For young children, it is quite common for the baby to have loose stools along with a high temperature. The simultaneous appearance of these symptoms indicates an acute intestinal, infectious or viral disease. Any of them carries a danger to a fragile child’s body. It is very important to take the necessary measures in a timely manner to prevent the baby’s condition from worsening and to prevent dehydration.
Causes leading to diarrhea and fever
Such symptoms can be associated with various reasons - it depends on what provoked such a combination as diarrhea and fever in a child how dangerous it is. These causes are of two types: infectious or non-infectious in nature.
Factors belonging to the second group, in rare cases, pose a threat and are quite easy to treat. While the reasons associated with the presence of infection are dangerous and require mandatory consultation with a doctor.
Non-infectious factors
There are three main reasons, not related to infections, that can lead to loose stools and fever (see also: what to do if your month-old baby has loose stools?). Usually in such cases the temperature does not exceed 37-37.5̊ C (for more details, see the article: what to do if a month-old baby has a temperature of 37 degrees?). This:
- Teething. The beginning of the process of teeth emergence most often occurs at the age of 5-8, sometimes 9-11 months. This is a natural physiological phenomenon that all children go through. It is often accompanied by diarrhea and a slight increase in temperature. Somewhere on the 2-3rd day of teething, these symptoms decrease or stop completely, without treatment (we recommend reading: How long can the temperature last during teething on average?).
- Personal intolerance to drugs. Some medications can cause an individual reaction in the child’s body to their use. It may manifest as diarrhea and fever. Rash and cough are also possible. If parents suspect that the child’s intolerance to the medication being used is the cause of his condition, then they should stop taking the drug and consult a specialist.
- Food poisoning. Poor quality food may well be the factor that leads to frequent bowel movements and a temperature of 39 °C. In case of poisoning, vomiting or skin rash is also possible, and in rare cases, an allergic cough. Such disturbances in the functioning of the digestive tract require mandatory medical intervention.
READ ALSO: Can teething cause diarrhea?
When fever and frequent loose stools are caused by one of these factors, intestinal symptoms usually subside within a few hours. At most, this can last several days.
Diarrhea and fever may also be associated with other factors. For example, in infancy with:
- pathology of intestinal development;
- non-compliance with diet by a nursing mother;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- overfeeding the baby;
- intolerance to certain foods due to an immature digestive tract with the early introduction of complementary foods;
- an individual reaction of the child’s body to a new product, which is also accompanied by a skin rash, itching and cough.
In older children this is associated with:
- fermentopathy;
- chronic diseases of the digestive system;
- leukemia in acute form;
- enterocolitis of various origins;
- intestinal dysbiosis caused by the use of antibiotics;
- psycho-emotional stress or stress.
Infectious factors
Cases when the child’s body is faced with an infection require a mandatory call to the doctor. Infectious diseases are dangerous in themselves, but they pose an even greater threat due to possible complications.
Temperatures above 39 °C together with loose stools are not the only symptoms of infection in the body. If they are accompanied by a cough and rash, then most likely the baby has fallen ill with one of the well-known childhood diseases such as measles, rubella or scarlet fever.
You must immediately seek help from a doctor to prescribe treatment. Trying to treat the baby on your own in this situation is contraindicated, since self-medication can lead to adverse consequences.
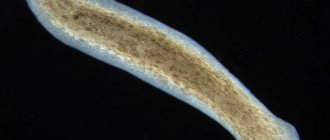
An intestinal infection is also a possibility. As a result of helminthic infestations affecting the intestinal mucosa, the child begins to have diarrhea and the temperature rises to 38 °C. In addition to these symptoms, intestinal infection is accompanied by general intoxication of the body, bloody discharge in bowel movements, sometimes hemorrhagic rash and cough. In this case, it is important to pay attention to the structure of the diarrhea. If the baby's stool has a watery consistency, this indicates the penetration of pathogenic pathogens into the intestines. The danger lies in the spread of toxic substances throughout the body, which are waste products of viruses and bacteria. They are responsible for high fever during diarrhea. You should definitely seek help from a pediatrician.
READ ALSO: what to do if a newborn has a temperature of 38 degrees?
Complications
Possible complications of diarrhea in combination with high fever:
- dysbacteriosis;
- convulsive syndrome;
- loss of consciousness due to severe dehydration;
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract – gastritis, pancreatitis, colitis;
- allergic reactions – atopic dermatitis, urticaria;
- renal failure.
When parents take preventive measures immediately, the risk of consequences is significantly reduced. Diet plays an important role in the treatment of diarrhea complicated by high fever. Therapeutic nutrition helps restore mucous membranes and replenishes vitamins and minerals.
We recommend: Why does diarrhea occur after taking antibiotics and how to treat it?
