Types of sphincter diseases
Most often, the internal sphincter of the rectum is subject to the following diseases:
- Anal sphincter spasm is a chronic condition characterized by pain and discomfort in the rectal area.
According to its clinical picture, spasm of the anal sphincter is not accompanied by serious development of pathologies in the intestine. The pain syndrome usually does not have an exact cause.
This disease depletes the rectal sphincter muscles. It lasts for quite a long time, exhausting patients not only physiologically, but also psychologically. For this reason, it is very important to diagnose such a spasm in a timely manner and begin proper treatment.
- Rectal sphincteritis is a disease that is accompanied by severe inflammation of the sphincter muscle. The disease progresses in waves, causing a lot of unpleasant symptoms in the sick person. Sphincteritis requires long-term treatment.
Treatment
There is a whole range of methods on how to relieve spasm of the rectal sphincter. It includes diet, lifestyle changes, as well as drug and surgical therapy.
Non-drug
Non-drug treatment involves the following methods:
- lifestyle correction;
- adherence to a specialized diet;
- traditional methods of treatment.
Lifestyle and diet
Sphincterospasm is treated with the following lifestyle adjustments:
- daily hygiene procedures;
- using soft toilet paper or wet wipes after a natural bowel movement;
- periodic, daily trips to the toilet;
- prevention of physical inactivity - exercise, sports (helps accelerate peristalsis in the intestines - prevents constipation);
- eliminating bad habits.
Diet treatment for spasm of the anal sphincter is aimed at preventing constipation and flatulence, as well as preventing irritation of the mucous membrane of the digestive tract.
The following recommendations must be followed:
- It is allowed to eat food in crushed or pureed form to reduce the load on the intestinal tract;
- the food consumed should not be too cold or hot;
- Spicy, salty, fatty foods are excluded from the diet - they irritate the mucous layer of the digestive tract;
- it is necessary to reduce the consumption of products that contribute to gas formation: sweets, butter products, legumes;
- food containing a large amount of plant fiber is limited (raw fruits and vegetables, unground cereals);
- It is important to adhere to the drinking regime - it is recommended to drink up to 2 liters per day.
For regular bowel movements, it is important to follow a diet - you need to eat food every 4-5 hours.
Causes of development of rectal sphincter diseases
Anal sphincter spasm develops due to involuntary contraction of the muscles located in the anus. In this case, the spasm itself can be of different frequency and intensity.
Typically, this disease occurs in middle-aged people, regardless of gender.
As for anal sphincteritis, it usually occurs in people with existing pathologies of the rectum. Moreover, such a disease further aggravates the course of chronic gastrointestinal diseases.
The following factors provoke the occurrence of sphincter pathologies:
- Unstable psycho-emotional state of a person. This can be frequent stress, depression, nervousness and even sleep disorders when a man or woman is chronically sleep-deprived, which leads to irritability and nervousness.
In this state, the body's defenses in people are quickly depleted, which leads to a tendency to develop gastrointestinal diseases, including sphincter spasm in the rectum.
- Untreated acute hemorrhoids. In addition, if you do not maintain your condition in the chronic form of this disease, it can also cause complications in the form of inflammation of the sphincter.
- Dysbacteriosis and other infectious and bacteriological lesions of the intestines.
- Oncological pathologies of the rectum.
- Rectal fissure.
- Passive lifestyle.
- Vitamin deficiency and acute lack of nutrients.
- Rectal injuries.
- Poor nutrition (overeating, eating spicy and fatty foods, eating on the run, etc.)
- Acute diseases of the digestive tract (stomach ulcer, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, etc.).
- Immunity impairment.
- Unhealthy lifestyle (drinking and smoking).
- Lack of physical activity.
- Hypothermia.
- Frequent constipation.
- Proctitis.
- The presence of pathological inflammation in the internal organs.
Spasms in the rectum
The same situation: severe periodic pain in the intestines during menstruation. It feels like a little more and the intestines will burst - the spasm is painful to the point of tears. With each period, the cramps become more frequent, and the pain intensifies and lasts longer. I went to the gynecologist, who sent me to a proctologist. Tomorrow I will go to him and report back.
