0
Author of the article: Marina Dmitrievna
2017.08.09
18 416
Platelets
Adults know what blood clots are and why their formation in blood vessels is dangerous. But if the human body did not know how to form blood clots, a person would bleed to death if a blood vessel was damaged. Platelets are responsible for the formation of blood clots in the body.
What are platelets? These are the smallest blood cells. They are called blood platelets because they do not have a nucleus. What do they mean for the body? They mean a lot because, in addition to stopping bleeding, platelets also perform other functions.
This is how the damage in the wall of the blood vessel is closed
Characteristics and functions
Platelets are formed blood particles that look like small plates. Their name comes from the merger of two Greek words “clump” and “cell,” which perfectly describes their main function. They are formed in the red bone marrow from the plasma of its cells (megakaryocytes).
Platelets lack a nucleus and color, but contain a large number of granules (about 200). In the normal state, their shape is oval or round, and their size is directly determined by the stage of maturation (young, mature, adult) and is 2-5 microns.
Upon contact with a surface that differs from the inner lining of blood vessels and cardiac cavities (endothelium), which is familiar to it, the platelet is activated, which looks like the appearance of about 10 processes, 5-10 times larger than itself. Thus, these small cells close the damage and stop bleeding.
Platelet granules contain substances that promote the formation of blood clots, the so-called platelet factors. They are necessary for the creation of B-lysine and lysocine, which can destroy the membranes of certain microbes, protecting the body from the introduction of pathogenic bacteria.
Thanks to their long pseudopods, platelets easily move through the bloodstream. These small plates are one of the most active participants in hemostasis (clotting system) and are also involved in the supply of nutrients to the endothelium.
The life cycle of a platelet is relatively short compared to other cells - 7-12 days, after which it is destroyed in the spleen, liver or lungs. If the balance between their production and decay is disturbed, then a person has a tendency to form blood clots or bleed.
This is interesting! Recently, scientists have discovered another function of platelets - participation in the healing and regeneration of damaged tissues. By releasing growth factors (polypeptide molecules), they stimulate cells to actively divide in the affected area.
Norm of platelets in men and women by age
The reasons that cause an increase in platelet values in the blood during gestation do not differ from the general ones.
But there are some additional reasons:
- Antiphospholipid syndrome leads to thrombosis. In the last trimester, there is a high risk of thrombotic exacerbations.
- Impaired water balance due to toxicosis, vomiting and diarrhea. Edema forces a pregnant woman to limit her fluid intake, which causes the situation to worsen.
A large number of platelets during pregnancy is not a pathology if the values do not go too far beyond the normal range.
A significant increase in platelet counts causes increased blood clotting and can cause miscarriage at any stage.
At this crucial moment, women usually closely monitor any changes in the functioning of the body. Also, constant monitoring is carried out by doctors, prescribing endless tests throughout the entire period. Compliance with all the requirements of the attending physician and careful attitude towards yourself will help to avoid complications.
Quantitative and qualitative blood content can show the state of the body, revealing various abnormalities that do not appear externally.
The presence of platelets in the blood determines its viscosity, which determines the regenerative function of the hematopoietic system. In the male body, the platelet level is much higher than in women.
However, platelets in the female body can also be elevated. Why this happens, how it manifests itself and what measures to take, we will analyze further.
Normal indicators
The number of platelets is measured in units per liter (*109/l) or per microliter (*103/μl or thousand/μl) of the biomaterial (blood) being studied. The norm in adults is in the range of 150-400 * 103 / μl, regardless of whether it is a man or a woman. The same values are considered reference values for children over 6 years of age.
In smaller ones, there are some differences, determined not only by the age, but also by the gender of the child. Thus, in newborns up to 2 weeks, the content of these cells is in the range of 114-449 in girls and in boys - 218-419 * 103 / μl. As they grow older, the boundaries narrow slightly, and by the age of 6, 189-394 for girls and 202-403 for boys are considered normal.
If for some reason the level of platelets in the blood increases relative to normal values, then the person is more likely to develop blood clots. With values reaching 1000*103/µl, the situation is considered critical. And, conversely, when the concentration drops to 50*103/μl, clinically dangerous signs of bleeding are observed, posing a serious threat to the patient’s life.