Possible additional symptoms
Typically, fever and diarrhea are accompanied by additional symptoms that can help determine the reasons for the child’s poor condition. For example:
- Bloody feces, general intoxication and fever are signs of an intestinal infection.
- Fever and stool with mucus indicate that pathogenic microorganisms have entered the body: cryptosporidium, salmonella, lamblia, enterotoxigenic or enteropathogenic coli, enterovirus, rotavirus.
- The addition of vomiting with the unpleasant odor of acetone from the mouth to this symptomatology indicates the presence of an acetonemic crisis. If at the same time the face becomes pale and the limbs are cold, food poisoning is evident.
- If an additional symptom is abdominal pain, then the cause presumably lies in the foods eaten in the last 24 hours.
- If, upon examination of the oral cavity, swelling, redness or inflammation of the gums is observed in a baby under 3 years of age, then fever and diarrhea may be caused by normal teething.
- The appearance of a rash against the background of these symptoms indicates possible scarlet fever, measles or rubella. This may also apply to manifestations of an allergy to a medicine, which usually occurs with individual intolerance to drugs that contain iron.
- When a child’s fever and diarrhea are accompanied by signs of a cold in the form of a cough, red throat, runny nose, sore throat, he has the flu, sore throat, otitis media or nasopharyngitis.
READ ALSO: how to stop vomiting without fever and diarrhea in children?
Parents' actions
If the child is one year old or older, the diarrhea is mild, and the temperature is not high, you can limit yourself to a gentle diet and give the baby more fluids. Symptoms should disappear after a day. If there are signs of infection or poisoning, action must be taken.
First of all, parents should inform the doctor about the illness. Before visiting a doctor, adults can provide first aid to the baby themselves.
It is allowed to give sorbents to the baby. Smecta and Activated carbon are acceptable. It is important to prevent the patient from dehydration. Therefore, it is necessary to replenish the water-salt balance using a rehydration solution.
If the temperature exceeds 38 degrees, you can give an antipyretic drug based on paracetamol. If a one-year-old baby has a fever, take an antipyretic in the form of suppositories. Fever in a two-year-old child - the drug is in the form of a suspension. A low temperature not exceeding 38 degrees does not require the use of medications aimed at reducing values.
The parent should isolate the child from other family members until the cause of the symptom is determined. You should absolutely not give your baby antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription. It is prohibited to treat intestinal infections on your own.
First aid
Below are the actions that you need to take first and what you should not do if your child has a fever and diarrhea. Necessary:
- call a doctor at home;
- until the true cause of watery diarrhea is understood, isolate the baby to prevent the infection from spreading further to other people;
- Carry out a careful examination for the presence of other symptoms;
- Give, if desired, enterosorbents such as activated carbon, Smecta or Enterosgel.
No need:
- panic;
- give antibiotics;
- bring down the temperature until the doctor arrives (see also: what temperature should be brought down in a baby?).
In cases where the wait for medical help is long, and the baby’s temperature is 38 °C or more, you can resort to drugs with paracetamol. For one-month-old babies and children under 10-11 months, it is better to use candles; children 1-2 years and older can be given syrup.
Possible causes of fever in children of different ages with diarrhea
When a baby develops diarrhea and fever, the first thing parents need to do is call an ambulance or a doctor at home. Do not panic and give your child any medications on your own. You especially need to avoid antibiotics. In this case, they can only worsen the baby’s condition.
It is advisable to separate the child from other family members and place him in another room for a while. Until the cause of the painful condition is determined, it is better to protect loved ones from the possible spread of infection. It is necessary to examine the baby; perhaps there are other accompanying symptoms on the body that will help diagnose the disease. You should not try to bring down the temperature on your own; it is better to wait for the doctor to arrive.
If the doctor will not arrive soon, and the baby’s temperature has already reached 38 degrees, you can give him an antipyretic drug, which is based on paracetamol. Aspirin should not be taken by children under 12 years of age, so its use in this case is not recommended.
Children under one year of age are recommended to be given fever-reducing agents in the form of rectal suppositories. Children 2 years and older can take syrups for high fever. You can also alleviate the child’s condition with such means as Smecta, activated carbon and Enterosgel. They will improve the baby’s condition and temporarily stop gagging or the urge to go to the toilet.
The type of intestinal disorder can be determined by accompanying symptoms and parental observations of stool characteristics.
The baby first of all complains of pain in the stomach, because poor-quality food damages the mucous membrane. Diarrhea may be accompanied by vomiting and an increase in temperature to 37.5–38°. Poor quality food is difficult to digest, causing rotting and fermentation in the intestines. As a result, bad breath occurs. A clear sign of food poisoning is cold extremities. Vomit resembles the smell of acetone.
