Gastritis is an inflammation of the inner lining of the stomach. Depending on the severity of the process, it covers not only the mucous membrane, but also extends to the submucosal and muscular layers. This determines the shape of gastritis.
In diagnosis, it is important that pain during gastritis is not caused by damage to the mucous membrane. It does not have pain receptors - nerve endings that carry signals to the brain. Therefore, such a sign as pain indicates a dysfunction of the muscle layer (stretching, inadequate contractions of individual groups of fibers).
Who has a stomach ache?
Statistics show that in the Russian Federation, 85% of the population has signs of gastritis. The most common people who suffer from stomach pain are:
- with a disrupted diet (long breaks in eating, overeating, starvation diets);
- addicted to fast food, fatty meat dishes, spicy seasonings, coffee lovers;
- alcoholics and heavy smokers.
A special group of adults are those who are afraid to see a doctor and prefer to independently take medications recommended by a pharmacist, neighbors, or friends. As a result of long-term use of drugs for headaches, for the treatment of joints containing salicylic acid, non-steroidal drugs, gastritis occurs.
At the same time, the stomach cannot withstand the negative combined effects of chemical irritants. How the stomach hurts with gastritis is well known to emotional and nervous patients who do not know how to deal with stress, suffer from insomnia, and changes in blood pressure.
Pain in the stomach (gastralgia) occurs not only with gastritis, but also accompanies gastroptosis (prolapse of the organ), cardiospasm of the esophagus, diseases of the liver, intestines and pancreas.
The digestive process is so connected with the functioning of the entire system that a disease of one of the organs causes a malfunction in the others, and inflammation quickly spreads. In 75% of patients, gastritis does not occur in isolation.
Folk remedies for stomach pain
Doctors recommend, if your stomach hurts, the use of herbs in the form of decoctions and teas. Eating honey, sauerkraut juice, and fresh potatoes effectively eliminates symptoms. Folk remedies for stomach pain are blueberry tea, which is used instead of tea leaves and drunk chilled. It is effective to use a decoction of chamomile flowers, which should be done as follows:
- put a glass of inflorescences in a jar;
- add the same amount of boiling water;
- insist;
- strain;
- drink in three doses throughout the day.
Find out what gastric polyposis is.
https://youtu.be/v55BFBAJwwE
Nature of pain
The stomach is projected onto the uppermost part of the abdomen, closer to the central zone (epigastrium). Patients indicate the place where gastritis hurts in the area between the joints of the lower ribs and a little lower.
Depending on the body type of a particular person, the stomach has a more horizontal or vertical (hanging) position. Accordingly, stomach pain with gastritis can also occur in the right and left hypochondrium or in the navel area.
The nature of the pain syndrome is described by patients as constant aching. At the beginning of the disease, pain occurs immediately after eating or excitement and does not subside throughout the day. In chronic cases, they do not depend on the time of eating. With each exacerbation, the pain becomes more intense and more difficult for patients to bear.
How does pain depend on acidity?
Patients familiar with diagnostics must undergo pH testing. This method determines the acidity of gastric juice and its fluctuations during the day. In gastroenterology, it is customary to include symptoms of pain in stomach diseases in syndromes of acid formation disorders. This explains the origin of the accompanying symptoms of gastritis.
With increased acidity
Hyperacid syndrome is characterized by increased production of hydrochloric acid and hyperactivity of pepsin, which increases muscle contractions of the wall (motility). This is typical for damage to the pyloric zone of the stomach in chronic gastritis.
The pain is intense and paroxysmal in nature due to spastic contractions of the muscle layer and pyloric sphincter. Located in the epigastrium and hypochondrium on the right, extending to the back. To select treatment, it is important that the pain mechanism is associated with excessive activity of the vagus nerve, therefore, in order to alleviate the patient’s condition, it is necessary to remove the influence of the vagus.
