Symptoms and degrees of dysbiosis
Dysbacteriosis of the vaginal microflora (gardnerellosis, bacterial vaginosis) is a gynecological disease, which increases the risk of infection with sexually transmitted diseases.
The development of pathological processes is due to an increase in the number of opportunistic anaerobic microorganisms. This reduces the number of lactobacilli. Polymicrobial vaginal syndrome is characterized by copious discharge from the genital tract with the absence of inflammatory changes in the vagina. Anaerobic pathogens produce substances (amines) that give the discharge an unpleasant odor. After sexual intercourse, the characteristic symptoms intensify.
The development of pathological processes is provoked by pathogenic microorganisms – gardnerella. They are present in the body of every woman, but they are activated and multiply only under the influence of certain factors. According to medical statistics, dysbiosis with a predominance of conditionally pathogenic anaerobic microorganisms is diagnosed in 20% of women aged 18 to 50 years.
Many diseases of the gastrointestinal tract lead to the development of vaginal dysbiosis. Activation of pathogenic microflora is observed. The walls of the rectum and vagina are in close contact. Therefore, intestinal dysbiosis in most cases disrupts the vaginal microflora.
| Name | Description |
| In the vagina |
|
| In the intestines |
|
In 50% of cases, bacterial vaginosis in women occurs without severe symptoms. Representatives of the fair sex turn to a gynecologist due to discomfort caused by copious vaginal discharge with an unpleasant smell of rotten fish.
Dysbiosis in some situations is accompanied by clinical signs that indicate the predominance of opportunistic anaerobic microorganisms:
- gray or white thick discharge, which becomes yellow-green in color as pathological processes progress;
- itching in the external genital area;
- pain in the perineum;
- disturbance of the urination process;
- heavy menstruation.
There is no hyperemia or swelling. During the examination, the gynecologist notes the presence of cervicitis, erosion, and scar formation.
| Name | Description |
| 1st degree (compensated bacterial vaginosis) | There is no beneficial microflora. High risk of contact of conditionally pathogenic microorganisms with the mucous membrane. |
| 2nd degree (subcompensated dysbacteriosis) | Pathological changes are characterized by a decrease in the number of beneficial bacteria (lactobacillus). There is an active increase in conditionally pathogenic microflora. |
| 3rd degree (decompensated vaginosis) | Pronounced signs of dysbiosis appear with a predominance of various pathogens. |
Symptoms of vaginal dysbiosis with a predominance of opportunistic microorganisms
A gynecologist will help determine the extent of damage to the reproductive system. The specialist will take into account all the woman’s complaints, prescribe additional diagnostics to determine the disease and select the most effective therapy.
During the period of bearing a baby, the negative influence of provoking factors increases. This is how vaginal dysbiosis occurs.
During pregnancy, a woman’s body undergoes a radical restructuring, against which the following symptoms appear:
- increased discharge;
- burning in the genital area;
- itching;
- painful sensations during sexual intercourse.
The treatment is carried out by a gynecologist. The main goal of therapy is to eliminate clinical symptoms and prepare the expectant mother for labor.
Measures to prevent dysbiosis will be the well-known and still relevant recommendations of doctors:
- active lifestyle;
- regular sex life;
- use of barrier contraception during new sexual intercourse;
- treatment of concomitant somatic diseases;
- personal hygiene;
- use antibiotics only as prescribed by a doctor;
- maintaining the body's immune system.
A normally functioning body is able to regulate its microflora, so first of all you need to take care of it.
conclusions
Intestinal dysbiosis in men is a common problem. It can only be dealt with in a comprehensive way after undergoing specific diagnostic measures. Treatment is prescribed only by a doctor. If there is no benefit to drinking prebiotics, an already serious condition may worsen. Self-medication is therefore unacceptable. In addition, the timeliness of starting therapy is important: the longer the patient waits, the more difficult it is to cope with the problem.
Dermatitis, dry skin, the appearance of cracks in the corners of the mouth or sudden allergic rashes to foods that have long been introduced into the diet are some of the most common complaints with which patients turn to a dermatologist. But no one can imagine that all these symptoms indicate the presence of intestinal dysbiosis, which has arisen as a result of long-term use of antibacterial agents or a carbohydrate diet, in which sweets and baked goods predominate.
