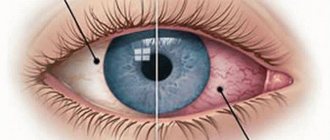
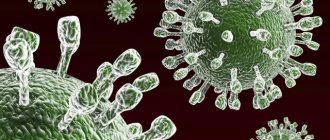
One of the benign diseases is molluscum contagiosum. All people of all ages are susceptible to this disease. There is a high risk of infection for those people who often come into contact with other people's skin, such as massage therapists or doctors. The number of rashes may increase over time, as the person himself spreads it over the skin. Diagnosis of the disease is simple; mollusks can be recognized without any procedures. Treatment is not always carried out; there are cases that the disease goes away on its own within six months.
You can also use traditional medicine methods. To do this, it is advisable to notice the disease in time so that the result pleases you. When choosing this or another treatment method, it is better to consult a doctor.
How can you get infected?
Molluscum contagiosum is most often transmitted through contact and household contact; it can lead to outbreaks in children's groups and damage to family members. The virus is transmitted through direct contact with a sick person, as well as through contaminated household items, clothing, water in a pool or natural reservoirs, and toys.
In the environment, the virus is quite stable and can persist in the dust of residential premises and gyms, infecting more and more people. In adults, the disease can occur after tattooing if the pathogen remains on the instruments used by the artist.
Penetration of the pathogen occurs through microdamage to the skin. Therefore, the risk of infection increases in the presence of dermatological diseases with itching, dryness or weeping of the skin, and disruption of the integrity of the epidermis. In women, the molluscum contagiosum virus often penetrates through the mucous membrane of the genital organs and the skin of the perineum. Moreover, to transmit the infection from a partner, sexual intercourse itself is not required; only contact with the affected skin areas is necessary. Therefore, although infection with molluscum contagiosum in adults is often associated with sexual contact, it is incorrect to classify it as a true STD.
Causes
The cause of molluscum contagiosum is the smallpox virus Molluscipoxvirus.
When it enters the cells of the epidermis, the DNA of the virus begins to actively multiply, after which the activity of T-lymphocytes is blocked. That is why during infection there is no immune activity, which creates favorable conditions for infection. Expert opinion Sakania Luiza Ruslanovna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist
Ask a Question
Molluscum contagiosum can be contracted through direct contact with a sick person. Infection through contaminated objects is also possible. Adults most often become infected with molluscum contagiosum through sexual contact.
In this case, infection occurs due to direct contact with the skin of an infected partner, and not through coitus. That is why some medical organizations do not classify molluscum contagiosum as a sexually transmitted disease.
When infected during sexual intercourse, the groin area, perineum, lower abdomen, inner thighs and external genitalia are most often affected. Despite the highly contagious nature of the pathogen, cases of infection are often isolated, although in kindergartens the disease can be endemic.
It is often difficult to determine the source of infection, since the incubation period for molluscum contagiosum ranges from several weeks to several months.
Pathogen
The virus affects only humans, is not transmitted by animals and is close to smallpox viruses. There are 4 types of molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV-1, MCV-2, MCV-3, MCV-4). Of these, MCV-1 is the most common, while MCV-2 usually appears in adults and is often sexually transmitted. Can also be transmitted through water (eg swimming pool). Inside the formation there is a liquid through which it is transported and multiplies.
Molluscum contagiosum is caused by a virus (molluscum contagiosum virus), which is part of the poxvirus group. This virus spreads from person to person through direct contact and is most common in children. In addition, it can be infected through sexual intercourse; people with impaired immune system functioning are most susceptible to the virus. Molluscum contagiosum can spread by scratching or rubbing the affected skin.
Skin lesions of molluscum contagiosum are sometimes confused with lesions caused by the acrochordona virus.
Symptoms of the disease
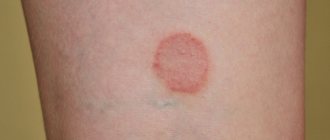
The only characteristic symptom of molluscum contagiosum is a rash on the skin (pink or lighter in color). The contents of pimples can give them the appearance of pearls. And, unlike herpes or chickenpox, they practically do not bother the child (there is no itching or pain).
From the appearance to the maturation of the lesion, an average of 2-4 weeks passes. If a bacterial infection occurs, an inflammatory process begins, characterized by mild itching.
In addition to the common type of rash (small semicircular papules), there are several atypical forms. They look like this:
- Giant - papules reach more than 2 cm in diameter (due to the merging of several lesions into one). This form occurs in children with weakened immune systems.
- Cystic - the nodules may be increased in size, but without the characteristic depression in the center.
- Horny - pimples have a whitish, slightly rough surface. This form of molluscum contagiosum is diagnosed in children with concomitant skin diseases or excessive dryness of the epidermis.
- Convex - the rash does not go away for a long time and after healing leaves noticeable scars on the skin. This form of the disease develops as a result of the addition of a secondary infection to the ulcers remaining after the opening of the papules.
To confirm the diagnosis, you must see a doctor and undergo an examination.
Molluscum contagiosum during pregnancy
During pregnancy, against the background of a natural decrease in immunity, activation of an existing infection or a fresh infection with molluscum contagiosum may occur. The clinical picture has no peculiarities. The molluscum contagiosum virus does not pose a danger to the fetus, but during childbirth and subsequent contact with the mother's skin, the child can become infected.
Treatment must be carried out immediately after detection of the disease, taking into account contraindications for some procedures. Shortly before birth, a repeat examination is carried out even in the absence of complaints. This is necessary to identify possible recurrent rashes on the genitals and areas of the skin that are inaccessible for self-examination.