The type of secretion is accompanied by heartburn and burning. Due to gastroesophageal reflux, acid refluxes into the cardiac zone of the esophagus with the development of esophagitis. Patients complain of burning pain in the chest, pain when swallowing, and a feeling of a “lump in the throat.”
Pain in hyperacid gastritis is relieved by:
- warm heating pad;
- drugs with antispasmodic effects (vagolytics);
- by any means that reduce acidity (eating, antacids).
Gastritis causes signs of dyspepsia: sour belching, nausea, spastic constipation with feces in the form of “sheep” discharge, vomiting, which relieves pain. Patients can independently relieve pain by inducing vomiting. This method removes accumulated acid and relieves pyloric spasm. The hyperacid state does not affect appetite, patients do not lose weight.
When acidity decreases
With gastritis with low acidity (hypoacid), acid synthesis is reduced until complete cessation (achylia) due to atrophy of the parietal cells. The muscle layer loses tone, the wall of the stomach stretches.
The mechanism is characteristic of chronic atrophic gastritis. Changes are also observed in the neuroreceptor apparatus, which normally responds to increased pressure in the stomach.
This contributes to the occurrence of pain even with normal wall tone or slight stretching.
The upper abdomen begins to hurt immediately after eating or after 30–40 minutes. The pain is characterized by dullness, a feeling of heaviness, lack of clear localization and irradiation. When the food leaves the stomach (after 2–3 hours), the pain subsides on its own.
Relieving pain from gastritis with low acidity is much more difficult. Prokinetic drugs (Motilium) usually help. Accompanying similar manifestations of dyspepsia, as with hyperacid gastritis, but the belching does not contain acid.
More pronounced intestinal symptoms:
They are explained by the ingestion of undigested food residues into the intestines. Patients typically experience decreased appetite and significant weight loss. Atrophic gastritis is one of the causes of malignant cell degeneration and increases the likelihood of progression to ulcers and stomach cancer.
Anatomical structure
The stomach has two openings: the inlet - cardia or cardiac, and the outlet - pylorus or pylorus. They are both circular muscles called sphincters that open and close as needed. The cardia connects the esophagus to the stomach, regulates the flow of chyme and prevents reflux. The pylorus connects the organ with the duodenum.
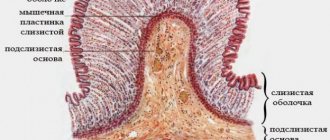
The body of the stomach is its most powerful part, which is anatomically called the lesser and greater curvature. Its walls consist of different layers: mucous membrane, submucosal, muscle and serous tissue. Muscular – the one that helps form a bolus. The fundus of the stomach, its highest part, is located on the left under the diaphragm. This is where gases accumulate. And the antrum or antrum is a narrow area that is located in front of the pylorus.
The stomach is smooth on the outside, wrinkled on the inside. Its inner membrane has small pores, which are the openings of the glands. They secrete gastric juice - a liquid containing hydrochloric acid, pepsin, gastrin and lipase. All these compounds are necessary for the high-quality digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats, the absorption of nutrients from them and their absorption into the blood.
The connection between gastritis and infection
Can gastritis accompany infectious diseases? Inflammation of the stomach is necessarily observed in foodborne infections, poisoning with toxic substances, and in the clinic of intestinal infections (salmonellosis, dysentery, cholera).
The manifestations are called gastroenteritis. Unlike somatic gastritis, in addition to pain and acidity disorders, intoxication plays a significant role in the clinic. In patients:
- temperature rises;
- headache and joint pain;
- nausea and vomiting are more pronounced;
- severe weakness;
- insomnia.
In recent years, serious attention has been given to viral gastroenteritis with influenza and herpes. In patients with a serious condition, signs of internal bleeding appear (pale skin, rapid pulse, drop in blood pressure). Unfortunately, it is extremely difficult to deal with. Mortality remains high.
How does the nature of pain change when gastritis turns into an ulcer?
