Pneumonia
Often, pressing pain in the pit of the stomach occurs due to pneumonia or, as this disease is popularly called, pneumonia.
Streptococcus pneumoniae – the causative agent of pneumonia © shutterstock
Pneumonia is a dangerous disease of an infectious nature. Until modern medicine took invented medications to a higher level, almost 80% of patients died from pneumonia. Today, these figures have decreased by half. However, pneumonia is considered one of the most dangerous diseases.
November 12 is World Pneumonia Day.
Experts have identified a number of factors and ailments that contribute to the development of pneumonia:
- Common cold or flu;
- Bronchitis;
- Past infectious diseases;
- Reduced immunity.
Pneumonia can be unilateral, bilateral, lobar, lobar and focal forms. Each form requires appropriate and immediate treatment.
Signs of illness
A common trigger for pneumonia is severe hypothermia, after which a person develops the following symptoms:
- Chest pain in the pit of the stomach when breathing or coughing;
- Wet cough;
- Fatigue;
- Fever, chills and sweating.
Under no circumstances should such symptoms be neglected . When the first pain in the pit of the stomach appears, you should immediately go to see a specialist. The doctor will conduct a thorough examination and give directions for tests and fluorography.
Treatment options
Treatment for pneumonia depends on the type of pneumonia you have, the germ causing your infection, and how severe your pneumonia is. The doctor takes into account the degree and severity of the illness that causes pain in the pit of the stomach, the age of the victim, and the presence of any complications.
“Pneumonia can be prevented through immunization, adequate nutrition and addressing environmental factors.” – WHO
Bacterial pneumonia is treated with medications called antibiotics.
Antibiotics don't work when pneumonia is caused by a virus. If you have viral pneumonia , your doctor may prescribe an antiviral medicine to treat it.
Why does my stomach constantly suck?
Every person has said that he sucks his stomach at least once in his life. This feeling can be caused by various factors, from anxiety, a sense of danger to problems with the digestive system. In this way, the body demonstrates to its owner the need to eat. The sucking sensation develops against the background of changes in stomach activity several hours after a meal. In the process of digesting food, the stomach contracts and food debris moves, followed by muscle contractions, spreading from the stomach to the intestines. At this moment, an unpleasant feeling of sucking in the pit of the stomach arises.
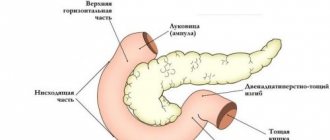
Hiatal hernia
When asked why there is pain in the pit of the stomach, doctors often answer – hiatal hernia. A hernia is a protrusion of abdominal organs, often the esophagus, stomach, or, less commonly, other organs.
The photo on the right shows a hiatal hernia © shutterstock
Hiatal hernia is divided into sliding or axial, paraesophageal, and combined forms of flow. The disease also has several degrees of severity, each of which manifests itself with its own symptoms and requires appropriate treatment.
Experts have identified some reasons that provoke the development of the disease:
- Changes in the diaphragm associated with age;
- Injuries;
- Birth defect;
- Pressure on nearby muscles when lifting heavy objects.
“The risk of getting a hernia hernia increases with age, and they often occur in people over 50.” – US National Institutes of Health
Signs of illness
- Heartburn;
- Reflux of stomach acid into the esophagus;
- Difficulty swallowing;
- Pain in the abdomen or chest in the pit of the stomach;
- Breathing problems;
- Vomiting blood or dark stools.
Experts recommend that if you experience pain in the pit of the stomach, immediately visit a hospital.
Treatment options
A routine doctor's examination will not help identify the presence of a hiatal hernia. To make an accurate diagnosis and determine the severity of the disease, the patient is prescribed an x-ray of the upper digestive system, endoscopy and ECG. The latter diagnosis is extremely important, since the specialist must exclude the presence of problems with the functioning of the heart.
Conservative therapy, including:
- Proper nutrition;
- Getting rid of bad habits;
- Antacids that suppress gastric secretion;
- Medicines to reduce acid production.
Surgical methods for treating hiatal hernia are associated with the lack of positive results from conservative therapy or with a too advanced stage of the disease.
Ulcerative colitis
Damage to the mucous membrane of the large intestine is revealed by ulcerative inflammation affecting the rectum. Distributes sequentially or simultaneously to all parts of the colon.
