World statistics say that intestinal diseases account for a significant portion of all gastrointestinal pathologies. One of the intestinal diseases is colonoptosis. This pathology leads to intestinal dysfunction and the appearance of a number of unpleasant symptoms. In addition, its presence negatively affects the condition of other organs, in particular the pancreas, liver, and stomach. How colonoptosis manifests itself, what kind of disease it is and what methods are used to treat it, read the article.
Etiology
Intestinal transversoptosis is a rather rare disease that can be either congenital or acquired. Predisposing factors will vary slightly.
The following reasons are noted for congenital pathology:
- congenital weakness of the abdominal muscles;
- curvature of the spinal column, in particular lordosis;
- abnormal position of the diaphragm.
The secondary form develops against the background of other diseases or the influence of negative factors. In such situations, the provocateurs are the following:
- excessive stress on the intestines when engaging in strenuous sports;
- rapid weight loss;
- previous surgical interventions on the organs of the digestive system;
- features of the profession;
- difficult pregnancy;
- numerous births.
Often, a bend in the transverse colon in the area of the hepatic or splenic angle will be a consequence of the completely natural aging process of the human body.
In any case, the following changes occur in the organ:
- impaired intestinal motility;
- problems with the towing function;
- increased susceptibility to constipation;
- the occurrence of inflammatory processes;
- disturbance of peristaltic movements.
Description of the pathology and factors provoking its occurrence
Transversoptosis is characterized by bowing of the transverse colon. It becomes similar to the English letter V. Deviation leads to the formation of a pronounced inflammatory process.
With significant deviations, motor skills are impaired. Colon prolapse most often occurs in people over 50 years of age. The pathology equally affects both men and women.
The risk group also includes people whose work activities involve lifting heavy objects. The deviation is characterized by prolonged constipation. Without treatment, the patient's condition becomes worse. The reasons for the formation of the disease are described in the table.
| Hereditary predisposition | The risk of developing the disease is high in those patients whose relatives have encountered the deviation. Prenatal organ development disorders play an important role. |
| Body Features | Pathology can occur against the background of decreased muscle tone, low position of the diaphragm and weakness of connective tissue. |
| Excessive exercise | The disease may be a consequence of heavy lifting or excessive physical activity. |
| Features of body weight | People with excessive body weight or those who have spontaneously and significantly lost weight may experience the pathology. |
Symptoms and treatment of intestinal coloptosis in adults vary from person to person. For successful therapy, it is necessary to eliminate the underlying pathology.
Prolapse of the bowel is usually accompanied by prolonged constipation
Symptoms
The first clinical manifestations, which are most often ignored by people or attributed to completely different pathologies, are increased gas formation and frequent disturbances in bowel movements (constipation).
The following symptoms are typical for transversoptosis:
- pain in the lower or middle part of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity of a constant, pressing and aching nature;
- a sharp increase in pain when straining during defecation or after eating food; excessive physical activity can provoke a painful attack - there is a decrease in the intensity of pain in a horizontal position of the body;
- periodic nausea, which only occasionally leads to vomiting - vomiting does not bring relief;
- severe headaches;
- causeless irritability;
- sleep disturbance, including insomnia;
- frequent mood changes;
- increased heart rate;
- increase in blood tone;
- signs of ischemic heart disease;
- fatigue and general weakness;
- unpleasant sensations during the emission of urine in males;
- painful menstruation in women;
- formation of external or internal hemorrhoidal cones.
Transversoptosis does not have specific clinical manifestations that would accurately indicate the course of this particular disease.
Diagnostics
Only a gastroenterologist can make a diagnosis of ceco-transversoptosis after the patient has undergone a whole range of diagnostic measures.
The clinician must personally carry out a number of manipulations:
- studying the medical history - to identify a pathological predisposing factor that could cause prolapse of part of the colon;
- familiarization with life history;
- collecting information regarding the course of pregnancy from female representatives;
- a thorough physical examination, necessarily including deep palpation of the abdomen;
- detailed survey of the patient - to establish the intensity and time of manifestation of the first symptoms of the disease.
The most important instrumental procedures in diagnostic terms:
- radiography of the peritoneum;
- ultrasonography of the gastrointestinal tract;
- irrigoscopy;
- radioisotope methods are the main methods for diagnosing the disease in children;
- gastroscopy;
- CT;
- MRI.
As for laboratory tests, analyzes are limited to general tests:
- clinical analysis and blood biochemistry;
- coprogram;
- general clinical urine analysis.