A woman’s platelet count can decrease during menstruation (up to 50%) or during pregnancy (by 10-20%). In the first case, such a reaction of the body is a protection against thrombosis, and in the second, it is the result of the emergence of a third circle of blood circulation.
In addition to the above, the concentration of these cells can be determined by the current state of both the male and female body, and minor fluctuations are sometimes associated with seasonality and time of day.
Norms for the main characteristics of platelets in a general blood test
Diet
Proper nutrition plays an important role in the treatment of thrombocytosis. All substances that enter the body with food affect the composition of the blood.
It is important to drink plenty of fluids. Dehydration is one of the reasons for the increase in viscosity. The ideal drink is pure water.
The diet of a woman prone to developing thrombocytosis must include:
- vegetable oils;
- fish fat;
- fresh fruits;
- vegetables;
- berries.
Food should be rich in unsaturated fatty acids. This has a beneficial effect on the condition of blood vessels. The arteries are gradually cleared of clots.
Fruits and berries replenish the supply of antioxidants - substances that prevent the release of free radicals.
The platelet count will be kept normal by consuming green vegetables or ginger.
Increase in platelets
An increase in platelets in the blood leads to an increased risk of thrombosis and, as a result, clogging of blood vessels. This condition is called thrombocytosis and is very dangerous for the health and life of patients. Pathology is divided into two types - primary and secondary.
The primary type of thrombocytosis is caused by dysfunction of bone marrow cells, which leads to an increased content of colorless platelets in the blood. The number of platelets increases, since their life cycle does not decrease, but at the same time they have an abnormal structure, which leads to dysfunction. The pathologically altered cells are very large, which increases the tendency to stick together and form blood clots.
In a blood test in such a situation, a very high level of platelets can be determined, reaching 800-1200 * 103 / μl and even higher. As a rule, this condition is diagnosed accidentally, since in most cases it is not accompanied by severe symptoms.
Only in isolated cases with primary thrombocytosis are the following manifestations noted:
- subcutaneous hemorrhages;
- headache;
- bluish skin tone;
- bleeding (nasal, uterine, etc.).
An increased level of the described cells in secondary type thrombocytosis can develop due to both physiological and pathological reasons. With this pathology, platelet counts are often less increased than in the primary type, and generally rarely reach 1000*103/μl.
Secondary, or, as it is also called, reactive thrombocytosis, is distinguished by the fact that platelets in it have the correct form and function, and increase when any disease occurs. With the secondary type of thrombocytosis, the indicators return to normal when the cause of the underlying disease is eliminated.
Physiological factors that can increase the number of colorless blood platelets are:
- living in high mountains;
- dehydration (in the heat or when vomiting);
- increased adrenaline in the blood;
- physical stress;
- pregnancy.
Why might thrombocytosis occur?
The reasons for an increase in platelets in a child’s blood are numerous and varied:
- In case of congenital as well as acquired pathologies of the circulatory system (autoimmune diseases, oncological processes, etc.), experts note the development of primary thrombocytosis.
- If the concentration of platelets in a child increases against the background of ongoing infectious processes in various organs and systems, we are talking about secondary thrombocytosis. It is considered as an additional factor in the body’s defense mechanisms, aimed at quickly eliminating the infectious focus. Secondary thrombocytosis is also characterized by a simultaneous increase in leukocytes.
Platelets can also increase in infectious diseases.
The reasons why platelet values can increase are very diverse. Of course, first of all, this indicates that the patient has health problems, so additional research should be carried out to determine the exact cause of the increased level of platelets.
The reasons for increased platelet levels are as follows:
- bone marrow pathologies;
- Kawasaki and Schonlein syndromes;
- fungal diseases;
- spleen diseases;
- spondyloarthritis;
- parasite infection;
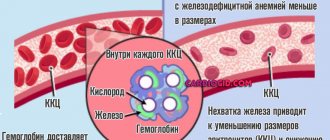
- acute iron deficiency;
- organ inflammation;
- sarcoidosis;
- infectious diseases;
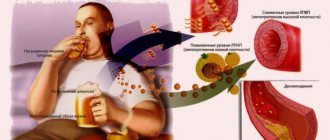
- alcoholism and smoking;
- injuries and operations;
- oncology;
- wrong lifestyle;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- collagenosis;
- taking certain medications.
