Features of the disease
Immunodeficiency conditions are manifested primarily by axillary lymphadenopathy, and in several places at once.
Axillary lymphadenopathy is inflammation and enlargement of the lymph nodes located in the armpits. The disease is quite common and potentially dangerous for the development of cancer. In approximately 3-4% of cases, an undiagnosed and untreated disease can develop into a malignant form.
Enlarged lymph nodes are palpable on their own. Lymphadenopathy of the axillary region can be either unilateral or bilateral.
There are many nodes located in the axillary region. With lymphadenopathy, several lymph nodes may enlarge at once. Enlarged lymph nodes do not hurt, but the pathology is accompanied by severe discomfort.
According to ICD-10, axillary lymphadenopathy is designated by code R59.0 - localized enlargement of the lymph nodes.
It should be noted that enlarged axillary lymph nodes, or lymphadenopathy, is often only a secondary symptom of other diseases. Detected lumps in the armpits require a detailed examination to exclude other diseases and pathologies that can lead to enlarged lymph nodes.
General rules and methods of treatment
The choice of treatment tactics depends on the type of pathology that contributed to the enlargement of intramammillary lymph nodes. However, regardless of the reason, it is important to seek qualified help as quickly as possible.
For inflammatory bacterial processes, antibiotics are prescribed. Preference is given to third-generation cephalosporins, and if necessary, fluoroquinolones, tetracyclines or carbapenems are added. If the process spreads significantly with the accumulation of pus, surgery is performed under general anesthesia - opening and draining the mammary gland.
In oncological pathologies, the type of tumor and its distribution in the body are of great importance. The optimal option is considered to be one in which the tumor can be removed once along with regional lymphatic tissues, and then a course of chemotherapy or radiotherapy can be carried out to prevent metastasis.
In case of hormonal disorders, it is necessary to establish their cause, and then correct them with medication. It is possible that the etiology of this process is also associated with neoplasms of the pituitary gland, hypothalamus or ovaries. In this case, consultation with a neurosurgeon or oncologist is required.
Axillary lymph nodes and mammary gland: where is the connection?
Axillary lymph nodes are a group of nodes located near the mammary gland. Their performance ranges from 15 to 45 knots. These nodes play a significant role in the immune system; they are the first to respond to the penetration of viruses and infections into the body.
The area where the arm and chest are located is called the armpit. Nodules accumulate here: on both sides and in the middle.
In excellent condition, the nodes should not bother you, but if an infection or other pathology occurs, the latter will increase.
According to the anatomy, this group has its own dimensions; if there is any pain, then the nodes change. Shifts are characteristic exactly where the painful process begins. The average volume is up to 1 cm. Some nodes can be felt with fingers, while others are inaccessible.
Nodules are classified into several groups based on placement:
- apical, number up to 10 pieces
- central, number up to 15 pieces
- lateral, there are single
- infants, number up to 9 pieces
- rear, up to 11 pcs.
In children, the norm is considered to be up to 4 nodules measuring 0.5 cm. Up to six years, the nodes are slightly enlarged, but this is not considered a pathology.
Nodes are like an immune organ that performs unique functions. They protect the body from the spread of infections. This is the very first organ that responds to any inflammation.
In the standard state, lymph nodes cannot be visualized. Although sometimes imaging occurs in the armpit, this is not at all scary. It is important that they are without inflammation or structural changes. A lymph node measuring up to 10 mm is considered normal.
An increased size of nodes indicates a developing pathology of an inflammatory or other nature. Inflammation of the nodes can occur anywhere.
This pathology is called lymphadenopathy. Diseased nodes can be characterized by size, density and thickness. To prevent the nodes from becoming denser, they need to be monitored using ultrasound.
This examination is recommended every 3 months.
With the inflammatory nature of the bundles, the etiology becomes: plague, tuberculosis, streptococcus, staphylococcus and various other viruses.
Enlargement of the axillary lymph nodes of the mammary glands can occur without inflammation. The consequence is the formation of a tumor in a certain area. High body temperature and pain may be completely absent.
