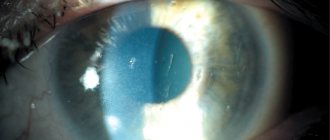
Sepsis is the most severe, generalized form of the infectious process, which develops either with a high pathogenicity of the pathogen or with an insufficient response of the body's defense systems. International consensus recommends using the following definition: sepsis is a life-threatening dysfunction of internal organs caused by dysregulation of the body's response to infection. With sepsis, general intoxication syndrome, thrombohemorrhagic syndrome (hemorrhages) and damage to internal organs are observed.
- Causes of sepsis
- Types of sepsis
- The first signs and symptoms of sepsis
- Diagnosis of sepsis
- Stages of sepsis development
- Treatment of sepsis
- Complications of sepsis
- Prognosis for sepsis
What is blood poisoning
Many adult illnesses are no different in severity from the same illnesses in a child. Often, a younger body, on the contrary, is able to persistently fight the problem. Blood poisoning or sepsis is a reaction to microorganisms and infections entering the bloodstream. Regardless of the patient’s age, this condition is considered severe and in advanced cases can be fatal .
According to the international classification of diseases, sepsis is indicated under two codes at once - A40 and A41, which implies streptococcal and other septicemia. The name for bacterial infection was not chosen by chance, because the causative agents are mostly streptococci. In other cases, the blood may be contaminated with microorganisms such as E. coli, staphylococci and pneumococci.
What is sepsis
The disease is a massive attack of pathogens. So, sepsis - what is it? Doctors clarify: a severe infectious disease, when poisons produced by pathogenic flora and inflammatory substances produced by the body itself spread throughout the body. Moreover, the immune system is powerless against them if it is very weakened.
This pathological process can also be considered as a generalized infectious blood disease against the background of acute immunodeficiency. It is easy to find sepsis in the international classification of diseases: the ICD-10 code is A41. Varieties of the disease have separate codes. For example, septic shock - A41.9, streptococcal septicemia - A40, newborn sepsis - P36.
Symptoms
Due to the differences in the forms of blood sepsis, it does not have any definitive symptoms. The course of infection can be rapid and, without allowing the patient to come to his senses, lead to disastrous consequences. Often the disease drags on for 5-7 days, during which its presence can be identified by its characteristic features and consult a doctor. Symptoms of human blood infection or sepsis may include:
- the appearance of herpes on the lips;
- sudden development of skin hyperpigmentation or pallor;
- the appearance of purulent inflammation on the body;
- breathing problems;
- unstable psycho-emotional state, apathy;
- depressions on the face in the cheek area.
Sepsis in newborns
One type of sepsis is neonatal, that is, developing in newborns due to a purulent process in the tissues and vessels of the umbilical cord. It is characterized by vomiting, diarrhea, complete refusal of the child to breastfeed, rapid weight loss, dehydration, the skin loses its elasticity, becomes dry, sometimes sallow in color, sometimes local suppuration in the navel area, deep phlegmons and abscesses of various locations are detected.
Sepsis in newborns can be caused by: infectious and inflammatory diseases in a pregnant woman (pyelonephritis, adnexitis, colpitis); “dirty” waters, deposits on the placenta; out-of-hospital birth; infections in the postpartum mother (endometritis, mastitis); the anhydrous period during labor is more than six hours.
The first signs of blood poisoning
Lightning-fast deterioration in health with asymptomatic progression is observed only in a number of diseases, to which blood sepsis may relate. If you suspect a possible infection, then listen to your own body - it will let you know whether there is cause for concern or not. As a rule, significant changes during infection occur in the first days. Signs of infection may include the following:
- increase or decrease in temperature, chills;
- increased sweating;
- intestinal disorders;
- redness of the skin, spots on the body;
- loss of consciousness.
The first signs and symptoms of sepsis
Identifying the first signs of sepsis can be difficult, even for specialists. This is due to the fact that, firstly, this syndrome develops against the background of an existing pathology, which can have a wide variety of symptoms, and secondly, in the presence of immunodeficiency, the clinical picture can be erased. However, there are some symptoms that suggest the onset of sepsis:
- Increase or decrease in body temperature - above 38 and below 36 degrees.
- Pressure drop below operating value.
- Increased heart rate.
- Increased frequency of breathing movements (shortness of breath).
- Decreased amount of urine excreted.
- General weakness, exhaustion.
- Impaired consciousness or behavior.
Particular attention is paid to the occurrence of these signs in chronic patients, in the presence of leukopenia, cancer, and in patients who have undergone trauma or surgery. If at least 2-3 of these symptoms occur, you should immediately contact your doctor.
Causes
Knowing about a possible danger, a person subconsciously tries to avoid it. When it comes to diseases, it makes sense to remember the main causes of their occurrence. It is impossible to protect yourself from everything in the world, but it is possible to protect yourself from the possibility of infection caused by an infection in the blood. The causative agents are various microorganisms: staphylococci, streptococci and others. When they enter the blood, especially against the background of decreased immunity, they lead to dire consequences. Among the causes of infection are the following:
- congenital or acquired defects of the immune system;
- drug use;
- non-compliance with hygiene rules in hospitals and beauty salons;
- performing an abortion in an inappropriate manner;
- infection in the blood due to radiation and other therapies that suppress the immune system;
- complications from wounds, cuts and burns.
Classification of sepsis
According to the primary focus, development is distinguished:
- wound sepsis;
- burn;
- pulmonary;
- cardiogenic;
- angiogenic;
- odontogenic;
- tonsilogenic;
- abdominal (biliary, pancreatogenic, intestinal, appendicular, urological, associated with inflammation of abdominal tissue);
- gynecological (caused by inflammation of the pelvic tissue or organs of the female reproductive system);
- postpartum, etc.
For reference. The clinical course of sepsis can be fulminant (the most unfavorable course, often ending in death), acute (from five to ten days), subacute (from two weeks to three months). In rare cases, chronic sepsis is possible, as well as a recurrent form of infection.
Chronic sepsis is extremely rare and is observed in patients in whom treatment of the primary source of infection has not led to the complete disappearance of sepsis symptoms.
How does blood poisoning occur?
Signs of blood sepsis can appear in a completely healthy person, but in patients with reduced immunity, the risk of getting sick increases significantly. Being a systemic inflammatory response syndrome of the body, infection can be obtained as follows:
- During the operation. When using unsterile instruments, doctors can introduce an infection into the blood through open wounds, which will multiply if the immune system is weak.
- During the treatment and removal of teeth. Microorganisms easily penetrate through an open channel into the blood if sterility is not maintained.