Transversoptosis must be differentiated from the following pathologies:
Diagnostic measures
It is difficult to identify the disease based on clinical manifestations alone. To make a diagnosis with high accuracy, you should consult a doctor. Diagnosis begins with the patient’s complaints, recognizing the symptomatic picture and taking an anamnesis. After this, the doctor needs to conduct a thorough physical examination and palpation of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity.
Informative research methods are:
- radiography of the abdominal organs;
- ultrasonography of the digestive tract;
- irrigoscopy;
- radioisotope techniques. They make it possible to diagnose congenital pathologies in children;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy;
- gastroscopy;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
Laboratory research methods allow for correct differential diagnosis. Therefore, patients may be prescribed:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- coprogram;
- general urine analysis.
After this, the doctor differentiates the disease from other diseases with a similar clinical picture in the form of:
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- helminthiasis;
- pancreatitis in acute and chronic form;
- cholecystitis;
- intestinal obstruction.
In some cases, consultation with a pediatrician, therapist, parasitologist or gastroenterologist is required.
Treatment
Treatment begins immediately after confirmation of the diagnosis. After confirming the diagnosis, they immediately turn to conservative methods of therapy:
- maintaining a gentle diet;
- wearing a special bandage;
- therapeutic exercises;
- manual or hardware massage of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity;
- taking medications to relieve symptoms;
- physiotherapeutic procedures, in particular paraffin baths, acupuncture, heating and medicinal electrophoresis;
- the use of traditional medicine, but only as an auxiliary treatment method and after the approval of the attending physician.
Diet therapy has a number of strict rules:
- eating large amounts of high-calorie foods;
- enriching the menu with fermented milk products, fruits, honey and sugar;
- ingestion of sufficient volumes of liquid - at least 2 liters per day;
- consumption of sweets (transversoptosis is one of the few diseases for which carbohydrates are allowed).
General rules
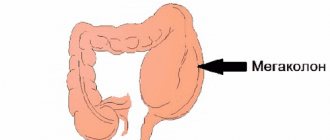
Colon prolapse (colonoptosis) is a pathology characterized by displacement of the loops of the large/small intestine towards the pelvis. The main reasons are inflammatory processes and decreased tone of the muscle structure of the intestine, weakness of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, heavy physical activity, pathology of the intestinal ligamentous apparatus, surgery on the abdominal organs, pathology of the spinal column, difficult pregnancy, and rapid weight loss. Symptoms of this pathology are not specific and manifest themselves mainly in the form of flatulence, chronic constipation, a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen, general weakness, and, less often, nausea and not profuse vomiting.
Prolapse of the intestine can be confirmed by a plain contrast radiograph of the abdominal cavity, performed over time. Treatment of the disease is complex and includes wearing a special bandage, gymnastic exercises to strengthen the abdominal muscles, and correction of the diet.
The diet for colonoptosis is aimed primarily at normalizing stool (preventing constipation and bloating), which is achieved by including in the diet foods that enhance intestinal motility. Such products include:
- Containing a large amount of dietary fiber - wholemeal bread, cereals (buckwheat, millet, barley, oatmeal, pearl barley), bran, raw vegetables, legumes, nuts, dried fruits.
- With a high content of organic acids - pickled/pickled vegetables, fermented milk drinks, sour fruits/juices, fruit drinks.
- Meat with a lot of connective tissue.
- Rich in sugars (cane sugar, milk sugar, jams, syrups, syrups, honey, dextrose, sweet dishes).
- Containing salt - salted vegetables/fish, canned snack foods.
- Fats (sour cream/cream), consumed in large quantities on an empty stomach, egg yolks.
- Carbonated drinks.
- Cold dishes (jellied dishes, okroshka, beetroot soup, cold drinks, ice cream) consumed on an empty stomach, since the difference in body temperature and the product is the leading factor that has a stimulating effect on the intestines.
It is mandatory to include in the diet such products as kumiss/kvass, which have a pronounced effect due to the content of carbon dioxide/organic acids, sauerkraut (a source of fiber/organic acids), bran/sea kale, which are prone to swelling with the attraction of fluid into the intestines, which helps soften the intestinal contents, as well as foods with a pronounced laxative effect (prunes, beets, plums, fresh kefir, vegetable juices).
At the same time, foods that slow down peristalsis and, accordingly, bowel emptying should be excluded from the diet: mucous soups, hot dishes, black coffee, cocoa, chocolate, strong tea, dogwood, lingonberries, jelly, pears, blueberries, pomegranate, pasta, red wine , as well as fried foods that enhance fermentation/rotting processes.