The main consequences of lymphadenopathy are:
- Inflammation of the hair follicle. With improper and untimely treatment, a carbuncle and furuncle are formed. This pathology develops where there is hair.
- Viral infection. These could be: cytomegalovirus, chickenpox, mononucleosis.
- HIV and AIDS infection. All groups of the lymphatic system increase in size.
- Mastopathy. This pathology is provoked by an increase in nodes.
- Oncological disease. These include: lymphoma, breast cancer, lymphogranulomatosis.
- Infectious diseases of a severe nature. These include: plague, tuberculosis, brucellosis, tularemia.
If a woman has an enlarged node when palpating the axillary region, then most likely it is a lobule of the mammary gland. It is located very close and increases due to some physiology. This could be: pregnancy, menstruation, breastfeeding.
However, you should not ignore this manifestation; you need to seek help from a doctor as soon as possible.
If you wean a child from the breast, involutive changes begin in the mammary glands. During pregnancy, the body prepares to produce milk.
After feeding is completed, the reverse process occurs, the breasts become the same, but decrease in size. In any case, involution occurs individually and without symptoms.
In order to recognize involutional changes, a woman must pay attention to the structure of the breast: it becomes flat and softened. In obese women, the opposite happens; the breasts become enlarged due to the fact that the glandular tissue is replaced by adipose tissue.
When the lymph nodes of the chest or other axillary area are enlarged, the main symptoms are pain exactly where the inflammatory process begins. In any case, the symptoms are different, it depends on the cause of the disease.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sQGvu8RYAB8
All signs of density are nonspecific; they are very similar to manifestations of inflammation. When the axillary lymph node hardens, they are characterized by redness of the skin and pain. The first manifestation of the disease may be the appearance of a soft-elastic lump in the armpit on the left or right. Typical symptoms include:
- heat
- low blood pressure
- cardiopalmus
- sweating during sleep
- changes in the gastrointestinal tract that lead to thinness
- enlarged liver or spleen
- painful sensations when touching the lump
- redness of the skin over the tumor
The main symptom that distinguishes this disease from breast cancer is painless enlarged nodes. If you suspect a dangerous etiology, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
In modern medicine there are many ways to determine the state of the lymphatic system. They begin with an examination for visual assessment and palpation of the breast. If signs of inflammation are detected, the presence of certain pathologies can be assumed by comparing them with photos on the Internet. Although for a specific diagnosis, radiation diagnostics is performed.
It is worth considering that lymphadenitis occurs in both women and men.
Ultrasound examination and radiography belong to radiation diagnostics. This group of studies also includes mammography, which is considered the most effective diagnostic method. Thanks to the images, the nodes of the axillary area are completely covered. New growths are detected using x-rays.
If the doctor suspects a woman has cancer, a cytological examination is performed in the lymph nodes. Biological material is extracted using a biopsy method. To do this, a needle is used to obtain fabric.
Next, this material is delivered to the laboratory for cytology testing and a study is carried out on the structure of the cells.
A biopsy is a painful procedure and is only performed when lymph node cancer is suspected.
Using axillography, the condition of the nodes is assessed. This method helps to visualize the organ, and its specific condition is also determined. However, not all clinics have the equipment.
If changes in nodes are associated with breast pathology, then other methods are used:
- X-ray examination using a contrast agent
- pneumocystography, if there is a suspicion associated with a cystic change in the chest
- ductography, ultrasound
- CT scan
- thermography
- MRI
- radionuclide inspection
After treatment has been completed, the lymph nodes become normal. Many diseases are completely cured, in addition to autoimmune and viral ones.
We suggest you read How to remove age spots at home - remove age spots and freckles
If cancer has been detected, the sooner treatment begins, the better. Late diagnosis will not help to completely recover from the disease.
Every year, a woman needs to be examined by a specialist for timely identification and elimination of the causes of the pathology, and for a long, comfortable life for the patient.
Treatment of lymphadenitis depends on the form of the disease. Therapy is always prescribed individually. If, for example, lymphadenitis develops without any serious pathologies, then treatment will be conservative. If the disease is purulent in nature, then surgery cannot be avoided.