Patients with a long history of the disease should notice what kind of pain with gastritis usually bothers them during an exacerbation and how they change. In case of pain ulcer formation:
- become much more intense;
- described as "cutting";
- clearly tied in time to food intake;
- have seasonality of exacerbations in spring and autumn.
Because the ulcers bleed, occult blood is detected in stool tests. When an ulcer perforates into the abdominal cavity, the pain is dagger-like in nature, accompanied by shock and peritonitis. A stomach ulcer may first appear as bleeding with vomiting blood and black, loose stools.
You can't do anything on your own. Just provide the patient with peace and prohibit movement. If the emergency doctor decides to hospitalize you, you should not refuse. The consequences can be life-threatening.
Why do gastritis worsen in the off-season?
https://youtu.be/lq4NM_0KOtY
Spring and autumn are transitional periods between summer and winter. In the off-season, the daily routine changes (the days become shorter, the nights become longer), the nature of the diet (the diet becomes less fresh fruits and vegetables, preference is given to meat, cereals, and pickles). Colds begin to intensify, depleting the immune system, and as a result, existing chronic diseases worsen. The emotional depression characteristic of autumn also affects the state of health.
Whether we like it or not, shortening daylight hours has a depressing effect on our mood, but practice shows that the emotional sphere is very closely related to the state of the gastrointestinal tract. Thus, a person living in a state of chronic stress has a much higher chance of developing gastritis than those who treat any problem philosophically. And all because during stress, a large amount of adrenaline is released into the blood - a hormone that causes vasoconstriction.
As a result, the blood supply to the gastrointestinal tract deteriorates, the nutrition of the cells of the gastric mucosa is disrupted, some of them atrophy and die, forming zones of inflammation, that is, gastritis. If this condition is not treated, over time, defects, erosions and ulcerations appear on the mucous membrane.
What diseases should be distinguished from gastritis pain?
The origin of gastralgia is not necessarily associated with inflammation (gastritis). Similar pains are observed in other diseases. Gastroesophageal disease is formed when the stomach is damaged in the upper zone, cardia and lower sphincter of the esophagus. The cause is usually an overfilling of the stomach, an increase in pressure in it.
This causes the bolus to be thrown back into the esophagus. But it already contains acid. It irritates the mucous membrane of the lower esophagus and causes chest pain immediately after eating. Characterized by severe heartburn, sour belching, hoarseness due to contact with the vocal cords during regurgitation.
How can you relieve pain with gastritis?
To eliminate pain, a complex of therapeutic measures is used to relieve inflammation. They are selected individually after examination. Pain is treated not only with medications; the doctor begins his recommendations with changes in diet and regimen.
- stop smoking and drinking any alcohol, including beer;
- ensure a rational rest regime, breaks from work for lunch and snacks;
- walk more;
- try to protect yourself from stress with interesting activities, meetings, and, if necessary, drink light herbal sedatives in tinctures (motherwort, valerian, Novo-Passit);
- achieve good sleep.
You will have to exclude from the menu:
- all fried and smoked dishes from meat, potatoes, fish;
- hot sauces, mayonnaise;
- strong tea and coffee;
- chocolate and confectionery;
- fresh baked goods;
- sparkling water;
- homemade pickles and marinades.
In case of severe pain, it is better to refuse food for a day and limit yourself to drinking warm, slightly sweet water. For a few days you should go:
- for low-fat broths with white croutons;
- liquid porridge with water (oatmeal, buckwheat, rice);
- slimy soups made from vegetable broth and cereals;
- boiled meat dishes rolled in a meat grinder (meatballs, steamed cutlets, meatballs).
You should eat small amounts of food up to 6-7 times a day. Dried fruit compote, rosehip decoction, and oatmeal jelly are suitable for drinking.
Use of medications
The selection of medications is the responsibility of the doctor. The choice is determined by the acidity in the stomach. When elevated, the following are prescribed: antacids to reduce acidity, suppress the synthesis of acid and pepsin (Ranetidine, Omeprazole), antispasmodics (Platifillin, Spazmalgon, rectal suppositories with belladonna).