When microflora is friendly with the body
The microflora of the genital organs, as well as the whole body, is populated literally in the first minutes after a person is born: first, microorganisms enter the skin and mucous membranes, and from there - into the genital organs.
In men, natural microorganisms are present in the initial segment of the urethra - at a distance of up to 5 cm from the external urethra. A large population of them is located in the area of the scaphoid fossa, since this area is less easily washed by the current of the outgoing stream of urine.
Frequent and rapid changes in the microflora occur with constant changes of sexual partners, since during new contacts new microorganisms penetrate into the urethra of men. With a monogamous lifestyle, the picture of the microbial landscape is usually more or less stable.
The main representatives of the microbiotic community of male genital organs are saprophytic and epidermal staphylococci. These are classic representatives of the coccal flora of the body, which feel quite comfortable in the neutral or slightly alkaline environment of the urethra. The frequency of their detection in a smear on the flora of healthy men ranges from 50 to 100%.
Somewhat less frequently (in about a quarter of cases) other representatives of the coccal flora are found - viridans streptococcus, fecal enterococcus, and rod-shaped bacteria: Escherichia coli, Proteus, bacteriodia, corynebacteria.
Even less common (in about five men out of a hundred) are Staphylococcus aureus, Neisseria spices and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In rare cases, you can find pathogenic microorganisms such as chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, as well as opportunistic Candida fungi as part of the normal male microflora.
Such a diverse picture of normal microbiocenosis makes the following question quite reasonable: what signs indicate that the microflora is currently disturbed and needs to be treated?
Representatives of normal microflora, even in the lower parts of the urethra, are found in fairly low concentrations. This is judged by the calculation of microorganisms during the examination of a stained smear and by bacteriological seeding of the contents of the walls of the urethra.
- when examining glasses stained using special methods, the laboratory technician normally sees up to 20 representatives of the coccal flora and single rods and fungi;
- during bacteriological culture, the degree of growth of microorganisms is determined; a normal smear is characterized by grades 1 and 2, ideally, bacterial colonies grow only in a liquid nutrient medium, there is no growth in a solid medium, their number is very scarce, does not exceed 20 colonies; This picture corresponds to normal flora or natural bacterial carriage.
If the numerical indicators of various representatives of the microbiocenosis increase significantly, dysbiosis of the genital organs occurs. Some experts consider the detection of even single representatives of sexually transmitted pathogenic microorganisms to be dysbiosis of the genital organs, and prescribe treatment if they are detected.
When examining a smear for flora, the laboratory technician determines the type and number of various cellular inclusions, and by their presence the presence of an inflammatory process is judged. Thus, normally the number of leukocytes does not exceed 5 cells in the field of view, there are no key cells, mucus, or neutrophils. If these indicators have changed, it means that the microflora has been disrupted, and microorganisms have provoked the development of an inflammatory reaction.
Thus, dysbiosis of the genital organs in men is a significant increase in the number of representatives of natural flora and pathogens, as well as the appearance of signs of an inflammatory reaction in a relatively normal microbial landscape.
How to decipher the results of a smear: identified diseases
The result of the bacteriological examination is standardized and issued in accordance with the identified etiologically significant microorganisms in a quantitative format, in CFU/tamp units, contains an antibiogram and a conclusion that helps the attending physician to better navigate the information provided.
Manufacturer of bacteriophages: Federal State Unitary Enterprise NPO Microgen, Ministry of Health of Russia, N. Novgorod, Perm, Ufa
Interpretation is carried out by a doctor taking into account clinical manifestations.
Attention! Sensitivity to the spectrum of antibiotics is carried out in case of detection of growth of pathogenic flora identified in any quantity and opportunistic flora in quantities of more than 104 CFU/tamp.
We draw your attention to the fact that the interpretation of research results, diagnosis, as well as the prescription of treatment, in accordance with Federal Law No. 323-FZ “On the fundamentals of protecting the health of citizens in the Russian Federation” dated November 21, 2011, must be carried out by a doctor of the appropriate specialization.