Prognosis and prevention
Self-healing is possible, but with the spontaneous disappearance of external manifestations, the transition of the virus to a low-active stage and its reactivation with a decrease in immunity cannot be ruled out. Complex treatment allows you to get rid of the disease, but does not prevent re-infection, because immunity is not developed during this infection.
After proper removal of the nodules or their spontaneous regression, the skin becomes clear. If the deep dermal layers are not damaged, scars will not form. But with the development of molluscum contagiosum against the background of atopic dermatitis, eczema and some other dermatological diseases, healing can occur with scarring.
For prevention, it is necessary to eliminate the main cause of molluscum contagiosum – contact with the virus. To do this, you must follow the rules of personal hygiene, do not use other people’s washcloths and towels, and wear shoes in public baths and swimming pools. If a child becomes infected, his toys must be sanitized daily, bedding and clothing must be washed daily, and the bathtub and sink must be disinfected after use by the child.
Molluscum contagiosum is an unpleasant but not dangerous disease. Before treating this infection, it is necessary to consult a doctor to confirm the diagnosis and select therapy.
Symptoms and photos
Most often, papules, which are direct signs of molluscum contagiosum (see photo), are localized in children on the face, torso and limbs, in adults - in the genital area, on the stomach and inner thighs.
Most often papules:
- small size (from 2 to 5 mm in diameter);
- do not cause pain, but are sometimes accompanied by itching;
- have a dimple in the center;
- have a core of white, waxy material;
- At first they are dense, dome-shaped, flesh-colored, and become softer over time.
Molluscum contagiosum usually goes away spontaneously in people with normal immune systems after several months or years. In people with AIDS or other diseases that affect the immune system, damage associated with exposure to molluscum contagiosum may be more extensive.
Symptoms
The resulting nodules are hemispherical in shape, with a small depression created in the center.
As a rule, nodules form separately from others, but it is possible that, as a result of their active development, they can unite with others, forming huge foci of infection. Expert opinion
Sakania Luiza Ruslanovna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist
Ask a Question
These formations, most often, do not cause any discomfort for humans, but sometimes they can cause itching. The shade of the nodules is comparable to the color of healthy skin, and sometimes it turns light pink.
If you press on these formations, a white and thick liquid will begin to flow out of them. Having examined these secretions using a microscope, it will be possible to detect vigorous activity of cells that look very much like mollusks. This is how this disease got its name.
With further infection of the formed nodules, they will gradually begin to develop new areas of the skin. When a bacterial infection is added to them, an inflammatory process will begin in these formations.
Diagnostics
In the classic form, the diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum is easy to make. The following factors are taken into account: childhood age, the presence of children with molluscum in the team, multiple spherical formations on the skin with an umbilical depression.
Difficulties in diagnosis rarely arise with atypical forms. But even with atypical appearances, dermatoscopy clearly shows umbilical depressions in the center of the molluscan papules.
Differential diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum is carried out with the following diseases:
- pyoderma (ulcers on the skin),
- chickenpox (chickenpox),
- filamentous papillomas (read a detailed article about filamentous papillomas),
- vulgar warts (read about vulgar warts),
- genital warts on the genitals (read about genital warts),
- milia.
In difficult cases, the doctor resorts to squeezing the papule with tweezers. If crumbly masses are squeezed out of the papule, with a 99% probability it is molluscum contagiosum.
In even rarer cases, they resort to diagnosis under a microscope. To do this, the crumb-like masses are sent to the laboratory, where a picture corresponding to the given disease is determined under a microscope. In this case, eosinophilic inclusions are found in the cytoplasm of the cells.
Signs and symptoms of molluscum contagiosum in adults
The incubation period of the disease varies from 2 weeks to 6 months. Rashes in the form of nodules occur spontaneously.
- The rash in adults is localized on the skin of the torso, face (often on the eyelids), neck, armpits, and sometimes in places of trauma. When the infection spreads through sexual contact, a rash appears on the skin of the pubis, abdomen, genitals, inner thighs and around the anus. The appearance of nodules on the scalp, tongue, lips and buccal mucosa has been recorded. The appearance of a rash on the soles and feet is an atypical localization. In children, nodules are localized on the face and torso.
- The number of rash elements varies - from single to multiple (in people with immunodeficiency). In HIV-infected patients, the rash is profuse (hundreds of nodules).
- The nodules are located separately, randomly, rarely merge into large conglomerates, which is called “giant molluscum contagiosum.”
- The color of the papules is pink, pink-orange, yellow, pearly white or the color of normal skin. They are shiny and translucent. They have a round, hemispherical shape with a depression in the center in the form of a navel, filled with horny masses.
- Most of the nodules have a depression in the center filled with horny masses, which is clearly visible when magnified using a manual lens, dermatoscope or otoscope.
- When pressed from the sides, a dense, cheesy-looking keratin mass emerges from the nodule, containing Lipschütz’s mollusc bodies, with a huge number of virions. In atypical or advanced cases, this sign is absent.
At the beginning of the disease, tiny papules (1 - 2 mm) appear. Over time, they increase and reach 2 - 4 mm, in some cases - 5 - 10 mm. The nodules reach their maximum size within 1 to 3 months.
Forms of molluscum contagiosum:
- Agminant. When papules merge, giant conglomerates (“giant molluscum contagiosum”) are formed, reaching a diameter of 2 cm.
- Horny. There is keratinization of the rash elements.
- Generalized. It is noted when the rash disseminates.
Within 1.5 - 3 months, under the influence of the body's immune system, the nodules disappear even without treatment, but if the infection spreads to other areas, the rash appears again and again. The total duration of the disease is 6 - 9 months. In some cases, molluscum contagiosum lasts up to 3 - 4 years.