Pain syndrome is observed in the abdomen.
Signs of ulcerative colitis include:
- the presence of blood in the stool;
- loose stools;
- constipation;
- flatulence;
- symptoms of intoxication (with severe spread of inflammation).
Diagnosis
It is carried out using instrumental and laboratory research techniques:
- endoscopic examination;
- histological analysis;
- X-ray with the introduction of a contrast agent;
- Ultrasound;
- MRI;
- blood and stool tests;
- bacteriological cultures;
- molecular genetic research.
Treatment
Therapy for ulcerative colitis is carried out both on an outpatient basis (in the initial and moderate stages) and in the hospital (in the severe stage). A special diet and medication are also prescribed. Among the approved drugs: Sulfasalazine. Mezavant. Hydrocortisone. Prednisolone. Cyclosporine. Methotrexate.
Suppositories, rectal droppers, and enemas are also used in treatment, which have a greater effect in inflammatory processes in the lower parts of the large intestine.
Pancreatitis
Pain in the pit of the stomach may be due to pancreatitis, an inflammatory disease of the pancreas. The disease is divided into acute and chronic forms, each of which manifests itself with its own symptoms and requires appropriate therapy.
© shutterstock
Women, men and even children are not immune from pancreatitis. Men suffer more often due to neglect of the symptoms that appear. They prefer to visit the hospital when the disease has almost completely consumed the organ, which entails long-term treatment.
“The most common cause of chronic pancreatitis is alcohol consumption.” – US National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Experts have been able to identify a number of causes causing pancreatitis:
- Alcohol abuse;
- Eating fatty foods;
- Cholelithiasis;
- Long-term use of medications;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Viruses or parasites.
Signs of illness
Signs of acute pancreatitis include:
- Severe pain in the pit of the stomach, which may result from painful shock or loss of consciousness;
- Fever;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Cardiopalmus.
Aching pain in the pit of the stomach may mean a chronic form of the disease, which does not manifest itself with pronounced symptoms. Signs of this form of pancreatitis include :
- Loss of body weight;
- Nausea;
- Vomit;
- Diarrhea;
- Fast fatiguability;
- Deterioration in general health.
When the chronic form of the disease worsens, a person experiences all the symptoms of the acute course of the disease. A sudden exacerbation often leads to tissue necrosis, which leads to acute pain in the pit of the stomach. In this case, the person needs urgent medical intervention and hospitalization.
Treatment options
Treatment for pancreatitis that causes stomach pain may include pain medication, antibiotics, a low-fat diet, or even surgery to remove the gallbladder.
Only timely therapy will help slow down the development of pancreatitis. To avoid various complications, it is recommended to consult with a qualified specialist rather than self-medicate.
Dysfunction of the liver and bile ducts
Biliary dyskinesia is characterized by impaired excretion of bile. This occurs due to a problem with the contraction of the gallbladder and ducts. Women are more prone to developing the disease. There are two forms of biliary dyskinesia.
With dysfunction of the liver and bile ducts, the patient is tormented by aching, sharp and paroxysmal pain.
They are localized in the peritoneum and right hypochondrium, radiating to the scapula and shoulder on the same side.
The presence of such symptoms indicates biliary dyskinesia:
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- worsening mood;
- weakness throughout the body;
- insomnia;
- lack of appetite;
- loose stools or constipation;
- decreased libido;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle.
Attending doctor
Gastroenterologist
Diagnosis An accurate diagnosis will be indicated by the following studies:
- blood test for biochemistry;
- ultrasound examination of the gallbladder and liver;
- bile analysis;
- X-ray of the gallbladder.
Treatment
One of the main methods of treating liver and bile duct dysfunction is diet. For a certain form of dyskinesia, it is necessary to adhere to a specific diet.
Antispasmodic and choleretic agents are used among the drugs.
Urolithiasis disease
Oddly enough, severe pain in the pit of the stomach may indicate urolithiasis.
© shutterstock
The population at risk is in the age category from 21 to 60 years . Men are more likely to develop kidney stones than women.
According to scientists, urolithiasis, which leaves pain in the pit of the stomach, is a consequence of an imbalance in the human body. Because there is no single reason that causes this disease.
You are more likely to develop kidney stones if you have certain conditions, including:
- blockage of the urinary tract;
- inflammation in the intestines;
- cystic kidney diseases;
- digestive problems;
- gout;
- obesity;
- taking diuretics.
