Hemorrhagic colitis or diarrhea with blood is one of the types of inflammatory process on the mucous membrane of the large intestine. The condition is cause for concern and requires medical supervision. Self-treatment is prohibited due to the risk of severe complications. There are many reasons for this condition and it is important to identify the provoking factor in time and eliminate it.
What is and features of hemorrhagic diarrhea
Loose stools with blood are an alarming symptom that indicates inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract. In this way, the body tries to protect itself from attack by pathogens. Some gram-negative bacteria produce toxic substances that can damage the blood vessels of the intestine. As a result, a specific clinical picture develops.
For diagnosis, a complex of examinations is carried out, the list of which includes laboratory tests - clinical blood test, bacteriological culture of stool, microscopic radiation, and hardware tests - colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy. After establishing an accurate diagnosis, conservative therapy is carried out.
Hemorrhagic diarrhea begins suddenly and develops rapidly over a short period of time. The patient's condition noticeably worsens, and the following symptoms may occur:
- profuse, watery bowel movements;
- unbearable abdominal pain;
- feverish condition;
- large amounts of blood in the stool.
In most cases, the disease lasts 7-10 days. If the sick child is a small child under 5 years old or an elderly person, the symptom may persist for up to two weeks. A long course of the disease threatens severe complications for a weakened body.
To undergo an examination, you must contact an infectious disease specialist.
Causes of the symptom
The phenomenon of diarrhea with blood may indicate various diseases. All of them require diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Common causes of bloody diarrhea:
- Infectious diseases.
- Internal hemorrhoids.
- Tumors of the rectal intestine.
- Violation of the structure of the mucous membrane of the anus.
- Chronic disease of the stomach and duodenal mucosa.
- Antibiotic therapy.
- Ulcerative-inflammatory lesion of the mucous membrane of the large intestine.
- Diseases caused by viruses.
This is a short list of pathologies that can cause bloody, loose stools in an adult. Drinking alcohol can affect changes in the consistency of excrement and contribute to the appearance of blood spots. Blood on paper during diarrhea may indicate the presence of benign neoplasms in the intestines - polyps. Green diarrhea with mucus indicates dysentery. Diarrhea with blood after antibiotics is a common occurrence in those who have undergone long-term therapy with potent drugs.
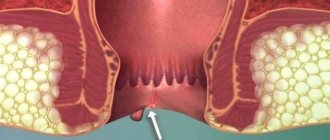
Anal fissure
Rectal fissure is a common disease of the rectum in the form of a mucosal defect up to 2 cm in size. It can develop due to inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract or mechanical damage.
The pathology is characterized by constipation, as a result of which it develops. But in case of digestive disorders or poisoning, the stool changes its consistency to liquid. There are stools with scarlet blood. Usually blood does not mix with feces and is located on the surface of the masses. Defecation is accompanied by severe pain and itching. The chronic form causes pain after bowel movements.
Internal hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are often the cause of blood appearing on toilet paper after diarrhea. The reason is that hemorrhoids begin to become inflamed and bleed. More often, the disease occurs in people whose profession is associated with a sedentary lifestyle - drivers, office workers. Or those whose work involves heavy physical work - loaders, athletes.
Pathology manifests itself in the form of bleeding during defecation. Mostly the hemorrhage is not severe - the blood comes out in the form of drops or streaks.
Neoplasms
Various neoplasms of the digestive organs lead to the release of blood during bowel movements. The higher the tumor is, the darker the stool. Cancer of the intestines and stomach is often accompanied by stool streaked with blood.
Oncology of the gastrointestinal tract requires special treatment. Diarrhea occurs regularly during illness - therapy is aimed at preventing anemia. The tumor is removed surgically.
Infectious diseases
A variety of infectious diseases: salmonellosis, dysentery and others cause diarrhea mixed with blood. The excrement is liquid, stools are frequent - more than ten times a day.
Feces with mucus and streaks of blood are observed in a number of acute infectious diseases. In addition to frequent loose stools, a person has a stomach ache and a sharp rise in temperature.