- For cuts. A cut received at home or in a salon, for example, when processing nails, is a “gateway” for infection.
Articles on the topic
- Constant erection - why it appears in an adult or child, diagnosis, therapy and consequences
- Bacterial diseases: treatment and prevention
- Routes of transmission of hepatitis: symptoms and types of diseases
Blood poisoning from a tooth
Not many people add visiting the dentist to their annual to-do list. In this regard, situations arise when it is not possible to help a diseased tooth and removal is the only way to get rid of painful sensations. Odontogenic blood sepsis is one of the possible consequences of such a decision. Infection occurs at the junctions between the hard part of the tooth and the gum. Due to difficulties in diagnosis, this disease is considered very dangerous, and it takes a long time to treat. However, even after the disease, immunity is not developed, which threatens relapse.
Signs of sepsis
The most typical symptoms for this disease are:
- the patient is shaken by severe chills;
- very high temperature – with sepsis it can have wave-like fluctuations;
- profuse sweating.
Sepsis may present with additional symptoms such as:
- skin rash;
- bleeding of mucous membranes;
- pressure drop;
- dyspnea;
- dehydration;
- "waxy" face;
- mild stupor or euphoria.
Kinds
The classifications of infections are very extensive and are divided into categories with a different number of items. The two largest groups are cryptogenic blood sepsis and secondary. In the first case, the entrance gate is not identified, but in the second, the source of infection can be identified. The following indicates the method by which blood sepsis occurred: through a wound, as a result of surgery, or by rupture of the birth canal. However, more important is the classification according to the location of the source of infection:
- odontogenic – the hard part of the tooth;
- intestinal – digestive system;
- cutaneous - skin;
- rhinogenic – nasal sinuses;
- urosepsis – organs of the genitourinary system;
- oral – oral cavity;
- otogenic – ears;
- tonsillogenic – tonsils;
- endocardial – heart valves.
Primary and secondary infection
Based on the location of the primary source of infection, the following types can be distinguished:
- primary (otherwise – idiopathic, cryptogenic sepsis);
- secondary.
Secondary sepsis also has several varieties, depending on where the source of infection is localized:
- Skin – blood poisoning causes skin damage: ulcers, purulent and infected wounds, burns, boils.
- Surgical – the infection enters the body during surgery.
- Obstetric-gynecological – sepsis is associated with complications during childbirth and abortion.
- Pleuropulmonary – the cause of blood poisoning is lung diseases: pleural empyema, pneumonia.
- Urosepsis is an infection spread throughout the body from the urinary system during diseases such as cystitis, prostatitis, pyelonephritis.
- Tonsillogenic is formed in severe forms of tonsillitis caused by staphylococci or streptococci.
- Peritoneal (intestinal) is caused by diseases of the abdominal cavity.
- Odontogenic – the primary localization in this form is diseases of the teeth and jaw: caries, apical periodontitis, peri-maxillary phlegmon.
- Otogenic – development occurs against the background of purulent diseases of the hearing organ.
- Rhinogenic – associated with inflammation in the nasal cavity, usually with sinusitis.
- Umbilical - typical for newborns and often accompanies omphalitis - inflammation of the skin near the umbilical wound.
Finally, blood sepsis can be classified according to the source of infection:
- Nosocomial - the infection entered the body during hospital treatment: after childbirth, operations and other medical procedures.
- Community-acquired - the occurrence of infection is in no way related to stay in a health care facility.
Stages of sepsis
You can prevent the spread of infection and toxins by understanding in time what stage the disease is at . The principle of treatment of infection, its duration and results depend on the stage of its progression. There are several of them:
- Initial stage of infection. The body reacts to microorganisms in the blood. Body temperature and skin color change, heart rate increases.
- Lightning fast. Accompanied by a sharp deterioration in health. Such an acute stage can lead to septicopyemia - the formation of abscesses.
- Late stage of infection. Characterized by disruption of vital organs and hypotension.
- Septic shock. The blood supply to organs is disrupted, which leads to death.
Diagnosis of sepsis
Timely diagnosis of sepsis is crucial for the patient’s recovery. The earlier treatment is started, the greater the chances of success. The diagnosis is made on the basis of clinical examination and laboratory and instrumental examination.
Clinical criteria:
- Body temperature is more than 38 degrees or less than 36 degrees.
- Heart rate is more than 90 or exceeds the age norm.
- Respiration rate more than 20 times per minute.
- Presence of edema.
- Confusion.
- An increase in blood glucose levels of more than 7.7 µmol/l in the absence of diabetes.
- Disturbance of hemodynamic processes - a decrease in systolic blood pressure of less than 90 mmHg, or its decrease by more than 40 mmHg. from the usual meaning.
Laboratory criteria
A general blood test is performed with a leukocyte count and platelet count. In case of sepsis, leukocytosis is determined by more than 12*109/l or leukopenia when the number of leukocytes is below 4*109/l. There is also the release of immature forms of granulocytes into the bloodstream and a decrease in the number of platelets.
A biochemical blood test shows an increase in C-reactive protein, creatinine, and bilirubin. But these are nonspecific signs that can be observed in other diseases. Therefore, the search for more informative diagnostic methods continues.
Today, the main such markers are procalcitonin, presepsin, and CRP. Based on this laboratory indicator, a diagnosis is made and the dynamics of the disease are monitored.
Bacteriological culture
Detection of microorganisms in the blood is an important, but not mandatory, manifestation of sepsis. Even with the use of the most modern diagnostic systems and careful adherence to material sampling techniques, it is possible to isolate the pathogen from the blood in less than half of the cases. Therefore, a negative culture result in the presence of clinical symptoms should not be regarded as the absence of sepsis, and, conversely, the isolation of microorganisms from the blood in the absence of symptoms should be regarded as transient bacteremia or viremia, but not as sepsis.
However, biological studies should in any case be present as one of the stages in diagnosing sepsis for the following reasons:
- Possibility of determining the etiology of the pathogen.
- Selection or change of antibiotic treatment regimens.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
- In some cases, it allows you to determine the source of infection, for example, catheter-related infection, endocarditis, etc.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7 (495) 151-14-53
How to determine blood poisoning
To identify the fact that a patient's blood is infected, at least two criteria indicating this must be present: hypothermia or hyperthermia, tachycardia and a low white blood cell count. In addition, there is a whole range of studies that can be used to detect infection:
- urine test (excess protein in the urine can confirm the diagnosis);
- comprehensive study of intravascular coagulation indicators;
- X-ray or ultrasound to detect purulent lesions of the body.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis in both children and adults is made on the basis of the clinical picture (presence of characteristic symptoms, identification of the source of infection and possible metastases), as well as on the results of clinical studies (complete blood count, culture for sterility).