Tata, no matter how funny it sounds, I quote: This is a lost fart. During menstruation, gases rush around in terror, trying to find a way out, crowding and creating a terrible crush. Moreover, in such a crowd they also reproduce faster. Anal China, in general.
From my own experience I realized that it’s all about these gases. And if your intestines are also naughty or you like spicy, carbonated foods, black bread and cabbage, THEN you are guaranteed these COLIC IN THE RECTUM! For girls, this is not a pathology, you just need to stick to a diet before menstruation and during pregnancy, avoiding gas-forming foods. Give it a try.
Anococcygeus pain syndrome
Anococcygeus pain syndrome is a polyetiological disease that requires a comprehensive examination to identify the possible underlying cause of pain and persistent complex conservative treatment, sometimes with the participation of a psychiatrist. This is a typical example of pain as an underlying syndrome. Treatment in most cases should be carried out in pain clinics.
Anococcygeal pain syndrome is often referred to as a harmless, unpleasant and incurable disease.
In the literature devoted to chronic pain syndrome of the anococcygeus region, a fairly wide range of terms is used to define this disease, however, only two are mentioned in the International Classification of Diseases - “proctalgia” and “coccydynia”. The definition of “anococcygeus pain syndrome” is a broader concept that unites a number of manifestations, the main symptom of which is pain in the perineum, anus or tailbone. Separately, only traumatic coccydynia should be considered, where the immediate cause of pain is an injured pathologically mobile tailbone.
Pain in the area of the sacrum and coccyx is most often associated with injury, and the injury itself could have occurred long before the pain occurred, but there may be other causes of such pain.
Causes of anorectal pain can be:
subtle disorders of the neuromuscular system of the posterior anal space and the entire pelvic floor;
Symptoms and signs of sphincter diseases
Most often, sphincter spasm and inflammation are manifested by the following symptoms:
- The appearance of itching and burning in the intestines.
- Feeling of discomfort and fullness in the anus.
- Abnormal stool (possible constipation or vice versa, diarrhea and diarrhea).
- Sharp paroxysmal pain during and after defecation is inherent in sphincter spasm.
- Drawing and aching pain in the abdomen.
- Loss of appetite.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Irritability may appear as a result of constant pain and poor sleep.
- Constant pain radiating to the lower back or perineal area.
- False urge to defecate. Moreover, such urges can be quite frequent (happen several times an hour).
- The appearance of bloody discharge in the stool.
- The appearance of mucus in the stool.
- Malaise and weakness.
- An increase in body temperature is possible with an acute inflammatory process in the sphincter.
- Pain that radiates to the right side of the ribs and is localized under them is characteristic of the acute development of inflammation of the sphincter.
- Nausea and a feeling of bitterness in the mouth.
- Fever and chills.
- Pain after physical activity. However, sometimes patients develop pain even after minor strains.
Important! In acute forms of sphincter disease, a person will suffer from pronounced symptoms of the pathology. This clinical picture changes if the disease has become chronic. Then all its signs may be less pronounced, periodic and as if erased. This will significantly complicate the diagnostic process and prolong treatment time.
Types of pathology
Spasms that cause pain may also be known as colic. There are several common types of colic:
- Primary volatiles - this means that a spasm in the rectum has a spontaneous, sharp onset and also disappears spontaneously and for no reason. Maximum volatile colic lasts several hours, and it is not possible to get rid of them with the help of painkillers. The causes of this symptom often cannot be determined.
- Secondary colic is colic that develops as symptoms of any disease of the gastrointestinal tract, be it hemorrhoids, anal fissures, rectal tumors or anything else.
- In women, colic may be the result of radiating pain caused by endometriosis of the uterus.
Depending on the type of pathology, treatment is selected, since most often simply relieving the spasm is not enough; relapses of the pathology must be monitored.
Spasm in the rectum can become a faithful companion to a large number of diseases. The most common causes of symptoms of spasms may be the following:
- Anal fissure is the most common cause of colic. Moreover, neither older people nor small children are immune from it. Pathology occurs in all age groups if there are factors that provoke its development.
- Paraproctitis can also be the reason why muscle spasm develops in the rectum, especially if the anal glands located close to the anus become inflamed, and a person aggravates the situation by scratching the itchy area in the early stages.