Stomach and duodenal ulcers
The pathology is chronic. It is characterized by the occurrence of severe pain after eating. With complications of the disease, the ulcers begin to bleed. Since the source of bleeding is located in the upper gastrointestinal tract, stool mixes with blood, which oxidizes as it passes through the intestines and becomes black in color at the exit. The person feels weak and dizzy. There is a drop in blood pressure.
Food poisoning
Food poisoning provokes diarrhea some time after eating low-quality food or drinks. At the same time, vomiting develops. The temperature rarely rises above 38 degrees. The patient feels weak.
It is not recommended to stop diarrhea in case of poisoning; harmful toxins are removed with feces. It is permissible to treat diarrhea with the help of sorbents.
Food intoxication is not always accompanied by bloody diarrhea, but in cases of serious poisoning, this symptom is observed.
What diseases may this indicate?
Diarrhea is a normal reaction of the body. It occurs in cases where purification from toxic substances, parasitic microorganisms and other dangers is necessary. If complications occur, diarrhea syndrome requires careful study and timely correct treatment. If the situation goes into a neglected state, irreversible consequences will arise.
Common diseases that cause bleeding:
- diseases of infectious etiology. Blood is a specific sign that appears during infection with dysentery, paratyphoid A, enterocolitis, salmonella, and enteritis. During the active life of parasites, the protective mucous membrane of the intestines is damaged and blood oozes from the wounds. The patient can diarrhea up to 20 times a day;
- hemorrhoids inside the intestine. It affects the anal passage and is manifested by the release of scarlet clots with feces. The diagnosis can be made by traces of blood on underwear and paper after bowel movement;
- malignant formations in the gastrointestinal tract. Bloody diarrhea is often the first and only sign of a dangerous disease. It indicates the growth of a cancerous tumor inside the body and its damage during the passage of processed food;
- Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. These diseases are expressed in damage to the walls of the large intestine, causing internal bleeding. Ulcerative formations can affect the stomach, esophagus, etc.;
- dysbiosis. Pathogenic bacteria suppress beneficial bacteria and upset the balance in the intestines. Antibiotics, medications, infections, and viruses can cause such disorders. The imbalance needs to be treated in time, before problems with the immune system begin and rashes and acne appear on the skin.
Diarrhea with blood in an adult occurs for various reasons. Conditions in which the body weakens and requires additional support can complicate the course of the disease: pregnancy, old age, exacerbation of chronic diseases, recent surgery.
Where does the blood in loose stool come from?
When diagnosing intestinal diseases, taking an anamnesis is of great importance. If you suspect inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) - ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease - or cancer, it is important to study the presence of these diseases in the family.
In case of rectal bleeding, you should study the overall picture of the patient’s condition, paying special attention to the medications that he is taking. Blood-thinning medications can cause blood to appear in loose stools.
Doctors rule out the infectious nature of the disease by studying stool in various ways. A stool culture is done, which provides information about pathogenic bacteria in the intestinal microflora.
A stool test is done for worm eggs and protozoan microorganisms, since infestations are one of the reasons for the appearance of blood in the stool.
A stool analysis is performed for leukocytes and epithelium. In a healthy person, only single leukocytes can be found in the preparation; an increase in their number indicates an inflammatory process localized in the intestines.
Video:
In this case, it is extremely important to correctly collect stool for analysis, since leukocytes can enter the material for study from the urethra or vagina, which will distort the picture of the disease.
Epithelial cells line the intestinal mucosa. Normally, a small amount of them is present in the feces as the epithelial layer is renewed. An increase in the number of epithelial cells will tell the doctor about inflammatory damage to the mucous membrane.
If diarrhea is present, it is necessary to examine whether polyfecality occurs, that is, whether the amount of feces exceeds the norm of 200 - 300 ml.
Another important diagnostic indicator is the presence of steatorrhea - increased excretion of fats in feces.
The type of steatorrhea will show which fats are in the stool - neutral or fatty acids, which will allow a diagnosis.
Interviewing the patient, studying his tests, studying his symptoms provides extensive diagnostic information, but in many cases the doctor needs to see what is inside.
The following methods are used for this:
- sigmoidoscopy, which allows you to examine the 60 cm of the large intestine closest to the anus;
- colonoscopy - examination of the entire large intestine;
- enteroscopy - methods of internal examination of the small intestine, which are performed through the mouth or through the anus - depending on the organs that are of more interest to the doctor from a diagnostic point of view.