The same infection can manifest itself differently in a baby. The nature of the course depends on the characteristics of the immune system. E. coli can enter the gastrointestinal tract with food, through contact with a sick person contaminated with sand or soil. Stools due to intestinal infection are watery and green in color. The stool sometimes contains inclusions of mucus and blood.
A severe intestinal infection of a bacterial or viral nature is accompanied by obvious signs of intoxication:
- fever;
- fever;
- decreased blood pressure;
- severe weakness;
- bouts of crying give way to sudden apathy.
Diarrhea is combined with a sore throat, runny nose, cough and high fever. In this case, loose stools are one of the signs of a serious illness. Most often, intestinal upset occurs with influenza, otitis media, sore throat, and nasopharyngitis. Diarrhea can be caused by medications for fever and pain based on ibuprofen and paracetamol.
The rash indicates an allergic reaction caused by medications. Another option is that the child fell ill with scarlet fever, measles or rubella. The rash is characteristic of an enterovirus infection.
Teething
Stool loosening in children under 3 years of age is often associated with teething. The condition can be recognized by swollen gums. The temperature can rise to 40° and above. The lower and upper molars begin to cut at 1–1.3 years, which is the most common cause of diarrhea in a one-year-old child.
Intestinal upset and an increase in body temperature to 38.5–39° are caused by drugs containing iron. This happens when a child has an individual intolerance to these drugs. An additional sign of an allergy is hives. It manifests itself as swollen blisters on the skin.
Food allergies
The temperature rises due to allergies in rare cases. A combination of fever and diarrhea occurs if the child has eaten a large portion of a product that causes an immune reaction. Food allergies provoke swelling and irritation of the gastrointestinal mucosa. There are pieces of undigested food in the stool.
Dysbacteriosis
The condition may be accompanied by diarrhea and fever. The balance of intestinal microflora is disrupted due to a decrease in the number of beneficial bacteria. The digestion process slows down. Food is not completely absorbed; undigested particles irritate the intestines, which leads to inflammation of the large and small intestines.
Diarrhea with fever in a small child at different ages can depend on various reasons. In infants, symptoms may appear due to improper nutrition of the nursing mother. In one-year-old children and between the ages of 1 and 3 years, unpleasant symptoms occur when complementary foods are introduced or as a reaction to fiber.
In children 4-6 years old, the intestines often react with similar manifestations to stressful situations. Stress at this age causes entry into kindergarten (change of environment) and a more conscious perception of the world. The appearance of fever and diarrhea in adolescents is often associated with eating heavy foods and carbonated drinks.
Ways to Prevent Dehydration
Dehydration is one of the dangers of the condition when fever is combined with diarrhea. Along with diarrhea comes a colossal loss of water, and the more fluid leaves the child’s body, the higher the temperature will rise (we recommend reading: what should be the normal body temperature of a newborn at 1 month?). If a child experiences increased sleepiness, mucous membranes become dry, a rash and cough appear, he does not go to the toilet for a long time, his heartbeat quickens and he begins to breathe deeper, you should not delay calling an ambulance. In very young children, dehydration can be fatal.
READ ALSO: What medications should be given to children under one year of age for diarrhea?
To prevent dehydration of the body, fluid loss should be constantly restored by giving the child water with rehydrants to drink. When breastfeeding, you should try to put the baby to the breast as often as possible. Breast milk has a calming effect on the gastrointestinal tract and has bactericidal properties. In cases where the baby is bottle-fed, it is preferable to feed him with a special medicinal mixture, which includes absorbent components.
Below are 2 recipes for rehydration solutions that will help you avoid dehydration. You can make them at home:
- To one liter of boiled water, cooled to room temperature, add granulated sugar - 1 tablespoon, table salt - a teaspoon, baking soda - half a teaspoon. Dissolve all components and give to the child every 5 minutes in small portions.
- Take 1 liter of boiled water, cooled to room temperature, add granulated sugar - 8 teaspoons, table salt - a teaspoon, fresh orange or grapefruit juice - 2 pieces. Dissolve everything and give it in portions to the child. This option is only suitable for those children who are not allergic to citrus fruits.
What diet does a child need?
Providing your child with proper nutrition can make him feel better and even speed up his recovery. Infants under one year old do not need to be weaned, the main thing is not to give them milk right during an attack. If the child eats artificial milk, it is better to temporarily replace it with soy formula.
Older children need to switch to a light diet, which includes vegetables, fruits, cereals, berries, boiled meat, fish, yoghurts, decoctions, soups and jelly. All solid products must be ground to a mushy state. Meat and fish should only be boiled or steamed.
If the child is over seven years old, then you will have to limit the consumption of all fatty foods, spices, fast food, sweets, chocolate, ice cream and various sweet drinks such as soda and juices.