- Injuries to hemorrhoidal cones - in this case, sharp pain most often occurs when trying to go to the toilet and empty the intestines, since large nodes with a delicate mucous membrane are easily injured by hard feces. Pain may also appear due to pinching or thrombosis of nodes.
- Anal muscle spasm is a pathology that rarely develops separately from any concomitant disease. It is more often perceived as a syndrome of a disease, rather than as an independent disease.
- Coccydynia - in this case, characteristic pain symptoms develop in a person in response to a bruise or other injury to the tailbone. The condition usually worsens when sitting.
- Hematoma in the anal area - this pathology occurs if, as a result of injury, damage occurs to the vein supplying blood to the anus. In most cases, the symptoms of the pathology disappear on their own without treatment.
- An ulcer in the rectum is a rather rare pathology, which, however, cannot be written off. Usually in this case, pain is combined with the development of bleeding every time the ulcer is injured by feces or other influences.
- Prostatitis, which occurs in men, can cause pain and spasms of the intestinal muscles, since the pain has radiating features.
- Ovarian cyst is a pathology characteristic of women. With a cyst, pain can radiate and provoke the formation of a symptom such as colic in the intestines.
It is worth paying attention to the causes of the pathology, since most often it is impossible to get rid of recurrent spasms of the rectum until the cause can be identified and eliminated.
Idiopathic colic is quite rare, and to make such a diagnosis, the doctor must exclude other possible causes of the characteristic symptoms.
Types of sphincter spasms
According to the duration of sphincter spasms, there are:
- fast (last 2-10 seconds);
- long-lasting (can last for several minutes).
According to etiological criteria, sphincter spasms are:
- Primary (develop as a neurological involuntary spasm).
- Secondary (develop as a consequence of untreated pathologies of the rectum).
A fleeting spasm develops suddenly and is accompanied by stabbing pain in the anus, which radiates to the lower abdomen. In this case, the person will also suffer from severe discomfort during bowel movements.
A long-lasting spasm will torment the patient for several minutes. Moreover, in this condition, the pain can be so acute and severe that a person will need to take painkillers or fast-acting analgesics.
Important! Diseases of the sphincter, be it spasm or inflammation, can lead to dangerous complications, so if the first symptoms of the disease occur, it is recommended to consult a proctologist as soon as possible.
Symptoms of the disease
Pain from proctalgia can radiate to the intimate area.
Proctalgia is a pathological deviation of the muscular system of the rectum. Manifestations of the problem:
- acute pain attacks radiating into the intimate area and across;
- painful bowel movements;
- pain symptom that disappears when taking a bath;
- spasms occur at night.
Features of sphincter spasm in hemorrhoids
As mentioned above, most often problems with the sphincter in people develop precisely because of hemorrhoids. This is justified by the fact that with the development of hemorrhoids or anal fissure, the nerve endings of the rectum are very irritated, which leads to inflammation of the mucous membrane, enlargement of hemorrhoids, pain and a sharp contraction of the sphincter - spasm.
Typically, such a spasm occurs during bowel movements, which distinguishes it from ordinary proctalgia. Moreover, this spasm in more severe cases can last for hours, until the next act of bowel movement.
In this condition, a certain vicious circle is created in the patient - rectal disease (hemorrhoids) causes severe pain and irritation of the intestine, which in turn provokes sphincter spasm.
Important! Most proctologists recognize sphincter spasm as one of the first signs of hemorrhoids, so in this condition, when diagnosing, there is no need to exclude the root cause of rectal spasms as hemorrhoids.
Causes
Damage to the anus can occur with almost any disease of the gastrointestinal tract. A large role is played by genetic predisposition due to congenital weakness or failure of the sphincters.
Rectal sphincteritis occurs due to the following reasons:
| Diseases | Impact of external factors |
|
|
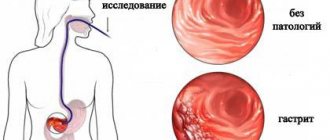
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of sphincter diseases has the following features:
- To begin with, the proctologist must collect the patient’s medical history and complaints.
- After this, the person needs to undergo a general blood and urine test.
- Next, the patient needs to undergo an examination of the anus and a digital examination of the anus.
