Renal colic is an acute painful attack that is caused by a sudden disruption of the passage of urine through the urethra, increased pressure inside the pelvis and, as a result, renal ischemia. Colic is characterized by severe cramping pain in the lower back, painful and frequent urination, psychomotor agitation, nausea and vomiting.
In urology, renal colic is regarded as a condition requiring immediate assistance, in which it is necessary to quickly relieve acute pain and normalize the functioning of the kidney. It is important to understand: colic is not just an attack of pain, it is a signal from the body that the kidney is in danger.
What is renal colic
Renal colic is accompanied by spasms of smooth muscle muscles. The disease manifests itself as severe pain. An attack involves several factors simultaneously, in particular the occurrence of spasms. An upper urinary tract obstruction causes urine to accumulate in the kidneys, causing severe pain.
Important! According to experts, in 15% of cases the disease is a consequence of other diseases, in particular, renal colic occurs in the presence of infectious diseases.
Picture of an attack of renal colic in women
Renal colic is not just an attack of pain. It comes with many important features:
- Pain in renal colic is felt, as a rule, in more than one lumbar region. It spreads along the ureter to the groin, perineum and inner thigh;
With renal colic, pain spreads to the groin area and inner thigh
- with renal colic, it is impossible to find any position of the body in space that alleviates painful sensations;
- The peculiarity of the attack is its sudden onset. Renal colic can develop against the background of complete well-being. At the same time, a woman may not be aware of the presence of problems in the urinary system;
- renal colic, as a rule, is preceded by one of the following situations: long walking, driving on uneven roads, heavy physical work, taking diuretic medications and a large volume of fluid;
- against the background of a painful attack, a woman may notice frequent urges or pain when urinating;
- at the end of the attack, a large volume of urine is released, often mixed with blood;
- intense pain often causes other disorders in the body: nausea, vomiting, bloating, stool retention, fever.
After the pain attack disappears, there is a high risk of recurrence of an episode of renal colic (80%).
Causes of renal colic and risk factors
Doctors are convinced that the main cause of colic is kidney stones. This is not an age-related disease; it occurs in both young and more mature people. Happens in both women and men. The most common causes that cause an attack of renal colic are:
- genetic predisposition;
- ignoring lumbar pain;
- various kidney diseases;
- intense physical activity;
- urinary tract infections;
- the presence of inflammatory processes in the body;
- narrowing or spasm of the ureter;
- insufficient fluid intake.
So, first of all, you should pay attention to such a factor as genetic predisposition. There is a high probability of the disease occurring in those who have close relatives suffering from urolithiasis.
Renal colic does not always occur immediately. Attacks of pain in the lumbar region can bother you for a long time; often a person does not even suspect that the discomfort in the lower back is a manifestation of a serious illness.
Ignoring painful attacks, many do not begin treatment in a timely manner. If pain in the lumbar region is a sign of stones or sand in the kidneys, renal colic is unlikely to be avoided.
If the pain is accompanied by a high body temperature, which persists for a month, this indicates that an infection with the blood or lymph has entered the kidneys. In this case, a symptom such as renal colic will certainly appear.
The triggering factor for an attack is serious overexertion, in particular heavy lifting or intense training in the gym.
Kidney colic occurs due to chronic urinary tract infections, impaired circulation of the renal vessels and insufficient fluid intake.
There are other causes of renal colic. Often the disease manifests itself due to untreated cystitis, nephritis, hydronephrosis. Pyelonephritis can cause renal colic in women. Often the factor causing colic is:
- polycystic kidney disease;
- diseases of the uterus;
- damage to the fallopian tubes;
- inflammation of the appendages;
- abortion or pregnancy;
- rupture of ovarian tissue;
- twisting of cysts.
Emergency care for renal colic
Help with renal colic should be provided by a doctor, so if severe pain appears in the abdomen and lower back, you should urgently call an ambulance. The fact is that, according to clinical signs, colic is similar to many other diseases and pathologies, which are also accompanied by lumbar and abdominal pain: acute appendicitis, aortic aneurysm, ovarian torsion, ectopic pregnancy, intercostal neuralgia, acute pancreatitis, thrombosis of mesenteric vessels, cholecystitis and etc.
If renal colic has not occurred to a person for the first time, and he is confident in this diagnosis, then before the ambulance team arrives, the patient’s condition can be alleviated.
Emergency care for renal colic is:
- Applying a heating pad to the lower back or placing the patient in a warm bath to reduce spasm of the ureter and blood vessels, this will improve the blood supply to the kidney, and a blood clot or stone may slip into the bladder;
- When taking any antispasmodic and analgesic drug, preferably Papaverine, Baralgin or No-shpa, as a last resort, if these drugs are not in the medicine cabinet, you can take Nitroglycerin.