As for prevention, it is recommended to strengthen the immune system and adhere to a healthy lifestyle, give up all bad habits, follow a routine, and eat well. Also visit a mammologist regularly.
Hello dear readers. Have you had an ultrasound of the mammary gland and your axillary lymph nodes of a certain size are located? Is this normal or a disease? The word “axillary” is alarming. Let's figure it out together.
Would you like us to tell you a little secret? There is no difference, just the axillary (axillary) cavity in Latin is called fossa (cavi) axillaris, that is, axillary. Therefore, the lymph nodes located in the area of the axillary fossa have the same name.
Their physical presence in your body is the norm! Unless, of course, these nodes are inflamed, enlarged, and some harmful tumor has not released its “roots” into them - metastases. But healthy axillary lymph nodes are not visualized during hardware diagnostics! If your card says “lymph node is visualized,” this is no longer the norm.
Lymph nodes are part of the immune system. In these organs, lymphocytes mature, and lymph and blood are cleared of bacteria, viruses, fragments of their DNA and their metabolic products. Axillary or axillary (axillary) lymph nodes clear the lymph flowing from the breast and arm.
There are quite a lot of such lymph nodes.
| Name of lymph node group | Apical | Central | Lateral (lateral) | Breasts | Subscapularis |
| Quantity | There are up to ten of them | From 2 to 12 pieces | Single nodes | From 1 to 9 pieces | From 1 to 11 pieces |
| Location | Scattered one at a time along the upper part of the armpit | Located in the center of the axillary fossa | Located on the outside of the axillary recess | Located on the inside of the axle recess | Located at the back of the axillary fossa |
| What organs do they “work” with? | Connected with other groups of lymph nodes by the vasculature of the arm and the breast area | Take lymph from the chest, upper limbs and back | Participate in the lymph flow of the “armpits” and cleanse the lymph of the deep and superficial vessels of the arm | Take lymph circulating in the mammary gland | These are regional nodes of the lymphatic system for the lateral surface of the chest, as well as the shoulder area |
| Practical interest of the doctor (when the lymph nodes are swollen, inflamed, painful) |
| ||||
| Size is ok | 5 to 10 mm (0.5-1.1 cm) |
- Endocrinologist of the highest category Anna Valerievna
- 50637
- Update date: October 2019
Some skin pathologies lead to axillary lymphadenopathy - these are psoriatic changes, neurodermatitis, etc.
Anatomy and functions of intramammary lymph nodes
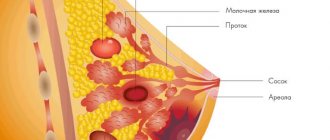
The human immune system has many components, and the lymph nodes are also part of it. Inflammations of various types in the female breast are the first thing the lymph nodes react to. They are located in the glandular and fatty tissue of the chest. Lymph nodes are considered normal if:
- They are not palpable.
- They cannot be seen upon inspection.
- They do not cause pain.
- Body temperature fluctuates within normal limits.
- The skin of the breast did not change its appearance.
The main function of the lymph nodes is to protect against infections throughout the body. Thanks to them, certain metabolic products are eliminated from the body, the immune system remains in its correct state, and, more importantly, cancer cells are delayed in their development.
Typical manifestations and symptoms
Enlarged lymph nodes in the axillary region are rarely accompanied by severe pain. Moreover, the presence of severe pain is an alarming sign and requires timely consultation with a doctor. Usually, enlarged lymph nodes hurt slightly, mainly upon palpation. Severe pain may indicate a purulent inflammatory process in the lymph node.
Other symptoms of axillary lymphadenopathy:
- the formation of one or several bumps that are easily palpable;
- redness of the skin over the bump;
- local increase in temperature of the epidermis around the inflamed node;
- general malaise.