A condition in which the number of platelets exceeds the norm is called thrombocytosis, and can be caused by the following processes:
- the life cycle of platelets has been exceeded;
- they are produced in excess by the bone marrow;
- vessels are affected by the atherosclerotic process;
- there is acute or chronic bleeding;
- The circulating volume of plasma decreases, but the volume of platelets and other cells does not change.
An increase in platelets may be due to the presence of ulcerative colitis.
The growth of blood platelets is influenced by the following factors:
- presence of erythremia;
- inhibition of the process of platelet destruction;
- unequal distribution of blood platelets - typical in the presence of overvoltage.
Thrombocytosis can occur in children of any age. We can talk about such a diagnosis when there is a significant increase in platelets. Much more common is a slight excess of the upper limits of the norm.
Secondary thrombocytosis develops against the background of such pathologies:
- ulcerative colitis;
- tuberculosis;
- rheumatism (active form);
- osteomyelitis;
- infections, acute and chronic;
- anemia;
- result of spleen removal;
- fractures of bones, in particular tubular bones;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- severe blood loss;
- multiple surgical interventions;
- oncology;
- amyloidosis.
In addition to diseases, the use of certain medications, namely the side effects of these drugs, for example, epinephrine, adrenaline, and corticosteroids, can affect the growth of this indicator.
Diseases accompanied by thrombocytosis
The pathological reasons for which high platelet values are diagnosed are most often the following:
- Inflammatory diseases of an infectious nature caused by fungi, parasites, viruses or bacteria (pneumonia, encephalitis, meningitis, hepatitis, candidiasis, etc.).
- Sarcoidosis is a systemic pathology of inflammatory nature that affects various organs (most often the lungs) with the formation of granulomas (nodular formations) in them.
- Removal of the spleen, the organ responsible for the disposal of obsolete platelets, in which about 30% of them are also stored.
- Extensive damage to tissue structures due to necrosis or pancreatitis.
- Traumatic damage to organs or tissues and surgical operations.
- Internal bleeding of various etiologies.
- Various oncological diseases.
- Lack of iron in the body.
In addition, elevated platelets can be detected when taking a certain number of drugs, which is why in some situations, especially if the patient has a tendency to thrombocytosis, the blood condition should be regularly monitored during therapy.
But still, the most common reason for the increase in the rate is old age, but in this case it can be controlled quite successfully with the help of daily intake of Aspirin and other blood thinning medications.
During pregnancy, it is very important to regularly check your platelet levels.
Norm of platelets in men and women by age
The condition of the plates is assessed not only by their number, but also by the speed of blood clotting. The unit of measurement is thousand per microliter (thousand/µL).
In women, the following indicators are considered normal platelet levels:
- from the moment of birth and during the first 10 days of life – 99-421 thousand/µl;
- from 10 days to a month – 150-400;
- from a month to six months – 180-400;
- from six months to a year – 160-390;
- from one year to 5 years – 150-400;
- from 5 to 10 years – 180-450;
- from 10 to 15 years – 150-450;
- from 15 years onwards – 180-320.
The number and norm of platelets is an unstable value, therefore, in order to understand what value is normal for a woman, a number of factors should be taken into account, for example, such as:
- physiological characteristics of the body;
- age.
Every woman who has reached menopause needs to take a blood test for platelet levels in order to be able to prevent the occurrence of potentially dangerous diseases in time.
It should be taken into account that the value of platelets may decrease during critical days. This is due to the fact that in this way the body tries to protect itself from possible bleeding. It is not worth carrying out a blood test at this time, as this will be an additional burden on the nervous and circulatory system.
For a man, the normal level is from 180 to 400 thousand/µl. But these values can also change depending on age:
- up to 16 years – 160-390 thousand/µl;
- 16-25 years old – 180-380;
- 26-35 years old – 180-400;
- 36-60 years old – 180-340;
- from 60 and older – 180-320.
Diagnostics
An increase in the described parameter can be detected quite simply and quickly by performing just one general blood test. In this method, the platelet index (indicated in the analysis form as PLT) is one of the mandatory coefficients for determination.
Normal PLT in blood test
In addition, MPV (mean platelet volume), thrombocrit, that is, the proportion of the volume of whole blood occupied by platelets, and PDW, an indicator of platelet heterogeneity or their relative distribution width depending on the total volume, are immediately assessed.
