals become infected.
People who permanently live in areas where opisthorchiasis is widespread most often develop opisthorchiasis. There are a lot of infected fish, so the likelihood of the worm penetrating the human body is high. It should be noted that infection with opisthorchiasis is impossible by airborne droplets. It is impossible to get sick from it through saliva.
When the excrement of people or animals infected with opisthorchiasis penetrates into fresh water bodies, the eggs of these worms swallowed by snails turn inside the snails into larvae, which, on average, after 2 months come out into the water, from which they then move into the bodies of fish. In general, opisthorchiasis is a very common disease in the world, and many people infected with opisthorchiasis are not even aware of their illness.
The most common carriers of opisthorchid among fish of the carp family are tench, bream, ide and chebak.
Opisthorchiasis can lead to anemia, some types of allergies and diseases of the pancreas and liver. In addition, it aggravates the course of some other diseases. Very often, opisthorchiasis does not manifest itself at all, but sometimes causes pancreatitis, hepatitis and even liver cancer.
There are acute and chronic forms of opisthorchiasis . Acute opisthorchiasis is observed in people who come from areas where this worm is not common. The disease appears suddenly.
There is a significant increase in body temperature, which may not drop for up to 2 weeks. Sometimes allergies occur. But the leading symptoms of acute opisthorchiasis are aches in the joints and muscles, fever, enlarged liver and vomiting.
Chronic opisthorchiasis most of the time does not manifest itself with any symptoms , however, in moments of overwork, nervous strain and poor diet, exacerbations of chronic opisthorchiasis sometimes occur, manifested by pain in the heart and right hypochondrium, loss of appetite, sweating, nausea, dizziness and headache.
Routes of infection
In order not to become infected with helminthic infestation, you need to understand the methods of transmission of opisthorchiasis. The source of the disease is an infected person or animal (domestic cats and dogs).
Methods of infection
The methods of infection with opisthorchiasis are few. Three routes of transmission of infection by the fluke parasite can be distinguished:
- fish dishes;
- tableware containing infected fish;
- pet (cat).
The main way helminths enter the body is through eating infected fish. Infection is possible when the menu includes river fish that has not undergone sufficient heat treatment (dried, undercooked, lightly salted). Most people suffer from opisthorchiasis from late spring to early autumn, when fish harvesting begins actively.
You can get an infection through a poorly washed cutting board or dishes where the invasive larva of the pathogen remains. The cook, who has cut up the infected fish, cuts baked goods and fruits with a knife. Helminths enter the mouth, then the stomach and other organs, where they become parasites. It is advisable to buy a separate board and knives for preparing fish dishes, and rinse them thoroughly with hot water after use.
There is a method of infection with fluke - infection through contact with a pet if it has eaten fish infected with parasites. The owner of an infected dog or cat runs the risk of becoming infected through a kiss or the saliva of a pet that has helminth larvae on its body. After being with an animal, you should wash your hands thoroughly. Most people believe that it is impossible to get opisthorchiasis from a sick animal.
What consequences can opisthorchiasis lead to?
The most common consequence of this disease is an allergy, which occurs due to injury by worms to body tissues and intoxication with substances formed during their decay. During the first time of its residence in the human body, opisthorchid primarily affects the bile ducts, and then epithelial tissues.
If there are a very large number of these parasites in the body, bile accumulates and stagnates, just as opisthorchids prevent its normal secretion.
The most dangerous possible complications of opisthorchiasis are cirrhosis and liver cancer, as well as pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer.
List of the most severe possible consequences of opisthorchiasis:
- cirrhosis;
- hepatitis;
- oncological diseases;
- inflammatory diseases of the digestive organs.
Are there any consequences of infection?
Of course there is. The most common outcome of infection is an allergic reaction. It may be caused by poisoning of the recipient's body by decaying parasite larvae. Or simply injury to the liver walls.
Parasites that have recently entered the body usually attack the bile ducts, while parasites that have already been in the body for a long time destroy the tissue covering the surface of the muscles and body cavities.
The most dangerous consequences include restructuring of the liver, liver cancer, and inflammation of the pancreas. These diseases are very difficult to treat or are generally incurable.
To avoid problems with the presence of parasites in your body, you must follow a number of rules:
- Stop eating raw fish, since opisthorchiasis infection occurs when eating unprocessed river product.
- Before consumption, thoroughly heat the fish.
- Salt the fish for at least 14 days using a solution at room temperature. The ratio should be as follows: 600 g of salt should account for about 2000 g of fish.
- After the fish has been salted for about three days, it must dry for at least 21 days.
- To remove parasites by freezing, it is necessary to keep the fish in the freezer at a temperature no higher than minus 30 degrees for about 1.5 days.
- When cleaning fish, you must ensure that scales or other particles do not fall into the oral cavity.
Thus, you can become infected with opisthorchiasis, but not from a person. The most common carriers of parasites are carp fish . Therefore, in order to get rid of worms in the product, it is necessary to carefully process them. Also, do not neglect the rules of personal hygiene after playing with pets, as they can carry parasite larvae on their fur.
Diagnosis of opisthorchiasis
It is impossible to identify this disease without using special research methods that are aimed specifically at establishing the presence or absence of opisthorchiasis. The likelihood of the appearance of certain symptoms of infection is determined by individual characteristics, as well as the duration of development of opisthorchiasis in the body.
The diagnosis of opisthorchiasis is made only after special parasitological studies. To eliminate errors, you should have your stool analyzed at least three times, since this worm can release eggs in different quantities on different days. At an early stage of the disease, the presence of its causative agent is determined by blood tests.
It is recommended that people belonging to risk groups be tested for opisthorchiasis. These are people who have eaten raw or insufficiently processed fish, since this is the main method of transmission of the parasite.
Only those fish dishes (including sushi) that have been prepared in compliance with all the rules can guarantee safety.
Prevention of opisthorchiasis
Infection with this disease can be excluded by adhering to the following rules:
- Complete exclusion of raw fish from the diet.
- Fry any fish for at least 20 minutes.
- Boil any fish for at least 20 minutes.
- Correct proportions when salting fish - you need at least 300 g of salt for every kg of fish. Keep the fish in brine for at least 2 weeks.
- When drying fish, it is first salted and then kept for at least 3 weeks.
- When processing fish, it is necessary to prevent pieces from getting into your mouth.
Judging by the fact that you are reading these lines now, victory in the fight against liver disease is not yet on your side.
Have you already thought about surgery? This is understandable, because the liver is a very important organ, and its proper functioning is the key to health and well-being. Nausea and vomiting, yellowish skin tone, bitterness in the mouth and unpleasant odor, dark urine and diarrhea. All these symptoms are familiar to you firsthand.
But perhaps it would be more correct to treat not the effect, but the cause? We recommend reading the story of Olga Krichevskaya, how she cured her liver. Read the article >>
Preventive measures
To avoid getting opisthorchiasis, you need to follow some recommendations:
- do not eat raw fish;
- boil or fry fish for at least 30 minutes;
- salting at home should last at least 2 weeks;
- You need to salt the fish correctly: for 1 kg of fish take 300 g of salt;
- to destroy parasites, you can keep the fish in the freezer for about three days (the temperature should be -26-28 °C);
- Vegetables and herbs should be thoroughly washed before use, preferably doused with boiling water;
- When in nature, observe hand hygiene;
- do not swim in unknown open waters.