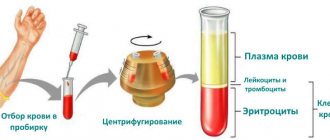
Nature of release
Blood in the stool can appear for various reasons. This is a symptom of quite dangerous diseases that affect not only the quality of life, but can also be fatal. These include malignant tumors, STIs, and ulcers. The sooner treatment is started, the higher the likelihood of full recovery.
Scarlet blood not mixed with stool
Often, the discharge of blood with feces during bowel movements indicates the occurrence of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract. Then the type of blood may be different, it does not look like the usual one from a wound, the color and consistency changes as a result of the passage of secretion throughout the digestive tract.
If the discharge is fresh, the appearance of scarlet blood is observed, which means that the source of blood loss is located near the anus, most likely the rectum or large intestine.
Streaks of blood in normally formed or loose stools
Stools with bloody discharge in the form of streaks and dark cherry clots indicate the presence of chronic intestinal diseases. The manifestations of such diseases can be different - abdominal pain, blood residue on underwear, diarrhea, changes in body temperature. With hemorrhoids, cancer, fissures, bloody stools appear.
Hidden blood in stool
A symptom such as hidden bleeding is almost impossible to notice, but it indicates the development of diseases in the gastrointestinal tract.
Diagnosis of occult blood in feces is carried out only in a laboratory setting, since it can be mistaken for undigested particles of foods that have a reddish tint, such as berries, tomatoes, and beets.
To make sure there is no false symptom, you need to avoid eating the above foods for several days, and then pay attention to the color of the excrement. If signs of blood persist, you should seek medical help.
Anal fissure
Cracks occur as a result of mechanical damage to the mucous membrane. This usually happens because the intestine is stretched too far. This is facilitated by constipation, which results in the formation of an extremely hard, highly compressed lump of feces.
Also, unhealed wounds often open during hard work.
Here, as in the previous case, a distinctive feature is the release of blood separately, and not as part of the feces. For this reason, it is often found on toilet paper or directly on laundry.
Discomfort in the anus
Characterized by the appearance of blood from the anus with difficulty defecating. In this case, trauma to the lining of the anorectal region occurs with solid feces. Upon external examination, making a diagnosis is not difficult.
The occurrence of acute pain and red blood from the anus after prolonged constipation is a pathognomonic sign of this pathology.
Treatment consists of taking laxatives or performing a cleansing enema, using ointments that accelerate regeneration and following a laxative diet. Prevention of the appearance of blood during bowel movements is anal exercises and compliance with hygiene procedures.
These benign formations come in different shapes and locations. If the polyp is small, there may be no signs. As it grows, bloating occurs in the abdomen, blood appears, and pain after bowel movements occurs. Diarrhea or constipation may develop that is not associated with a change in diet. Hemorrhoids may occur after diarrhea. Surgery is used to treat large polyps.
Causes of blood in stool
It often happens that several diseases fit one symptom. The appearance of blood in feces during bowel movements without pain indicates the presence of infection in the body, mechanical damage or malignant neoplasms, and other anomalies.
There can be many reasons, and they all require an ambiguous approach and individual treatment.
Infectious causes
STDs such as gonorrhea or syphilis may cause symptoms such as bleeding during bowel movements and blood in the stool. The reason is a violation of the integrity of the intestinal mucosa. As the disease develops, complications may begin in the form of arterial damage or intestinal ischemia. The appearance of blood may indicate the presence of erosion.
Haemorrhoids
Varicose veins of the rectum, or hemorrhoids, are manifested by the appearance of dark cherry-colored blood in the stool. Basically, the appearance of the disease is facilitated by an increase in pressure inside the gastrointestinal tract, or stretching.
Hemorrhoids are divided into external and internal. In the first option, during a routine examination, you can notice the presence of varicose veins; if the patient has internal hemorrhoids, special examination equipment is used. Treatment can occur either with or without surgery; medication can only be used at the beginning of the development of the disease.
Anal fissure
Bright red blood, separated from the feces, is the most common sign of an anal fissure. If it is bright, most likely the damage is located near the anus, since passing through the intestines, the color of the stool will most likely change. Constipation can contribute to the fissure when a person makes great efforts to empty. The volume of blood released from such damage is insignificant. An accurate diagnosis can be made through a routine medical examination; diet and stool thinners are usually prescribed.
Intestinal polyps
Polyps are benign neoplasms that appear on the walls of the intestine. The disease affects all categories of the population, regardless of gender and age. If the pathology is hereditary, there is a possibility that it will turn into a cancerous tumor, so polyps are often treated with surgery and removed. Blood clots in the stool of an adult are the main symptom, which can be combined with bloating, constipation and itching.
Often the disease is asymptomatic. Currently, there is no exact answer to the question of the reasons for the appearance of polyps. It is believed that the reasons may lie in chronic inflammation of the intestines, dysentery, living in an area with poor ecology, poor nutrition, the appearance of polyps in the womb and their gradual development, food allergies.