"["serv_cost"]={amp}gt; NULL ["cito_price"]={amp}gt; NULL ["parent"]={amp}gt; string(3) "542" [10]={amp}gt; string(1) "1" ["limit"]={amp}gt; NULL ["bmats"]={amp}gt; array(6) { [0]={amp}gt; array(3) { ["cito"]={amp}gt; string(1) "N" ["own_bmat"]={amp}gt; string(2) "12" ["name"]={amp}gt;
string(14) "Ejaculate" } [1]={amp}gt; array(3) { ["cito"]={amp}gt; string(1) "N" ["own_bmat"]={amp}gt; string(2) "12" ["name"]={amp}gt; string(54) “Prostate secretion” } [2]={amp}gt; array(3) { ["cito"]={amp}gt; string(1) "N" ["own_bmat"]={amp}gt;
string(2) "12" ["name"]={amp}gt; string(55) “Vaginal smear/discharge” } [3]={amp}gt; array(3) { ["cito"]={amp}gt; string(1) "N" ["own_bmat"]={amp}gt; string(2) "12" ["name"]={amp}gt; string(40) “Uterine cavity aspirate” } [4]={amp}gt;
array(3) { ["cito"]={amp}gt; string(1) "N" ["own_bmat"]={amp}gt; string(2) "12" ["name"]={amp}gt; string(49) “Smear/urethral discharge” } [5]={amp}gt; array(3) { ["cito"]={amp}gt; string(1) "N" ["own_bmat"]={amp}gt; string(2) "12" ["name"]={amp}gt; string(76) “Smear/discharge from the cervical canal” } } }
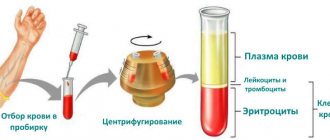
One of the most effective tests for identifying the picture of vaginal biocenosis is Femoflor screening. This technique is based on the polymerase chain reaction PCR technique. This is a molecular biology method that allows you to isolate the DNA of a particular virus, fungus or bacteria. As a result, the doctor receives a picture of the composition of microorganisms - pathogenic and beneficial.
From minor children under 16 years of age, material can only be collected for study under the supervision of an adult. Pregnant women with a gestational age of more than 22 weeks do not take a smear for bioflora due to the high likelihood of complications.
| Group | Name of microorganism | Normal indicators | Pathology indicators | What does it mean |
Facultative anaerobic | Lactobacillus spp (lactobacteria) | 80-95% of the total number of bacteria | Less than 80% indicates the displacement of lactic acid bacteria by pathogenic flora, mainly cocci. In combination with leukocytes, it indicates inflammation. | Responsible for the cleanliness of the vagina. They are present in large quantities in young girls, but tend to decrease with age. Determines the acidic environment of the vagina |
| enterobacterium spp (enterobacteria) | No more than 1% of the total number of microorganisms | More than 1% occurs due to incorrect selection of antibiotics | This anaerobic gram-negative bacterium is opportunistic. In its normal state it does no harm. When immunity decreases, it causes the development of infections. | |
| streptococcus spp (streptococci) | Any detection in a smear is not normal | Detection does not indicate infection | Is opportunistic microorganism, treated with antibiotics | |
| staphylococcus spp (staphylococci) | No more than 1% of the total number of microorganisms | Speaks of weakened immunity, eliminated with antiseptic drugs | Infected as a result of unprotected sexual intercourse or inaccurate hygiene procedures | |
| gardnerella vaginalis (gardnerella), Prevotella bivia, Porphyromonas spp | No more than 1% of the total number of microorganisms | More than 1% indicates infection with another disease | Normally it is not dangerous, but in combination with other infections. The most dangerous form is gardnerellosis, which leads to disastrous results. | |
Obligate anaerobic | Eubacterium (eubacteria) | 0,8% | Indicates bacterial vaginosis if all other indicators are normal | Gram-positive anaerobic bacterium, develops in women |
| Sneathia spp, Leptotrihia spp, Fusobacterium spp | 0,8% | Indicate bacterial vaginosis if all other indicators are normal | Gram-negative anaerobic rods | |
| Megasphaera spp, Lachnobacterium spp, Clostridium spp | 1% | Gram-positive rods cause bacterial vaginosis | ||
| Lachnobacterium spp, Clostridium spp | 1% | Gram-positive rods and cocci develop bacterial vaginosis | ||
| Peptostreptococcus spp. | Less than 1% | Promotes the development of genitourinary infections and abscesses | Anaerobic gram-positive rod. | |
| Atopobium vaginae | Up to 1% | Causes vaginosis | Anaerobic gram-positive rod. | |
mycoplasma | Mycoplasma | Up to 1% | Provokes the development of mycoplasmosis | A bacterium without a cell wall that causes STDs. |
| Ureaplasma | Up to 1% | Provokes the development of ureaplasmosis | A bacterium without a cell wall that causes STDs. | |
Yeast-like fungi | Candida spp. | Up to 1% | If the norm is exceeded, curdled discharge appears | Fungus that causes thrush. |
Based on the results of the analysis, the presence of pathogenic bacteria in the body can be determined. An increase in the content of one or more opportunistic microorganisms indicates an inflammatory process, the presence of a foreign body (fibroids, cysts), STDs (STIs), etc. The Femoflor analysis is carried out quickly and gives instant results. That. at one time the doctor can see the complete picture of a woman’s biocenosis.