Rice. 7. The photo shows elements of a rash during the disease.
Could there be complications?
The development of molluscum contagiosum in the normal course does not lead to the formation of any problems over time, and often the elements can gradually disappear from the skin without leaving any traces on it. This can happen even without treatment for about three to four years.
- Some treatments may cause scarring on the skin.
- Sometimes the infection can reactivate, in which case a larger area of skin is affected.
- In the presence of severely weakened immunity, the development of molluscum contagiosum can take a generalized and pronounced form.
When the elements appear abundantly on the face and body, or become large in size and can change in appearance, treatment becomes difficult. In such cases, active therapy with drugs, both local and to stimulate systemic immunity, is indicated.
What should not be done if it is present on the skin?
- squeezing out shellfish yourself with your hands, nails or tweezers - this can only spread the infection throughout the body
- cauterization of shellfish with celandine or garlic - this can lead to screening out of the shellfish and injury, damage to the skin
- combing, scraping shellfish
Any manipulation of the rash should be carried out exclusively by a doctor; he will select the most effective therapy and methods for its implementation.
Treatment of molluscum contagiosum
Currently, molluscum contagiosum in women, unless the nodules are localized on the eyelids or in the genital area, is recommended not to be treated at all, since after 3 to 18 months the immune system will be able to suppress the activity of the orthopoxvirus, and all formations will disappear on their own, leaving no traces on the skin any traces (scars, scars, etc.).
The fact is that immunity to the molluscum contagiosum virus is developed, but this happens slowly, so the body needs not a week to heal itself from the infection, as in the case of ARVI, but several months or even up to 2 - 5 years. And if you remove the nodules of molluscum contagiosum before they disappear on their own, then, firstly, you can leave scars on the skin, and secondly, this increases the risk of their reappearance, and in even larger quantities, since the virus is still active. Therefore, given that self-healing always occurs, and it is only a matter of time, doctors recommend not treating molluscum contagiosum by removing the nodules, but simply waiting a little until they disappear on their own.
The only situations when it is still recommended to remove nodules of molluscum contagiosum are their localization on the genitals or eyelids, as well as severe discomfort caused by the formation to a person. In other cases, it is better to leave the nodules and wait for them to disappear on their own after the activity of the virus is suppressed by the immune system.
Where does molluscum come from in children?
Infection with molluscum contagiosum in children occurs through contact with sick children or adults, or through the belongings of these patients, common objects. So, you can get sick:
- upon contact with a child who has mollusks on their skin (kindergarten group, less often in a camp or school)
- when sleeping on the bedding of an infected person
- when playing with an infected person's toys
- when using a shared towel or washcloth
- when swimming in pools or open water where sick children have swum
- when playing in the sandbox where sick children played
If there are viral rashes, children scratch or scratch them, spreading the mollusk throughout their body and infecting surrounding objects that they handle. Viruses are relatively persistent and can remain on objects for some time.
For adult women and men, these ways are less relevant; their main way to “pick up” a mollusk will be through sexual intercourse. And the localization of their rashes will be appropriate, in intimate areas.
Removal of molluscum contagiosum
If a person wants to remove the nodules, then this is done. Moreover, the reason for such a desire, as a rule, is aesthetic considerations. For the removal of molluscum contagiosum nodules, the following surgical methods have been officially approved by the Ministries of Health of the CIS countries:
- Cryodestruction (destruction of nodules with liquid nitrogen);
- Curettage (scraping out nodules with a curette or Volkmann spoon);
- Laser destruction (destruction of nodules with CO2 laser);
- Electrocoagulation (destruction of nodules by electric current - “cauterization”);
- Husking (removing the core of nodules with thin tweezers).
In practice, in addition to these officially approved methods for removing molluscum contagiosum nodules, other methods are used. These methods involve exposing the nodules of molluscum contagiosum to various chemicals in ointments and solutions that can destroy the structure of the formations. Thus, currently, ointments and solutions containing tretinoin, cantharidin, trichloroacetic acid, salicylic acid, imiquimod, podophyllotoxin, chlorophyllipt, fluorouracil, oxoline, benzoyl peroxide, as well as interferons alpha-2a and alpha 2b are used to remove nodules.
Such chemical methods for removing shellfish cannot be called traditional methods, since they involve the use of medications, as a result of which they are considered to be unofficial, practice-tested methods, but not approved by the Ministries of Health. Since these methods, according to reviews from doctors and patients, are quite effective and less traumatic compared to surgical methods for removing molluscum contagiosum nodules, we will also consider them in the subsection below.
How to get rid of molluscum contagiosum
There are several radical methods to effectively get rid of molluscum contagiosum. They involve mechanical removal of foci of infection. Previously, removal of molluscum contagiosum with tweezers or a scalpel was actively used, but over time, more gentle techniques appeared, which pushed aside these outdated techniques.
Removing tumors allows you to forget about the presence of infection forever. But the procedure must be carried out by a competent, qualified and attentive specialist. If you miss even one element, then a new spread of viral invasion is possible.
Cryodestruction
Cryodestruction of cutaneous mollusk elements involves the use of liquid nitrogen. The procedure is carried out for formations of any localization, and the manipulation itself is painless due to the cooling effect of the nitrogen solution. After the procedure, there may be a slight burning sensation and redness of the treated area. Do not wet the area for three hours after nitrogen treatment. The pathological element dries out within a few days and disappears, leaving no scar changes. In its place, a small wound surface forms, which heals in a couple of days.
Surgical excision
At the moment it is considered a rather outdated technique. It is used in hard-to-reach places and for large lesions. Surgical excision of molluscum contagiosum, its price and cosmetic effect are somewhat inferior to other methods. There is always the possibility of incomplete excision of the tumor or contamination of nearby tissues. Therefore, molluscum contagiosum may reappear after its removal. Moreover, excision of large areas leads to the appearance of scars and cosmetic defects.
Electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation of clusters of molluscum contagiosum is carried out with a special device.
Electrocoagulation of clusters of molluscum contagiosum is carried out with a special device - an electrocoagulator. This is a non-contact manipulation that allows you to remove multiple skin lesions in a short time. If the pain threshold is low, electric cauterization can be performed after irrigating the skin with local anesthetics. The neoplasm is exposed to direct current for several seconds, and the element dries out. It leaves a crust that falls off on its own after 3-4 days. Electrocoagulation has a good cosmetic and therapeutic effect.
Folk remedies
The most effective means for treating the disease in question from the category of “traditional medicine”:
- Prepare a concentrated solution of potassium permanganate - it should be dark purple. A cotton swab is moistened in it and applied (cauterized) to the papule. Please note that after using potassium permanganate, burns may form on the skin - be extremely careful, treat the papule specifically, acting on it point by point.
- The string grass is crushed and a decoction is made - 300 ml of water per 100 grams of raw material, cook for 3 minutes. Then the broth should brew for 60-90 minutes. Only after this can you strain it through a strainer or several layers of gauze. A decoction of the string is used as a lotion and for wiping off papules. There are no restrictions on the number of procedures per day.
- Grind a few cloves of garlic (in a blender or on a fine grater), add 30-50 grams of butter (soft) to them and mix everything thoroughly until a paste-like mixture is obtained. The product must be applied to the affected areas of the skin 2 times a day. Please note that garlic can cause burning and even irritation on healthy areas of the skin, so try to use this product with extreme caution.
You can also use some plants that will help get rid of papules in a short time. For example, the juice from bird cherry leaves copes with this task perfectly (it is squeezed out and stored in a cool, dark place) - a cotton pad is moistened in it and the skin is treated after removing the nodules. Moreover, this remedy can be used for a long period, until all wounds are completely healed.
Treatment in children and adults
In children and most adults, without treatment, the symptoms of molluscum contagiosum go away on their own as soon as antiviral immunity is formed. The term is 4-6 months, sometimes 1-2 years.
Molluscs on the body can only be treated for medical reasons: trauma, inflammation. Cosmetic indications are solely at the request of the patient.
Directions for treatment of molluscum contagiosum:
1) Removal of formations
2) Local treatment
3) General treatment
4) Treatment of complications (inflammation, allergies, skin ulcerations)
Removal of cutaneous molluscum
According to reviews of most dermatologists, removal of skin rashes is so far the most effective method of treating cutaneous molluscum.
1) Removal with tweezers or a surgical spoon (curette)
- First, the doctor performs local anesthesia of the skin with Emla cream or another surface anesthetic.
- The doctor squeezes the jaws of the tweezers and squeezes out the contents of the papule (as in the video below). If necessary, the resulting small cavity can also be scraped out with tweezers or peeled out with a curette (a sharp Volkmann spoon). If the papules are small, then no curettage will be needed.
- After this, the doctor carefully removes the curdled masses and cauterizes the resulting wound with 3% hydrogen peroxide and tincture of iodine.
- Some patients at home perform an independent opening of the molluscum papules with a needle, as in this video. We remind you: it is not recommended to do this yourself. By wiping the skin with a napkin, thereby spreading and rubbing viruses into neighboring areas of the skin, you only spread the infection even further.
- After removing the mollusk, the wound should be treated with iodine or brilliant green once a day for another 3 days.
- With proper removal of the elements of molluscum contagiosum, no scars remain on the skin.
2) Electrocoagulation
The doctor cauterizes the papule with an electrocoagulator (electric knife). Subsequently, after such treatment, scars may remain.
3) Liquid nitrogen (cryodestruction) - read more
The doctor burns the papule with liquid nitrogen. Cells with the virus freeze and die. When cryodestruction is carried out correctly, there are no scars left on the skin. But the procedure can be painful.
4) Laser - read about laser removal
The doctor evaporates the mollusk papule with a laser beam. There are also no scars left.
Local treatment
Antiviral creams and ointments are used:
- Viferon-ointment,
- 3% oxolinic ointment,
- 1% gel viru-merz serol,
- Infagel,
- Acyclovir ointment,
- Virolex ointment,
- Gripferon spray.
General treatment
Stimulation of general immunity and antiviral drugs.
- isoprinosine tablets (details about isoprinosine)
- Viferon in candles,
- polyoxidonium in candles,
- anaferon for children in tablets,
- other interferon drugs.
Treatment of complications
A complex of medications is used to relieve complications:
- antibiotic ointments - to treat bacterial inflammation,
- antihistamines to reduce allergic skin reactions.
Traditional methods at home
Folk remedies against molluscum contagiosum are ineffective. Therefore, they cannot be recommended by a dermatologist for the treatment of this disease in either children or adults.
Remember: the cause of molluscum is a virus, the predisposing factor is decreased immunity. Therefore, among traditional methods, you should use general immunity-strengthening techniques and antiviral agents.
1) Increasing immunity using natural methods. Read a detailed article about strengthening the immune system.
2) Antiviral plants.
- Garlic. Crush a clove of garlic in a garlic press and place on the papules for a few minutes. There will be a slight burning sensation. Apply 3-4 times a day also during the entire period of the rash. You don’t have to apply it, but simply lubricate the skin.
- Lubricating papules with a solution of potassium permanganate, fucorcin, an alcohol solution of iodine or brilliant green. This is an ineffective method, since such antiseptics have practically no effect on the molluscum contagiosum virus. The only use of such solutions is to lubricate wounds at home after removing mollusks with tweezers or a curette.