When choosing a diet, the presence of concomitant gastrointestinal diseases should be taken into account. The diet for colonoptosis requires the consumption of a sufficient amount of free fluid - at least 2 l / day due to the fact that with a lack of fluid in the sigmoid colon, water is absorbed from the feces and they harden, thereby complicating the act of defecation. Food is prepared mainly by boiling/baking and served uncut. Vegetables in the diet should be present mainly raw and partially boiled.
Prevention and prognosis
These simple preventive rules will help reduce the likelihood of developing the disease;
- maintaining a healthy and moderately active lifestyle;
- proper nutrition;
- strengthening the abdominal muscles;
- avoiding excessive physical activity;
- body weight control;
- Regularly undergoing a full medical examination.
The prognosis for transversoptosis is favorable. However, we should not forget about the development of complications, so postponing treatment is not recommended. The danger lies in the fact that even after surgery the possibility of frequent relapses of transverse colon prolapse cannot be ruled out.
- Insomnia
- Painful periods
- Chest pain
- Abdominal pain
- Fast fatiguability
- Haemorrhoids
- Headache
- Constipation
- Unpleasant sensations when urinating
- Dyspnea
- Increased gas formation
- Psycho-emotional instability
- Irritability
- Vomiting without relief
- Decreased performance
- Nausea
- Deterioration of general condition
- Cardiopalmus
- Feeling broken
Transversoptosis is a change in the anatomically prescribed position of the large intestine. As the pathology progresses, the transverse colon prolapses: on x-rays it will have the shape of the letter “V”.
Anyone can suffer from the disease, regardless of age and gender. There are a number of both pathological and completely harmless predisposing factors.
The main manifestation of the clinical picture is increased gas production. Against the background of this symptom, other signs develop: pain of varying severity in the abdominal area, periodic nausea leading to vomiting, and other manifestations of deterioration in well-being.
Prolapse of the transverse colon can only be detected using instrumental diagnostic procedures. Laboratory tests and primary diagnostic measures are only of an auxiliary nature.
Treatment begins with attempts to conservatively get rid of the problem by taking medications, following a gentle diet and performing exercise therapy. If there is no positive effect, surgical intervention is considered.
Intestinal colonoptosis symptoms and treatment in adults
Pathological changes in internal organs affect not only the general condition of a person, but also the ability to provoke the development of various complications. In this regard, when the normal arrangement of internal organs is changed due to their prolapse, the consequences of deterioration in health can be very serious. Most often, prolapse of various parts of the colon, differing in clinical picture, is observed. Perhaps its most important section is the colon, which consists of four sections: ascending, transverse, outgoing, and sigmoid. It serves to absorb water and undigested food debris from the small intestine. Prolapse of the colon, known as a colon, is called colonoptosis.
1/19/ · Therefore, it is very important to know the symptoms of adhesive intestinal disease, especially for those who recently had to undergo surgical treatment of abdominal pathologies.5/5(1).
Etiology
Transversoptosis of the intestine, in particular the transverse colon, is a rather rare disease. Pathology can be congenital or acquired. The triggering sources will be somewhat different.
The congenital variant of this disease is caused by the following factors:
- weakness of the abdominal muscles, which is considered a congenital abnormality;
- damage to the spinal column (curvature);
- specific localization of the diaphragm.
Acquired transversoptosis is always secondary, that is, the disease develops against the background of some disease or under the influence of any other negative factor.
The most common reasons:
- professional participation in heavy sports - there is an excessive load on the intestines;
- a sharp decrease in body weight;
- previous surgery on the gastrointestinal tract;
- complicated course of the period of bearing a child;
- frequent births.
Among the physiological sources of the formation of an inflection of the transverse colon in the area of the hepatic or splenic angle, it is worth highlighting the natural aging process of the human body.
Regardless of what provoking factor influences colon prolapse, the following changes develop:
- problems with intestinal motility;
- disorder of evacuation function;
- high susceptibility of the body to chronic constipation;
- formation of inflammation;
- violation of peristalsis.
It is noteworthy that the main risk group for secondary transversoptosis or Payr's disease is the elderly - their pathology is most severe.
Colonoptosis of the intestine - prolapse of the transverse colon
World statistics say that intestinal diseases account for a significant portion of all gastrointestinal pathologies. One of the intestinal diseases is colonoptosis. This pathology leads to intestinal dysfunction and the appearance of a number of unpleasant symptoms.
In addition, its presence negatively affects the condition of other organs, in particular the pancreas, liver, and stomach. How colonoptosis manifests itself, what kind of disease it is and what methods are used to treat it, read the article. Colonoptosis is a pathological prolapse of the colon that occurs when the ligaments that hold it in the abdominal cavity are weakened. The disease can be congenital or acquired.