You need to understand: the procedures described will help, provided that it is really renal colic. Otherwise, thermal procedures and painkillers can only do harm, for example, in case of acute appendicitis, a person’s condition sharply worsens after taking a bath and No-shpa.
Upon arrival, the emergency doctor also uses analgesics and antispasmodics to relieve the attack, but in the form of injections - they are more effective.
Symptoms
Until the disease begins to actively manifest itself, as a rule, a person does not take seriously the periodic pain in the kidney area.
The most striking symptom of renal colic manifests itself in the form of unexpected, severe, ongoing pain that requires immediate treatment. It is paroxysmal in nature.
The pain syndrome is very strong, the person literally cannot find a place for himself, trying to take a comfortable position. All attempts to lie down and not move, so as not to cause yourself even more pain, are in vain.
During an attack, pain is often localized in the iliac region, but can also affect the lower abdomen. At the same time, pain appears when urinating, because of this, emptying the bladder becomes problematic, and the urge is constantly present.
Renal colic can be unilateral or bilateral. Renal colic on the left occurs when there are problems with the left kidney; with right-sided pain syndrome, the right kidney is unhealthy. When both kidneys are diseased, bilateral renal colic occurs. The latter type is accompanied by pain that radiates to the stomach and lower back.
Renal colic manifests itself with various symptoms and requires treatment. Often pain occurs in different parts of the abdomen and is accompanied by the urge to have a bowel movement. Due to the unpleasant pain, it is extremely difficult to go to the toilet, and intestinal bloating occurs.
Symptoms of renal colic are nausea and vomiting, which are often accompanied by fever.
An attack of renal colic is often provoked by long runs or brisk walking. Pain occurs in the abdomen, lower back, hips and perineum.
The symptoms of renal colic are the same for both women and men:
- pale skin;
- increased sweating;
- weakness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- thirst;
- fever, chills;
- pressure surges;
- bloating;
- pain shock.
Important! The patient experiences severe pain (on average four hours), it constantly intensifies. Conventionally, pain can be divided into three phases:
- acute;
- constant;
- extinction phase.
The first phase disturbs a person at night or early in the morning, thereby awakening him. At first it is quite soft and aching. Afterwards it slowly but gradually intensifies.
Attacks occur with varying frequency. The aching pain is replaced by a sharp one. Often, too much pain leads to loss of consciousness, shock, and numbness of the limbs.
The second phase is characterized by the duration of attacks from approximately one to ten hours. It is simply impossible to endure such pain for a long time, so during this time, as a rule, the patient manages to seek help from a doctor.
The last phase is extinction. Its duration is about three hours. Often the pain exhausts a person so much that after taking a painkiller tablet he falls asleep.
When the attack ends, the pain syndrome subsides. A person stops experiencing pain when urinating.
To establish the cause of renal colic and select the correct treatment regimen, you need to consult a doctor. It is important to do this immediately.
After examination and diagnosis, the doctor will rule out diseases with similar symptoms:
- appendicitis;
- pancreatitis;
- cholecystitis;
- hernia;
- stomach ulcer.
As you can see, the range of diseases with similar symptoms is extremely wide.
Our doctors
Kochetov Sergey Anatolievich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
32 years of experience
Make an appointment
Mukhin Vitaly Borisovich
Urologist, Head of the Department of Urology, Candidate of Medical Sciences
32 years of experience
Make an appointment
Perepechay Dmitry Leonidovich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
Experience 38 years
Make an appointment
Khromov Danil Vladimirovich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
33 years of experience
Make an appointment
First aid
Sometimes it is not immediately possible to contact a qualified specialist. You should know how to properly provide first aid to a person who has an attack of renal colic.
For pain, thermal procedures are a very effective remedy: apply a heating pad or take a hot bath. A painful attack will be relieved by a strong analgesic; it should be taken as early as possible.
Tablets are not the most effective remedy. It is advisable to administer the drugs intramuscularly or intravenously. Medicines can relieve the effects of renal colic, in particular seizures.
Complications and prognosis
The prognosis for treatment of renal colic is usually favorable. However, a prolonged attack, in which help was not provided in time, can lead to negative consequences:
- renal failure;
- kidney infection;
Pyelonephritis is a common companion to renal colic
- penetration of bacteria into the vascular bed from the source of inflammation in the kidney (urosepsis).
Diagnostics
Before treating a symptom of renal colic, you should visit a specialist. He will carry out the necessary differential diagnosis of the disease and make a diagnosis.