- Retromanoscopy and ultrasound of the rectum will help to study the condition of the rectum in more detail.
- Blood test for immune status and bilirubin.
- Probing.
In addition to examination by a proctologist, the patient is recommended to undergo a consultation with a therapist, endocrinologist and neurologist. A CT scan of the rectum should also be performed.
Diagnosis of anal sphincter spasm
Diagnosis of sphincter diseases has the following features:
- To begin with, the proctologist must collect the patient’s medical history and complaints.
- After this, the person needs to undergo a general blood and urine test.
- Next, the patient needs to undergo an examination of the anus and a digital examination of the anus.
- Retromanoscopy and ultrasound of the rectum will help to study the condition of the rectum in more detail.
- Blood test for immune status and bilirubin.
- Probing.
In addition to examination by a proctologist, the patient is recommended to undergo a consultation with a therapist, endocrinologist and neurologist. A CT scan of the rectum should also be performed.
Any disruption of these processes leads to problems with the intestines, and as one of the consequences, pain in the rectum may appear.
However, it cannot be said that this alone can be the cause of pain in the area of the ampoule and the rectum itself.
There are many factors that can lead to pain in the rectum actively bothering the patient. Very often, patients do not seek advice and help from specialists in a timely manner. People are embarrassed by problems in this area. Often, after a doctor’s examination, it turns out that precious time has been lost, this is especially dangerous for intestinal cancer.
Causes of pain
As for the reasons that provoke pain in the rectum, they can be divided into several main groups.
- Disorders, disorders of the digestive and motor functions of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Infectious diseases.
- Injuries and fissures of the anus.
- Diseases of the abdominal and pelvic organs.
- Tumors of the rectum, intestines.
The main thing is that a careful and attentive attitude to your health is the key to a normal, fulfilling life and the ability to take responsibility for yourself. Regularly occurring pain in the rectum or anus is a reason to immediately consult a doctor for advice, putting aside any embarrassment, especially true when it comes to cancer.
The gastrointestinal tract begins in the oral cavity and ends in the rectum. Any disorder of normal digestion, peristaltic movement of food and feces can lead to serious problems with the abdominal and pelvic organs.
Digestion of food occurs in stages with the help of many enzymes in various parts of the gastrointestinal tract and moving further into the small and then large intestine. Neglect of eating rules, an unbalanced diet, alcohol abuse or insufficient fluid intake can lead to constipation.
Constipation also occurs after eating a large amount of flour and fatty foods. This is especially true on holidays, when a large amount of food is not balanced by physical activity. After heavy feasts, many people spend time in inactive rest. Constipation is accompanied by pain in the rectum.
A painful sensation and fear of pain appear. The patient deliberately restrains the urge to defecate, which further aggravates his condition. In addition to pain in the rectal area, there is:
- bloating;
- lethargy;
- apathy;
- decrease in emotional background.
Such conditions can be alleviated by taking laxatives or an enema followed by a diet.
Similar problems include gallbladder dyskinesia. Insufficient or irregular secretion of bile leads to poor digestion and absorption of fats, and spastic disturbances of peristalsis may appear.
A feeling of constriction appears in the lower abdomen, stool becomes irregular, reminiscent of “sheep feces.” These phenomena may also be accompanied by pain in the rectum due to its spasm and at the same time a large amount of contents.
This includes intestinal infections and helminthic infestations. Infection with pathogens of intestinal infections usually occurs through consumption of drinks or foods that contain the pathogen in an infectious dose. This can be almost any product that can become a breeding ground for a microorganism. Most often they are:
- dairy products;
- meat and meat products;
- confectionery;
- unprocessed water and drinks.
In this way you can become infected with salmonellosis, dysentery, amoebiasis, and escherichiosis. Among helminthic infestations, roundworms deserve attention because they can gather in the intestinal lumen into balls and damage its wall.
To a greater extent, the rectum begins to hurt during infections that are accompanied by diarrhea, especially dysentery. It is characterized by “tenesmus” - a very painful urge in the lower abdomen in the rectal area. Prolonged loose stools lead to irritation of the paraproctal area after numerous bowel movements, as well as due to the release of aggressive decay products.