People at risk should be attentive to the signs that their body gives them. Hence, visit hospital facilities on time.
Signs of illness
The manifestation of symptoms depends on many factors, including the shape, degree, size and location of the stones. Small tumors may not cause discomfort to a person for many years. At that moment, one uneven pebble can cause significant inconvenience.
In medicine, there are several main signs:
- Pain when urinating;
- Acute pain in the back, side, lower abdomen or groin;
- Blood in the urine;
- Cloudy or bad-smelling urine;
- Inability to urinate.
If such symptoms occur, you should immediately visit a qualified specialist.
Treatment options
Pain in the pit of the stomach caused by urolithiasis can be relieved using conservative therapy.
Unfortunately, drug removal of formations does not bring 100% positive results . Experts consider this method of treatment more of a preventative measure that helps prevent the appearance of new stones and pain in the pit of the stomach.
A urologist can remove a kidney stone or break it into small pieces using the following procedures:
- Shock wave lithotripsy;
- Cystoscopy and ureteroscopy;
- Percutaneous nephrolithotomy.
Non-drug treatment
If discomfort in the epigastric area occurs immediately after eating, first of all, special attention will have to be paid to diet therapy. Rational nutrition has no effect on inflammatory processes in the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, but helps eliminate pain and heaviness in the stomach. In addition, when ulcers form in the mucous epithelium, it is advisable to reduce food intake, since caustic gastric juice is released to digest it. It is this substance that contributes to the destruction of the walls of the intestines and stomach in the event of the formation of erosions and wounds on their surface.
How to quickly eliminate pain in the epigastric region? Doctors do not recommend resorting to the use of analgesics without an accurate diagnosis. This will only lead to a “blurring” of the symptomatic picture and make it difficult to determine the causes of the problem. If discomfort occurs continuously over several days, you should not postpone a visit to the therapist. After a preliminary examination, the doctor will most likely refer you to a gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist or endocrinologist.
Myocardial infarction
The causes of pain in the pit of the stomach may lie in the development of myocardial infarction - a well-known emergency condition in which the flow of blood to the heart is blocked by a blockage. Interruption of blood flow can damage or destroy part of the heart muscle.
© shutterstock
According to statistical studies, myocardial infarction, which causes pain in the pit of the stomach, is diagnosed more often in men than in women.
Among the causes include:
- Increased cholesterol in the blood;
- High blood pressure;
- High blood sugar due to diabetes;
- Overweight and obesity;
- Tobacco smoking;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Advanced age;
- Constant stress.
“Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death worldwide.” – WHO
Signs of a heart attack
Periodic pain in the pit of the stomach in the chest area is a consequence of coronary heart disease, which leads to a heart attack. Many people know that they have heart problems, so they take medications to help relieve pain in the pit of the stomach in the sternum area. But it is important to use only medications prescribed by your doctor.
Myocardial infarction manifests itself:
- Pain in the pit of the stomach on the left side;
- Chest pain or discomfort;
- Pain or discomfort in one or both arms;
- Hesitant breathing;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Sudden dizziness;
- Cold sweat;
- Fatigue.
No person should ignore pain in the pit of the stomach and the symptoms described above, as the disease can be fatal.
Treatment options
Once the diagnosis of a heart attack causing pain in the pit of the stomach is confirmed, doctors immediately begin treatment, trying to restore blood flow through the blood vessels that supply the heart.
The two main treatments are clot-busting drugs and percutaneous coronary intervention, also known as coronary angioplasty, a procedure used to open blocked arteries.
The rehabilitation period will last for six months. A person must give up bad habits and lead a correct lifestyle . By following all the recommendations of the attending physician, repeated myocardial infarction, causing pain in the pit of the stomach, will not bother the patient for a long time.
Typhus
This disease is classified as infectious. Typhus occurs cyclically and affects the cardiovascular and nervous systems. There are several stages of the disease.
The pain worries in the epigastric region and affects the solar plexus.
At the initial stage:
- temperature rises;
- headache, dizziness, fatigue, muscle aches appear;
- the occurrence of insomnia;
- rashes on the abdomen, chest and limbs;
- lowering blood and blood pressure;
- sinus rhythm disturbance;
- redness of the skin on the face.