- Celandine. Celandine juice is poisonous and has antiviral and antitumor effects. Clams are lubricated with celandine juice 3-4 times a day throughout the entire period of skin rashes.
- Lubricating papules with juice from bird cherry leaves, infusion of string, calendula - these folk remedies have a very weak effect.
- Super celandine, molustin and molutrex. A lotion called Molyustin is sold in Russia. The drug is not a medicine. This is a mixture of plant extracts + potassium lye. Causes a chemical burn to the skin, as a result of which the mollusk papules die. The effectiveness against molluscum contagiosum is low. MOLUTREX is a French analogue of molustin. In fact, MOLUTREX is pure potassium hydroxide, without additives, that is, caustic alkali, the French analogue of Supercleaner. Causes chemical burns to the skin. Does not work on viruses. Super celandine is a completely different drug than the herb celandine. This is a set of alkalis. Leads to a chemical burn of the skin, as a result of which the mollusk papules die off. Read more about super cleanser. When treating at home with supercelandine, molutrex and molustin, you should be extremely careful not to cause deep skin burns and subsequent scar formation. You cannot use cauterizing drugs to remove molluscs on the face, labia in women and penis in men.
Prevention
The main thing that should be applied constantly is the prevention of molluscum contagiosum.
- strengthening the immune system using natural methods,
- You can’t take a hot bath - you can only shower,
- You can’t rub your body with a washcloth - only soap yourself with your hands,
- You can’t rub your body with a towel - just blot it,
- You should not open skin papules yourself, so as not to spread the infection to other areas of the skin,
- a patient with molluscs on the body should be provided with separate personal hygiene items and bedding. Wash his clothes separately. Steam the laundry thoroughly with an iron,
- Always use only personal hygiene items!
Prevention
Preventive actions:
- examination of children in schools and kindergartens in order to prevent the spread of molluscum contagiosum;
- early detection of the disease;
- isolation of the patient from the team during treatment;
- regular wet cleaning of premises to eliminate dust containing viral particles;
- examination of co-residents and team members for the presence of papules;
- daily change of underwear;
- strictly personal use of personal hygiene items;
- selectivity when choosing sexual partners;
- mandatory shower after visiting the bathhouse, sauna, swimming in the pool and after sexual intercourse;
- patients are contraindicated from visiting massage rooms, swimming pools, saunas for the period of treatment;
- It is forbidden to comb papules; after accidental injury, treat the damage with an antiseptic;
- if papules are localized on the face, do not use harsh scrubs; men should be careful when shaving;
- isolation of the patient and the objects he uses within the family;
- strengthening the immune system (hardening, moderate physical activity, walking in the fresh air, swimming).
In the vast majority of cases, with molluscum contagiosum, the prognosis is favorable. The disease has virtually no complications and is easy to treat. The prognosis is significantly aggravated by the state of immunodeficiency, against which generalized forms of the disease develop with large formations that cannot be treated.
Treatment methods
Medicines (mainly for external use) and folk remedies are used as therapy. In severe cases (for example, with extensive spread of molluscum contagiosum affecting large areas of skin), doctors resort to surgery, which involves laser removal of papules, cryotherapy and diathermocoagulation. Each of these methods is selected individually, depending on the baby’s health condition and the severity of the disease.
Medicines, creams, ointments
The basis of therapy is antiviral drugs, since bacterial agents, although effective, cannot cope with the disease. And, if in mild forms of viral dermatitis patients are prescribed topical agents, in more severe cases they cannot do without pharmaceutical drugs for oral administration.
Thus, drugs for internal use (in the form of tablets, injections) include:
- Interferon has an antiviral, antitumor, immunomodulatory effect on the body. In cells not infected with the virus, protective mechanisms are formed that prevent the spread of pathogenic microorganisms. The drug is available in ampoules of 10 pieces. Average price: 90 rubles.
- Altevir has a powerful antiviral and immunomodulatory effect and is used in complex therapy. The product is available only in ampoules and is used for intravenous and intramuscular injections. Price: 1200 rubles (pack contains 5 ampoules of 1 ml each).
- Isoprinosine is an immunomodulator with an antiviral effect that reduces the symptoms of a viral infection and promotes recovery of the body. The drug is available in tablet form. Average price: 650 rubles (20 pieces, 500 mg each).
As for products for external use, these include:
- Acyclovir (ointment) - the drug is applied in a thin layer to the affected areas of the skin up to 5 times a day (on average every 4 hours). The duration of the course is 7-10 days. Price: 30 rubles (5 g).
- Zovirax (cream) - the product is recommended to be applied 5 times a day to problem areas, including healthy skin bordering areas of the disease. Zovirax should be used for 5-10 days. The cream is applied with clean hands or a cotton swab. Average price: 190 rubles (5 g).
- Panavir (gel) - the drug is applied in a thin layer to the affected skin (4-5 times a day). The average course of therapy is 5 days. Price: 135 rubles (3 g).
What it is?
There is a special virus from the smallpox group that loves to “visit” children under 5 years of age. It is at this age that children have the weakest and most vulnerable immunity, which is still in its formation stage. The virus infects the skin and sometimes mucous membranes. There are four types of foreign agents, two of which are more common in adults and are sexually transmitted. The other two are typical “children’s” ones, they are transmitted through contact with a sick person, through shared household items, toys, dishes, and so on, less often - by airborne droplets. The virus spreads by scratching and rubbing affected areas of the skin.
Thus, molluscum contagiosum is a viral skin disease that is not as rare as it might seem at first glance.
The incubation period lasts from 2 to 8 weeks. The likelihood of infection increases significantly in hot climates and poor sanitary conditions.