The patient complains of a bursting, pulling or sharp pain in the lower abdomen, gluteal region, which causes suffering and forces one to look for a comfortable body position.
Damage can occur after surgery on the abdominal organs, rectal cancer, bruises of the pararectal area, after defecation due to constipation or infectious diseases, hemorrhoids.
Enlargement of rectal hemorrhoids often occurs in people who lead a lifestyle with little physical activity, abuse fatty and carbohydrate foods, and do not drink enough fluids during the day.
The pain with such problems is nagging and can be paroxysmal in nature. Cracks and injuries are dangerous because they are difficult to heal and can be complicated by an infectious process - an abscess or paraproctitis. The surrounding tissue below becomes inflamed, which leads to increased pain, signs of intoxication, bleeding from the damaged area, and deterioration of the general condition.
The appearance of pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen or directly in the rectal area can be due to a benign tumor or cancer of internal organs. The pain often radiates downwards, so the large intestine is mistaken for its source. These organs include the internal genital organs and the skeletal system. Namely:
- prostate in men;
- uterus or ovaries in women;
- pelvic bones or spine.
With cancer of any of these organs, metastases can spread to the rectum. Often, a malignant tumor primarily affects the rectal intestine. In cancer, pain is a secondary symptom, as a consequence of malignant tissue breakdown.
There is constant pain in the lower abdomen, not associated with external irritants; formations may appear in the anus, protruding under the skin. Only after a thorough examination and collection of all test results will it be possible to make a correct diagnosis.
Prostatitis, endometritis, salpingoophoritis are often accompanied by pain radiating to the gluteal or pararectal area. It can be mistaken for pain directly in the intestine, so once again we need to remind you of the importance of a differential approach to such a symptom and the need to contact a specialist as soon as possible.
Listen carefully to your body. Constant or regularly occurring pain in the rectal area should not be ignored. Its causes may lie not only in the intestines, but also in other organs. Treatment is prescribed only by a doctor.
Digestive disorders are corrected with a proper diet, nutrition regimen, and the prescription of enzyme and laxative medications. For anal fissures, local treatment is necessary with suppositories and suppositories, compresses, and baths. In this case, prevention of infectious suppurations is mandatory.
Helminthic infestations and intestinal infections can be cured by taking antibiotics, nitrofurans and antiparasitic drugs.
Proper nutrition, a balanced diet, a regime of physical activity, a healthy emotional background, and regular preventive examinations will help maintain health and activity for a long time.
What to do if symptoms of sphincterospasm occur? If such a problem develops, it is necessary to contact a proctologist who will conduct a thorough diagnosis. The set of measures includes clinical and additional methods.
Clinical
Clinical diagnosis involves:
- Collecting complaints - a specialist determines the nature of the pain, the characteristics of which are an important criterion for establishing the form of the disease: the short duration of the unpleasant sensations indicates primary sphincterospasm, duration - secondary. The doctor also analyzes the connection between this manifestation and the act of defecation.
- Taking an anamnesis - the doctor collects information about possible pathologies that the patient has and identifies risk factors for developing the disease.
- Physical examination - a specialist conducts a general examination of the patient (skin, mucous membranes, etc.), assesses the functioning of vital organs and systems.
- Examination of the anus - the doctor evaluates the anus for the presence of anal fissures or external hemorrhoids;
- Digital examination of the rectal area - a specialist diagnoses possible proctological diseases.
Additional
After implementing clinical methods, the doctor refers the patient to a number of additional studies. Among them:
- general and biochemical blood tests - carried out to assess the patient’s condition, identify inflammatory and other pathological processes;
- invasive research methods (sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy) - carried out for the purpose of visual examination of the mucous membrane of the large intestine, to exclude inflammatory or oncological diseases;
- irrigoscopy - X-ray examination of the intestines with the introduction of contrast - allows you to evaluate the relief of the organ and the presence of tumors;
- MRI, CT are informative research methods that are prescribed when the diagnosis is unclear or difficult.
To carry out a differential diagnosis of anal spasms, the patient is prescribed consultations with a psychiatrist, neurologist, gastroenterologist, and infectious disease specialist.