Diagnostic methods that are commonly used to diagnose diseases of the urinary system:
- Analysis of urine;
- general blood test;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- urography;
- chromocystoscopy;
- CT (computed tomography);
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
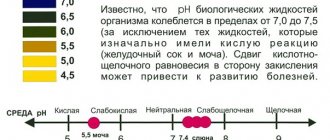
A very important laboratory diagnostic method for determining the disease is urine analysis. If there are blood streaks in it, this may indicate the presence of kidney stones. The pH level is no less important.
In order for the diagnosis to be as accurate as possible, it is advisable for the patient to provide a pebble for analysis. To get it, you need to urinate into a container (preferably through a strainer).
The results of a general blood test will also help establish the diagnosis. With renal colic, the patient experiences an increased level of white blood cells and an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
Ultrasound of the kidneys and urinary tract is an equally effective method for diagnosing the disease. With the help of this study, the presence of not only stones, but also malignant formations is detected.
Stones in the urinary system are visible on X-ray examination.
During chromocystoscopy, the doctor uses a cystoscope to examine the condition of the mucous membrane of the bladder and ureter. Next, the patient is injected with a substance that causes the urine to turn dark blue.
The specialist makes a conclusion about the presence or absence of kidney pathology based on the rate of excretion of colored urine and the color intensity. The procedure does not require special preparation, is quite simple and safe, but is performed under anesthesia, as it is quite painful.
If there are difficulties in making a diagnosis, a CT scan of the pelvis and retroperitoneum is performed. Thanks to the three-dimensional image, the specialist is able to view the affected organ from the desired angle. This method is one of the most effective. CT scan is prescribed for complex cases or before surgery.
During the initial examination, the doctor collects an anamnesis of the disease. The specialist pays special attention to genetic predisposition to the disease. He makes the first conclusions after talking with the patient, based on complaints and symptoms.
The nature of the pain, its provoking and relieving factors are important. The doctor also palpates the patient's abdomen and pelvic organs. Pain occurs in the lumbar region during tapping.
Important! There is a high probability that additional examination will be needed to determine renal colic, especially if the symptoms are unclear. Hospitalization is often required.
Renal colic occurs not only in adults, but also in children. It manifests itself mainly as pain in the abdomen and lower back. The attack is quite short (about 15 minutes). The baby cries, the body temperature is elevated, weakness, vomiting and dizziness are observed. In this case, you cannot try to cope on your own. You should call an ambulance as quickly as possible.
The same recommendations must be followed if renal colic occurs in a pregnant woman, because the disease can provoke premature birth. There is a high probability of an attack in the third trimester. Symptoms: pain in the lower back, radiating to the genitals and hips.
There are no symptoms that are characteristic only of renal colic and exclude any other disease, so it is important to consult a doctor who will distinguish the disease from other diseases.
Features of the formation and excretion of urine
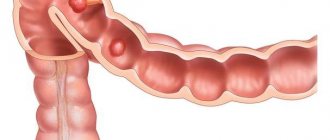
To remove all waste and toxic substances in the human body, there is not just one organ, but a whole system of several interconnected structures. It is dominated by special paired organs located in the lumbar region - the kidneys. This is where the path of all metabolic products to be removed from the body begins. All blood passes through a special filter located in the vascular glomeruli many times a day. Here, the liquid part of the blood, deprived of its cells, under pressure pumped by the heart muscle, passes from the vascular bed into the structures of the glomerulus.
Nephron is the main structural element of the kidney
However, this filtrate contains quite a lot of useful substances, which the kidneys return to the bloodstream. This process of separation into useful and harmful occurs in special tubes - the renal tubules. Their final sections are collected in several cups, from which the urine of the composition enters the pelvis. It is a cavity that serves to temporarily accumulate urine, which subsequently enters a long tube - the ureter. It connects the renal pelvis with the bladder, from where urine, after temporary storage, is discharged in portions through the urethra (urethra).
The kidney is the main organ of the urinary system
All the blood, from which harmful substances are subsequently filtered, is delivered to the kidney through the renal artery system. In the area of the cups there are special vascular venous plexuses - fornixes. Purified blood is carried through the renal vein towards the heart.
Renal colic is a sudden attack of intense pain in the lumbar region, which occurs against the background of a violation of the outflow of urine from the kidney . Often found in women, including during pregnancy. This situation requires medical intervention, since a prolonged attack can destroy a functioning kidney.
Further treatment
Treatment of renal colic in women and men begins with stopping the attack. To do this, you need to take a painkiller tablet and apply heat to the sore spot. There is no need to refuse hospitalization; only in a hospital you don’t have to worry, because the patient’s condition is monitored by specialists around the clock.
In case of a prolonged attack, the patient is prescribed drugs containing novocaine. Antibiotics are prescribed when there is an inflammatory process in the body. If stones are present, special methods are used to crush them and remove them from the body. During this time, the patient takes painkillers.