These parameters are called platelet indices and are determined during a detailed blood test. If required, additional examinations are prescribed, such as a coagulogram, which allows one to evaluate the main characteristics of the hemostatic system, and other necessary techniques.
Based on the diagnostics performed, the most appropriate method for correcting thrombocytosis is selected, which will depend on the severity of the patient’s condition and the possible risk of complications.
Average thrombotic cell volume
Mean platelet volume is an index (MPV) that shows the degree of maturity of blood platelets. Their lifespan is limited to a few days.
What it is?
The average number of platelets per unit of blood should not be confused with thrombotic cell volume (MPV). Its average volume reflects not a quantitative, but a qualitative characteristic of the blood plate; what this means is not difficult to understand.
There is a constant renewal of platelets in the blood. The lifespan of a blood plate is from 6 to 10 days. Therefore, they have different degrees of maturity and, accordingly, different sizes. Old cells are smaller, and young cells are larger. Naturally, they have varying degrees of activity and ability to influence blood clotting. With a normal number of platelets per unit of blood, the average thrombotic cell volume may be increased or decreased.
Why does it deviate from the norm?
If the average thrombotic cell volume deviates from the norm upward, it means that young and immature forms of platelets are present in the blood to a greater extent.
If the average volume of a thrombotic cell deviates from the norm towards a decrease, it means that there are more old, and therefore small, forms of blood platelets in the blood.
This deviation may be due to a number of factors:
- pathology of the spleen or red bone marrow;
- chronic diseases;
- diseases of the immune system;
- effects on the body of viruses, fungi, parasites;
- exposure to radiation, chemicals, varnishes, paints on the body;
- alcohol, drugs, smoking.
These and other unfavorable factors can cause changes in the formation and development of the thrombotic cell, and therefore significantly affect its volume.
What is the threat?
An increase in the average volume of a thrombotic cell threatens various unpleasant health consequences:
- development of thrombocytopenic purpura;
- thrombosis.
What are the dangers of thrombocytosis?
A slight increase in platelets for a short time is quite harmless, but if there are too many of them, it is very dangerous for a person’s health, and sometimes for his life. This directly depends on the reasons, which should be clarified by a qualified specialist.
If platelets increase to values of 1000-1200*103/μl, then the likelihood of thrombosis in the extremities, strokes or heart attacks is very high, which often leads to the death of patients. Thrombocytosis is extremely dangerous in pregnant women - a sharp increase in colorless cells can become a serious problem for both the expectant mother and her baby.
An increase in the indicator can lead to arterial and venous thrombosis and in some situations can provoke antiphospholipid syndrome. But the worst thing is that in such cases miscarriages often occur, and this can happen at absolutely any time. In this regard, the famous pediatrician and presenter of scientific programs Komarovsky recommends that expectant mothers regularly take blood tests to monitor their condition.
Symptoms of excess colorless cells
If platelets are elevated, it means that blood clotting is impaired in the body.
Numbness of the limbs indicates poor blood clotting
The problem is signaled by:
- numbness of the limbs;
- headache;
- chronic fatigue;
- decreased visual function;
- frequent mood changes;
- painful sensations in the arms and legs;
- nosebleeds.
At the initial stage, the symptoms are mild and the person does not pay attention to them.
Therapeutic approach
Treatment of thrombocytosis will be determined by the underlying cause of the disorder, which means most likely the underlying disease. The choice of therapy aimed at pathology, and therefore at reducing platelet levels, will be influenced by the state of the patient’s immune system, the degree of complexity of the disease and how much colorless cells exceed the norm. That is, initially, before choosing a method to reduce platelets in the blood, you should determine what caused the increase.
Medications
Unfortunately, there is no clear and universally suitable method for getting rid of this condition, which means that an individual approach has to be developed for each patient.
Most often, in order to reduce the platelet count, Aspirin or drugs that have a similar effect, which also include acetylsalicylic acid, are prescribed. In more serious situations or when the desired result cannot be achieved, medications are prescribed that inhibit the production of these cells in the bone marrow.
An increased platelet volume is reduced with hydroxyurea and Interferon-alpha, which are very strong and far from harmless drugs, as evidenced by serious adverse reactions when taking them. Therefore, doctors are trying to resort to more gentle forms of therapy, combining them with lifestyle and nutrition correction.
