When a patient complains of pain in the abdominal cavity or dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, the doctor may prescribe an x-ray. Considering the structural features of the abdominal organs, this method cannot be called the most informative. To obtain a clear image, a special contrast agent is injected.
Barium sulfate is used as a contrast agent, which fills all cavities. This powder is poorly soluble in water and is resistant to acids and alkalis, while also having the ability to reflect X-rays. Since barium is not absorbed through the intestinal walls, the possibility of it entering the bloodstream arises only in the presence of open ulcers and other damage to the integrity of the walls. The substance is excreted from the body in feces.
Operating principle
The essence of this diagnostic method is based on exposure of the abdominal cavity to a permissible dose of radiation. When X-rays pass through a cavity filled with contrast, a fairly clear picture is obtained, on the basis of which a radiologist can identify many pathological changes and establish the correct diagnosis.
Despite the fact that the patient is exposed to radiation during the study, barium radiography of the abdominal cavity is actively used in modern medicine. Firstly, the radiation dose is insignificant and does not exceed the established daily norm. Secondly, the procedure does not take much time and does not cause discomfort to the patient. And thirdly, x-rays with a contrast agent are an inexpensive and fairly informative diagnostic method.
Modern equipment used for radiography procedures makes it possible to strictly regulate radiation activity. Thanks to this, neighboring organs are practically not exposed to radiation.
Advantages of plain radiography
Unlike classical x-rays, survey radiography
is a more informative study.
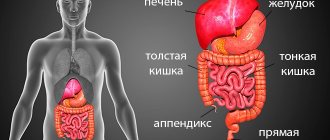
A diagnostician evaluates the condition of not only the liver or kidneys, but all abdominal
. It is possible to evaluate the individual nuances of the location of organs and recognize existing pathological processes.
Computed tomography is based on the same principles as x-rays
: Using ionizing radiation, various areas of the human body are scanned.
The advantage of plain radiography
is that the method accurately visualizes bone tissue and is safer for health due to minimal radiation exposure to the body. In addition, X-ray diagnostics are cheaper and accessible to most patients.
What will a barium x-ray of the abdomen show?
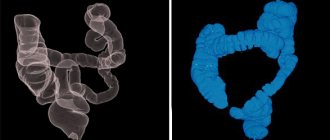
An abdominal x-ray using a contrast agent provides a clear image of the gastrointestinal tract. After examining the image, the radiologist can see pathological changes in the mucous membranes, the presence of tumors, the formation of perforations, changes in the width of the lumen in the intestine, the elasticity of the intestinal walls, motor function, the presence of foreign bodies in the intestine, and fluid accumulation.
Radiography may be routine - to establish a diagnosis for a patient who has consulted a doctor with complaints of pain in the abdominal area. It can also be emergency - when a patient is admitted with abdominal injuries or acute pain, or suspected internal bleeding.
A radiologist interprets the resulting image. He issues a conclusion on the basis of which the attending physician can determine the cause of pain and discomfort.
What does the condition indicate?
The appearance of Kloiber's cups in the organ cavity is a specific sign of the development of acute intestinal obstruction. This condition occurs due to a violation of the separation of contents from the digestive system associated with blockage of the intestinal loop.
The appearance of an obstacle in the path of food masses leads to the fact that the contents accumulate in the cavity of the organ. In this case, liquids are retained in the lower part, and gases accumulate in the upper part. This leads to the emergence of a specific clinical picture of the disease.
Indications for radiography
X-ray of the abdominal cavity with barium allows you to study in detail the condition of the stomach and intestines, in particular to see the sections of the small and large intestines, the appendix, and the gall bladder. In the vast majority of cases, x-rays are used for diagnostic purposes or to monitor the effectiveness of therapy.
Phenomena and symptoms in which a patient is advised to undergo an abdominal x-ray with a contrast agent are as follows:
- chronic diarrhea or persistent constipation;
- the presence of blood in the stool;
- suspected internal bleeding;
- sudden weight loss;
- pathological change in the color and consistency of stool;
- chronic or acute pain in the abdominal cavity and lower back;
- suspected internal organ damage;
- abdominal injuries;
- retroperitoneal abscess;
- intestinal obstruction.
In most cases, X-rays using contrast media are preceded by a plain plain X-ray. This is done to ensure that there are no internal damages through which barium can enter the blood.
What does an x-ray show?
A doctor with the proper level of qualifications will be able to detect the following diseases and phenomena on an x-ray:
- tumors at any stage of development;
- appendicitis;
- inflammatory process (peritonitis, cholecystitis, etc.);
- nephrolithiasis (formation of kidney stones);
- pancreatitis;
- polyps;
- internal hematomas;
- abnormal structure of hollow organs;
- cholelithiasis;
- polycystic disease;
- diverticulitis;
- intestinal obstruction;
- various injuries;
- biliary and hepatic colic.
In the X-ray images, Kloiber's cups are visualized on the left, on the right - a crescent symptom. In a young child, using X-rays, you can determine the location of swallowed foreign objects: coins, buttons, needles, beads, nuts, etc. Sometimes a specialist is able to detect quite dangerous phenomena on photosensitive film: cups Kloibera and the crescent sign.