Urgent hospitalization is needed if:
- renal colic has spread to both sides;
- body temperature is increased;
- the painkiller does not work;
- the patient has only one kidney;
- disease in the acute stage;
- there is a suspicion of an inflammatory process.
During treatment, the patient should adhere to bed rest and remain completely at rest. In addition, a strict diet is required (by the way, it should also be followed for prevention).
According to the prescription of specialists, a person with renal colic is recommended to eat a diet according to table menu No. 10, that is, under no circumstances should one eat fatty, spicy, smoked foods, baked goods, dairy products, or sweets.
It is important to eat balanced and on time. It is necessary to rest, properly distribute the load and adhere to the correct daily routine.
If stones are present, sometimes they are removed surgically to relieve spasm if drug treatment is ineffective. Also indications for surgery are cyst rupture, purulent abscesses, and blockage of the urinary tract.
If an illness occurs, the patient should not take pills for pain on his own, because large doses will be required, which will negatively affect both the underlying disease and the condition of the body as a whole.
Important! If you are not absolutely sure that the pain is caused by the passage of stones, you should not heat the sore spot.
It is possible to exclude a relapse and eliminate all the causes that provoked the occurrence of renal colic. The main thing is that you should not endure pain or try to cope with colic on your own, without the participation of a doctor. It is advisable to exclude all factors that can provoke the disease; first of all, you need to cure urolithiasis.
If desired, you can combine traditional medicine with folk medicine. There are many effective recipes for decoctions that will help cope with the disease and the pain that accompanies it.
Lingonberry leaves
To prepare the decoction, you need to use dry leaves of the plant, which are poured with boiling water and brought to a boil over low heat. The broth should be cooled and strained. You can add a little honey to it. You need to drink throughout the day a few minutes before meals.
Carrot seeds
Carrot seeds must be poured with boiling water and left in a warm place for 10-14 hours. After this, you should drink 3 tablespoons five times a day, half an hour before meals. This remedy is very effective for kidney diseases, including stones.
Chamomile + yarrow
You need to heat the olive oil well, then put chamomile flowers and yarrow into it. Bring almost to a boil, set aside, cool. Use the resulting mixture as a compress. It's better to use gauze.
Treatment
Renal colic in men leads to a deterioration in the general condition and leads to bedridden conditions. Therefore, if pain and signs of intoxication appear, you should consult a doctor. After the condition improves, it is necessary to go to a medical institution to see a generalist - a general practitioner, who, after an initial history and examination, refers the patient to a urologist and nephrologist. Specialist doctors prescribe diagnostic procedures that help determine the cause of renal colic. If a disease of the digestive system is suspected, the therapist refers the man to a gastroenterologist.
Diagnostics
When making a diagnosis, differential diagnosis plays an important role, since renal colic, as a symptom, can indicate many pathologies:
- Acute appendicitis occurs with a similar symptomatic picture. The pain covers the right side of the lumbar region, side and abdominal cavity. Inflammation of the appendix and renal pathologies can be distinguished by the nature of vomiting, in the latter case it occurs immediately, and by the position of the patient - with appendicitis the patient lies motionless, when with colic “there is no place.”
- Hepatic colic has similar symptoms, but it can be differentiated by the distribution of the pain syndrome. In the first case, the pain covers the chest, right shoulder blade and shoulder, in the second it radiates to the bottom - the groin, thigh, leg.
- Intestinal obstruction is characterized by pain in the intestinal area and has a cramping nature, occurring with hyperthermia above 380C. With renal colic, the pain syndrome is constant, and the body temperature does not exceed subfebrile levels.
- Radiculitis has a more pronounced pain syndrome and does not lead to an increase in thermometer readings, unlike renal colic.
- Inflammation of the genital organs and renal colic can be differentiated by the location of the pain. The first pathology leads to pain in the lower abdomen, which radiates to the sacral region, while the second causes discomfort in the lumbar region.
To make a diagnosis, laboratory tests of urine and blood are prescribed. Gemma allows you to determine the presence of an inflammatory process in the body, the performance of paired organs, acid-base balance, as well as the level of electrolytes, calcium and sodium.
An increase in the number of leukocytes in urine indicates an infection of the kidneys, hematuria - blood in urine - indicates urolithiasis. Protein and mucus also indicate the presence of pathological processes. A change in acidity indicates the presence of bacterial flora or calculi. To identify the causative agent of the infectious-inflammatory process, a bacteriological urine test is prescribed.
To study the condition and performance of paired organs, instrumental research methods are used - ultrasound, X-ray, excretory urography, CT and MRI.
Drug treatment
Based on the data obtained, symptomatic treatment of renal colic in men is carried out.