If you have thrombocytosis, you should definitely stop smoking
In particularly severe conditions, therapeutic thrombopheresis can be used to lower platelet levels. This is a procedure in which, using a specially designed apparatus, the blood is filtered while simultaneously removing excess cells.
Important! It should not be forgotten that an excessively low platelet count is also very dangerous for health, so during therapy you must strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Diet and lifestyle
With mild thrombocytosis, in many cases, correction of diet and lifestyle is sufficient to reduce platelets. In addition to introducing dietary restrictions, patients with thrombocytosis should sleep enough, not be overtired, not nervous, and minimize bad habits - smoking and alcohol, or better yet, give them up completely.
In addition, you should reduce the amount of carbohydrates you eat. Thus, a diet for thrombocytosis involves avoiding bananas, mangoes, nuts, pomegranates, rose hips, and including in the diet such foods as:
- grapes, apples, blueberries, cranberries;
- lemons, ginger, sea buckthorn, beets;
- seafood, seaweed;
- fish oil, tomatoes, onions, garlic;
- flaxseed and olive oil;
- cranberry juice;
- Orange juice;
- green tea.
All products that can thin the blood, with a high content of ascorbic and malic acid, as well as magnesium, are allowed. In addition, it is important to maintain a drinking regime, which means drinking at least 2.5 liters of liquid per day. Folk remedies that have been proven over the years help very well, such as, for example, green tea with ginger and lemon; cranberry juice is also considered universal in such a situation.
What to do if platelets are higher than normal?
When there are many large platelets in the blood, a thorough examination is necessary.
If platelets are elevated, donate blood for a leukocyte formula
The person is referred for a consultation to a hematologist, who prescribes additional tests:
- blood for leukocyte formula;
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- bone marrow biopsy.
Treatment is selected on an individual basis. In case of secondary thrombocytosis, it is aimed at relieving the diseases that caused the pathology.
Medicines
- To normalize coagulation, blood thinning drugs are prescribed: Cardiomagnyl, Aspirin, Trental.
- To improve microcirculation, Vazonit, Persantine, Dipyridamole, Flexital are prescribed. Medicines reduce platelet aggregation, normalize capillary permeability and cell metabolism.
- To slow down the blood clotting process, antithrombotic drugs are used. These include Warfarin, Sinkumar. The tablets improve blood properties and prevent the formation of blood clots.
- To protect the vascular walls from damage, angioprotectors are prescribed: Phlebodia, Ascorutin.
- Taking interferon will help strengthen the immune system.
Trental normalizes blood clotting
How to reduce with folk remedies?
In complex therapy, it is possible to treat thrombocytosis with folk remedies. To prepare the recipes, natural substances that cleanse and thin the blood are used.
- Remove 2 heads of garlic from their films and chop. Place in a glass container and pour in 200 ml of vodka. Close the lid and leave for 10 days. Strain and drink 1 tsp. morning and evening 2 weeks.
- Buy apple cider vinegar. Every morning, dissolve 2 tsp in 250 ml of warm water. vinegar and drink in small sips before breakfast. Course 1-2 months.
- Take 1 tbsp daily. l. flaxseed oil on an empty stomach. The product reduces blood viscosity, removes harmful cholesterol, prevents blood clots and vascular atherosclerosis.
- Grate the ginger root. Measure out 1 tsp. shavings and brew with boiling water in a liter thermos. Leave overnight and strain. Take warm 4 times a day, dividing into equal portions, half an hour before meals. Add 1 tsp to the warm liquid. honey and a slice of lemon before use. Continue treatment for 1-2 weeks.
- Pour 200 ml of boiling water 1 tsp. sweet clover or white willow bark. Wrap the container with a towel and leave for an hour. Filter and drink 100 ml 2 times a day.
Ginger root with honey helps reduce platelet levels
To strengthen the immune system and thin the blood, it is useful to drink 1 liter of rosehip infusion per day. You can prepare a delicious medicine. Take 3 lemons, pour boiling water over them and grind through a meat grinder. Combine with honey 1:1 and stir thoroughly. Eat 1 tsp. 3 times a day regularly for several months.