At risk of developing pathology are women carrying a child, as well as adults who often lift heavy objects. Due to the natural aging of the body, organ prolapse can occur in old age. Often, colon prolapse is combined with prolapse of other abdominal organs. Colonoptosis can be right- or left-sided. Most often, right-sided colonoptosis is observed, in which the right part of the colon descends.
This type of pathology is characterized by prolapse of nearby abdominal organs. In addition, total colonoptosis is distinguished. With the development of this type of pathology, the entire colon descends into the pelvic area.
Intestinal colonoptosis can develop in both sexes, regardless of age. However, there are a number of factors that increase the likelihood of pathology occurring. These include:. Women during pregnancy should know that rapid labor increases the risk of developing colonoptosis.
Rapid labor can lead to ruptures of ligaments and muscles, which provokes intestinal prolapse. In addition, the risk of colonoptosis will be higher in those women who are carrying 2 or more babies at the same time. Their heavy weight puts pressure on the intestines, increasing stress on the ligaments, which can cause the organ to sink down. When the colon prolapses, its peristalsis is disrupted, which leads to retention of feces in it.
This provokes the development of constipation and bloating - the main symptoms of intestinal colonoptosis. Sagging of the intestine into the pelvic area leads to severe pain, which decreases when the patient takes a horizontal position. When stool stagnates in the intestine, it compresses the organs of the genitourinary system.
This negatively affects their functions and can lead to the development of inflammation in them. Due to problems with bowel movements, patients experience nausea and vomiting, and decreased appetite. Headaches may occur due to fecal intoxication. If symptoms of bowel prolapse appear, you should contact a gastroenterologist for a thorough examination.
The main diagnostic method for detecting pathology is irrigoscopy. The procedure involves injecting a contrast agent into the intestine using an enema and taking an X-ray of the intestine. During the examination, the doctor determines the extent of the pathology and the location of the intestine.
Another instrumental method for examining the intestines, colonoscopy, can also be used. During this procedure, an instrument is inserted into the anus, which is a probe, at the end of which there is a lighting device and a mini-camera. By moving the colonoscope through the intestine, the doctor can examine its walls and detect various neoplasms, erosions, and ulcers on the mucous membrane.
In addition, using a colonoscope, the doctor can take pieces of tissue in places where the intestinal mucosa has changed for a biopsy. Treatment of intestinal colonoptosis can be carried out conservatively and surgically. The main goal of therapy is to restore intestinal motility. If the disease was detected at an early stage and treatment began immediately, it is possible to use conservative methods: diet therapy, medication, herbal medicine, and therapeutic exercises. Acupuncture and acupressure may be effective.
Popular folk recipes for getting rid of illness are based on taking herbal decoctions that remove toxins from the body, have a calming effect, and normalize intestinal function. The doctor may also recommend that the patient wear a bandage for colonoptosis. It allows you to fix the intestine in the correct position and restore its tone. However, you should not use a bandage without consulting a doctor. Separately, it is worth mentioning the nutrition of patients with colonoptosis.
The diet for intestinal prolapse has 3 goals: to stop the progression of the pathology, to smoothly normalize the patient’s weight, and to improve stool. The patient needs to get rid of excess weight, but it is important to remember that sudden weight loss can only aggravate the pathological condition, so the diet should be designed in such a way that weight loss occurs smoothly.
Dietary nutrition will make bowel movements regular, relieve the patient from excessive bloating and eliminate the resulting spasms and discomfort in the intestines. A properly formulated diet will help avoid constipation, normalize bowel movements and relieve abdominal pain. It is recommended to consult a doctor for a diet plan. Colonoptosis is prolapse of the colon. The colon is attached to the posterior wall of the abdominal cavity by means of ligaments, which, when weakened or partially torn, sag.
Violation of normal spatial orientation changes the functioning of the intestine, its motility and causes symptoms of partial obstruction and fecal intoxication.
The condition is differentiated from dolichomegacolon, when the intestine of excess length sags. With ptosis, the length of the intestine and its parts is normal, physiological, only the position in the abdominal cavity is disturbed. Bloating and constipation impair digestion of food, and patients may lose weight due to refusal to eat. Concomitant inflammation of the digestive canal is common.
These are signs of fecal intoxication due to untimely removal of decay products, as well as disturbances in other organs: The remaining examination methods - laboratory and instrumental - are of an auxiliary nature. Sigmoidoscopy is sometimes used, but this is at the discretion of the attending physician. Additionally, ultrasound of the abdominal organs and computed tomography can be used if the clinical situation requires it.
The main task is to restore motor skills and normalize the movement of food, eliminate bloating and constipation. For this purpose, diet, medications, bandages, and physical therapy are used. Food should be large in volume, but low in calories. It is useful to eat dishes of contrasting temperatures. Losing body weight and regularly filling the intestines with rough foods helps eliminate constipation. Laxatives are used only as prescribed by a doctor for a short course.