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs, fluoroscopy, magnetic resonance imaging, biopsy of intestinal tissue and many other methods are also used.
Diarrhea is an unpleasant phenomenon from which no adult is immune. Diarrhea is not an independent disease. This is a symptom that signals that any of the organs of the digestive tract is unhealthy or that there is a malfunction in the digestive system. More often, the phenomenon does not require urgent medical attention if the cause is stress, overeating or drinking alcohol. But if blood is found in the excrement, there is a serious reason to visit a doctor.
These circumstances do not allow self-medication; diseases that provoke pathology are often fraught with complications.
Home treatment for bloody diarrhea
If diarrhea with signs of blood suddenly occurs, the main goal is to select treatment to eliminate the provoking factor.
A mandatory component is a diet; stool turns red or dark when certain foods are consumed. This effect can be given by a preparation with iron or activated carbon. This method is only suitable for cases where there is no pain or other symptoms.
If increased fluid loss is observed, restoration of the water-salt balance is required. The pharmacy offers a wide selection of products. The medicine Regidron is highly effective.
In case of poisoning or infection, enterosorbents, which attract harmful compounds and envelop the intestinal mucosa, will help it to heal faster.
Folk experience will help with digestive tract disorders.
№1 Dry chamomile leaves 15 g, steamed with 200 ml boiling water. Infuse for 3-4 hours in a glass jar, covered with a warm towel, or in a thermos. Take the product after meals in an amount of 30 ml 4 times a day.
№2 Potentilla erecta 2 tbsp. without peas, shepherd's purse 3 tbsp., burnet rhizomes 2 tbsp. Combine in a bowl and brew 200 ml of boiling water. Drink a homemade drink 4-6 times a day, 30 ml.
If an adult patient suffers from a peptic ulcer, the doctor prescribes conservative therapy. An important condition for a quick recovery is following the prescribed diet and taking medications to stop bleeding and prevent scarring. It is necessary to be able to prevent serious complications in time.
Symptoms
If the pathological condition does not go away within 24 hours, you need to immediately contact a doctor and find out the cause. The situation is especially dangerous when the following symptoms are observed:
- black stool;
- there is blood in the stool;
- liquid diarrhea with bloody contents;
- drop in blood pressure;
- stomach twists;
- severe dizziness;
- the skin becomes pale;
- there is general weakness;
- body temperature rises;
- there is a feverish state;
- strong pains in the lower abdomen are recorded.
In this case, you must immediately call an ambulance and go for inpatient treatment to the infectious diseases or surgical department. In other cases, the doctor may prescribe a diagnosis and send you for home treatment.
Factors causing the disorder
Loose stools with blood, mucus, and various clots are most often a symptom of one of the serious diseases or a harbinger of various pathologies:
- blood clots in the stool indicate erosive processes in the stomach or intestines;
- bright streaks in the stool are an indicator of bleeding due to anorectal fissures, hemorrhoidal disease, however, hemorrhages are always accompanied by additional symptoms: discomfort during bowel movements, itching, burning;
- diarrhea with bloody mucous lumps is a symptom of diverticulosis, which occurs more often in older people and is provoked by adynamia;
- tumor growth in the digestive tube produces blood in liquid stool;
- blood clots with diarrhea are characteristic of Crohn's syndrome, dysbacteriosis, and other chronic pathologies;
- impurities of blood in dark-colored stool indicate severe bleeding in different parts of the gastrointestinal tract (the higher the source of bleeding, the darker the blood);
- dysentery is a severe infection that causes bloody diarrhea, accompanied by fever, abdominal pain, requiring an urgent call to the doctor.
After antibiotics
When using antibacterial drugs (antibiotics), both harmful and beneficial microorganisms are destroyed in the human body. As a result, the intestinal microflora may be disrupted, leading to diarrhea, which can develop in various forms of severity.
After consuming antibiotics, the bacteria Clostridium difficile, which is not susceptible to antibiotics, multiply intensively in the body, which leads to inflammation in the intestines. At the same time, there is blood in the stool, diarrhea may be accompanied by weakness, vomiting, and fever.
Therefore, it is worth monitoring the use of antibacterial drugs, since many diseases can be treated without their use.