Almagel A has a good enveloping and rapid analgesic effect. It contains a locally active substance - anesthesin. Other drugs (Gefal, Denol) help relieve inflammation. If a connection with Helicobacter infection is established, the patient is prescribed a course of specific treatment.
For atrophic gastritis with low acidity, it is recommended to take gastric juice, Acidin-pepsin, Plantaglucid, prokinetics (Domperidone) to improve the motor function of the stomach. Prescribing drugs in the form of injections is more justified. This helps protect the stomach lining from unwanted irritation.
Physiotherapy helps in treatment. They use: electrophoresis with drugs on the epigastric area, UHF, phonophoresis for pain relief. For mild pain at home, you can take a warm decoction of chamomile and flax seeds.
Pain with gastritis indicates a disorder in the structure of the organ, a dysfunction. The future health of the patient’s digestive tract depends on timely treatment. Diagnostics helps prevent dangerous consequences.
Pain itself is an unpleasant feeling that signals problems in the body. This syndrome has protective properties. Soreness has a different character. To assess pain, its location, prevalence, irradiation, connection with eating, and changes in body position are determined.
Clinical picture
Pain in the stomach in different pathologies has its own characteristics. A detailed description of a person’s abdominal pain will help to quickly make a correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment. Symptoms of stomach pain and their characteristics:
- intensity;
- nature of stomach pain.
The objectivity of such a symptom is questionable, since each person has a different sensitivity threshold. With gastritis, the pain is barely noticeable - the patient may not treat the pathology for a long period. Mild pain is observed during cancer formation. With gastric ulcers, the pain is more severe and the patient is forced to seek help from a specialist. An ulcer with perforation can cause shock in the patient. Background diseases (diabetes mellitus), previous surgical interventions can reduce the symptom of pain until it disappears completely.
Any pathology of the stomach has its own characteristic of pain. Chronic gastritis is characterized by aching pain, heaviness in the abdomen, and distension. Burning painful sensations during gastritis indicate the appearance of solaritis (increased acidity and activity of hydrochloric acid). Symptoms of pain and discomfort in the abdomen intensify with the development of pancreatitis, colitis, and cholecystitis.
Ulcers are characterized by sharp and cramping pain in the stomach. When the ulcer perforates, the syndrome becomes sharp and dagger-like in nature. Pain in the stomach of a prickly, cutting and cramping nature also occurs with chronic duodenitis.
Traditional methods
If there are no medications at home, then you can use traditional methods of treating gastralgia at home. Herbal infusions (chamomile, linden, sage) with lemon balm or mint will help reduce nausea and abdominal pain on the right side. To prepare, you need to pour boiling water over 1 spoon of raw material and leave the resulting drink for 2 hours. The decoction is carefully filtered and drunk 3 times a day before meals.
If the cause of gastralgia is increased acidity, you will need to prepare natural juice based on potatoes or carrots. To do this, the fruits should be peeled and placed in a juicer or blender. Take half a glass of natural juice twice a day before eating.
Fresh honey and agave juice help relieve heartburn. For treatment, you need to mix the products, leave them for 2 hours, and then take 50 ml before meals. Honey can also be used in its pure form. To do this, patients should dissolve the natural product one teaspoon at a time 3 times.
Additional symptoms
Discomfort in the stomach and intestines indicates the development of dysbiosis. Identifying the true cause of such a symptom will help prescribe effective treatment for such a pathology. Discomfort can also occur with dyspepsia and irritable bowel syndrome. Dyspepsia is a functional disorder of the gastrointestinal tract. It can develop against the background of ulcers, chronic pancreatitis, cholelithiasis and gastroesophageal reflux pathology.
Functional dyspepsia occurs with an unbalanced diet, prolonged stress, and taking certain medications. Depending on the abuse of certain foods, dyspepsia is classified into the following subtypes:
- fatty – occurs when consuming large amounts of fat;
- putrefactive - occurs after abuse of protein foods;
- fermentation - from excess carbohydrates in the diet.