To relieve pain, oral or intravenous administration of antispasmodic and analgesic drugs is prescribed: No-shpa, Papaverine, Analgin, Ibuprofen. In case of intolerable syndrome and lack of effectiveness of these medications, novocaine blockade is performed by injecting the drug into the perinephric tissue.
To reduce body temperature, antipyretic drugs are used - Paracetamol, Panadol, Efferalgan. Anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs are also prescribed, which will help not only cope with hyperthermia, but also stop the inflammatory process. Such drugs include Ibuprofen and its derivatives, Ketorolac, Analgin, Acetylsalicylic acid.
Next, treatment is carried out for the underlying cause of the disease, which led to the development of renal colic. To treat nephritis, antibacterial drugs of the penicillin series (Amoxicillin), cephalosporins (Cefuroxime, Ceftriaxone) and macrolides (Erythromycin) are prescribed. In the case of a viral etiology of inflammatory pathologies, antiviral drugs are used, in case of a fungal nature - antifungal agents (Biseptol, Etazol).
For urolithiasis, medications are prescribed that will help dissolve and remove stones from the organs of the urinary system: Cyston, Avisan, Olimentin.
Other therapies
If the symptoms are clearly expressed and do not improve after drug therapy, the doctor recommends surgery. In case of urolithiasis, surgical intervention is aimed at crushing and removing stones. For this purpose the following is used:
- Remote lithotripsy involves the destruction of stones at a distance using ultrasound or laser waves. May cause damage to healthy tissue.
- Contact lithotripsy involves the destruction of stones with air, laser and ultrasound. They are performed through a puncture in the skin (percutaneous nephrolithotomy) and the urethra (urethroscopy). The methods help prevent damage to neighboring organs.
- Endoscopic surgery involves 3 incisions in the tissue in the kidney area, through which the solid tumor is removed.
- Open abdominal surgeries are used when there are contraindications to minimally invasive methods and to provide emergency care.
If renal colic is a sign of nephrolithiasis, then ureteral catheterization is used to relieve pain. Helps relieve symptoms and remove stones without damaging the ureteral tissue. In addition, installing a drainage system allows you to restore the normal outflow of urine and remove crushed stones.
An important place in treatment is occupied by diet, which is based on treatment table No. 7 and its modifications. Allows you to reduce the load on paired organs and prevent complications. During treatment, the patient must give up “harmful foods”: fried, fatty, smoked, carbonated, sweet drinks, canned food. The basis of the diet should be vegetables, fruits and cereals. For the treatment of urolithiasis, the diet is prescribed based on the chemical structure of the stones.
Renal colic is not an isolated disease. This is a symptom that indicates the presence of pathological processes in the kidneys. Most often it is a sign of urolithiasis. Occurs with severe symptoms of intoxication and hyperthermia. To relieve pain, antispasmodics and painkillers are used, as well as treatment aimed at eliminating the underlying cause of the disease.
Causes
The causes of renal colic in men are associated with the age and place of residence of the patient. The average age of people with this disease is 30-50 years. A hot climate, high humidity and poor environmental conditions contribute to the occurrence of renal colic.
Impaired outflow of urine can be caused by the presence of stones in the urinary organs, clots of pus or blood, swelling of the mucous membranes, tumor formations, kinking or compression of the ureter.
In medicine, the following 8 private risk factors for the development of renal colic are identified:
- Heredity - in 50% of cases there is a disease transmitted from generation to generation.
- Professional activity: working with heavy weights, in a hot shop.
- Excessively intense physical activity.
- Congenital anatomical disorders of the urinary system.
- Malabsorption is a violation of the absorption of nutrients in the small intestine.
- Improper diet - excess salt and protein foods.
- Dehydration or losing too much fluid.
- Trauma to an organ due to blows or an accident, causing compression of the urinary tract.
A symptom in the form of renal colic occurs with the following diseases: nephrolithiasis, urinary disease, wandering kidney, cancer, inflammation, kidney tuberculosis.
The formation of kidney stones in men is 3 times more common than in women, which is associated with the anatomical structure of the urethra. The male urethra is long and narrow, which makes it difficult for stones to pass on their own. The reasons for their formation are metabolic disorders, damage or compression of the organs of the urinary system, congenital anomalies of the structure of the ureters and urethra.
Inflammation of the kidneys - nephritis, pyelonephritis - blood clots or pus can cause difficulty urinating, and as a result, renal colic. Kinking and narrowing of the ureter is caused by changes in the location of the kidney due to congenital anomalies or injuries to the organ.
Colic is not a disease, but a symptom that requires immediate diagnosis.
Colic in the kidneys. What to do?