For an accurate diagnosis and differentiation of sepsis from other diseases, it is recommended that cultures be carried out three times. A general blood test reveals leukocytosis, hypochromic anemia, and accelerated ESR.
If there are indications, the following may additionally be prescribed: ultrasound of individual organs, x-ray diagnostics, magnetic resonance or computed tomography.
Treatment
To save a person from the consequences of the penetration and spread of dangerous bacteria in the blood during infection, doctors can resort to radical surgical methods to remove necrosis or limit themselves to more conservative treatment. It all depends on the stage of the disease and the condition of the particular organism, so self-medication is unacceptable here. Treatment for blood sepsis may include:
- anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapies that kill microorganisms and increase resistance to them;
- administration of water-salt solutions intravenously to detoxify the body after infection;
- plasma transfusion from a donor in the most advanced cases.
Antibiotics
An infection in the blood prevents a person from living normally due to the dysfunction of his internal organs. Antibiotics inhibit the growth of living cells, which also include dangerous microorganisms. When infected, this option will be the most effective at first and in the initial stages. The drug can be taken only on the recommendation of a doctor and in combination with an excipient. To treat blood sepsis use:
- Gentamicin . It disrupts protein synthesis by acting through the cell membrane of microorganisms. The downside is the side effects associated with long-term use of the drug.
- Vancomycin . Slows down the biosynthesis of bacterial cell walls, which has a detrimental effect on them. Contraindicated in renal diseases.
- Amoxicillin . Belongs to the group of penicillins, works due to its inhibitory effect on infected cells. This group is very allergic.
Treatment of sepsis
Treatment of sepsis is based on three principles:
- Sanitation of the primary lesion. This can be achieved with surgery and/or adequate antibiotic therapy. If a primary lesion is discovered that can be treated surgically, it is necessary to do this as soon as possible. This may include opening and drainage of abscesses, removal of infected invasive devices (catheters, implants, etc.), drainage and lavage of the abdominal cavity, etc.
Antimicrobial therapy is another cornerstone of sepsis treatment, and its timeliness and adequacy are important. For example, if septic shock develops, drugs should be administered within an hour of the onset of symptoms. In this case, the drug must cover the entire spectrum of suspected pathogens and, importantly, penetrate the primary infectious focus. If it is necessary to prescribe combination therapy of several drugs, they are used for no more than 5 days, after which data from biological research methods must be obtained and the treatment regimen must be adjusted.
- Ensuring oxygen transport - all clinical manifestations of sepsis are aggravated in conditions of lack of oxygen, so it is very important to control this process. To do this:
- Hemodynamic support - infusion of solutions that ensure replenishment of water and electrolyte balance, medications are prescribed to maintain blood pressure, etc.
Respiratory support - artificial ventilation, oxygen masks, etc.
- Correction of metabolic disorders
- Ensuring the supply of necessary nutrients (proteins, fats, carbohydrates). If the patient is unable to take food or nutritional formulas on his own, replacement therapy is considered.
Monitoring glucose levels.
- Detoxification activities.
One of the effective ways to treat sepsis is selective sorption on TORAYMYXIN columns. This technique is successfully used in many countries around the world. Currently, more than 200 thousand patients with septic shock and severe forms of sepsis have undergone such treatment. The effectiveness and safety of the technology has been confirmed in clinical studies.
Consequences
Scary photos and videos depicting complications after blood sepsis are amazing and frightening. The most dangerous consequence is septic shock, which impedes blood circulation in the internal organs. Even if the disease has not reached this state, the danger to health is enormous, since various pathologies can develop:
- heart or kidney failure;
- liver tissue damage;
- significant increase in shortness of breath;
- instability of temperature and pressure;
- the appearance of bedsores;
- blockage of blood vessels and tissue necrosis;
- bleeding.
Complications of sepsis
Sepsis is often accompanied by the development of various complications, among which the most common are renal, adrenal, cardiovascular and respiratory failure, bleeding and thromboembolism.
The most dangerous condition is infectious-toxic shock . Its characteristic manifestations are circulatory disorders, hyperthermia, a critical decrease in blood pressure, and increased heart rate up to 160 beats. Mortality reaches 90%.
Prevention
It is not possible to predict that a healthy person will suddenly develop a disease. One person may be completely insensitive to any virus in the blood, while another may fall ill instantly. However, there are preventive measures that can reduce the risk of infection and protect yourself from severe consequences:
- Strengthening the immune system. This set of effects will create a barrier to infection. If your immune system is weakened, consult a doctor to select therapy.
- Maintaining hygiene rules. This point especially applies to the administration of injections and the treatment of open wounds.
- Accuracy. Reducing the level of injury will not allow bacteria to penetrate inside.
How to treat sepsis
The patient is prescribed emergency drug treatment:
- antibiotics;
- painkillers;
- immunomodulators;
- infusion therapy solutions;
- medications that normalize blood pressure;
- drugs that restore the functions of the heart, liver, kidneys;
- vitamins, antioxidants.
Antibiotics for sepsis play a vital role in the complex treatment of the disease. Intravenous injections are prescribed immediately. More often these are two or three drugs from different groups in the highest possible doses. Immunomodulators increase the body's defenses. Infusion blood substitutes, saline and protein solutions help restore blood composition, water-salt balance, activate blood circulation, and cleanse the body of toxins.
However, until the source of sepsis is eliminated, drug treatment cannot give the necessary effect, so surgical intervention is carried out as early as possible. The surgeon opens the abscess and removes its purulent contents along with necrotic tissue. Adequate patient care is very important. Sepsis cannot be transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person.
Reliable disease prevention is provided by:
- patients' personal hygiene;
- timely elimination of local abscesses;
- strict compliance by health workers with asepsis requirements;
- minimum terms of use of catheters;
- competent antibiotic therapy;
- vaccination of problem patients.
Blood poisoning - causes, signs, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and prevention
The diagnosis in both children and adults is made on the basis of the clinical picture (presence of characteristic symptoms, identification of the source of infection and possible metastases), as well as on the results of clinical studies (complete blood count, culture for sterility).
For an accurate diagnosis and differentiation of sepsis from other diseases, it is recommended that cultures be carried out three times. A general blood test reveals leukocytosis, hypochromic anemia, and accelerated ESR.