The sphincter is a circular layer of muscle fibers that are found at the end of the rectum. It regulates the process of bowel movement and the release of gases. It is a valve device; when it relaxes, an act of defecation occurs. When under tension, it is impossible to carry out this process.
At the doctor's appointment
Treatment methods
Therapeutic therapy for sphincter diseases is prescribed for each patient individually, depending on the complexity of the patient’s condition, symptoms and the cause of the disease.
Sphincter diseases can be treated in the following ways:
- With the help of medications.
- Surgically.
- Traditional medicine.
- Using physiotherapy treatment.
Drug therapy involves prescribing the following groups of drugs:
- Analgesics are prescribed for severe pain.
- Preparations to enhance immunity and vitamin complexes.
- Antibiotics are used for infections.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Antipyretic medications are used for high fevers.
- Antispasmodics are prescribed for spasms (No-shpa).
- Use of pain-relieving rectal suppositories.
- Suppositories and ointments (Posterizan, etc.).
- Laxatives are prescribed for constipation.
Surgical treatment is used for advanced sphincter disease. It provides the following:
- Carrying out choledochotomy.
- Establishment of bile duct drainage.
- Carrying out papillosphincterotomy.
The recovery period after surgical treatment is quite long. In this case, the patient will definitely need to regularly observe hygiene of the anus and lubricate the rectum with healing ointments.
Physiotherapeutic treatment is considered supportive. It is prescribed after drug therapy and provides the following:
- Conducting UHF currents.
- Diathermy.
- Electrosleep.
- Darmonvalization.
- Thermal procedures.
- Conducting microenemas using antiseptic and oil products.
Traditional treatment involves the use of the following procedures:
- Carrying out sitz baths.
- Establishment of enemas.
- Formation of therapeutic tampons.
To prepare sitz baths you need to use the following recipes:
- Potassium solution:
- make a weak solution of potassium in warm water;
- take a bath for twenty minutes;
- after this, introduce an oil anesthetic rectal suppository;
- repeat the procedure every day for a week.
- Herbal solution:
- make a weak decoction of dry chamomile, St. John's wort and oak bark;
- take a bath in such a warm solution;
- repeat the procedure morning and evening for seven days.
- Oil solution:
- mix 2 tbsp. l. sea buckthorn oil with two glasses of boiling water and a spoonful of calendula herb;
- leave for ten minutes, strain and take such a bath for ten minutes;
- repeat the procedure daily for five days.
To prepare microenemas, you need to mix chamomile, calendula and yarrow in equal quantities. Boil the herbs in two liters of water and use for microenemas. Repeat the procedure every day before bed for ten days.
Very effective for treating this disease is the use of rectal suppositories with healing injuries. The best recipes for this purpose are:
- Herbal candles:
- mix flax flowers, oak bark and chamomile in equal groups;
- chop the herbs and mix them with 100 g of lard;
- use as tampons in the rectum three times a day;
- leave the tampon in the intestine for no more than two hours;
- repeat the procedure for five days in a row.
- Hop tampons. To prepare them you need:
- mix three tablespoons of crushed hop cones with 300 g of fresh lard;
- add 1 tbsp to the mixture. l. olive or sea buckthorn oil;
- Soak a tampon with the prepared mixture and use it to install at night for five days.
Important! Before using traditional medicine recipes, you should always consult with your doctor.
Intestinal spasm treatment and prevention
How does intestinal spasm occur and how to deal with it?
Intestinal spasms are paroxysmal pain sensations that appear due to various changes that occur in the intestines. There are two types of pain: aching and sharp (intestinal colic). Colic is a short-lived cramp-like attack. Aching pain lasts a long time, then intensifies.
Intestinal spasms can occur for the following reasons:
- unhealthy diet (spicy, fatty, sour, stale, poorly prepared food);
- constipation;
- nervous experiences;
- intestinal infections;
- ARVI;
- intestinal obstruction;
- dysfunction of intestinal motility;
- food allergies;
- presence of helminths (worms);
- intoxication.
Intestinal spasm is usually accompanied by the following symptoms:
- bloating;
- false urges;
- violation of feces formation;
- nausea;
- mucous discharge;
- dizziness;
- stool disorder;
- increase in blood pressure.