The child’s body develops immunity to the virus that causes the disease, but immunity is not permanent, and after some time the child may become infected with the skin virus again.
What is it and what does it look like
Molluscum on a child’s face manifests itself in the form of a rash that looks like nodules that rise above the general level of the skin and have an oval shape. They either match the color of the skin or have a more pink tint.
Molluscum on a child’s face looks like purulent pimples.
At the beginning, the size of each formation is small - only 12 mm, but then the disease progresses, and papules can grow up to 7-10 mm, and with weakened immunity and lack of treatment, large nodules absorb neighboring ones, resulting in the formation of especially large formations.
There is also a reticular form of the disease, in which the nodules are connected to the skin through a thin stalk.
Once it appears, the rash quickly spreads. Some nodules (about 10-15 percent of the total) have indentations in the center. If you press on it, a white mass comes out. When examining the contents under a microscope, the mollusks themselves will be visible. Nodules develop in the absence of an inflammatory process.
The disease does not lead to any complications associated with internal organs, but does not look aesthetically pleasing. If you do not undergo special treatment, it will go away on its own within up to 4 years.
How does infection occur?
The disease spreads through contact and household contact, when the contents of the nodules, due to friction on clothing or scratching, fall on household items.
If we talk about children, we should especially be wary of infection:
- children who do not yet go to school;
- for allergy sufferers;
- those who are forced to take hormonal medications;
- non-compliance with hygiene rules;
- living in unhealthy environmental conditions;
- exposed to stress and overwork.
Infection with molluscs can occur through common household items, such as bedding, hygiene items, toys, and through touching surfaces in a kindergarten, on the playground, or in the pool. The virus is present in both the air and street dust. A child can become infected not only from children, but also from adults, since in them molluscum contagiosum also appears on the face and body.
Diagnosis of the disease
It is quite simple for a specialist to identify molluscum contagiosum on the skin of a child. To achieve this, the following activities are carried out.
- Carrying out a thorough examination of the skin to detect characteristic signs of infection.
- In particularly difficult situations, histological examination may be required. A good clue to the development of molluscum contagiosum will be the presence of special agents located in the cytoplasm of epithelial cells.
Photos can be of great help in identifying molluscum contagiosum. However, during activities carried out by specialists, in order to detect molluscum contagiosum, it is necessary to use the following methods:
- PCR diagnostics. When carrying out its purpose is to establish the presence of HIV or detect antibodies to this virus.
- Search for infections that can be spread sexually.
Differential diagnosis
When making a diagnosis, it is very important not to confuse molluscum contagiosum on the skin of a child with other dermatovenerological diseases , since they are distinguished by the presence of similar symptoms. The group of common symptoms includes the following:
- lichen planus;
- warts that are provoked by the human papillomavirus;
- keratoacanthoma and various forms of its manifestation;
- epithelioma, which is a benign neoplasm.
In some cases, when traditional diagnostic methods do not allow an accurate diagnosis to be made, it is necessary to resort to histological examination of the child’s skin. Thanks to it, it is possible to identify rashes characteristic of the underlying disease, which are not observed during the development of the tumor process. The group of such morphological characteristics consists of the following:
- acquisition of epithelium by cells of the keratinized surface, usually it appears in material from nodules;
- the presence of oval mollusc bodies located in the cytoplasm. As they develop, they grow, as a result, the cell nucleus moves to the periphery;
- the highest level of virus concentration is observed in the basal layer of the epithelium.
Main clinical symptoms of the disease: description and localization of lesions
Rashes occur at the sites of virus penetration and are located in children mainly on the following parts of the body:
- on the face (mainly on the forehead and eyelids);
- on the chest;
- in the armpits;
- on the neck;
- on the back of the hands.
They never appear on the palms and soles - this is their difference from papillomas. Dense shiny papules of irregular shape rise above the unchanged skin, not different in color from healthy skin, yellowish or pinkish. In the center of each nodule there is a visible depression in the form of a navel with a small hole, from which, when pressed, a whitish mass is released, the consistency of which resembles cottage cheese. Rash blisters can be isolated or grouped, multiple or few (5–10 pieces per patient).
Inside each papule there is a curdled content that comes out when pressed.
The elements of the rash are non-inflammatory and translucent; their diameter usually varies from 1 to 8 mm. But in patients with immunodeficiency, a giant form of molluscum contagiosum can form, in which papules reach a size of 1.5–2.5 cm or more. They merge with each other, forming large tumor-like formations. In addition, some patients also have atypical clinical variants of rashes:
- single;
- keratinizing - covered with a dense layer of skin;
- ulcerative-cystic - large papules formed by the fusion of several small ones that ulcerate or cysts form on them;
- reticular (Molluscum contagiosum pediculatum) - with this type of rash, the papules have a thin stalk, resembling a mushroom;
- miliary (Molluscum contagiosum miliare) - when the vesicles are located in small scattering throughout the body.
Often nodules do not cause any subjective sensations in a sick child and are more of a cosmetic defect than a disease. However, in children suffering from allergic dermatitis, the rash may be accompanied by unbearable itching. Sometimes there is irritation on the skin, as a result of which erythema appears - its abnormal redness.
The color of molluscum contagiosum papules can vary from flesh-colored to red with a pearlescent tint
The course of this pathology is unpredictable. Spontaneous remission of the disease often occurs after 2–6 months. But this period of time is enough for the molluscum contagiosum virus to penetrate the skin in other parts of the body and also be transmitted to other people. Children with atopic dermatitis and immunodeficiency are not prone to spontaneous recovery, so they need urgent treatment. Otherwise there may be serious complications:
- the occurrence of lesions in large numbers;
- cellulite around rashes;
- development of various types of dermatitis in combination with each other;
- damage to the orbits with visual impairment.