If there are indications, the following may additionally be prescribed: ultrasound of individual organs, x-ray diagnostics, magnetic resonance or computed tomography.
As soon as the first symptoms of blood poisoning are noticed in a person or there is a suspicion of what could be the cause, you should immediately consult a doctor to receive competent treatment recommendations and avoid dire consequences.
Self-medication in such situations may not be safe and will likely only make the problem worse. Being attentive to your body is very important, especially if you do not exclude the possibility of infection.
Many adult illnesses are no different in severity from the same illnesses in a child. Often, a younger body, on the contrary, is able to persistently fight the problem.
Blood poisoning or sepsis is a reaction to microorganisms and infections entering the bloodstream.
DETAILS: Structure of function and norm of neutrophils in the blood
Regardless of the patient’s age, this condition is considered severe and in advanced cases can be fatal.
According to the international classification of diseases, sepsis is indicated under two codes at once - A40 and A41, which implies streptococcal and other septicemia.
The name for bacterial infection was not chosen by chance, because the causative agents are mostly streptococci.
In other cases, the blood may be contaminated with microorganisms such as E. coli, staphylococci and pneumococci.
Due to the differences in the forms of blood sepsis, it does not have any definitive symptoms. The course of infection can be rapid and, without allowing the patient to come to his senses, lead to disastrous consequences.
Often the disease drags on for 5-7 days, during which its presence can be identified by its characteristic features and consult a doctor.
Symptoms of human blood infection or sepsis may include:
- the appearance of herpes on the lips;
- sudden development of skin hyperpigmentation or pallor;
- the appearance of purulent inflammation on the body;
- breathing problems;
- unstable psycho-emotional state, apathy;
- depressions on the face in the cheek area.
Lightning-fast deterioration in health with asymptomatic progression is observed only in a number of diseases, to which blood sepsis may relate.
If you suspect a possible infection, then listen to your own body - it will let you know whether there is cause for concern or not.
As a rule, significant changes during infection occur in the first days. Signs of infection may include the following:
- increase or decrease in temperature, chills;
- increased sweating;
- intestinal disorders;
- redness of the skin, spots on the body;
- loss of consciousness.
Causes
Knowing about a possible danger, a person subconsciously tries to avoid it. When it comes to diseases, it makes sense to remember the main causes of their occurrence.
It is impossible to protect yourself from everything in the world, but it is possible to protect yourself from the possibility of infection caused by an infection in the blood. The causative agents are various microorganisms: staphylococci, streptococci and others.
When they enter the blood, especially against the background of decreased immunity, they lead to dire consequences. Among the causes of infection are the following:
- congenital or acquired defects of the immune system;
- drug use;
- non-compliance with hygiene rules in hospitals and beauty salons;
- performing an abortion in an inappropriate manner;
- infection in the blood due to radiation and other therapies that suppress the immune system;
- complications from wounds, cuts and burns.
Signs of blood sepsis can appear in a completely healthy person, but in patients with reduced immunity, the risk of getting sick increases significantly. Being a systemic inflammatory response syndrome of the body, infection can be obtained as follows:
- During the operation. When using unsterile instruments, doctors can introduce an infection into the blood through open wounds, which will multiply if the immune system is weak.
- During the treatment and removal of teeth. Microorganisms easily penetrate through an open channel into the blood if sterility is not maintained.
- For cuts. A cut received at home or in a salon, for example, when processing nails, is a “gateway” for infection.
Not many people add visiting the dentist to their annual to-do list. In this regard, situations arise when it is not possible to help a diseased tooth and removal is the only way to get rid of painful sensations.
Odontogenic blood sepsis is one of the possible consequences of such a decision. Infection occurs at the junctions between the hard part of the tooth and the gum. Due to difficulties in diagnosis, this disease is considered very dangerous, and it takes a long time to treat.
However, even after the disease, immunity is not developed, which threatens relapse.
The classifications of infections are very extensive and are divided into categories with a different number of items. The two largest groups are cryptogenic blood sepsis and secondary.
In the first case, the entrance gate is not identified, but in the second, the source of infection can be identified. The following indicates the method by which blood sepsis occurred: through a wound, as a result of surgery, or by rupture of the birth canal.
However, more important is the classification according to the location of the source of infection:
- odontogenic – the hard part of the tooth;
- intestinal – digestive system;
- cutaneous - skin;
- rhinogenic – nasal sinuses;
- urosepsis – organs of the genitourinary system;
- oral – oral cavity;
- otogenic – ears;
- tonsillogenic – tonsils;
- endocardial – heart valves.
Stages of sepsis
You can prevent the spread of infection and toxins by understanding in time what stage the disease is at. The principle of treatment of infection, its duration and results depend on the stage of its progression. There are several of them:
- Initial stage of infection. The body reacts to microorganisms in the blood. Body temperature and skin color change, heart rate increases.
- Lightning fast. Accompanied by a sharp deterioration in health. Such an acute stage can lead to septicopyemia - the formation of abscesses.
- Late stage of infection. Characterized by disruption of vital organs and hypotension.
- Septic shock. The blood supply to organs is disrupted, which leads to death.
To identify the fact that a patient's blood is infected, at least two criteria indicating this must be present: hypothermia or hyperthermia, tachycardia and a low white blood cell count. In addition, there is a whole range of studies that can be used to detect infection:
- urine test (excess protein in the urine can confirm the diagnosis);
- comprehensive study of intravascular coagulation indicators;
- X-ray or ultrasound to detect purulent lesions of the body.
Treatment
To save a person from the consequences of the penetration and spread of dangerous bacteria in the blood during infection, doctors can resort to radical surgical methods to remove necrosis or limit themselves to more conservative treatment.
- anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapies that kill microorganisms and increase resistance to them;
- administration of water-salt solutions intravenously to detoxify the body after infection;
- plasma transfusion from a donor in the most advanced cases.
Antibiotics
An infection in the blood prevents a person from living normally due to the dysfunction of his internal organs. Antibiotics inhibit the growth of living cells, which also include dangerous microorganisms.
When infected, this option will be the most effective at first and in the initial stages. The drug can be taken only on the recommendation of a doctor and in combination with an excipient.
To treat blood sepsis use:
- Gentamicin. It disrupts protein synthesis by acting through the cell membrane of microorganisms. The downside is the side effects associated with long-term use of the drug.
- Vancomycin. Slows down the biosynthesis of bacterial cell walls, which has a detrimental effect on them. Contraindicated in renal diseases.
- Amoxicillin. Belongs to the group of penicillins, works due to its inhibitory effect on infected cells. This group is very allergic.