They cannot be used often, as addiction to them quickly develops. Anti-inflammatory agents, enveloping agents, and digestive enzymes may sometimes be used. To improve motor skills, Proserin is used, a cholinomimetic that improves neuromuscular transmission. However, injections must be repeated periodically. This is a medical product whose purpose is to support the abdominal organs.
The bandage is an elastic belt, which is selected individually according to size. You need to put it on in bed before getting up, wear it throughout the day, and take it off before going to bed while lying down. The bandage is most effective for stretching the muscles and white line of the abdomen, which happens after pregnancy and sudden weight loss. Used in extreme cases, the operation is abdominal and very complex. Its essence is to suture intestinal loops to weakened ligaments with a non-absorbable thread.
The complexity of the operation is that there is no guarantee of a return to health - adhesions may form at the site of the threads, and the ligaments may weaken even more. The prognosis is generally favorable; this condition is not life-threatening. Young women may develop infertility due to compression of the pelvic organs, but this is rather a casuistry, and in practice it is extremely rare. Complications include various inflammatory processes and digestive disorders, which require separate treatment.
Prolapse occurs in many people at different ages. The reason for this is various factors that disrupt the normal functioning of the digestive system. Symptoms of prolapse often lead to the development of numerous chronic diseases in the body.
Therefore, it is necessary to carry out proper treatment of this pathology in the early stages of its occurrence. The condition of the body associated with intestinal prolapse in women and men is called colonoptosis. Intestinal colonoptosis is very dangerous for the functioning of many internal organs, as it negatively affects the activity of blood flow. When certain parts of the intestine descend, an increased background of pressure is created on the surface of the bladder, the male prostate gland and the female genital organs.
This state of the internal cavity has a detrimental effect on the operation of the listed systems. Against the background of such changes, various types of stagnation begin to arise in the body. Painful bowel prolapse most often affects older people.
In most cases, this is due to the weakening of muscle tone and ligamentous strength with old age. At the same time, significant changes occur in the body, negatively affecting the activity of the genitourinary organs and digestive system.
Based on this, it should be concluded that if bowel prolapse occurs, you should immediately seek help from a qualified medical facility. This will prevent unpleasant consequences and further organ loss. These reasons lead to changes in the position of the small and large intestines, which has a detrimental effect on the performance of other organs and leads to a decline in their healthy activity.
Therefore, it is necessary to treat this disease, preferably in the early stages of its occurrence. In the early stages of its development, this pathology is practically devoid of symptoms, so identifying it becomes very problematic, especially if a person practically does not visit hospitals and does not suffer from diseases of the digestive system.
Symptoms
The first sign of pathology is excessive gas formation. Very often, people simply ignore this external manifestation, attributing it to other disorders.
Ceco-transversoptosis has the following symptoms:
- disruption of the bowel movement process, which most often results in constipation;
- the occurrence of a pain syndrome localized at the bottom or in the middle of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity, the pain is constant, pressing and aching in nature;
- a sharp increase in the intensity of pain during straining, which occurs during the act of defecation - often increased pain is observed after eating food or against the background of excessive physical activity, but the pain decreases in a horizontal position of the body;
- periodic occurrence of nausea, which only occasionally leads to vomiting, which does not bring relief;
- severe headaches;
- increased irritability;
- insomnia;
- emotional instability;
- increased heart rate;
- increase in blood tone;
- the appearance of signs characteristic of coronary heart disease;
- rapid fatigue and decreased ability to work;
- general malaise and weakness;
- discomfort when emptying the bladder in men;
- painful course of critical days among female representatives;
- formation of hemorrhoids.
It is advisable to relate all clinical manifestations to patients of any age category.
Treatment
Treatment begins with the following conservative methods:
- diet therapy;
- wearing a special bandage;
- Exercise therapy - gymnastics is compiled on an individual basis;
- abdominal massage - can be water, manual or machine;
- taking medications aimed at relieving pain and accompanying symptoms;
- physiotherapeutic procedures - paraffin baths, acupuncture, heating and medicinal electrophoresis;
- folk remedies.
Treatment with diet involves following these rules:
- the basis of the diet is high-calorie foods;
- enriching the menu with fermented milk products, fruits, honey and sugar;
- ingestion of sufficient volumes of fluid;
- carbohydrate consumption.
Surgical intervention has the following indications:
- severe intoxication of the body;
- detection of intestinal obstruction during instrumental procedures;
- constant pronounced pain syndrome;
- ineffectiveness of conservative therapy.