Such children should be carefully examined to identify the causes of the immunodeficiency state.
Types of disease
This disease has several varieties:
- Classic - single hemispherical nodules with a depression in the center appear on the surface of the skin.
- Generalized - large formations are observed on the surface of the skin, collected in clusters of up to several dozen pieces in one place.
- Giant - formations merge into one large nodule up to 2 cm in size.
- Pedicular - nodules merge into flat plaques, covering large areas of the skin.
Treatment
Not all doctors recommend treatment for molluscum contagiosum in children. Some experts suggest waiting until the baby’s own immunity copes with the infection. Should you follow this advice? It's up to the parents to decide.
Baby molluscum is not dangerous, but it causes a lot of discomfort and limits the child’s activity. In addition, this disease is very contagious.
Medicines
Despite the many methods for dermatological removal of formations, doctors prefer not to use them in children. At an early age, treatment with antiviral and immunostimulating external agents is much more effective.
To get rid of molluscum contagiosum, the following is prescribed:
- Ifagel;
- Viferon cream;
- Acyclovir;
- Oxolinic ointment 3%.
Ifagel and Viferon products, created on the basis of human interferon alpha-2b, perfectly strengthen local immunity, have a strong immunomodulatory and antiviral effect, and prevent infection of healthy skin areas.
Ointments are applied pointwise to each mollusk several times a day. Treatment continues until the pathological elements disappear completely.
A prerequisite for eradicating a contagious infection is strengthening the child’s immunity. For this purpose use:
- Isoprinosine.
- Groprinosin.
- Amiksin.
- Viferon candles.
The inclusion of the drug Lipoferon in the complex therapy of molluscum contagiosum significantly increases its effectiveness and prevents the development of complications even with aggravated course of the disease. In addition, the immunomodulator is well tolerated and approved for use in children from birth.
Folk recipes
Molluscs in children have been treated with folk remedies for a long time. This therapy is not only effective, but also recognized by classical medicine.
The juice of celandine or garlic, string herb, chamomile, calendula, fresh birch leaf helps very well with the disease:
- Fresh bird cherry or birch leaves (preferably May leaves) are passed through a meat grinder and the juice is squeezed out. Each mollusk is lubricated with the concentrate separately; in case of extensive rashes, lotions are applied. The product is very useful after removing nodules - the wounds heal quickly without leaving marks on the skin.
- Infusions and decoctions of all of the above medicinal plants are used for compresses or washing affected areas of the body. The medicinal solution is prepared at the rate of 1 tsp. dry raw materials per 200 ml of boiling water. Leave for at least an hour and use 5-6 times a day.
- Contagious nodules are also treated with celandine juice. It is better to take it from a freshly picked plant and apply it locally to each papule. If necessary, the medicinal concentrate can be prepared for a long period. To do this, the fresh, juicy above-ground part of the plant is passed through a meat grinder, the juice is squeezed out and stored in the refrigerator.
- Garlic is used in the same way. Its juice is more caustic, so it should be used carefully. For the first treatment, it is recommended to dilute the concentrate a little with water. The product is applied to the mollusk 2-3 times a day, covering the adjacent area of healthy tissue - so that the infection does not spread further.
Without removing their contents, shellfish can be treated with essential oils of tea tree, eucalyptus, fir, juniper, and calendula.
Removal
Parents who decide to remove nodules from their child’s skin for aesthetic reasons should know that cosmetic procedures will not prevent their reappearance and certainly will not cure the virus.
There are several officially approved methods for destroying molluscum contagiosum:
- laser destruction;
- cryodestruction;
- curettage;
- electrocoagulation;
- husking.
For hardware removal, a pulsed or CO2 laser is used. After irradiation, each papule is treated with iodine solution and the appearance of a crust is monitored. If a week after the procedure the scab has not appeared, the manipulation is repeated.
As a rule, laser therapy eliminates 90% of formations after the first procedure. Fallen mollusks rarely leave scars, so the device is suitable for manipulations on the face.
Cryodestruction involves removing formations with liquid nitrogen. The procedure is quite painful and leaves noticeable scars and areas of depigmentation.
Curettage and enucleation involve physically scraping out the molluscum contagiosum with a special spoon or removing it with tweezers. The manipulations are very unpleasant and painful and may be accompanied by bleeding. Often, such treatment only aggravates the disease and leads to the appearance of a huge number of new contagious nodules.
Dermatologists often advise removing candida molluscum using cauterization. This method is no better than the others - it is just as painful, leaves scars and often requires repeated manipulation. Although, according to the observation of many parents, electrocoagulation really removes mollusks forever.
None of the options considered can be called the best. All of them cause pain, crying and extreme stress, leave scars and are poorly tolerated by young children. You should not try to remove molluscum contagiosum on your own, as there is a huge risk of causing additional infection.
Is it possible to cure molluscs on the skin at home?
Doctors categorically prohibit treating pathology on their own. There are several good reasons for this:
- Improper removal methods at home contribute to the development of new tumors on the body. An infection that enters the body can cause the development of lipomas or milia. But this is not the worst outcome. Cases are often recorded when self-removal of inflammation ends in the development of an oncological tumor. Moreover, this outcome occurs quite often.
- Some special forms of molluscum contagiosum are one of the complications of the AIDS virus developing in the body. By using the wrong treatment methods, you can provoke the accelerated development of pathology. In addition, it is necessary to take care of such inflammations with a special approach. Only a qualified doctor will prescribe a specific course of treatment for you.