Normocenosis
It is characterized by contamination in the range of 106-108 CFU/tamp. Most of the microflora is represented by lactobacilli. Opportunistic pathogenic microflora (OPM) is completely absent or observed in a low titer ({amp}lt;104 cfu/tamp.). When examining epithelial cells microscopically, cells of the superficial layer are found, less often of the intermediate layer. In some cases, “false key” cells are encountered.
Under aerobic conditions, the growth of microorganisms is not observed or a weak growth of UPM is observed. The titer of lactobacilli is reduced ({amp}lt; 104 cfu/tamp.). The microflora of the vagina contains gardnerella and anaerobes. There are “key cells”. Lactomorphotype bacteria are completely absent or detected in small quantities.
It is divided into candidal vaginitis, asymptomatic carriage of fungi and a combination of candidal vaginitis with bacterial vaginosis, depending on the number of UPM and fungi. With candidal vaginitis, the number of all microorganisms reaches 108 cfu/tamp., fungi - {amp}gt;104 cfu/tamp., lactobacilli - {amp}gt;106 cfu/tamp.
Characterized by a low content of lactobacilli and the absence of their growth. Fungi and “key cells” are present. The predominant morphotypes are Gardnerella. Epithelial cells are multilayered.
Asymptomatic carriage of fungi can be determined by an increase in the number of lactobacilli and fungi. The epithelium is represented by cells of the superficial layers. The leukocyte reaction is weakly expressed. Yeast-like fungi are not visualized or are isolated in the field of view.
The increase in the number of one of the UPM representatives is noticeably predominant. The number of lactobacilli decreases sharply or is equal to zero. The epithelium is represented by heterogeneous cells. The microflora is dominated by gram-positive cocci or polymorphic rods.
The culture shows an increase in the number of lactobacilli in a high titer ({amp}gt; 108 cfu/tamp.). Epithelial cells are presented in a disintegrated form. There is no growth of pathogenic microflora. Lactomorphotypes are visualized in large numbers.
Vaginal atrophy
There are no opportunistic microflora and lactobacilli. When studied in depth, the epithelium is represented by cells of the intermediate layers. This depends on the degree of atrophy. Microflora is practically absent or occurs in isolated cases. The number of leukocytes is 10-15 per field of view.
Characterized by a decrease in the number of lactobacilli, there is no growth of microflora. The epithelium is represented by superficial cells. There are no more than 10 leukocytes in the field of view, there are “key cells”. The amount of microflora is moderate. Anaerobes predominate.
Reasons for deviation from the norm
The normal interaction of microorganisms with each other and with the male body is a very fragile system that is destroyed at the slightest change in any component.
- The main cause of disruption of the microflora of the male genital organs is the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into them (the urethra), that is, a sexually transmitted infection, or a descending bacterial infection that penetrates the urethra from inflamed kidneys. Pathogens upset the balance. For example, Trichomonas vaginalis absorbs small representatives of the microbial flora.
- The cause of disruption of microbiocenosis can be a significant decrease in the body's immune defense. The immune system clearly controls the number of microbes present in the body and, if they begin to multiply rapidly, quickly brings their number back to normal, sending protective cells there. If for some reason the immune system is weakened (for example, during viral infections, hypothermia, injuries, when a person is being treated with chemicals), microorganisms get out of control and the microflora is disrupted.