The sickle symptom is an accumulation of free air caused by a violation of the integrity of one of the sections of the gastrointestinal tract. Externally, it is a lightened crescent-shaped spot, which is most often located under the right dome of the diaphragm - the muscular septum separating the abdominal cavity from the chest. Kloiber's bowls resemble bowl-shaped two-layer elements filled not only with gases, but also with liquid.
If the number of vertically oriented spots prevails in the image, then the patient has obstruction of the large intestine, and if horizontal, then obstruction of the small intestine. Both cases considered indicate the presence of extremely advanced pathologies, which after X-rays should be eliminated as soon as possible.
Preparing for the study
The information content of the result depends on the accuracy of compliance with all the rules of preparation for radiography using a contrast agent. During a planned procedure, the patient is prescribed a special diet with a limitation of foods that cause increased gas formation - 3 days before the study. Additionally, the doctor prescribes medications with a laxative effect and describes a regimen for taking them. Two days before an X-ray with barium, you should exclude alcoholic beverages, coffee and tea from your diet, and it is advisable to completely stop smoking. In the last 24 hours before the diagnosis, you should not eat solid food - you can drink broths, herbal teas, and still water.
During the preparation period, taking medications is not recommended. If complete abstinence from medications is not possible, you should drink plenty of water with each dose of medication.
Immediately before the procedure, the patient needs to change into suitable clothes - his own or hospital clothes. It is also worth removing all metal objects, including removable dentures.
Contraindications
X-ray
the abdominal area is not performed with caution and is performed in the following cases:
1. Women during pregnancy and nursing mothers.
At this time, diagnostics using ionizing radiation are prescribed in exceptional cases. This is due to the fact that the effects of exposure to x-rays
on the baby have not been fully studied.
2. Children under 12 years old.
Radiation exposure can negatively affect a child's development. If possible, use alternative research methods.
Patients with a history of bronchial asthma, cystic fibrosis and other serious pathologies should have an x-ray
only after consultation with your doctor. The presence of piercings, iron implants, or tattoos is not a contraindication to the procedure.
Features of the procedure
Best materials of the month
- Why you can't go on a diet on your own
- 21 tips on how to avoid buying stale food
- How to keep vegetables and fruits fresh: simple tricks
- How to curb your sweet cravings: 7 unexpected products
- Scientists say youth can be extended
Since the procedure is performed only on an empty stomach, it is usually prescribed in the morning. If interpretation of the image does not reveal reasons for urgent hospitalization, the patient can go home immediately after the examination.
Barium sulfate in powder form is mixed with water and introduced into the gastrointestinal tract through a tube. Another way to introduce a contrast agent into the intestine is through the rectum using a thin tube that is inserted through the anus. The contrast injection procedure itself is painless, although it may be accompanied by some discomfort. If acute pain or other unpleasant sensations occur during the administration of barium, the x-ray technician performing the procedure should be informed about this.
While the images are being taken, the patient must hold his breath and remain motionless. The procedure itself takes 1-5 minutes - during this time a series of images is taken, on the basis of which a conclusion is written.
How to prepare for a chest x-ray
A chest x-ray does not require much preparation on the part of the patient. The person will need to remove any jewelry, glasses, piercings or other metal objects on the body before the procedure itself. Because this may make it difficult to make a correct diagnosis and obscure the image. Be sure to tell your doctor if you have a surgically implanted device, such as a heart valve or pacemaker. This determines which diagnostic method can be used in a particular case. Chest X-rays may be performed when the patient has metal implants. But other scans, such as MRIs, can be risky for people who have a metal device inside. Women with long hair are recommended to pin it up, since foreign bodies are prohibited from entering the diagnostic area. If hit, the quality and information content of the x-ray image drops significantly.
You will also need to undress to the waist before the x-ray and follow the instructions of the laboratory assistant. X-rays of the heart can be performed in three types of projections. During the procedure, the laboratory assistant will ask you to hold your breath for literally 10 seconds to get clear contours of the image.
How does the research procedure work?
The X-ray image looks like a black and white photograph. Areas that are translucent and transmit X-rays are shown in black, and areas that cannot transmit ionizing radiation are highlighted in white. That is why the bones and heart muscle in the image are white.
The X-ray machine is located in a special large room with a movable X-ray camera attached to a large metal arm called an arm. The patient should stand next to the “plate”. This plate contains X-ray film or a special sensor that records the images on a computer. The laboratory assistant will tell you how to stand correctly - raise your arms and bend them at the elbows, and record in the front and side projections. Usually the manipulation is carried out in two projections, but for a more accurate and specific diagnosis it can be carried out in three or four - anterior, lateral left, oblique left and right, at an angle of forty-five degrees. It is the images in the oblique projection that help to view the walls of the aortic arch and the walls of the myocardium, which are not examined in the lateral view. For example, oblique right imaging makes it possible to examine all parts of the heart.
While the images are being taken, you will need to take a deep breath and hold your breath as requested by the technician, and to keep your body completely still. If you move, the pictures may turn out blurry. This procedure takes about ten minutes, after which you need to get dressed and go about your business.
This diagnostic method is one of the cheapest and most painless, non-invasive studies of the heart muscle. Only with an X-ray with contrast, the patient can taste the lime barium solution.