Consequences
Scary photos and videos depicting complications after blood sepsis are amazing and frightening. The most dangerous consequence is septic shock, which impedes blood circulation in the internal organs. Even if the disease has not reached this state, the danger to health is enormous, since various pathologies can develop:
- heart or kidney failure;
- liver tissue damage;
- significant increase in shortness of breath;
- instability of temperature and pressure;
- the appearance of bedsores;
- blockage of blood vessels and tissue necrosis;
- bleeding.
DETAILS: Magnesium: What is magnesium
Prevention
It is not possible to predict that a healthy person will suddenly develop a disease. One person may be completely insensitive to any virus in the blood, while another may fall ill instantly.
- Strengthening the immune system. This set of effects will create a barrier to infection. If your immune system is weakened, consult a doctor to select therapy.
- Maintaining hygiene rules. This point especially applies to the administration of injections and the treatment of open wounds.
- Accuracy. Reducing the level of injury will not allow bacteria to penetrate inside.
Blood culture helps identify the causative agents of sepsis
To select therapeutic measures to eliminate sepsis, it is necessary to determine how the pathogen entered the body. Only through timely diagnosis is it possible to identify sepsis or a short-term infection at the initial stage.
About the symptoms of the disease
Depending on the type of disease, its symptoms vary.
1. What are the symptoms of septicemia:
- It is characterized by lightning-fast flow. In a particularly difficult case, death occurs in less than two days,
- usually diagnosed in children under three years of age,
- causative agent of the coccus family,
- The outcome of the disease depends on how quickly the diagnosis is made and treatment is started. As a rule, the disease begins with symptoms of a respiratory infection, then other symptoms appear over a short period of time,
- with this type of disease it is difficult to determine the presence of inflammatory processes.
The disease develops as follows:
- There is an increase in temperature of about forty degrees. This is explained by the fact that when a person becomes ill with pathogenic bacteria, toxins are released that affect the area in the brain of the head that is responsible for regulating the temperature of the body. An increase in temperature is accompanied by increased heart rate, sweating and chills,
- formation of subcutaneous hemorrhages occurs. The reasons for their appearance are the destruction of the walls in the vessels by the own immune system and bacteria. At first it appears in the form of small dots, then they become large and red, the body becomes covered with blisters,
- the desire to eat disappears,
- due to liver dysfunction, the skin takes on a jaundiced tint. The entry of bilirubin (which is not processed by the liver) into the bloodstream leads to its deposition in the brain cells and on the skin,
- the patient’s blood pressure decreases, the pulse increases, and there are disturbances in his breathing,
- The digestive organs are affected, the patient begins to feel sick, vomiting, and symptoms of diarrhea appear.
2. What are the symptoms of septicopyemia:
- This is the presence of a large abscess,
- internal organs are damaged by pustules,
- the disease is characterized by a long course, but not as severe as the previous type of disease,
- the main pathogen, along with Pseudomonas aeruginosa, is also cocci,
- First, ulcers appear in the lungs, then in other organs.
This type of disease develops as follows:
- The patient's temperature rises to forty degrees, it is of an abrupt nature. Its increase is explained by the entry of new bacteria into the bloodstream. All this is accompanied by severe headaches, lethargy, and irritability. Then the patient feels better for a certain time,
- heart vessels and muscles are affected. The disease is accompanied by the formation of blood clots, which impair blood flow. For this reason, the development of endocarditis may begin, accompanied by rapid heartbeat and low blood pressure,
- There are disturbances in the activity of the kidneys. This is expressed in lumbar pain. Urine may contain pus, its volume becomes smaller,
- the liver is affected. It becomes larger, the patient’s skin acquires a yellow tint,
- the patient's lungs are affected, shortness of breath appears, pain behind the chest, the patient suffers from a severe cough, some have blue lips and fingertips. Pneumonia occurs
- brain damage occurs, in some patients - the development of encephalitis and meningoencephalitis,
- the development of purulent arthritis begins.
3. What are the symptoms of septic endocarditis:
- There is an increase in temperature,
- heartbeat increases,
- the patient's condition is characterized by tinnitus, headache, darkness in the eyes, shortness of breath,
- arrhythmia occurs
- the patient suffers from a severe cardiac cough mixed with blood.
Diagnosis and treatment
Sepsis is treated only in a hospital - in the intensive care ward and resuscitation department, since every fourth patient undergoes artificial ventilation.
Basic treatment is a combination of large doses of antibacterial drugs: antibiotics and sulfonamides.
Treatment of sepsis is always complex - along with antibiotics, detoxification therapy is carried out using saline and colloid solutions, the immune system is strengthened, including through the transfusion of donor leukocytes, and the protein composition of the blood and the activity of damaged organs and systems are normalized. Be sure to remove the accessible primary source of infection.
Treatment is complex and includes antibacterial, detoxification and immunotherapy
Sepsis is a disease with a very high mortality rate. It is precisely because of this factor that treatment should be urgent and carried out in a hospital. The likelihood of death is high if the pathological process covers most organs and systems.
The main treatment for blood poisoning is taking antibacterial drugs. It is important to choose a potent drug that matches the sensitivity of the pathogen.
The result of the therapy depends on the stage of severity of the disease, the characteristics of the pathogen and the body’s resistance. In addition to taking antibiotics, protein medications are prescribed, blood transfusions are performed, and special serums are administered.
In childhood, the elimination of sepsis also involves local therapy. The wound is treated with drugs with an antiseptic effect, purulent exudate and dead cells are removed. If the pathology becomes complicated, then intensive and surgical therapy is resorted to.
Sepsis can cause death
If timely treatment for blood poisoning is not carried out, multiple damages always develop throughout the body, which are simply incompatible with life. If the pathogens are highly sensitive to treatment and there is a marked improvement in the condition, antibiotic therapy is carried out for about 2-3 weeks.
If sepsis is detected late and the necessary treatment is not carried out, gangrene of the extremities and necrosis of their tissues may develop. In addition, irreversible changes in internal organs and hemorrhages in the adrenal glands are possible. Unfortunately, such complications are considered fatal.
With timely treatment, it is possible to reduce body temperature and cleanse the body of toxins accumulated in it. After some time, the manifestations of the disease disappear, the development of complications is avoided and recovery occurs.
If the patient’s test is confirmed, he is hospitalized in the intensive care unit or intensive care unit and treatment begins. The main method is antibacterial therapy. Treatment is carried out by an infectious disease specialist together with an anesthesiologist-resuscitator.