Dietary recommendations
Adjusted nutrition can reduce platelet volume. Remove sugar, baked goods, fatty foods, smoked foods, and fast food from your diet. Bananas, potato dishes, carbonated water, and simple carbohydrates are prohibited. These products thicken the blood and reduce its quality.
Strawberries reduce blood viscosity
To reduce blood viscosity, you need:
- berries: raspberries, currants, strawberries, viburnum;
- fruits: figs, oranges, pomegranates;
- vegetables: sweet peppers, beets, carrots;
- walnuts, seeds.
It is useful to enrich your diet with freshly squeezed juices from sour berries, tomatoes, apples, and grapes.
Green peas increase platelet levels
Foods that increase platelets:
- fish fat;
- olive oil;
- skimmed milk;
- beans;
- green pea;
- seafood.
Be sure to drink 2-3 liters of clean water per day. It transports nutrients into cells, improves metabolism, removes waste products and restores blood structure.
Melt water brings great benefits. To prepare, fill an incomplete bottle of purified water, close it and put it in the freezer. When it is completely frozen, take it out. Wait for the liquid to thaw at the edges, pour into another container and drink throughout the day. Do not use any ice remaining in the center. Oxidizing agents and other harmful substances accumulate in it.
Meaning
Platelets are flat blood cells that do not have color or a nucleus. They are produced by the bone marrow from large megakaryocytes through division. In the individual’s body, they perform one of the important functions - they participate in the process of blood clotting. Thanks to them:
- blood is maintained in a liquid state;
- damaged vessel walls are eliminated;
- the bleeding stops.
According to their physiological properties, platelets can stick to the surface of the wall of a blood vessel, stick together to form a blood clot, and settle on the surface. Using these properties, they repair damaged blood vessels. It should be noted that the lifespan of flat blood cells is no more than ten days, i.e., the process of their renewal is constantly underway, as well as the disposal of dead ones.
Additional recommendations for prevention
There are several simple rules that will help keep platelet levels normal:
- You need to drink enough water every day. The daily norm should be 8 glasses. It doesn't matter whether the water is warm or cold.
- Rest should be complete. An adult should get at least seven hours of sleep. With thrombocytopenia, sleep should last about nine hours.
- Make time for physical exercise. Cardio training will improve blood circulation and strengthen the immune system. If thrombocytopenia is present, exercise should be performed with caution so as not to provoke bleeding (for example, from the nose).
- For prevention purposes, take a seasonal vitamin complex. Pay special attention to vitamin K, which is responsible for the ability of blood to clot.
- Eat foods that have Omega-3 and other fatty acids.
Possible complications
Thrombocytosis is a serious disease that requires immediate medical treatment. If the course of this disease is ignored for a long time, serious complications can arise. We strongly recommend that you find out what the rest of your blood counts that are abnormal indicate. A complex disorder may indicate more serious problems.
What are platelets
Among the most dangerous are:
- The risks of blood clots forming in blood vessels and veins are increased. Such formations block the blood flow,
- Blood clot rupture – such a formation can enter an artery. Because of this, inflammation and swelling occurs at the site of injury,
- Stroke is a rupture of a blood vessel that causes bleeding in the brain.
- Myocardial infarction is a violation of the contraction of the heart muscle,
- Thromboembolism of the pulmonary vessels is the entry of a severed vessel into the lung tissue.
- Death - in 90% of cases, advanced thrombocytosis leads to immediate death.
How to increase platelets in the blood
However, you can try to raise your platelet levels on your own using folk remedies and nutritional correction. But in general, even these “mild” self-medication options should be under the strict supervision of a doctor.
It is important not to overdo it in this matter: you must understand that platelets can be increased excessively, which will also entail certain problems with hemodynamics. Excessive blood thickness is no less dangerous than poor blood clotting
People with excess platelets experience vascular occlusions and other potentially dangerous pathologies of the circulatory system. Therefore, if you decide to use certain pharmaceutical drugs, be sure to check with your doctor about the regimen, duration, frequency and dosage that is optimal for your case.
Is it possible to increase platelet levels on your own?