Symptoms of renal colic in men: treatment with tablets and folk remedies
The manifestation of the disease can be provoked by diseases of the urinary tract. To calm general symptoms, you should lie in hot (moderately) water, use a warm heating pad, and drink an antispasmodic.
If the patient has previously been diagnosed with the diagnosis described in our article, the medications are taken at home, without being provoked by stress factors. All the patient has to do is take a lot of fluids, lie in bed more and use warm heating pads. If a relapse occurs, you must immediately go to the hospital for re-examination.
After an individual consultation with a doctor, you can drink simple decoctions of herbs and berries that help tone up your general condition. You cannot treat yourself with folk remedies. After recovery, the patient must register with a specialist - a nephrologist.
If the cause of the disease were large stones that cannot pass out naturally, surgical methods are used - the stones are crushed inside the organ and removed.
Causes of colic
Colic is a symptomatic complex that occurs when there is difficulty in the flow of urine from the kidney. In this case, the pelvis becomes full, its walls are stretched, and the smooth muscles of the walls of the ureters contract convulsively, trying to remove the obstacle. Due to a decrease in fluid outflow, a narrowing of the blood arterial vessels occurs, which bring blood to the organ for purification and at the same time supply it with oxygen. Blood flow becomes less, and kidney tissue experiences oxygen starvation. As a result, the person experiences severe pain.
The most common cause of colic is the passage of a stone due to urolithiasis. But there are other diseases in which there is a narrowing of the lumen of the ureter and urinary retention in the kidneys. These include:
- inflammatory processes - blockage occurs with mucus or pus;
- tuberculosis - dying tissue can also partially or completely close the outflow;
- nephroptosis, stricture or dystopia lead to twisting or bending of the ureter;
- other diseases (tumors of neighboring organs, edema, hematomas, prostate adenoma, etc.) that put pressure on the urinary duct;
- inflammation of the ducts themselves (hydronephrosis, urethritis, etc.);
- thrombosis of the veins leaving the kidney, their embolism and renal infarction;
- congenital anomaly of the urinary tract.
Colic often occurs during pregnancy due to exacerbation of previously undetected diseases or as a result of pressure on the ureter. In order not to cause harm when acute pain occurs, you need to know what to do in case of renal colic, and what actions are best avoided.
Causes of colic
How to give first aid
When symptoms of the first renal colic appear in men, pain relief must be performed as quickly as possible, since the patient’s condition can deteriorate sharply. It is urgent to call an ambulance, describing in detail the patient’s signs and behavior. To help a person with a pronounced illness, you can resort to the following procedures:
- Take a pain reliever that reduces spasm. If possible, administering an antispasmodic drug intramuscularly will speed up and significantly enhance the effect.
- The influence of heat, for example, applying a heating pad to the lower back with moderate water temperature, dulls the pain. The bathroom helps a lot.
- An important point is preparing the container so that the patient can go to the toilet. The stone that comes out of the canal should be examined for possible chemical reactions, which will further help in selecting the correct therapy.
Possible complications
If the patient was not provided with timely assistance, the disease is in an advanced stage, or treatment was carried out using non-standard medicine methods, or was not carried out at all, the consequences can be extremely severe:
- Serious pathologies of the heart, blood vessels, respiratory organs and nervous system can provoke painful shock, which occurs from acute attacks and spasms.
- Pyelonephritis develops against the background of an advanced state of the genitourinary system or untimely consultation with a doctor.
- Poor bladder function is a serious consequence of poor quality treatment. In the future, the person will not be able to completely empty his bowel movements.
- Purulent discharge inside inflamed organs.
- A gradual state of atrophy that occurs due to the almost complete replacement of parenchyma by connective tissues.
- Significant narrowing of the urinary canal, as a result - atrophy of the urethra.
- Constant retention of urine inside the organ.
- Urinary infection spreads throughout all organs and systems of the body, leading to urosepsis. This complication in 90% of cases is the death of a person.
The disease is associated with male infertility, this should not be forgotten. The optimal solution would be to consult your doctor about reproductive disorders and take the drug Prostatilen AC, which helps keep men's health in good shape.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment of renal colic in men includes supportive care and the administration of medications, which are selected in each individual case separately, as well as the correct dosage:
- Non-narcotic analgesics - for example, Optalgin.
- For severe pain, narcotic analgesics are prescribed (for example, Codeine, Butorphanol, Morphine Sulfate, Oxycodone, Hydrocodone, Meperidine, Nalbuphine).
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - for example, Ketorolac, Ketorolac intranasally, Ibuprofen).
- Inhibitors (for example, Allopurinol).
- Antiemetics (eg, Metoclopramide).
- Antidiuretics.
- Antibiotics (eg, Ampicillin, Gentamicin, Ticarcillin/clavulanic acid, Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin, Ofloxacin).