Antibiotics are selected for the patient depending on what infections caused sepsis (Ampicillin, Lincomycin, etc.). If the probable causative agent of the disease cannot be identified, the patient is prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics.
The patient is given infusion therapy to increase blood pressure and detoxify. For this purpose, saline or electrolyte infusion solutions are used. To relieve edema, forced diuresis is performed. Hemosorption or plasmapheresis is used.
The course of therapy includes drugs that strengthen the immune system, for example, Imudon, Pentoxyl. Patients are prescribed a diet containing vitamins, especially vitamin C. Resistance to infection is increased by administering antistaphylococcal plasma and leukocyte transfusions.
Symptomatic therapy is carried out to eliminate the various clinical manifestations of the disease.
- For arterial hypotension, hydrocortisone or Prednisolone is administered.
- Ibuprofen, Diclofenac or Paracetamol are used to relieve pain and relieve fever.
- Albumin or donor plasma is used to restore protein balance.
For kidney problems, hemodialysis is prescribed. To prevent blood clots, Heparin and Warfarin are used.
If necessary, the purulent focus is removed surgically. The original sources of infection are revealed. Wounds on the body must be disinfected. Antiseptic dressings based on Levomekol and Dioxidine ointment are applied to the surgical site.
Correctly prescribed therapy leads to the disappearance of chills, a decrease in temperature, and band neutrophils in the blood test decrease. No more rashes appear on the body.
Blood poisoning can only be cured comprehensively, getting rid of the pathogen, the source of infection and supporting the immune system. For effective treatment, it is necessary to know where the outbreak is located and what pathogens kill a person.
Diagnostic measures are very important: studies of blood, urine, feces, and sometimes cerebrospinal fluid, as well as MRI and ultrasound of internal organs, inflammation of which could cause blood poisoning. The pathogen can be isolated in several ways.
Isolation of the pathogen from the blood, inoculation into a nutrient medium. After 5 days, we can tell which microorganism caused the inflammation and how sensitive it is to the effects of antibiotics.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a diagnostic method that allows you to identify the pathogen by several molecules using multiple cloning of a certain DNA section, which allows you to get an accurate answer within 2 hours about which microorganism caused sepsis.
Test for procalcitonin - a polypeptide synthesized in the thyroid gland, in a healthy body does not enter the bloodstream, being converted into calcitonin. The presence of procalcitonin is considered one of the most accurate indicators of the presence of sepsis.
Since accurate diagnosis is very important for the complete cure of the patient, laboratory tests are carried out without fail.
But most often these studies take quite a lot of time; express tests such as PCR require high-tech equipment, which is not available everywhere. That is why, most often, treatment begins even before test results are received, given the danger of the condition to human life.
Anti-inflammatory measures: broad-spectrum antibiotics come to the rescue; they are also called reserve, since they are used only in the most serious situations and are able to cope with the overwhelming number of existing pyogenic bacteria and fungi.
Sanitation of the site of inflammation, excision of dying, festering tissue, treatment of the edges of the wound with an antiseptic - the work of a surgeon is extremely important, especially in cases of infection after wounds, surgical interventions, or injuries.
Detoxification therapy: intravenous infusions of glucose and water-salt solutions.
Blood transfusion: in acute sepsis and in a number of other cases with suppressed immunity, the patient requires a transfusion of blood or its components in order to raise the level of leukocytes and increase resistance.
With the right treatment, the result will be noticeable within 2-5 days - a decrease in temperature, an improvement in well-being. If foci of secondary infection appear, like metastases, spreading further and further from the source of infection, the treatment method should be urgently changed.
DETAILS: Heart excitement, sharp pain - All about hypertension
Treatment is carried out only in a hospital, in an intensive care ward, under the constant supervision of doctors and medical staff.
It is impossible to cure blood poisoning in a short time; no less work and time will be required to restore strength, therefore not only treatment, but subsequently following all the doctor’s recommendations are important for the patient and his health.
Therapy is aimed at fighting the disease and increasing the body's defenses. Treatment includes several stages and should be carried out exclusively in a hospital setting.
Surgical intervention consists of complete removal of the affected tissue (if possible), as well as fluid accumulating in the wounds, ensuring a constant outflow of pus. Sutures are placed on the surface of the wound.
- levomekol;
- dioxidine ointment;
- levosin.
Intensive treatment includes taking antibiotics and using antiseptic drugs. Before using them, it is necessary to analyze the sensitivity of identified microorganisms to them.
- cefatoxime metronidazole;
- cephelim metronidazole;
- ampicillin aminoglycoside.
In the absence of a response from the body, the following may additionally be prescribed:
- vancomecin;
- fluconazole;
- linezolid;
- caspofungin.
The duration of taking antibacterial drugs is determined by the attending physician and ranges from 6 to 10 weeks. Additional measures are shown:
- anti-inflammatory therapy with glucocorticoids (hydrocortisone, methylprednisolone);
- detoxification treatment – removal of toxic substances from the body;
- infusion therapy - transfusion of electrolytes, fat and protein emulsions;
- immunoreplacement therapy - taking immunoglobulins. The most effective is the administration of pentaglobin for 3 days at a dosage of 5 ml/kg;
- prevention of thromboembolic complications (administration of sodium heparin).
Forecast
It should be noted that sepsis is quite severe. The mortality rate, depending on the type and nature of the course, can reach 50%, and with the development of a septic shock state, this figure is even higher.
The prognosis for blood poisoning is always serious. In the fulminant course of sepsis, mortality is inevitable in 85–99% of patients exposed to bacterial aggression.
The disease is most severe in elderly patients and newborns.
Causes and mechanism of development of sepsis
The development of the disease is due to the spread of pathogens along with the bloodstream throughout the body. As a result of transportation, bacteria infect various systems. A massive attack of tissue leads to rapid damage to organs and membranes. This aggravates the course of the pathology.
Most often, blood sepsis develops as a result of infection from the external environment through the respiratory system. This is due to the presence of bacteria in the air. The risk of infection increases if a person is forced to stay in unfavorable conditions for a long time or be near infected people. Less commonly, pathology develops due to infectious diseases of the abdominal cavity or genitourinary system. Additionally, lesions can be found in the oral cavity, after surgery, etc.
Cryptogenic sepsis is characterized by the absence of a gate of entry. The diagnosis is made if during examination and treatment it was not possible to detect the source of infection, but bacteria and characteristic symptoms are present.
Most often, the cause of pathology is bacteria, but in some cases infection occurs by parasites, fungi or viruses. Previously, cases of infection with gram-negative strains were more often recorded. Currently, most incidents involve infection with gram-positive bacteria. The most common pathology is caused by staphylococci; Klebsiella, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli are also found. The development of fungal sepsis in most cases is associated with infection with Candida.