Establishing a diagnosis
The most important thing when a baby has diarrhea and high fever is timely treatment, before complications arise (see also: diarrhea in a baby while breastfeeding). Unfortunately, it is impossible to establish an accurate diagnosis only by visual examination. In order to prescribe the right drugs, it is necessary to undergo certain laboratory diagnostics, which will confirm and clarify the previously made diagnosis. Such laboratory diagnostic methods include:
- Coprogram. With its help, you can find out about digestion disorders of specific substances.
- Analysis of stool for dysbacteriosis. Determines deviations from the norm in the intestinal microflora.
- Fecal analysis for helminths. Detects parasite eggs.
- General blood analysis. Shows the level of eosinophils in the blood. Its increase indicates a possible inflammatory process, allergy or helminthiasis.
- Blood chemistry. Detects disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas and liver.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. Provides information about inflammation of the liver, gall bladder, and pancreas.
Modern equipment designed for diagnosing various diseases makes it possible to obtain quick results. They, in turn, help to establish the true cause of diarrhea and fever. Based on them, the gastroenterologist or therapist already prescribes the necessary treatment.
How to get rid of parasites
When identifying worms in a child, anthelmintic drugs (Nemozol, Veromox, Pirantel) are first used. The dosage is determined by the doctor in accordance with the form and stage of the disease. Treatment must be carried out not only to the child, but also to relatives in contact with him.
The condition for successful removal of helminths from the body is proper nutrition and adherence to personal hygiene rules. During the therapy period, the baby needs to change his underwear and bed linen daily. Before eating and after using the toilet, you should wash your hands thoroughly with soap.
Treatment methods
In case of diarrhea and increased temperature, it is necessary to treat the disease that led to such symptoms. At the same time, therapy should be carried out aimed at overcoming such unpleasant and dangerous symptoms. This is done in order to prevent dehydration and normalize the functioning of the stomach. For these purposes, medications and a special diet are used.
Drug therapy
To help the body cope with diarrhea, adsorbent agents are prescribed. These include Smecta, Enterosgel, activated carbon, Neosmectin, Polyphepan. A fairly effective way is to rinse the stomach with plain boiled water or use a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
To prevent dehydration, rehydration therapy is used, which involves drinking plenty of fluids. This helps restore fluid in the body. Such drinks are: Regidron, compotes, saline solutions, mineral water, glucose, acidified tea.
Medicines containing paracetamol will help reduce fever above 38.5 °C. In critical condition or when blood appears in the stool, treatment with fluoroquinol antibiotics or third-generation cephalosporins is prescribed. To restore the intestinal microflora, you need to take lactobacilli and bifidobacteria.
Diet
The purpose of the diet in case of diarrhea is related to the prevention of dehydration and normalization of gastrointestinal functions. It has its own characteristics:
- it is necessary to maintain feeding the baby five times a day, but the portions should be smaller;
- components of the diet of children over one and a half years of age are chopped vegetables, boiled cereals and large volumes of liquid consumed;
- any dish should be steamed, or boiled and served mashed or pureed;
- when the child’s condition gets better, you can try giving him lean fish and meat, and gradually adding dairy products to the diet.
If the symptoms in question are observed in a baby up to one year old, there is no need to interrupt breastfeeding, but it is not recommended to apply it to the breast at the time of an attack. It is better to switch children who are bottle-fed to soy formula for a while.
For older children, the diet for the first few days consists of cereals, carrots, jelly, bananas and apples, blueberries, fish, boiled chicken, natural yoghurts, rice water and soups. For a while you will have to give up sugary drinks, coffee, soda and juices such as grape, apple and peach.
Products that should not be consumed include:
- dairy products;
- fresh fruits and vegetables;
- soups cooked in fatty broth;
- preserved and smoked products;
- fast food, nuts, crackers, chips and other store-bought treats;
- chocolate, ice cream, candy.
Prevention
Unfortunately, it is quite difficult for parents to protect their child from various infectious diseases, since it is not always possible to control the actions of the baby, as well as all his meals.
And yet, in this case, you should not forget about some simple rules that can significantly increase the chances of preventing infection and the manifestation of unwanted symptoms.
- Teach your child to wash his hands before eating and monitor his hygiene. Explain why it is important to sanitize fruits and vegetables before using them;
- Watch your baby's diet. It must be balanced, containing the necessary vitamins and elements. Also, make sure that the products you give your baby are compatible;
- Do not forget that an excess of vitamin substances is just as bad for the human (and especially children’s) body as a deficiency. Don't go to extremes;
- Strengthen your immune system;
- You should not bathe your child in bodies of water unknown to you;
- Try to monitor your child’s social circle as much as possible. Limit his contact with sick people.
Now, knowing what is described above, you can more effectively deal with problems such as diarrhea and fever in a child.
Always remember that preventing a disease is better than treating it . Protect your child, carefully monitor his diet, and then children will grow up healthy and happy, without giving parents reasons to worry!