Surgical treatment is carried out in several ways:
- resection of the affected area of the transverse colon and securing the remaining part to the posterior wall of the peritoneum;
- suturing the prolapsed area of the large intestine to the stomach;
- reduction in intestinal length in children.
How is colonoptosis treated?
Treatment of intestinal colonoptosis can be carried out conservatively and surgically. The main goal of therapy is to restore intestinal motility. If the disease was detected at an early stage and treatment began immediately, it is possible to use conservative methods: diet therapy, medication, herbal medicine, and therapeutic exercises. Acupuncture and acupressure may be effective. Popular folk recipes for getting rid of illness are based on taking herbal decoctions that remove toxins from the body, have a calming effect, and normalize intestinal function.
The doctor may also recommend that the patient wear a bandage for colonoptosis. It allows you to fix the intestine in the correct position and restore its tone. However, you should not use a bandage without consulting a doctor.
Diet
Separately, it is worth mentioning the nutrition of patients with colonoptosis. The diet for intestinal prolapse has 3 goals: to stop the progression of the pathology, to smoothly normalize the patient’s weight, and to improve stool. The patient needs to get rid of excess weight, but it is important to remember that sudden weight loss can only aggravate the pathological condition, so the diet should be designed in such a way that weight loss occurs smoothly. Dietary nutrition will make bowel movements regular, relieve the patient from excessive bloating and eliminate the resulting spasms and discomfort in the intestines.
Find out how effective gastric banding is for obesity.
Read: what is autoimmune hepatitis.
We advise you to find out how anal papillitis is treated.
Basic nutritional recommendations are as follows:
- Dishes and drinks that slow down intestinal motility are removed from the menu: slimy porridges, cream soups, strong tea, jelly, pasta and baked goods;
- You need to drink at least 2 liters of water daily;
- products that lead to fermentation in the intestines (fresh vegetables and fruits, legumes, yeast baked goods, sweets) are excluded from the diet;
- it is necessary to avoid foods that are difficult for the stomach: fatty meat, mushrooms, rich broths;
- refuse herbs, marinades and spices;
- It is recommended not to eat protein foods for dinner, since if they are not completely digested, they provoke gas formation.
A properly formulated diet will help avoid constipation, normalize bowel movements and relieve abdominal pain. It is recommended to consult a doctor for a diet plan.
Colonoptosis is prolapse of the colon. The colon is attached to the posterior wall of the abdominal cavity by means of ligaments, which, when weakened or partially torn, sag. Violation of normal spatial orientation changes the functioning of the intestine, its motility and causes symptoms of partial obstruction and fecal intoxication.
Prevention and prognosis
It is impossible to avoid congenital prolapse of the large intestine, but in order to prevent the secondary development of pathology, it is enough to follow these simple rules of prevention:
- maintaining an active and healthy lifestyle;
- good nutrition;
- strengthening the abdominal muscles;
- avoiding excessive physical activity;
- maintaining body weight within normal limits;
- Regularly undergoing a full medical examination.
Transversoptosis in most situations has a favorable outcome. However, even surgical treatment does not eliminate the risk of frequent relapses of transverse colon prolapse.
Transversoptosis is a change in the physiologically correct position of the transverse colon of the large intestine. It becomes V-shaped, which makes it difficult to fully function. The development of pathology is preceded by a disturbed structure of the spine, weakened abdominal muscles, and incorrect location of the diaphragm. Less commonly, transversoptosis is a congenital pathology. The disease has an ICD-10 code – K63.8, K63.9 (depending on the factor clarifying the root cause of the condition).
Intestinal dolichocolon: causes, symptoms and treatment
Intestinal prolapse can become a serious problem. Human internal organs are arranged in such a way as to function without harming each other. Any change in the position of one or another organ leads to a violation of their anatomical structure. And in most cases, this pathology is associated with prolapse of internal organs. In medicine - ptosis.
Each digestive organ in the human body has its own normal location. The correct location of the stomach and intestines is determined by nature itself.
Symptoms of transversoptosis
The disease is preceded by multiple pregnancies, sudden weight loss, and abnormal physical activity on the body. Transversoptosis rarely leads to the development of health complications - in 90% of cases it is detected in a timely manner. If the body’s condition is nevertheless aggravated by complications, the following occurs:
1. Insufficient local blood supply. 2. Descent of the transverse colon into the pelvic cavity. 3. Frequently recurring episodes of intestinal obstruction, progression of problems with the motor-evacuation function of the colon. 4. Insufficient urine outflow (due to compression of the bladder and ureters).