Treatment and prevention of intestinal spasms. Pain Relief Methods
The following methods will help relieve pain during intestinal spasms:
1. Medication method. Antispasmodic and painkillers are prescribed (No-shpa, Papaverine, Baralgin, Spazmalgon).
2. Physiotherapeutic method. Therapeutic exercises, cold rubdowns, cold showers, dousing the abdomen and massage are used. It is recommended to engage in sports such as light running, walking, swimming.
3. Psychotherapeutic method. Conduct talk therapy or hypnotherapy.
4. Dietary method. The daily diet should include foods containing fiber (brown bread, buckwheat porridge, honey, vegetable soups, peas, mushrooms, mashed potatoes, white bread), lean meat and fish. Fresh vegetables and fruits will help eliminate intestinal spasms: plums, prunes, figs, apples, cucumbers, turnips, beets, cabbage. Fermented milk products are useful: kefir, kumiss, yogurt.
5. Folk remedies. There are many different traditional medicine recipes that help eliminate some intestinal problems. Let's look at a few of them:
- prepare a decoction of blueberries, gooseberries, blackcurrant leaves and plums in equal quantities;
- every 2 hours, drink a spoonful of vegetable oil, washed down with chamomile decoction;
- soak the birch mushroom for 4 hours, then crush it, pour the resulting mass with warm water and leave for 2 days, then filter and drink 6 times a day before meals;
- pour wormwood (70 g) with spring water and leave for a day, then boil the mixture and filter; sprinkle the resulting broth with granulated sugar (350 g) - you can replace it with honey, boil; take the product 4 times a day, a teaspoon.
6. Surgical method. If all of the above methods do not help, then surgical intervention is possible.
Prevention of intestinal spasms
We list several measures used to prevent pain in the intestines. So, you need:
- Healthy food;
- drink vitamins;
- defecate regularly;
- do not abuse alcoholic beverages and smoking;
- drink plenty of fluids;
- use medications only when absolutely necessary;
- exercise regularly;
- You can use propolis for prevention (on an empty stomach every day).
Intestinal spasm can accompany the development of diseases such as colitis, pancreatitis, enteritis, appendicitis, dysentery, cholecystitis. Don't put off visiting your doctor. Consult a gastroenterologist and get all the necessary tests.
Nutrition during treatment
Nutrition plays a very important role in the treatment of sphincter diseases. During this period, the patient should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Don't overeat. Portions should be small.
- There should be four to five nutritious meals a day and two snacks of nuts or fruits.
- You need to consume low-fat fermented milk products every day. It can be cottage cheese, kefir, fermented baked milk or all kinds of yoghurts. They will improve digestion and create favorable microflora in the intestines.
- The last meal should be no later than seven o'clock in the evening, so as not to overload the gastrointestinal tract at night.
- You should avoid eating fatty fish and meat. Instead, it is better to eat steamed or boiled food. You are allowed to eat chicken, turkey and lean fish.
- It is important to stop smoking, drinking coffee and drinking alcohol.
- Oils, especially olive oil, can be consumed in large quantities. It will simplify the act of defecation and relieve the problem of constipation.
- The following should be completely excluded from the diet:
- carrot;
- cabbage;
- potato;
- plums;
- smoked meats;
- sausages;
- semi-finished products;
- fried food;
- legumes
This is explained by the fact that the above products can complicate the digestion process, which should not be allowed in case of diseases of the rectum.
- You are allowed to drink fruit jelly, green tea and compotes. You can also drink chamomile tea.
- It is not advisable to eat too hot or cold food.
About diagnostics
In most cases, the help of specialists such as a gastroenterologist or therapist is needed
They must carefully analyze the medical history, pay attention to all the patient’s complaints; it often becomes necessary for a surgeon to take part in the treatment
When treating, it is necessary first of all to understand what exactly ailment caused such symptoms; for this purpose, studies are carried out, both instrumental and laboratory. For the timely detection of anemia, a general blood test is necessary; a urine test will help to understand if there are problems in the pelvis. To quickly assess the condition of the liver, as well as the kidneys and pancreas, it is necessary to conduct a biochemical blood test
It is very important to understand if there are pathological processes in the intestines, for this it is necessary to carry out a stool analysis