Crohn's disease
Impaired immune function can lead to the development of Crohn's disease. Patients with measles, allergy sufferers, as well as people with bad habits are at risk of developing pathology. Diagnosis is carried out using medical equipment.
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis
When such a disease occurs, the intestinal mucosa may be destroyed. The presence of blood in excrement is not the only symptom of the development of the disease; it is often accompanied by pain, diarrhea, fever, and has symptoms of poisoning of the body.
Intestinal diverticulosis
Diverticulosis is almost asymptomatic or the symptoms are similar to other intestinal diseases. The disease affects people of mature and old age. The essence of the disease is that bulges of ten to twenty millimeters in size appear on the intestinal walls. The appearance is promoted by malnutrition, excess weight, vitamin deficiency, and insufficient physical activity.
Acute intestinal infection
This disease occurs with pronounced symptoms: the appearance of blood in the stool, a jump in body temperature, and diarrhea.
Diagnosis is carried out using laboratory testing of feces and blood; antiviral, painkillers, probiotics and other drugs are prescribed as treatment, which are selected by the doctor based on the age and condition of each patient.
Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis is a type of inflammatory disease that occurs as a result of stagnation of contents in protrusions of the intestinal walls. Develops in people of mature age in most cases; women are most susceptible to the disease. Causes may include lack of fiber, constipation, poor diet, weak immune system, and genetic predisposition.
Peptic ulcer
Symptoms of bleeding from gastrointestinal ulcers manifest themselves in hard, black stool, attacks of nausea and vomiting with blood, and chills. This condition requires urgent surgical intervention. A complication of the existing disease is often perforation of the ulcer. Symptoms are severe pain, weakness, increased heart rate, cold sweat, and fainting. In such a situation, emergency assistance from surgeons is required.
Phlebectasia
This condition implies dilation of the veins and pathology of valve function. The name of the disease speaks for itself, literally translated as “stretched vein.” Mature men are most susceptible to the disease. The cause is a violation of blood flow. At first, the disease does not manifest itself in any way; at later stages of development, patients complain of pain in the gastrointestinal tract. For diagnosis, an x-ray examination is necessary.
Proctitis
The causes of proctitis can be infections that provoke chlamydia, CMV, herpes, syphilis, tuberculosis. Anal sex, mechanical damage, cracks, injuries during childbirth also provoke the development of pathology. Alimentary proctitis can develop as a result of poor nutrition, frequent consumption of spicy and fatty foods, and bad habits.
Worm infestations
Helmintic infestation – infection with worms. They can enter the body through close contact with infected people and animals, through unwashed vegetables and fruits, water, and meat. Symptoms: anemia and vitamin deficiency, frequent colds. In the absence of proper treatment, they can seize and damage the organ. They may appear in stool or in laboratory tests.
Granulomatous enteritis
Young people under 30 years of age are most susceptible to this disease. This is a chronic disease that affects the walls of the gastrointestinal tract. Only anamnesis and thorough research will help identify the correct diagnosis.
Oncological diseases
The main manifestations of oncology of the gastrointestinal tract are obstruction, blood in the stool, diarrhea, constipation, false urges, and the development of anorexia. In any case, you need to be examined in time for the presence of cancerous tumors and begin treatment as early as possible.
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease
This pathology affects the gastrointestinal tract and is always accompanied by ulceration followed by scarring of the walls.
The exact cause of the disease has not yet been established. Some scientists believe that it is of an autoimmune nature, others believe that the provocateur is an infection, and others are sure that the disease should be classified as genetic.
Her signs are as follows:
- intestinal pain;
- pain directly in the anus;
- diarrhea with bloody discharge.
This is a group of intestinal diseases that have similar clinical manifestations, but are characterized by different morphological patterns.
Colitis of ulcerative nature
- temperature increase;
- general weakness;
- fast fatiguability;
- pain in joints and muscles;
- prolonged diarrhea, the appearance of blood and mucus in the stool.
The reasons for the development of this disease have not yet been clarified; there is a hereditary predisposition and autoimmune factors.
Pseudomembranous colitis
A disease that occurs as a complication of uncontrolled use of antibiotics or other medications. During an endoscopic examination, a yellow coating is observed on the patient's intestinal mucosa. The terminal sections of the large intestine are usually affected.
This disease is characterized by bleeding from the anus after frequent bowel movements, nausea, vomiting, general weakness and fever. Etiotropic and symptomatic treatment is carried out.
Diverticular disease
Very often a complication of this pathology develops in the form of inflammation - diverticulitis.
Characterized by the following symptoms:
- Blood appears after constipation.
- Possible unstable stool.
- At the onset of the disease, the temperature rises to high levels, nausea, and increased flatulence occur.
A complication of this disease may be bleeding during bowel movements. It usually develops suddenly. In this case, emergency medical care is required.