Diagnosis of the condition
The criteria for identifying sepsis are:
- the presence of a focus (it is not always possible to detect it);
- symptoms of general severe intoxication;
- multiple organ failure;
- secondary purulent metastases;
- positive blood culture results for sterility.
It should be taken into account that in infections without sepsis, bacteria are also detected when they are in the blood for a short time, and with antibiotic therapy, a quarter of patients with a septic process have negative indicators. Therefore, a blood test should be performed at least 3 times, preferably during the period of maximum temperature rise.
Patients are also indicated for microbiological examination of sputum in case of a lesion in the lungs, urine in case of urological infections, cerebrospinal fluid in case of brain lesions, discharge from a wound or the contents of a purulent skin lesion.
In order to urgently identify the pathogen, PCR diagnostics of infections is used. It is based on the detection of microbial DNA in any biological fluid. Its reliability exceeds the result of cultures or other blood tests (detection of anemia, high ESR and leukocyte levels with a shift to the left).
The main symptoms of septicemia and the mechanism of its development
Signs of septicemia:
- The current is almost always lightning fast. This condition lasts only a few days. In the most severe cases, death can occur very quickly;
- normal work and, of course, the body’s condition deteriorate greatly;
- most often occurs in children under 3 years of age;
- The causative agents of the disease are considered to be the cocci family;
- the patient’s life will depend on quick diagnosis and timely treatment, since the onset of the disease manifests itself only as a respiratory infection, and other symptoms can appear very quickly;
- the inflammatory focus is usually quite small in size, sometimes it is impossible to determine it.
The development of symptoms occurs in several stages:
- Body temperature rises to 40. This happens because the toxins released by pathogenic bacteria immediately affect the center of the brain that is responsible for regulating body temperature. As a result, this condition leads to the production of “excess heat,” which manifests itself in an increase in temperature. The patient's pulse quickens, severe chills and sweating appear.
- Subcutaneous hemorrhages. They are usually formed due to the fact that bacteria and their own immune system destroy the walls of large and especially small vessels. As a result, they burst and blood gets under the skin. At first, only small dots appear on the body, which later merge into large red spots. After this, blisters and ulcerations appear.
- The normal functioning of the entire body is disrupted. Appetite decreases sharply.
- Severe yellowness of the skin and visible mucous membranes. Jaundice appears due to liver dysfunction. Bilirubin, which must be processed in the liver, begins to enter the circulatory system and settle in the cells of the brain and skin.
- The function of breathing and blood circulation is impaired. Breathing becomes shallow, pulse quickens. There is also a strong decrease in blood pressure.
- Damage to the digestive system. With sepsis, the intestines, stomach and pancreas are affected. Severe nausea, uncontrollable vomiting and diarrhea appear.
Types of cryptogenic sepsis
Based on the time course, there are five types of blood poisoning:
- Fulminant. It is also considered the sharpest. It got its name because all the symptoms appear very quickly. The process of purulent inflammation itself occurs almost at lightning speed. There is a persistent disruption in the normal functioning of most internal organs. The general condition of such patients deteriorates quite quickly, so in this case, the patient’s death is possible after two days.
- Acute—symptoms appear more slowly. This condition can last about 1.5 months.
- Subacute - characterized by a duration of 1.5 to 4 months.
- Recurrent - the course of the disease is wavy. Remission is followed by a deterioration in general condition. This type of sepsis is considered to be one that lasts more than six months.
- Chronic septic condition. Since all the protective functions of the body are reduced, there is an area in the body that is stably affected by the inflammatory process, which does not heal for too long. The chronic form can last for years, thereby increasingly depleting the patient’s body.
There are several types of disease in accordance with changes in some organs:
- Septicemia. A persistent disruption in the functioning of the entire body begins. The general condition of a person is noticeably disturbed. Although the process of inflammation occurs in many organs, there are still no purulent foci. The progression of this form is almost always extremely rapid or acute.
- Septicopyemia is a type of blood infection that causes the formation of foci of suppuration of various sizes in some internal organs.
- Septic endocarditis.
The basic principle of treating blood poisoning is based on finding and eliminating foci of infection.
The maximum possible doses of antibiotics are selected for the patient, depending on the pathogen identified, for example, for staphylococcal sepsis, the drugs “Fuzidin” and “Refampicin” are used.
Sepsis is one of the terms used to describe blood poisoning. This is a potentially life-threatening infection caused by large numbers of bacteria entering the bloodstream. Sepsis affects thousands of patients every year.
It is for this reason that people with existing diseases are at risk for blood poisoning. Severe infectious diseases, in particular pulmonary ones, often lead to the development of sepsis.
These signs are typical of meningococcal septicemia, a type of blood infection caused by the bacterium meningococcus, which can also cause meningitis.
A strong immune system is the best defense against sepsis. Elderly people and newborns are at particular risk of developing sepsis.
Sepsis can also occur with any type of treatment that requires the use of invasive equipment, such as the insertion of a catheter.
In addition, sepsis can cause septic shock, as a result of which the patient experiences a sharp decrease in blood pressure, leading to multiple organ failure.
Sepsis is treated by administering antibiotics intravenously. When tests determine the presence of specific bacteria that cause sepsis, specialists prescribe a specific type of drug to treat septicemia.
Sepsis is caused by bacteria that enter the bloodstream from the intestines, mouth, skin surface, urinary tract and other organs and tissues.
However, this does not mean that every purulent process necessarily ends in sepsis.
We will try to answer these questions in our article, but first we will dwell a little on the classification of sepsis in general and introduce the reader to the main types of this serious disease. Therapeutic sepsis occurs against the background of profound immunodeficiency in weakened patients.
In the acute form of sepsis, events do not develop so rapidly (up to a week). Whether chronic sepsis exists in children is a controversial issue.
This is a summary of sepsis in general, but the subject of our discussion is sepsis in newborns (neonatal and postnatal), which we should return to.
If according to statistical data, sepsis occurs in up to 0.4% of cases per 1000 newborns, then premature babies make up the majority in this proportion.
How is sepsis treated?
In this regard, hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN), included in the list of factors contributing to sepsis, is not ignored. Severe intoxication, signs of multiple organ disorders, a significant shift in the general blood test formula and other laboratory tests indicate the height of the disease.