- In the male genital organs, a relatively low temperature is constantly maintained, which does not allow the bacteria present in them to multiply intensively. If this condition for maintaining the balance of microflora is violated (for example, in the presence of an inflammatory process in the pelvis, which increases the local temperature), colonies of coccal flora and bacilli begin to grow rapidly.
- The secretion of the prostate gland has an antimicrobial effect - it contains complexes of substances that have a pronounced antibacterial effect. If prostate function is impaired (for example, hormonal deficiency) or if sexual activity is irregular, the urethra does not naturally cleanse itself of excess bacteria.
- Disruption of circulatory processes in the pelvis is important, since slowing down blood flow and stagnation causes a local increase in temperature, which has a beneficial effect on multiplying microorganisms. The causes of regional hemodynamic disorder can be venous insufficiency, alcohol intoxication (leading to vascular paralysis), nicotine intoxication (causing constant vasospasm), and a sedentary lifestyle.
- A disturbance in a man’s microflora can occur if for some reason the vaginal microflora of his sexual partner is disrupted.
https://youtu.be/KpkOKVs-Sh0
Identifying and eliminating the cause of disturbances in the microbiocenosis of the genital organs is the key to ensuring that the prescribed treatment will be effective.
Forecast
Timely and adequate therapy is a guarantee of getting rid of dysbiosis. Restoring microflora will speed up a man’s tendency to recover even in the presence of complications. If dysbiosis provokes additional pathological processes, and its symptoms are ignored by the patient, then the consequence may be irreversible deviations in the functioning of internal systems (chronic diseases of the genitourinary system, diseases of the digestive tract, immunodeficiency).
Video on the topic: Candidiasis (thrush) in men.
How and when does bacterial vaginosis develop?
Normal healthy microflora consists of 95% lactic acid bacteria (lactobacillus). Under normal reproduction conditions, they create a favorable environment, a protective barrier that does not allow pathogenic microorganisms to grow. Lactobacilli are responsible for the production of lactic acid, which is necessary for their vital activity and suppression of the growth of harmful bacteria.
Dysbiosis with a predominance of conditionally pathogenic anaerobic microorganisms develops as a result of an imbalance in the correct balance of microflora. Characteristic symptoms appear, including discharge and an unpleasant odor.
What pathogens are identified by smear analysis of biocenosis and what data is obtained from the analysis?
The result of a smear test for bioflora can be the identification of microorganisms such as:
- Lactobacilli are the main representatives of normal biocenosis;
- Opportunistic microorganisms: enterococci, streptococci, enterobacteria, hemophilia, corynebacteria, gram-negative bacilli, staphylococci, Candida fungi.
By analyzing a smear for bioflora, the doctor receives information:
- About the growth of pathogenic microflora or its absence.
- About the number of fungi, bacteria and lactobacilli;
- On the degree of sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics (at a quantity of {amp}gt;104 CFU/tamp.).
A study on the sensitivity of microflora to antibiotics is not carried out when the growth of concomitant and opportunistic flora is in low titer.
Fighting the disease
Treatment of genital dysbiosis should be based on identifying the main imbalances of the microflora. So, if a large number of fungi are detected in a smear, treatment should begin with adequate antifungal therapy, and if trichomonas are detected, dysbiosis should be treated with the drugs that best destroy these protozoa.
https://youtu.be/Dwa2Szzee3U
In order for the treatment of banal microflora, which has turned into pathogenic, to bring the most pronounced and lasting results, it is necessary to inoculate the contents of the urethra in order to isolate the most active representatives of the microbiocenosis and determine their sensitivity to antibacterial drugs. Without this, treatment is often ineffective, since microorganisms often show resistance to the most common antibiotics.
The reason for this is that a person could take these medications in order to treat other somatic diseases; often the course is not completed, but until the symptoms are eliminated, as a result of which the bacteria adapt to the antibacterial components entering the body, and their new generations acquire innate stability.
It is not necessary that dysbiosis can be eliminated only by the newest generations of antibiotics. Often, bacteriological culture reveals sensitivity to the simplest and even outdated drug.
Dysbacteriosis in a nursing mother
During pregnancy, a woman’s body undergoes a significant change in hormonal levels and a decrease in the body’s immunity. This is necessary for bearing the fetus, but has a significant impact on almost all organs and systems of the mother’s body. In addition, diet and lifestyle usually change. All these reasons may well provoke a pronounced disturbance of the vaginal microflora.