Transversoptosis of the colon is accompanied by excessive accumulation of gases, constipation, nausea, vomiting, and a feeling of insufficient bowel movements. Particularly noteworthy is the pain syndrome inside the abdominal cavity - a pressing or stabbing nature. Enlargement of the abdomen on the right with transversoptosis indicates involvement of the cecum in the pathology.
Symptoms are supplemented by headaches, irritability, and weakness. The intestine of a disturbed structure does not perform its function - absorption of nutrients. The skin becomes pale, anemia and hypovitaminosis increase.
Causes
- multiple pregnancy, when the abdominal organs are compressed and displaced by an overly enlarged uterus;
- sudden weight loss, when the size of the abdominal omentum quickly decreases and the intestines lose their usual support;
- heavy physical activity and especially repeated lifting of weights - a sharp rise in intra-abdominal pressure contributes to prolapse;
- scoliosis and other curvatures of the spine, in which the intestines are deprived of the possibility of normal attachment;
- abnormalities in the structure of the colon, in particular weakness of the ligamentous apparatus;
- chronic stress, which contributes to constant intestinal spasms;
- prolapse of other organs located in the abdominal cavity, especially the stomach;
- disturbances of hormonal homeostasis, under the influence of which tissue elasticity changes;
- surgical removal of large tumors, after which free space is formed in the abdominal cavity;
- old age, when the density of all tissues decreases;
- severe obesity.
One person may have several causes at the same time.
Loading …
Diagnosis of transveroptosis
The diagnosis of “transversoptosis” is made only on the basis of the results of a comprehensive instrumental examination of the digestive canal.
You will need a differential diagnosis of intestinal dysfunction with pathological conditions, which include:
• Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). • Intraintestinal infections (bacterial, viral origin). • Inflammatory processes (nonspecific ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease). • Diverticular disease. • Presence of intestinal parasites. • Oncological neoplasms of the digestive canal. • Common types of proctoanal disorders (perineal prolapse, isolated rectal ulcer).
Informative types - radiation diagnostic methods: irrigography, study of barium passage through the sections of the digestive tract, proctography in 2 projections.
Attention! It is important to carry out diagnostics comprehensively. It is not always possible to identify forms of colonic ptosis using irrigography alone. Isolated observation of the passage of suspension does not in all cases make it possible to trace the condition and structure of the intestine. Especially if the patient’s body is characterized by slow movement of contents through the digestive canal.
Sonography is aimed at visualizing the bends and segments of the loops of the colon. Significantly helps when examination is difficult during X-ray examinations. Pressure manometry within the cavity of the large intestine serves as an addition to methods for assessing its function. The invention of portable recorders has made long-term monitoring easier. Manometry allows you to confirm the presence of indications for surgery.
Algorithm for diagnostic studies for suspected transversoptosis
As can be seen from the above information, the disease in question does not have clinical symptoms characteristic of it. There is not a single pathognomonic symptom by which this pathology could be reliably determined. All of the above symptoms can occur with any disease of the gastrointestinal tract - intestinal obstruction, irritable bowel syndrome, helminthiasis and many other pathologies.
In this case, it will be fundamentally important to correctly establish the diagnosis for the reason that there is a violation of an anatomical and not a functional nature (as with the same irritable bowel syndrome). And any disease of this kind requires the most responsible approach, since it will never go away “on its own.”
Without a doubt, assessing the objective status and performing deep palpation of the abdomen will be important, but these examinations are not enough to make a diagnosis.
It will be necessary to conduct a number of instrumental and laboratory studies. It all starts with an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs - it will allow you to get a general picture and exclude the presence of cholecystitis, pancreatitis and some other pathologies that are in some way associated with functional disorders.
In any case, X-ray contrast examination (barium suspension is used) will be decisive for clarifying the diagnosis. The image will show a characteristic filling defect, usually in two places - this is the most characteristic radiological symptom for this pathology. In some cases (usually in pediatric practice), the radioisotope method is used along with fluoroscopy - this makes it possible to make the most accurate diagnosis, but the study is very expensive.
Treatment of transversoptosis
Conservative therapy is recommended for patients with satisfactory peristalsis. Colostasis, if Hirssprung's disease is excluded, is the basis for colectomy. Transverse colon resection is a last resort. An alarm signal is if patients constantly perform cleansing enemas to empty themselves.
Conservative treatment
Drug treatment of intestinal transversoptosis is reduced to eliminating the main disorders caused by changes in the structure of the digestive canal. To improve the general well-being of the patient and the function of his gastrointestinal tract, the following types of medications are used.
Drugs that dissolve feces.
In order to normalize the consistency of stool, experts recommend increasing water consumption. The absence of a positive result is an indication for the use of stool thinners.