The disease is accompanied by symptoms of a pronounced inflammatory process. When the lymph nodes are enlarged, a person feels weak, gets tired quickly, and sleeps poorly. With axillary lymphadenopathy, patients report chills, increased sweating, loss of appetite, and general malaise. The presence of such symptoms and the detection of enlarged lymph nodes in the armpit area is a reason for an early visit to the clinic or mammologist’s office.
Several axillary lymph nodes may be affected at once. The presence of multiple foci of inflammation increases pain and negatively affects overall well-being.
Definition of the concept
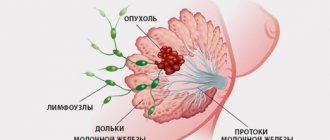
To understand the characteristics of the pathology in question, it is necessary to consider the anatomy of the mammary glands. Lymph nodes, along with the ducts and vessels that run through the chest, form part of the body's immune defense system. They are the first to respond to pathogenic agents. The lymph nodes of the mammary glands are located between the layers of fatty and glandular tissue in the chest area. Upon palpation, these formations are not detected and do not cause pain.
Lymph nodes perform the following functions:
- take part in the processes responsible for removing metabolic products from the body;
- provide the correct immune response;
- support the maturity of lymphocytes;
- prevent infection;
- neutralize cancer cells, preventing their spread.
Intramammary lymph nodes ensure normal drainage of lymph from the breast. If these formations become infected or a malignant tumor grows, they increase in size. With such lesions, painful lumps form in the upper part of the mammary glands.
Solving the problem of enlarged lymph nodes in mastopathy
Can a lymph node become enlarged with mastopathy? We will talk about this in the article.
Can lymph nodes become enlarged with mastopathy? When a woman is diagnosed with diffuse type mastopathy, it will not be accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes.
If the diagnosis is fibrocystic dysplasia, then in this case mastopathy and the lymph nodes under the arm are interconnected.
That is, it can cause complications in the form of lymphadenopathy.
An increase in axillary lymph nodes is especially observed with mastopathy shortly before the start of the menstrual cycle.
Because at this time the woman’s hormonal state changes, which also affects the disease.
After the menstrual cycle ends, the acute symptoms of the disease also disappear.
- Stage one is characterized by the fact that before the menstrual cycle, 7-9 days before the menstrual cycle, the internal structures of the mammary glands begin to coarse. These manifestations begin to be noticeable during self-examination. Inflammation of the lymph nodes during mastopathy may not be observed, or they will not have painful manifestations.
The age at which this phase of the disease usually manifests is from 20 to 30 years. The menstrual cycle does not change in any way in terms of regularity, but becomes short up to 21 days. - In the second stage, one can note the presence of cysts and the onset of symptoms 2-3 weeks before the start of the menstrual cycle. The age group in which this phase of mastopathy occurs is from 30 to 40 years. The lymphatic system becomes inflamed more often and is accompanied by aching pain; sometimes the pain can be stabbing in nature and manifest itself in the area of the diaphragm and heart.
- At the third stage of development, which mostly affects the age after 40 years, the pain of the mammary glands themselves is of low intensity, but there is a large accumulation of cysts. Additionally, there is a brown-green discharge that can be observed by pressing on the nipples.
At the same time, the lymph node is enlarged due to mastopathy. There is also acute pain of a shooting nature, which can manifest itself in the cervical spine, collarbone or stomach.
Enlarged lymph nodes may not always be accompanied by a disease such as mastopathy, no matter what type it is.
If the lymph nodes change their normal state and become enlarged, then this is a signal that pathological changes are beginning to occur in the body.
If we consider inflammation and enlargement of the lymph nodes, starting from the fact that mastopathy has been diagnosed, then the following nodes are more susceptible to this:
- axipilar (those located under the armpit);
- clavicular and subclavian.
Inflammation of these particular lymph nodes occurs due to the fact that blockage (formation of cysts and nodes) in the chest and mammary glands affects the normal movement of lymph through the woman’s body system.
The lymphatic system in this area is designed in such a way that the outflow of lymph goes directly to the armpit area and the supraclavicular region.
It is impossible to say with certainty where exactly the inflammatory process will manifest itself in the lymph nodes.