Postnatal sepsis usually allows some time to think and take action. It does not develop so quickly, since the formation of the primary focus will take a couple of days, or even weeks. Indicators of a general blood test change slightly; only symptoms of intoxication indicate the disease.
The course of this process is acute, with a significant shift in the general blood test (a huge number of leukocytes). In case of intrauterine infection, it is mandatory to examine the placenta by a pathologist in order to identify the inflammatory process that caused sepsis in the newborn.
And this applies not only to umbilical sepsis, but to the entire infectious process. Sepsis leads to death in every fourth case of the disease, since a large number of bacteria and toxins enter the patient’s blood. Sepsis is diagnosed based on a medical history, a physical examination, and blood tests to check for bacteria.
Source: https://rawalan.freezeet.ru/kak-dolgo-protekaet-sepsis/
Diagnosis of pathology
To make an accurate diagnosis, a specialist needs to draw up a clinical picture and conduct some types of diagnostics. If we are talking about a suspicion of an advanced stage of the disease, in this case, diagnostics and the necessary manipulations are carried out exclusively in a hospital setting. To confirm the diagnosis, the patient must undergo the following:
- Determine whether the norm of basic indicators in the blood and urine is elevated.
- Identify the causative agent of the disease (bacteria, infections, fungi), if any.
- Conduct an ultrasound examination of the organs that are most often affected by sepsis. These include the kidneys and liver.
- Assessment of thyroid function.
- Undergo fluorography and, if necessary, take an x-ray of the lungs on four sides. This manipulation is needed to assess the condition of the lungs.
Classification
Depending on the speed of development, sepsis is divided into:
- fulminant – this species is characterized by rapid development of all manifestations in 1–2 days. Patients experience significant deterioration in the functioning of all organs. The likelihood of death is very high;
- acute – the disease develops slowly, symptoms of blood poisoning appear gradually over 5–7 days. The patient experiences chills, bluish skin, rapid breathing and heartbeat, increased sweating, clouding of consciousness;
- subacute – lasts up to 4 months, develops against a background of weakened immunity. It is distinguished by the presence of a pronounced rash and wave-like changes in temperature. Consciousness remains clear. Mortality reaches 50%;
- chronic – develops over several years, symptoms may appear periodically. In some cases, the patient is found to have a long-term non-healing focus of inflammation, and a significant deterioration of immunity is recorded.
The changes occurring in the body make it possible to distinguish:
- septicemia – a general deterioration in the body’s condition, characterized by the acute development of an inflammatory reaction and the absence of foci of infection in the internal organs;
- septicopyemia - a condition characterized by the formation of multiple ulcers in various organs;
- septic endocarditis – inflammation found on the surface of the heart valves.
Depending on the mechanism of development of the condition, the following are distinguished:
- surgical – occurs as a complication of purulent diseases after surgery. Develops when an infection enters the blood;
- obstetric and gynecological – manifests itself after complicated childbirth and abortion;
- urosepsis – occurs as a consequence of inflammatory phenomena of the genitourinary organs (cystitis, urethritis, prostatitis, pyelitis);
- cutaneous – the spread of infection occurs through damage or purulent diseases of the skin (burns, wounds, boils);
- pleuropulmonary – develops as a complication of purulent lung diseases (pneumonia, pyothorax);
- intestinal – differs in the location of the source of infection in the abdominal cavity;
- otogenic – is a complication of purulent otitis. May spread to the brain and contribute to the development of meningitis;
- rhinogenic – develops with extensive spread of infection from the nasal sinuses;
- tonsilogenic - detected against the background of severe sore throats.
Clinical manifestations of sepsis are divided into symptoms of intoxication of the body and symptoms of damage to organs and systems.
Symptoms of body intoxication:
- intermittent or intermittent fever - alternation of close to normal and sharply elevated body temperature (40 degrees or more). A rise in body temperature is accompanied by chills; decrease in body temperature - profuse sweat;
- severe weakness, loss of appetite;
- pale icteric, pale gray skin color;
- pointed facial features;
- shortness of breath, tachycardia, low blood pressure.
Symptoms of damage to organs and systems:
- violation of blood clotting and vascular permeability: hemorrhages in internal organs; hemorrhagic skin rash;
- signs of heart failure: shortness of breath, symmetrical swelling of the legs, tachycardia, arrhythmia, heart murmur, heart valve damage, etc.;
- signs of pulmonary failure: rapid breathing, cough, wheezing or lack of breathing in the lung (segment, lobe of the lung), etc.;
- signs of renal failure: weakness, pallor, high levels of urea, creatinine, potassium in the blood, decreased specific gravity of urine, etc.;
- signs of liver cell destruction and liver failure: yellowness of the sclera and skin, enlarged liver, high levels of bilirubin and liver enzymes (AST and ALT), etc.;
- adrenal insufficiency: severe weakness, low blood pressure, sweating, cold hands and feet, cardiac arrhythmia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, decreased amount of urine, confusion, encephalopathy, coma;
According to the speed of flow, sepsis can be:
- fulminant - symptoms develop in 1-2 days;
- acute - a week;
- subacute - up to a month;
- chronic - lasts for months and years with periodic exacerbations.
Based on the presence of secondary (metastatic) purulent foci:
- with the presence of metastatic abscesses - septicopyemia. Manifested by intoxication and symptoms of organ damage from metastatic ulcers;
- without metastatic abscesses - septicemia. It manifests itself in a lightning-fast and acute course with clear signs of intoxication of the body.
According to the severity of the course, sepsis is divided into:
- normal course (sepsis);
- septic shock is an extremely severe course of the disease. The symptoms are similar to those during the normal course, with the exception of sharply reduced blood pressure, which cannot be normalized even with the help of resuscitation measures. As a result, microcirculation suffers and a deficiency of tissue blood flow is formed. The mortality rate from septic shock is at least 50%. Patients die from increasing tissue hypoxia.
Neonatal sepsis is one of the main causes of death in children in the first month of life. The causative agent of infection (staphylococcus, streptococcus, E. coli, etc.) enters the body of the fetus (intrauterine variant) or newborn (neonatal variant) through the umbilical cord or umbilical remnant, damaged skin upon contact with the infected birth canal of the mother, through the mother’s blood.
Based on the time of development, sepsis in newborns is divided into early neonatal (up to 8 days after birth) and late neonatal (8-28 days after birth).
Symptoms of sepsis in newborns: increased body temperature above 40 degrees (in premature babies - a decrease in body temperature to 35-36 degrees), dirty gray skin color, lethargy, refusal to eat and regurgitation of food, tachycardia, low blood pressure, shortness of breath, swelling, hemorrhages on the body.