- Self-treatment can provoke a rapid relapse of the disease. You can get rid of a few molluscs that appear on your body, but soon the rash will appear again and in larger numbers. And in this case, curing the disease is much more difficult. It is strictly forbidden to squeeze shellfish yourself. You definitely won’t be able to remove the root of the disease without practical skills and experience.
Consequences and complications
In most cases, the disease proceeds without complications .
In rare cases, various dermatitis may develop against the background of skin lesions from molluscum contagiosum.
There is also a risk of penetration and development of other infectious diseases, since the immune system is weakened .
How does urticaria manifest in children? Find out the answer right now.
What does Dr. Komarovsky advise?
According to Dr. Komarovsky, a child does not need to be “poisoned” with pills or “experimented” using folk remedies. He advises not to treat children at all if there is no threat to their life and health.
It is enough to strengthen the immune system so that the body can cope on its own.
If the rash is in an unpleasant place or the child has a complex because of this, then you can contact a cosmetologist and remove the formations, however, according to him, this is also undesirable .
What are the first signs of measles in a child? Read about it here.
Forecast
The prognosis for molluscum contagiosum in children is favorable. When purulent complications occur, rough scars and spots with disturbed pigmentation may subsequently remain on the skin.
Molluscum contagiosum in children does not pose a serious health hazard and in most cases does not require treatment, as it tends to resolve spontaneously within 6–24 months.
Given that the disease most often affects children with weakened immune systems, a medical examination of the child is required in order to establish the cause of the immunodeficiency. The presence of a profuse form of the disease or giant molluscum contagiosum is the basis for testing for HIV.
Surgical removal of tumors
We also recommend:
How to treat pityriasis versicolor
One of the frequently used methods of treating the disease is scraping out the body of the mollusk. For both adults and children, the procedure requires hospitalization, since it is performed in a clinic under anesthesia. It is strictly prohibited to independently violate the integrity of the neoplasm. Single cases of molluscum, as well as small neoplasms, are subjected to curettage.
The mollusk is scraped out with a Volkmann spoon with a sharp edge, which removes the neoplasm almost completely, but this may affect areas of healthy skin. To prevent the virus from spreading further, the site where the mollusk is removed is thoroughly treated with a special solution. In this case, rough scars may remain on the skin after the intervention.
This method of combating molluscum contagiosum is quite outdated and is used only in rare cases when a medical institution is not able to help with other, more progressive means.
Another method for removing large tumors is cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen. This is one of the most popular procedures, which has an acceptable price-quality ratio. Cryodestruction of the tumor is performed under local anesthesia. Under the influence of liquid nitrogen, the mollusk itself and a small area around it are destroyed. After the procedure, there are almost no scars left, but the only drawback of cryodestruction is the need to act more than once. In some cases, the procedure is effective only the fourth or fifth time.
Treating affected skin with liquid nitrogen is an effective way to get rid of unwanted formations.
You can also get rid of molluscum contagiosum using a more “ancient” method – electrocoagulation. Under the influence of current, the skin heats up, and the basis of the pathology seems to be burned out. They prefer not to treat molluscum contagiosum in children in this way, since it is quite traumatic and leaves marks on the delicate children’s skin.
Removal of tumors is also possible using a laser. The latest methods in the treatment of pathology are now used in almost any medical institution, so curing molluscum contagiosum with a laser is not difficult. You can also note the undeniable advantages of the laser molluscum removal procedure:
- during the procedure, the possibility of further infection is excluded;
- there is no danger of blood poisoning and the development of suppuration;
- the procedure is completely sterile;
- It is highly safe, so the procedure can be done even for children;
- the tissues located next to the molluscum contagiosum are not injured.
Laser removal of molluscum is a modern method of combating the disease
For molluscum contagiosum, laser removal is carried out as follows: the skin is treated with anesthetic cream, its surface is heated with a laser to high temperatures (about 150 degrees). At such temperatures, viruses die, and tissues transformed under the influence of the virus are evaporated.
The laser beam removes molluscum contagiosum so carefully that it can penetrate only half a millimeter into healthy tissue. This eliminates trauma to healthy layers of skin, so there are no rough scars left after the procedure. The procedure usually takes no more than twenty minutes, after which the patient can be free until the next session.
Several sessions may be required to remove large mollusks. They are usually carried out at short intervals, as soon as the redness around the skin goes away after the first session. After laser exposure to the skin, you should not wet the affected area for three days and sunbathe in direct sunlight or in a solarium.
Contraindications to surgical treatment
Surgical removal of tumors is carried out if other methods cannot cure the patient and clear the surface of his skin from rashes. But even radical measures cannot always bring success, since they have a list of contraindications.
Treatment of molluscum contagiosum cannot be carried out in the following cases:
- in newborns;
- in women during pregnancy;
- in the presence of serious skin pathologies (severe allergies, fungal skin infections);
- with diagnosed severe vascular and heart diseases;
- in patients with epilepsy and mental disorders.
For these categories of patients, other methods of treating molluscum contagiosum are selected.
Routes of infection
A DNA-containing virus, which belongs to the group containing the smallpox virus, is the cause of the development of molluscum contagiosum. Scientists suggest that only humans are the natural carrier of this virus, but it is known for sure that the route of infection with molluscum contagiosum is contact.
It should be taken into account that the threat is posed not only by an already infected person, but also by household items, towels, bedding, clothing, and toys. Moreover, the DNA-containing molluscum contagiosum virus affects people of different age groups. The most widespread spread of the disease in question is recorded in childhood, if the child attends educational institutions - kindergartens, schools and any children's groups, in which even an outbreak of an epidemic of molluscum contagiosum may occur.
If the localization of rashes for the disease in question in adults is in the genital area, then the sexual route of infection is quite possible.