With mastopathy, the supraclavicular lymph nodes may also enlarge.
IMPORTANT If swollen lymph nodes are detected, you should immediately consult a specialist, because self-medication in this case is unacceptable, because lymph nodes can be enlarged for more serious reasons.
We suggest you read: Chicken ass: how to effectively remove a wart
An enlarged and swollen lymph node indicates that the body is fighting some kind of infection that has entered the body. With the help of the lymphatic system, the body gets rid of foreign objects.
Reasons why lymph nodes may be enlarged:
- The simplest reason lies in non-compliance with hygiene rules or incorrect selection of cosmetic care products. For example, deodorant clogs the sweat glands or lack of self-care due to excessive sweating.
- Sometimes pregnancy and lactation cause enlarged lymph nodes, but this manifestation does not require treatment, because in fact it is not a disease.
- The cause may be boils or suppuration on the shoulders, arms or chest.
- In childhood, inflammatory lymph nodes may occur if chickenpox, measles or monoculosis are present. In this case, you should treat the underlying disease.
Considering the swelling of the lymph nodes, we can name the following diseases that provoke this process:
- tuberculosis;
- brucellosis;
- tularemia;
- syphilis;
- plague;
- some systemic diseases, such as rheumatism;
- oncological diseases: breast cancer, lymphogranulomatosis, lymphoma.
https://youtu.be/dgQAgrbUJ54
Swelling may also occur in the lymph nodes in the event of a disease such as axillary lymphadenitis.
It can be recognized by symptoms of fever, chills and malaise. Several nodes can be inflamed at once, which either retain their mobility or become fused with nearby tissues.
Pain syndrome is not always accompanied by such diseases. If acute lymphadenitis is caused by tuberculosis infection or syphilis, then pain may not be observed. There is also no pain with cancer or blood diseases.
When mastopathy hurts under the armpit, what should I do? When the pain from an inflamed lymph node becomes very severe, then initially it is worth eliminating the pain with any medication with painkillers and anti-inflammatory effects.
But you need to do this only in order to be able to get to the doctor and undergo an examination.
Self-diagnosis and self-treatment will not lead to the desired results, because it is not possible to understand the cause on your own.
The following measures may be prescribed by a doctor for enlarged lymph nodes:
- If the lymph node does not stop showing pain within 21 days and the causes have not been identified, a puncture and even a biopsy are prescribed.
- When a cause is discovered, all efforts are directed toward treating the disease that caused the inflammatory process in the lymphatic system.
- If the cause is mastopathy, then treatment methods will depend on the type of disease. Basically, the examination is carried out by doing a mammogram, ultrasound, taking a course of medications and contraceptives containing hormones in order to equalize the hormonal level in a woman’s blood.
- In some cases, inflammation can only be eliminated through surgery.
If the pain syndrome is so severe that it is not possible to get to the hospital on your own, you should call an ambulance, which, after a superficial examination, will refer you to the right department in the hospital to a specialist.
If swelling of the lymph nodes is detected that is not accompanied by severe pain, you should contact your doctor, who will give you a referral to the right specialist.
This should be done when the patient has no idea why the lymph node is inflamed.
If you have previously been diagnosed with one of the types of mastopathy or such symptoms were discovered during breast self-examination, then you need to contact a mammologist.
To avoid such a disease, it is better to take preventive measures and monitor your health.
You should also undergo regular checkups to ensure that your breasts remain in stable, normal functioning and healthy condition.
When implementing preventive measures, there is a chance to detect the disease and get rid of it in the early stages, which is much easier and less painful.
Diseases of the intramammary lymph node of the breast
A marked increase in the size of the lymph nodes is defined as “axillary lymphadenopathy.” It is not an independent pathology and always acts as a clinical symptom of some disease.
The severity of the danger to the patient’s body depends on the nature of the disease present.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes is characteristic of various diseases, including incurable ones. Therefore, if their deviation from the norm has been identified, it is imperative to establish the cause of such an abnormal condition:
- The node has a soft structure, is mobile and painful - a sign of infection in the mammary glands.