Human dyspepsia is characterized by heaviness in the stomach and bloating. Possible nausea and vomiting. Irritable bowel syndrome is another cause of abdominal discomfort. The cause of this pathology may be stress, trauma, or vegetative-vascular dystonia. Pathology can often be caused by intestinal infection or poisoning. Doctors identify the following symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome:
- discomfort and pain in the abdomen;
- alternating constipation and diarrhea;
- bloating that gets worse after eating;
- depression, anxiety;
- migraine, dizziness;
- nausea, heaviness in the stomach;
- lump in throat, panic.
To alleviate the patient’s condition, the diet is adjusted; it is recommended to take sedatives and enzymatic medications. The symptomatic therapy regimen is determined in each case individually.
Associated symptoms
How does a person’s stomach hurt, and what symptoms accompany it? Most often – dyspeptic disorders. This includes a feeling of heaviness (especially after eating), nausea, vomiting, sour belching, heartburn, and a burning sensation in the chest. Characteristic is a sharp decrease in appetite. An aversion to meat may lead to suspicion of the development of malignant neoplasms.
Upon examination, you can detect pallor of the skin. This is a sign of anemia, which develops against the background of chronic gastric bleeding. In addition, there is a rapid heartbeat (tachycardia), severe general weakness, and dizziness when walking. The presence of blood clots or black feces in the vomit is a symptom of active gastric bleeding.
When examining the oral cavity, a white coating on the tongue is often found. In addition, there may be an unpleasant odor, which indicates a bacterial process.
Active inflammatory processes in the stomach are also sometimes accompanied by an increase in temperature to subfebrile levels (37-38°C).
Diarrhea is typical for food poisoning, fermentopathy or stomach diseases that are accompanied by low acidity (hypoacid gastritis, a condition after organ resection). Constipation, on the contrary, is more typical for peptic ulcer disease or hyperacid gastritis.
Symptoms and diseases
The causes of stomach pain are associated with various pathologies. Gastritis is asymptomatic for a long time. Then a dull, aching pain occurs. The pain is aggravated after sour, fried foods. At the end of the meal, my stomach is full. The patient regurgitates frequently. Characterized by heartburn, unpleasant taste in the mouth, and a tendency to constipation. Main symptoms of the pathology:
- weakness, fatigue;
- nervousness, irritability;
- changes in blood pressure;
- drowsiness, pallor of the skin and mucous membranes;
- increased sweating;
- burning tongue;
- numbness and cramps in the limbs.
Gastric ulcer is characterized by severe pain that occurs several hours after eating. “Hungry” pains also occur, when pain develops when you want to eat and disappears immediately during a meal. Periods of exacerbations may occur (spring, autumn). Patients suffer from sour belching and heartburn. Nausea and vomiting are possible.
Appetite decreases and the patient loses weight. If acute, stabbing pain occurs, we can talk about the development of perforation of the ulcer (a hole develops, the contents of the stomach pass into the abdominal cavity). This is a deadly complication, the pain is unbearable. Immediate surgical intervention is required.
Polyps in the stomach are a rare pathology that is characterized by aching pain in the abdomen. Nausea, vomiting, and bleeding often develop. With oncological tumors, persistent, low-intensity, but constant pain is observed. Initially, appetite decreases, patients quickly become satisfied with small amounts of food. There is heaviness in the stomach, poor digestion of food. Anemia develops, an aversion to meat foods, and body temperature rises (up to 38°C). In the terminal stages, such tumors cause bleeding. Vomiting blood occurs and the stool turns black.
First aid
You need to know how to provide first aid if intense abdominal pain occurs, and what can be done to eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
Basic rules for providing first aid for acute pain in the gastrointestinal tract:
- First, place the patient in bed, he should be at rest.
- Try to find out if he has any chronic or congenital pathologies of the digestive organs or genitourinary system. If something like this has already happened to him, he can tell you what to do.