• Use docusate sodium
. Saturates feces with water, promotes their dissolution and painless movement through the digestive tract. Prescribed orally 150 mg 2-3 times. per day, less often – 100 mg rectally 1 time per day.
• Vaseline oil
characterized by relaxing ability, improves the movement of feces. Use 0.5-1 tbsp. l. 2-3 times a day.
• Castor oil
. It is often used in gastroenterology and acts similarly to Vaseline.
Laxatives with osmotic ability. They contain ions that are not absorbed and create an osmotic intestinal gradient. This prevents constipation, softens stool, and improves propulsion. Reasons for normalization - water is retained inside the intestines. In patients suffering from renal or cardiac dysfunction, osmotic laxatives are contraindicated. In them, drugs of this group cause disturbances in electrolyte metabolism (a sharp imbalance of sodium, magnesium or phosphorus occurs).
• Lactulose
. The drug increases osmotic intestinal pressure while simultaneously reducing pH levels. This process promotes fluid retention, dissolution of chyme, and an increase in its quantity. But the most important thing is that peristalsis is activated. The effect occurs 6-8 hours after the medicine enters the body, so it is prescribed to be taken before bed. Lactulose is not addictive, which allows its use for a long period of time. The advantage of the drug is the absence of irritation of the mucous membrane of the digestive organs. The optimal dosage is 15-30 g.
• Polyethylene glycol (Forlax)
. It is a polyhydric alcohol. It does not break down and is not absorbed inside the intestine. The medicine is used before bedtime, 10-20 g, pre-dissolve it with water.
• Normaze
. As monotherapy or as part of basic medical prescriptions. Relieves coprostasis of predominantly mild degrees of development.
The listed drugs are supplemented with infusion therapy - in order to compensate for water and electrolyte losses and protein deficiency. Active vitamin therapy is also required, which is caused by a violation of the absorption function of the intestine. Especially if ceco-transversoptosis has occurred, which suggests a violation of the structure of the cecum.
Surgical intervention for transversoptosis
Surgical intervention is performed if conservative therapy is ineffective.
Indications for the operation:
1. Complaints of constant pain inside the abdominal cavity (unpleasant sensations have a stabbing nature). 2. Bloating, tension in the anterior abdominal wall, difficulty passing gases. 3. Hypotension of the transverse colon. 4. Constant constipation, eliminated through the use of laxatives.
At stage 1 of obstruction of the colon, surgical correction is indicated (provided there is severe pain). Stage 2 involves eliminating chronic obstruction using organ-preserving operations. At stage 3, exclusively resection methods of surgical intervention are used (right or left hemicolectomy, in some cases - subtotal colectomy).
Diet for transveroptosis
If the structure of the colon is disrupted, it is difficult for patients to do without the use of laxatives. The diet for transversoptosis is aimed at reducing the use of all means that cause defecation. Including cleansing enemas.
The doctor’s task is to teach the regulation of intestinal emptying through the use of natural motility stimulants - dietary fiber. To ensure the full functioning of the digestive canal, a daily intake of 30-45 g of this raw material is necessary. The indicated volume corresponds to an average of 1 kg of fruits and vegetables.
It is advisable to use wheat bran. They contain dietary fiber and absorb water. Without being broken down by enzymes of the small intestine, they increase the amount of feces and dilute them. Pour boiling water over the bran and leave for at least 1 hour. Then they can be added to first courses and fermented milk products. The volume of bran is determined individually, taking into account the degree of intestinal motility disorder. Daily dosage – 2-8 tbsp. spoons
Having abandoned the idea of treatment with folk remedies, it is better to supplement the diet with the Mucofalk
– the drug contains plantain seeds. Helps increase the volume of intestinal contents, stabilizes the evacuation capacity of the digestive canal, and prevents the development of coprostasis. Prescribe 1-2 sachets before bedtime, pre-brew with boiling water.
Conclusion
In identifying transversoptosis, an important role is played by diagnosis. It is strictly contraindicated to wait for the onset of decompensated colostasis. In 9 out of 10 cases, it ends with excision of the organ or part thereof. Given the likelihood of negative consequences, it is important for the patient to consult a doctor in a timely manner. The first signs (pain, constipation, nausea) indicate problems in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Therapy using non-traditional methods
Traditional medicine is also used in the treatment of the disease.
Important! Before using traditional methods, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
One of the effective recipes. 10 g of crushed buckthorn bark is poured into 0.3 liters of boiling water. After which the infusion is boiled for 15 minutes, cooled and filtered. An equal amount of water is added to the broth. Then take 100 ml after waking up and before going to bed.
This method allows you to normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and eliminate constipation.