As you know, ethanol is an important component of any alcoholic drink. By its nature, the human body is not adapted to drinking ethyl alcohol. Therefore, the first use of alcohol often ends in vomiting or diarrhea. And only over time the human body partially adapts to ethyl alcohol. However, this does not protect the body from harmful influences.
Ethyl alcohol is a kind of antiseptic that, when it enters the human body, destroys not only harmful, but also benign microorganisms, disrupting the intestinal microflora, which can lead to diarrhea or vomiting.
After drinking beer, diarrhea may occur, since it contains a large number of flavors, dyes, concentrates and other chemical additives that help extend the shelf life of beer. Of course, there is beer that does not contain such chemical compounds, but it is more expensive and has a shorter shelf life.
Frequent alcohol consumption leads to damage to blood capillaries. This may cause vomiting and bloody diarrhea.
To get rid of diarrhea after drinking alcohol, include boiled eggs, strong tea without sugar, and rice porridge in your diet. If diarrhea does not go away within two days, you should consult a doctor.
Oncology
Blood from the anus is often observed with tumors of the digestive organs. The higher the tumor is located, the darker the stool will be. Bloody discharge from a tumor is often found on the surface of the stool. Often blood in stool can be seen in cases of intestinal and stomach cancer.
Oncology requires special specific treatment. When diarrhea becomes the norm with a malignant tumor, it is necessary to direct therapy to eliminate anemia and take iron-containing drugs. Surgery can help eliminate a malignant tumor.
When to see a doctor
If bloody diarrhea occurs, it is important to begin treatment quickly. It is imperative to undergo an examination and accurately establish a diagnosis, and then choose a treatment strategy. If the patient experiences vomiting and severe attacks of abdominal pain, hospitalization is necessary. In some cases, these symptoms pose a danger to life and health.
Emergency assistance should be called in the following cases:
- there are signs of dehydration;
- severe stomach pain and vomiting;
- elderly age of the victim;
- body temperature from 38 degrees and above;
- there are scarlet streaks in the stool;
- diarrhea is black in color.
It is unacceptable to treat yourself in this situation. Lack of adequate treatment and timely medical assistance can lead to a deterioration in the patient’s condition. If there is heavy bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, a person may die.
Diarrhea can develop due to poisoning, digestive system disorders, or serious illnesses. It doesn’t matter how the disorder developed, after eating sea fish or porridge, you need to consult a doctor to make an accurate diagnosis. Not only red feces, but also black ones should alert you. This may indicate hidden bleeding inside, requiring urgent hospitalization.
The article has been approved
by the editors
Haemorrhoids
Damage to blood vessels and the formation of anal fissures cause bloody discharge in the stool. Hemorrhoids often cause bloody stools. Blood on toilet paper is observed due to the fact that internal hemorrhoids bleed, anal fissures occur, and blood circulation in the intestines and anal canal is disrupted.
Diarrhea due to hemorrhoids with blood is treated with drugs that eliminate inflammation of the nodes and stabilize the stool. If a prolapsed hemorrhoid is detected, it is necessary to use healing anti-inflammatory ointments and rectal suppositories. As soon as the medication begins to act, bleeding in the anal canal will disappear. Sea buckthorn suppositories and propolis-based suppositories help eliminate bleeding and diarrhea. You can use the drug Relief.
Diagnostics
Identification of the source of bleeding is subject to a special diagnostic algorithm, which includes:
- history taking, physical examination;
- OAM, UAC, biochemistry;
- feces for worm eggs, occult blood, coprogram;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- X-ray examination;
- anoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy, irrigoscopy;
- if necessary, biopsy with histology.
In some cases, MRI, CT, FGDS, and other instrumental studies of the digestive system are needed.
Treatment is impossible without identifying the causes of the symptom and making a diagnosis. Diagnosis is an important step on the path to recovery. The doctor gives a referral for laboratory testing of blood and urine. A study is carried out - stool culture to check for infections.
Ultrasound diagnostics is recommended to identify pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
Your doctor may recommend examining your intestines with a colonoscope. The method will help identify tumors in the organ and the degree of their development. Also, during colonoscopy, it is permissible to take material for histological examination directly during the procedure.