The use of antibiotics for one reason or another after childbirth is also a risk factor for the development of dysbiosis.
The manifestations of vaginal dysbiosis in a young mother are no different. In the same way, discharge may appear or intensify, and various types of discomfort arise - itching, pain, burning, dryness, etc.
Treatment of vaginal dysbiosis in women during breastfeeding has a number of features. Since during this period of time the use of most drugs that are used to treat the disease is strictly prohibited or undesirable, help is reduced to symptomatic treatment, that is, elimination of the manifestations of the disease.
Mikhail Sovetov, urologist-andrologist
Diagnostic features
Dysbiosis with a predominance of opportunistic anaerobic microorganisms requires a thorough medical examination. The disease must be differentiated, since many symptoms are similar to those of other pathologies.
| Name | Description |
| Microscopy | A smear is examined. |
| General blood and urine analysis | The results allow us to identify associated pathological processes. |
| Sowing for microflora | The examination helps determine the degree of development of vaginal dysbiosis. |
| Application of API systems | A diagnostic method that allows you to determine the type of causative agent of pathological processes. |
| Amino test | Study of secretions. The reaction to isonitrile is checked. We are talking about a substance that gives the discharge an unpleasant smell of rotten fish. It is released as a result of the vital activity of pathogens of vaginal dysbiosis (gardnerella). |
To examine the vaginal environment, pH measurements are performed. For bacterial vaginosis, it is alkaline. In a serious situation, a woman is prescribed an intravaginal ultrasound examination or ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
More often, the gynecologist recommends that two partners undergo examination in order to prevent a relapse of the disease and the latent course of pathological processes in the future.
Treatment options
Therapy is carried out comprehensively; it is important not only to eliminate the cause of the disease, but also to increase the body’s defenses. Medicines and folk remedies are used, and you should also adhere to proper nutrition. The success of therapy depends on the woman’s timely visit to the hospital.
Pharmacy drugs
The medications are selected by the gynecologist, since many medications provoke an adverse reaction.
| Group of drugs | Name | Application |
| Antibacterial drugs | "Trichopol", "Metrogil" | Eliminate pathogens. The therapeutic dosage is 0.75 g 3 times. per day. The medicine is taken after meals or during meals. The course of therapy lasts at least 7 days. |
| Antiseptics | "Hexicon", "Pimafucin" | The drugs eliminate infectious and inflammatory processes. Use tablets intravaginally or suppositories. A woman is prescribed 1 tablet. 1-2 r. per day for 7-10 days. |
| Probiotics | "Lactobacterin", "Acilacta" | The drugs stimulate the natural growth of vaginal microflora. Reduce the likelihood of relapse of dysbacteriosis. The medicine is prescribed to a woman 1 suppository 1-2 r. per day for 10 days. In some situations, treatment of vaginal dysbiosis lasts 3-4 weeks. |
| Immunomodulators | "Polyoxidonium", "Immunal" | The drugs strengthen the body's defenses. They help him fight the pathological process and bacteria on his own. Vaginal suppositories are used according to a specific scheme. The first 3 days, 1 suppository, then every other day. One course – 10 candles. |
During drug treatment, a woman is recommended to adhere to protected sexual intercourse. Additionally, to support immunity, the patient is prescribed a vitamin course to replenish minerals and vitamins (Vitrum, Biomax).
Nutrition
Dysbiosis with a predominance of opportunistic anaerobic microorganisms requires not only complex treatment, but also dietary nutrition. Junk food increases blood glucose levels, which creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria.
| Recommended Products | Prohibited foods |
|
|
Excess weight negatively affects the vaginal mucosa because it disrupts hormonal levels. It is recommended for women to follow a diet not only during treatment for vaginal dysbiosis, but also after treatment for some time in order to prevent a relapse of the disease.
Folk remedies
Non-traditional methods can be used to combat dysbiosis, but after consultation with a doctor. Many components of the recipes of witch doctors and healers provoke an allergic reaction.