At its height, the rash spreads throughout the body, and cyclical, intensifying headaches appear. Also, the pain syndrome concerns the lower back, which indicates the occurrence of pathology in the vessels of the kidneys.
The stage ends with a dangerous disease - meningitis.
The patient is concerned about:
- flatulence;
- constipation;
- urination disorder (painful);
- swollen tongue;
- occurrence: swallowing disorders, symptoms - different pupil sizes, rapid eye movements, weakened pupils.
The severe form of the rash type is characterized by:
- symptoms continue for a week;
- enlarged: liver, spleen;
- the appearance of destructive behavior;
- the occurrence of motor disturbances, which are expressed in different degrees;
- the occurrence of memory gaps.
Attending doctor
GastroenterologistDiagnostics
The diagnosis is determined thanks to:
- blood test;
- cerebrospinal fluid analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- Ultrasound;
- ECG;
- X-ray of the lungs;
- EEG.
Treatment
Bed rest is one of the important treatment measures; these also include a special diet and hospital stay.
Treatment is aimed at relieving symptoms.
Drugs used:
- Levomycetin;
- Erythromycin;
- Adrenalin;
- Diazolin;
- Tavegil.
Treatment lasts two weeks, after which the patient is discharged.
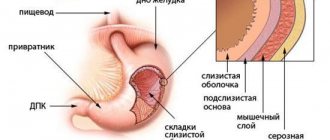
Gastritis
Often, pain in the pit of the stomach occurs due to gastritis, a pathology that causes inflammation of the mucous membranes of the stomach.
Illustration of inflammation due to gastritis © shutterstock
Among the causes that provoke gastritis are::
- H. pylori infection;
- Stress;
- Alcohol abuse;
- Regular use of painkillers;
- Bile reflux;
- Autoimmune response.
Signs of gastritis
Clinical manifestations of the disease include:
- Pain and burning in the pit of the stomach;
- Discomfort in the upper abdomen;
- Nausea;
- Vomit;
- Shortness of breath;
- Dizziness or weakness;
- Red blood in vomit;
- Black, tarry stool;
- Red blood in stool;
- Weakness;
- Pallor.
Treatment options
To get rid of pain in the pit of the stomach caused by gastritis, you must first treat the main cause that caused gastritis.
If the cause of gastritis is long-term use of painkillers, the doctor may advise the patient to limit their use. If the cause is an infection, the doctor should prescribe treatment with antibiotics.
All treatment methods, in strict order, must be selected by a specialist , based on the individual characteristics of each patient.
© shutterstock
Diagnostics
In women, a sucking feeling in the stomach appears due to hormonal changes during pregnancy.
Visualization of internal organs will help make the correct diagnosis.
If you often suck in your stomach for no apparent reason, you should consult a doctor and undergo an examination. Diseases detected at the initial stage of development are eliminated faster and easier than advanced pathologies. The following methods are used to make a diagnosis:
- Anamnesis collection. The doctor analyzes the existing complaints, their nature and frequency of occurrence.
- Clinical blood test. Indicates the presence and degree of inflammation in the body.
- Fibrogastroscopy. Reveals the condition of the stomach walls, the presence of an inflammatory or erosive process, ulcers.
- Probing and analysis of gastric juice. It is used when it is necessary to determine the acidity and characteristics of the enzymes of an organ.
Return to contents
Sucks in the stomach
Everyone knows what it feels like to have a stomach suck. This phenomenon is provoked by various factors, from nervous strain to serious gastrointestinal diseases. Often, if the stomach sucks, it means that it is asking for food. During the digestion of food, its walls contract. After the food ball drops lower, muscle contractions occur, spreading from the stomach to the nearest parts of the intestine. At this time, an unpleasant symptom is felt.
Hunger pains and their signs
Hunger pains can be very intense
Hunger pain is called a pre-ulcerative condition, which manifests itself in the presence of advanced inflammation of the stomach or in the presence of erosive duodenitis (intestinal disease).
Painful sensations occur in the pit of the stomach or slightly lower, the pain intensifies when pressing with your fingers.
Additional symptoms of a peptic ulcer: nausea, sour vomiting that occurs at the peak of pain, heartburn and even constipation. A fairly common reaction to hunger pain is loss of appetite. This is usually a psychological problem; the body rejects food because it is too heavy for it.