- Call emergency services immediately if a person has diarrhea and vomiting blood, black stool, urinary retention, or blood in the urine.
- You are allowed to take some safe and effective antispasmodics - Papaverine, No-Shpu, then inform your doctor about this.
- You can apply ice or a bubble of ice water to the abdominal cavity.
- If the injured person is unconscious but has a pulse and breathing, turn the person onto their stomach and place their head to the side. Thanks to this technique, you can avoid a person choking on vomit.
- If there is no pulse and breathing cannot be heard, urgently place the person on a hard surface, try to provide primary resuscitation: chest compressions, artificial mouth-to-mouth breathing.
It is strictly forbidden to do the following: leave the victim alone, give him food, analgesics, laxatives, clean the stomach or give an enema, and also warm this area of the body.
Acute abdominal pain is a dangerous condition that can signal serious illness. It is necessary to immediately call an ambulance, find out the cause of the symptoms and begin a course of therapy.
Additional pathologies
- Functional imbalance occurs due to overeating and alcohol abuse. The pain is oppressive. The patient feels pressure in the stomach, a feeling of fullness. Nausea and vomiting are possible. Constipation and flatulence develop.
- Poisoning is characterized by sharp and intense pain. Nausea and severe vomiting appear. Sweating, weakness, and malaise develop. On average, the first symptoms of poisoning appear 2 hours after a meal. The clinical picture of poisoning will depend on the nature of the substance that caused the poisoning. Headache, dizziness, and possible loss of consciousness often occur.
- Pain may occur due to intolerance to certain substances (lactose). Patients at risk cannot consume dairy products. They develop flatulence, bloating, and loose stools. Nausea and vomiting increase. The pain is aching and of medium intensity.
- With pancreatitis, pain is localized in the upper abdomen and may have a girdling character. Severe and intense pain often radiates to the back. The patient is concerned about bloating, vomiting and nausea, an increase in body temperature, and a drop in blood pressure (in advanced cases). The reason for this condition is the inability of the gland to produce enough enzymes.
- The cause of painful colitis is an infection of the large intestine. Characterized by constant rumbling, flatulence, bloating, blood in the stool. The frequent urge to defecate is disturbing. Colitis occurs due to stress, allergies or hereditary predisposition.
- The diaphragm is a muscular organ that separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities. If the blood supply to this organ is poor, spasm may occur. This is manifested by severe, sharp pain of a shooting nature. This pain intensifies with deep breathing and sudden changes in body position. Often, pain in the abdomen in children develops against the background of anxiety, stress, and fear of school. In this case, the pain has a spasmodic, cramping nature, and a frequent urge to defecate is possible.
- “Hunger pain” is diagnosed with gastritis, stomach ulcers, and develops in the pit of the stomach. The syndrome has a prickly and sucking character, less often cramping. More often the syndrome occurs at night and early in the morning. The pain increases significantly with physical activity, errors in diet (eating spicy, fatty, fried, sour foods).
Is it possible to do treatment on my own?
You can use home therapy while waiting for a full examination or doctor's appointment. It is also necessary to take medications on your own in cases where the patient already knows the diagnosis (for example, he has undergone a previous examination and took appropriate medications according to the doctor’s recommendations). It is acceptable to take painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs for single outbreaks of pain. Self-medication is prohibited if the following symptoms are detected:
- acute pain that prevents the patient from straightening up;
- persistent vomiting and nausea;
- severe diarrhea;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- diarrhea;
- bad breath;
- blackening of stool;
- the appearance of blood clots in the stool;
- general intoxication syndrome (head pain, fever, tachycardia);
- increase in body temperature.
You cannot take pills on your own to normalize the functioning of the gastric glands if the patient experiences shortness of breath, tachycardia, or presyncope. Self-medication is contraindicated for pain in the epigastric region, which is accompanied by loss of appetite and sudden weight loss. Such signs may indicate the development of a malignant tumor. It is strictly forbidden to independently prescribe medications for pain in the middle of the stomach in a child. This is fraught with allergic reactions and complications.