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Soothing baths | Mix walnut leaves, oat straw, juniper berries, chamomile, oak bark. Put on fire, boil for 30-40 minutes. Cool and strain. | Add the resulting broth to a previously prepared bath. Herbs have antimicrobial, antiviral and antifungal effects. |
| Douching | Pour 1 tbsp water. bird cherry fruit. Place on medium heat, heat for 20-25 minutes. Cool the resulting infusion and strain well. | The product is used to rinse the vagina. |
| Herbal decoction | Mix sweet clover, marshmallow root, pine and birch buds, dried grass, nettle leaves, clover flowers, coltsfoot. Add cucumber, calendula, bearberry, eucalyptus, mint, St. John's wort, bergenia and leuzea. Pour hot water over the components. Leave and strain. | It is recommended to take 100 ml of the decoction 20-30 minutes before meals, 3-4 r. per day. |
| Vitamin tea | Grind quince (1 pc.), 2 tbsp. cherries, lemon (1 pc.), 10 cloves of garlic, 2 apples (Antonovka variety). Add 9 tbsp. hot water. Leave the resulting mixture overnight. Strain and take according to the scheme. | The medicine is taken 0.5 tbsp. 4 rub. per day. |
Treatment is carried out comprehensively. It is impossible to get rid of dysbiosis with a predominance of opportunistic microflora using alternative medicine recipes alone. Competently such therapy will allow, under the supervision of a gynecologist, to eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of dysbiosis and discomfort, and also restore the beneficial microflora of the vagina.
Complications
The danger of the disease lies in its frequent asymptomatic course. Vaginal dysbiosis in women bearing a child, without treatment, provokes termination of pregnancy or premature birth. Dysbiosis with a predominance of opportunistic anaerobic microorganisms disrupts the protective mechanism of the vaginal mucosa.
| Name | Description |
| Bacterial vaginitis | An inflammatory process that affects the mucous membrane in the vaginal area. The pathology is accompanied by more pronounced clinical signs. |
| Infectious infection | The risk of infection with sexually transmitted diseases (gonorrhea, chlamydia, inflammatory pathologies of the pelvic organs) increases. |
| Infertility | The progressive inflammatory process spreads to the uterus, tubes and ovaries. The menstrual cycle is disrupted and the likelihood of infertility increases. If the uterine wall is inflamed, the egg will not be able to attach to it. |
| Neoplasia of epithelial tissue of the cervical canal | The disease is also called cervical dysplasia and is a precancerous condition. |
The spread of infection causes not only serious diseases (endometritis, cervicitis, adnexitis, peritonitis). Pathogenic anaerobic microorganisms infect the urethra, which leads to urethritis, cystitis, and pyelonephritis. Complications due to vaginal dysbiosis also include peritonitis, intestinal diseases, and cervical erosion.
Prevention
The main methods of preventing vaginal dysbiosis are aimed at eliminating the causes that contribute to the imbalance of microflora. For targeted immunoprophylaxis, the SolkoTrichovak vaccine is used, consisting of special strains of lactobacilli.
Particular attention should be paid to the hygiene of the genital organs: washing with soap has a negative effect on the microflora. Douching, which simply washes away the delicate lactoflora of the vagina, is also unacceptable. During the acute period of the disease, you can use special gels for intimate hygiene, but in the future you should only wash with water.
The state of the intestinal microflora is of great importance. Therefore, women prone to relapses of dysbiotic processes should visit a gastroenterologist and optimize their diet.
If you notice signs of vaginal dysbiosis, this is a reason to visit a doctor. Modern medicine can easily cope with such problems. This should also force you to pay attention to the state of your immune system, diet or hygiene nuances. After proper treatment, unpleasant symptoms will no longer bother you, and you will feel fresh all day long.
Quite often you can hear from representatives of the fair sex that all modern women's diseases were specially invented by gynecologists and manufacturers of medications. In fact, you shouldn't trust these speculations. The appalling state of the environment, poor-quality and unbalanced nutrition, frequent changes of sexual partners are what lead to the appearance and spread of pathogenic bacteria. That is why every modern woman should be more attentive to her body and respond to all the changes occurring in it.
Vaginal dysbiosis is a disease that in most cases occurs without pronounced symptoms, which is its insidiousness. But if you are regularly examined by a specialist and follow all personal hygiene measures, you will probably notice an increase in vaginal discharge and the appearance of an extremely unpleasant odor.
Be attentive to your health, trust only qualified specialists, only in this case you will not have to fight an advanced infection in the future, resorting to potent drugs with many side effects.