At home, you can stabilize the quantitative platelet count in three steps. Step 1. It is necessary to review your diet, since blood counts may depend on the food consumed and the vitamins that enter the body
Therefore, it is very important to eat foods rich in iron, as well as enough vegetables and fruits.Step 2
Pay attention to a proper diet and avoid fatty, spicy foods. A person suffering from low platelet levels should forget about eating sausages, lard, canned food, pates and other rich fish and meat dishes. Step 3
Consult a doctor who will prescribe special medications that will help normalize platelet counts if this cannot be achieved with proper nutrition.
Classification
The division can be carried out according to the severity of the pathological process.
In this case, the following varieties are called:
- Thrombocythemia is mild. The cell level is slightly increased. There are no symptoms. The patient is unaware of the problem. Such forms are usually physiological and do not require special treatment. Although options are possible.
- As the disorder progresses, it enters the second phase. Moderate. There is a group of manifestations such as an increase or decrease in blood density. The rheological properties of the fabric are disrupted. There is a tendency to form blood clots. The clinic is unstable, so it can subside and recover on its own. Therapy is necessary.
- Severe form of thrombocytosis. Accompanied by a pronounced increase in the concentration of formed blood cells. Occurs in complex infectious and inflammatory processes, less often in other conditions. A qualitative correction of the main diagnosis is necessary.
- Extreme or critical form. It is observed against the background of cancerous tumors, malignant blood diseases, also sepsis, and dangerous inflammatory phenomena. Without correction, the patient will most likely die from the primary disorder. The risk of bleeding increases. Therefore, the condition itself poses a great threat to life.
There is another way to subdivide the process - by etiology (origin):
- Essential thrombocytosis, also known as primary. It develops as a result of damage to the hematopoietic system itself. Often tumors. Occurs in approximately 10% of cases from the total mass of clinical situations. The therapy is complex, in a hospital. Follow-up is indicated in an outpatient setting to prevent critical complications.
- Reactive thrombocytosis is also secondary. The most common type of condition. It accounts for over 80% of situations. This is the result of infectious and autoimmune inflammatory disorders. Also anemia of various origins.
- Mutation or familial species. Caused by a critical disorder of platelet production at the hereditary level. Despite the general complexity of the condition, with proper correction of symptoms, the patient can live a long and high-quality life. Not counting the most dangerous cases.
- Finally, we can call false thrombocytosis. They are the result of incorrect laboratory evaluation of biomaterial. Usually an automatic analyzer. In controversial cases, the study is carried out several times to eliminate errors and confirm the condition.
Treatment
The task of therapy is complex; it is based on the fight against the root cause.
Secondary varieties of the pathological process can be corrected in this way:
- Anemia. Requires the introduction of iron supplements in a system with vitamin C and ascorbic acid. The course is short-term, there are no big problems in recovery.
- Infectious processes. They assume the use of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and agents to combat a virus or fungus. The names are determined by a specialist.
- Autoimmune processes require the administration of glucocorticoids. Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, Methylprednisolone or others. This allows you to correct the condition. If ineffective, immunosuppressants (Methotrexate and similar) are indicated.
- If there is a tendency to thrombosis, the use of antiplatelet agents is necessary. Ticlopidine, Aspirin, Thrombo-ass, Clopidogrel, Reopoliglucin and others.
- As a symptomatic measure, the use of hydrourea and interferon is practiced.
- Malignant primary conditions are corrected by bone marrow transplantation.
Treatment of thrombocytosis is multifaceted, determined by the etiology and severity of the process.
Symptoms of the primary disease
An elevated platelet count is difficult to notice until a complete blood count is taken. Although blood clotting and blood flow are impaired in the body, vascular problems arise. Manifestations of the disease are different. People with essential thrombocytosis experience the following symptoms:
- severe fatigue, apathy, pain;
- the occurrence of various bleedings: intestinal, nasal, uterine;
- tingling sensation in the fingertips;
- swelling of the tissues and their bluish tint;
- the appearance of hematomas not associated with bruises;
- skin itching;
- spasm of blood vessels in the fingers, constant feeling of cold;
- pain in the right hypochondrium associated with an enlarged spleen and liver;
- obvious increase in platelets;
- Signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia often appear: severe headaches, rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, thrombosis of small vessels, increased blood pressure.
If such signs are detected, you must consult a doctor and take a general blood test to refute or confirm thrombocytosis in children or adults, the causes of which are listed above. It should be noted that the primary type of the disease often becomes chronic.