Health care
If such a symptom occurs, you should immediately seek help from a doctor. Only after a thorough examination will complex treatment be prescribed.
Moderate pain does not cause much discomfort, so patients self-medicate by taking painkillers.
This sign indicates the development of gastritis, ulcers, or damage to organs adjacent to the stomach.
Sharp, burning pain can occur when poisoned by poisons or poor-quality food products, and a sharp stabbing pain is a sign of perforation of the ulcer. Such pathologies require immediate hospitalization, as they are extremely life-threatening. Refusal to undergo examination is a direct path to progression and worsening of the condition. In some cases, the doctor may pronounce death.
Stomach pain is one of the symptoms of many diseases. Moreover, it is often not directly related to this digestive organ and indicates problems with others. What can pain in the stomach indicate, how to find out its cause and what makes sense to take to relieve pain?
Treatment
At the first manifestations of such conditions, the following measures must first be taken:
- Take a comfortable position that reduces pain.
- Drink a glass of plain water.
- Loosen clothing in the abdominal area, get rid of the belt that puts pressure on the stomach.
- Take activated carbon.
- Do not eat heavy food.
- If possible, empty your bowels.
- If you have symptoms of bloating, you should avoid taking gas-forming foods (sweets, fruits, flour products).
Such first aid measures are available to every person. Of course, in severe cases, you should call an ambulance or consult a doctor who probably knows how to cure any patient.
Traditional treatment
When unpleasant sensations annoy and interfere with the normal flow of life, a person sooner or later wonders what pill to take to quickly get rid of pain, and how to treat the stomach at home? Then traditional medicine comes to the rescue. The pharmaceutical industry has a wide range of drugs used to relieve such gastric conditions and treat pain. These medications are divided into categories:
- Medicines for the treatment of stomach and duodenal ulcers.
- Enzymatic preparations.
- Antienzyme substances used in the treatment of pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas).
In gastroenterology, enzyme preparations, painkillers, antispasmodics, laxatives, antacids, hepatoprotectors, vitamins, drugs that normalize intestinal microflora, and enterosorbents are used.
The most popular gastroenterological drugs prescribed by doctors:
- No-Shpa;
- Maalox;
- De-Nol;
- Flemoxin Solutab;
- Festal;
- Mezim;
- Gastal;
- Gastrofarm;
- Omez;
- Papaverine;
- Control;
- Creon.
The treatment regimen, dosage and duration of therapy are prescribed by the attending physician, because each patient is individual, and if the stomach hurts, it is important to accurately determine the diagnosis.
Causes of stomach pain
The first question your doctor will ask you will be about the nature of your stomach pain. It is the answer that can say a lot about the disease that caused the pain.
- Acute stomach pain that occurs suddenly often indicates pancreatitis, cholecystitis and duodenal ulcers.
- Sharp, sudden pain can be caused by a chemical burn of the mucous membranes or poisoning.
- Very severe sharp pain, which patients describe with the words “as if a knife had been stuck,” is often a consequence of perforation of the ulcer.
- A burning sensation is characteristic of an ulcer or gastritis, and a dull aching pain in the stomach is a sign of the same diseases in a chronic or initial form. With gastritis, there is a clear connection with food intake: pain appears either immediately after eating, or when a person is fairly hungry.
- Spasmodic, cramping pain is often a sign of an ulcer or inflammation of the duodenum. This pain often occurs at night or a few hours after the last meal.
- Acute but short-term (a few seconds) “shooting” pain that occurs when inhaling or a sudden change in body position is typical of diaphragm spasms that occur due to inflammation or circulatory disorders.
- Constant mild aching pain in the stomach often accompanies malignant neoplasms, as well as gastric polyps. When cancer spreads to the pancreas, the pain becomes stabbing.
- Severe cramping pain is most typical of gastrointestinal infections.