- Alkalizing agents - (for example, potassium citrate, sodium bicarbonate).
- Corticosteroids (eg, Prednisone, Prednisolone).
- Calcium channel blockers (for example, Nifedipine).
- Alpha blockers (eg Tamsulosin, Terazosin).
But spa for renal colic
Na-spa is an antispasmodic that brings tangible relief during an attack of renal colic, but the pain is usually very intense, so in most cases, according to patients, only 4 tablets taken together bring relief, after which the pain subsides a little, the ureter relaxes and gives way accumulated urine.
IMPORTANT! You can take no-shpa or other antispasmodics (Baralgin, Optalgin, Ketanov) only if pain is present on the left side. But if pain occurs on the right side, it is better to immediately call an ambulance, since the cause of pain in this case can be not only renal colic, but also other diseases that require urgent medical attention, including appendicitis.
The sequence of first aid for renal colic:
- In case of sudden intense pain, applying heat to the sore spot is recommended. This could be a heating pad or a very hot bath. However, if an elevated temperature is present along with an attack of pain, heat is contraindicated, as in cases of chronic cardiovascular diseases.
- Taking one of the above-described antispasmodics (No-shpa, Baralgin), dosage on the package.
- Urgently call an ambulance, since the symptoms of renal colic are very similar to the symptoms of other serious diseases; in this case, treatment and relief of pain is directly related to the precise determination of the cause of the pain.
Characteristics of the disease
Since the attack is provoked by a pathology of the urinary system, the pain zone is in the lumbar region, one side hurts (two at once - very rare). The cause is muscle spasm of the urinary organs. The explanation for the appearance of this spasm is simple: the stones, trying to pass through the thin walls of the ureter on their own, scratch and damage them, and the canal becomes blocked.
Factors that provoke pain
There are a number of certain factors in response to which such an attack may occur in the body:
- Poor diet - spicy, too salty or spicy foods can contribute to the formation of this problem.
- A sharp increase in active physical activity.
- Lifting large loads jerkily.
- Excessive intake of alcoholic beverages.
- Previous surgery.
Causes of the disease
The most common cause of renal colic is urolithiasis. Sand or kidney stones move along the urinary tract of a man along with urine. These stones irritate and injure the surface of the ureters from the inside, causing acute, burning pain.
Urolithiasis is diagnosed in men of all ages, with one peculiarity: in people of productive age, the kidneys and ureter are more often involved in the pathological process, and in older people, the bladder.
The formation of sand and stones is facilitated by dietary errors, hard water, alcohol abuse, thyroid disorders, and gastrointestinal diseases.
A little less often, the cause of colic can be a pathological process in the kidney, which affects the unhindered outflow of urine: its inflammation (pyelonephritis), prolapse (nephroptosis), dilatation (hydronephrosis), tumor. To this list you can add tumor processes in the ureter, as well as any injuries that lead to a narrowing of its passage.
Differentiation from similar diseases
Diagnosing renal colic is quite difficult because it is associated with a group of diseases with similar symptoms. Acute diseases of the abdominal organs are also characterized by nausea, fever, and stabbing pain in the lower back. These include acute appendicitis, biliary colic, gastric ulcer, and volvulus.
It is important to distinguish renal colic from the acute form of appendicitis. In the first case, the pain cannot be reduced and pulsation occurs in the thigh, pubic area, and head of the penis. With appendicitis, the pain is localized in the right iliac region and is relieved by lying on the back or right side.
Hepatic colic is very similar in symptoms to renal colic. The patient also experiences persistent pain, nausea, and fever. But in patients with biliary colic, the nature of the disease is different - symptoms occur after eating too fatty foods, and the pain pulsates in the area of the scapula and collarbone.
The difference between renal colic and acute intestinal obstruction can be done by urinalysis and listening to the abdomen to help detect bowel sounds. The initial symptoms of both diseases are very similar - constant, incessant pain, nausea and vomiting.
Treatment options
Most often, men who have previously been diagnosed with a disease of the urinary system - nephrolithiasis - go to the doctor with renal colic. In this case, you should take a hot bath or put a heating pad on your lower back, take a painkiller tablet (Baralgin, Noshpa, Analgin, Spazgan, Nitroglycerin). An antispasmodic will help relieve pain and spasms, relax the smooth muscles of the excretory organs.
If these symptoms are observed for the first time, then you should not take any action until the doctor arrives. After confirming the diagnosis, drug treatment is prescribed to relieve pain. The main drugs for the disease are: Ketorolac, Drotaverine, Baralgin M.
In cases where renal colic occurs in men with previously identified diseases of the urinary system, the patient has the opportunity to be treated on an outpatient basis, that is, at home. The patient is prescribed plenty of fluids, bed rest and heating pads. If your condition worsens, you should consult your doctor again.
Folk remedies are often used to eliminate renal colic, such as decoctions based on lingonberries and cranberries, taking hot baths and using heating pads. After eliminating all symptoms, you need to undergo additional examination by a nephrologist. Further treatment is formed in connection with the underlying disease, and consists of eliminating the cause of renal colic.
For stone formation, physiotherapy (crushing stones in order to change their position and exit), cystoscopy (an operation to remove stones) is used.
For inflammation of the genitourinary system, drug treatment is prescribed, drugs that reduce the spread of infection, such as Amoxil, Amoxicillin, Cephalexinan, Cefaclor, Ofloxacin.
Prevention and diet
To avoid this painful symptom, preventive measures should be taken.
A diet for renal colic in men includes the consumption of lean meats and fish, eggs, pumpkin, apples, honey, premium pasta, watermelon and melon, decoctions of medicinal herbs (rose hips, cranberries, raspberries, chamomile, lingonberries), and jelly. It is necessary to exclude from the diet foods containing excess salt (salted fish, liver, kidneys, broths, smoked meats, canned food).
The patient should reduce the amount of alcohol, garlic, mushrooms, mustard, cocoa, coffee, chocolate, tomatoes, carrots, spinach, beets, jam, confectionery and flour products. Monitor fluid intake (at least 2 liters per day), avoid stressful situations and hypothermia. To live an active lifestyle.
Consult a doctor in a timely manner for infectious and viral diseases, visit a urologist every six months and undergo general urine and blood tests. Observe daily hygiene measures for the care of the external genitalia, avoid unprotected and promiscuous sexual intercourse.
By nature, representatives of the stronger sex have a predisposition to the formation of calculi (stones), much more often than in women, since the anatomy of the urethra is specific. The urethra is narrow, which prevents the passage of stones naturally. As a result, foreign bodies provoke the process of inflammation, urine flow becomes difficult, and as a result, unbearable cutting pain occurs. In our article we will look at what renal colic is in men on the left: symptoms, causes and signs, treatment, diet, and also how to do first aid for the disease.
Causes and development factors
Renal colic is classified as a nonspecific symptom, since it can be triggered by various causes. Among them:
- Urolithiasis disease. Stones formed in the kidneys can pass through the urine into the ureter. The movement of a stone along a narrow channel causes an unbearable attack of pain. Some stones have sharp “spikes” and can injure the ureter (which is why blood appears in the urine). And sometimes the stone gets stuck in the canal. This leads to a deterioration in the outflow of urine and expansion of the renal capsule.
- Jades. The appearance of renal colic can be caused by various inflammatory processes occurring in the kidneys (for example, pyelonephritis). Such ailments provoke irritation of the bean-shaped organ, as a result of which the latter reacts with intense spasms.
- Kidney tumor. A neoplasm in the structure of an organ may not bother the patient for a long time. The growth of the tumor over time leads to tissue compression. This causes irritation of the kidney, which immediately responds with spasms.
- Kidney tuberculosis. An infectious disease affects the kidney tissue. This leads to organ irritation and spasms.
- Nephroptosis. This is a pathology in which kidney prolapse is diagnosed. The mobility of the bean-shaped organ can provoke an attack of severe pain.
- Kidney injuries. Any damage or blows to the lumbar region can lead to severe, bursting pain.
- Anomalies of the urinary system. Severe discomfort may be based on congenital or acquired changes in organs. For example, the outflow of urine becomes significantly more difficult when the urethra or ureter narrows.
- Tumor processes in neighboring organs. The growth of tumors in the prostate gland and rectum can compress the ureter.
Provoking factors
The appearance of renal colic can be caused by the following events:
- excessive physical activity;
- eating hot, spicy food the day before;
- jumping;
- lifting weights;
- alcohol abuse;
- shaking.
Eating spicy food can trigger an attack of renal colic.
But sometimes painful discomfort occurs without any previous factors. Some patients note that renal colic appeared at rest, interrupting night sleep.
One summer, when I escaped from all the worries of the city to the dacha, at three o’clock in the morning I was woken up by the persistent ringing of my mobile phone. My neighbor, a 50-year-old man, asked me to come see him immediately. It was clear from his voice that the man was feeling bad. But the state in which I found him simply shocked me. The dream instantly disappeared. The neighbor was pale and vomited periodically. He painfully grabbed his lower back, then his stomach. The sufferer could not even properly explain what was bothering him. I immediately called an ambulance. Meanwhile, the man groaned again from a painful attack. “I need to relieve the spasms,” I thought. There was No-Shpa in my first aid kit. Of course, the pills did not completely relieve the pain, but the neighbor said that it became a little easier.