- Intense pain in the upper abdomen, which subsides after a couple of days but remains constant, is a fairly characteristic symptom of pathologies of the large intestine, in particular colitis.
- Severe pain in the navel area, which moves to the right upper abdomen over several hours, may indicate appendicitis.
These are not all the causes of stomach pain. Sometimes such a symptom accompanies other diseases - irritable bowel syndrome, intestinal vascular thrombosis, abdominal aortic dissection, intestinal obstruction, stomach trauma, coronary heart disease, some nervous diseases, allergic reactions, etc.
Most diseases accompanied by this symptom are very serious and require immediate medical attention. Moreover, in some cases, the word “immediate” has a literal meaning - with appendicitis, perforated ulcers and severe poisoning, hours can count, and even a slight delay can become fatal.
What to do if you have pain in the stomach
Whatever causes stomach pain, you cannot treat it on your own. Even an experienced doctor with many years of practice cannot reliably make a diagnosis based solely on external signs. And a person without a medical education is even more unable to do this.
The number of first aid measures that can be provided for stomach pain is very small. The most you can do before the doctor arrives is to take an antispasmodic or analgesic. For heartburn, take antacids - drugs that reduce acidity, or antisecretory drugs that inhibit acid production. However, heartburn is not always associated specifically with increased acidity, so taking such medications may not only be useless, but also worsen the condition.
In general, special care should be taken with medications: the effects of medications can distort symptoms and create difficulties in diagnosis. It is also important to understand that modern painkillers are very effective and can completely eliminate stomach pain for quite a long time. This creates a false impression of recovery. However, the disease does not disappear anywhere. By relieving stomach pain with pills, you are only wasting precious time: you are treating the effect, forgetting about the cause.
You can help your doctor make a diagnosis. To do this, you will need to provide him with as much information as possible about your condition. Therefore, before your appointment at the clinic, try to remember and formulate in as much detail as possible:
- the circumstances of the pain (before, after or during meals, day or night) and its nature (sudden or gradually increasing, sharp, aching, sharp, burning, cramping). Try to remember whether the source of pain moved, and if so, how.
- diet in the last days before the onset of pain: what, when and in what quantities did you eat (food and drinks).
- a list of medications you take (including dietary supplements and vitamin complexes).
- all additional symptoms. It is important for your doctor to know if you have had nausea and vomiting, bitterness in your mouth, diarrhea or constipation, belching and bloating, blood or mucus in your stool, rash, fever, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat and dizziness, or any other pain ( head, muscles, joints).
- recent changes in health status. These include both natural (pregnancy, childbirth, lactation, menopause) and pathological. Remember all the recent illnesses, nervous shocks, and episodes of severe fatigue. Factors such as sudden weight gain or unreasonable weight loss, the development of anxiety and depression, and changes in lifestyle may be significant.
Causes
The most common cause of such sensations is gastritis. Gastritis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the digestive organ. There are different forms of this disease, differing from each other by the causative agent of the disease:
- Viral (viruses).
- Eosinophilic (allergens).
- Bacterial (bacteria).
- Stressful (severe stress).
- Erosive (salt, potent substances: acids, alkalis, drugs).
It is quite possible that you have one of the forms of gastritis. How to quickly get rid of this disease and how to relieve painful sensations will be discussed below.
Other reasons
In addition to gastritis, the following diseases may be the root cause of discomfort:
- Viral and bacterial lesions of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Ulcer.
- Polyps in the intestines.
- Appendicitis.
- Abdominal injuries.
- Oncological diseases.
- Pancreatitis.
- Damage from toxic substances (poisoning).
This list does not reflect the complete picture of possible diseases, because only the most common causes are listed. And stomach colic is not always caused by illness. Often the reasons lie in the patient's lifestyle.
Factors leading to discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract:
- drinking alcohol;
- smoking;
- experienced stress;
- excessive physical activity;
- eating heavy fatty or spicy foods.
That is why, for a comfortable state of health, you should exclude such factors that provoke gastrointestinal diseases from your habits.