- The swelling of the lymph node is characterized by symmetry and elasticity - the presence of a benign formation.
- A unilateral (right or left) painless and hard heterogeneous node connected to adjacent tissues or other nodes is a malignant process in the chest area.
- Bilateral lymph node swelling indicates infection.
- Inflammation of the axillary nodes during pregnancy and pregnancy is the presence of an infectious disease. The occurrence of swelling indicates that the body is trying to suppress the activity of pathogenic organisms.
- It also happens that enlarged lymph nodes occur after an injury to the right or left arm or after a vaccination given to the shoulder.
Usually, after thorough treatment of the provoking factor, the lymph nodes shrink and acquire their normal size.
| Reasons for enlarged regional lymph nodes | Features of manifestation |
| Mastitis | Inflammation of the breast occurs against the background of the penetration of pathogenic organisms into the tissue of the mammary glands: 1. During lactation. 2. After breast injury. 3. Due to the presence of a chronic infectious disease. |
| Mastopathy | Benign dense inclusions form in the breast. |
| Cancer | Malignant tumors form in the mammary glands. |
| Silicone leakage after breast implant placement | After mammoplasty, leakage of the silicone substance may occur, which causes swelling of the lymph nodes. |
In addition to the above reasons, the occurrence of an intramammary lymph node is facilitated by:
- HIV.
- Measles.
- Tuberculosis.
- Chronic stress.
- Weak immunity.
- Endocrine disorders.
- Taking certain medications.
- Hypothermia of the body or bust.
Methods for diagnosing breast diseases
A larger number of breast diseases can only be detected in a clinical setting. To diagnose tumor diseases, a woman must undergo an ultrasound, mammography, and biopsy. Only with the results of these studies in hand can a specialist make a diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment.
At home, women should examine and palpate their breasts monthly and, if there are any changes in their structure, contact a specialist. Mammography examinations must be carried out on a regular basis: women under 40 years of age - once every 3 years, after 40 years - once a year.
If discomfort occurs in the armpit area and lumps form, a woman should consult a mammologist or therapist; for a man - to see a therapist. After a physical examination and palpation, the doctor will refer you for additional examinations. The diagnosis is made based on the results:
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands;
- ductography (x-ray with contrast);
- computed tomography;
- MRI.
In addition, it is necessary to exclude a number of infectious and inflammatory diseases, so the patient is sent for a biochemical blood test, based on the results of which additional examinations are prescribed.
Axillary lymph nodes in the mammary gland: norm and size, inflammation
An inflammatory process in the mammary glands (mastitis) is dangerous for a woman. At the same time, the woman experiences severe pain. Over time, the skin on the chest may harden and redden, and body temperature often rises.
Inflammation most worries women from 18 to 35 years old or 15-50 years old. During this period, hormones are especially active, which is why mastitis develops.
Is it possible to prevent breast inflammation? Why is mastitis dangerous? What treatment methods are there?
- Lactostasis, when milk stagnates in the breast. Most often this happens at the beginning of lactation, when the newborn does not eat the entire breast, but milk is constantly supplied.
- Mammary duct injury.
- Anatomical pathology of the nipple.
- The nipple was damaged at the beginning of lactation, because of this, pathological microflora constantly develops in it.
- Scratches on the chest lead to infection.
- The infection enters through the bloodstream from other inflamed areas of the skin.
- Weakened immunity after childbirth.
- Chest hypothermia.
- Various hormonal imbalances in the body.
- Acute development of thoracic and cervical radiculitis.
- Injury to the mammary gland during which it becomes infected.
- After experiencing severe stress.
- Benign or malignant breast tumor.
During the inflammatory process, the sensitivity of the breast first increases, then severe pain begins to bother you. The following signs may also be observed:
- Various compactions occur.
- Body temperature rises, sometimes up to 40 degrees.
- The breasts swell noticeably, so the mammary gland appears larger.
- Lymph nodes may become enlarged.
- Tachycardia (an infectious form of chest inflammation).
- A blood test shows a significant increase in leukocytes in the blood.
It is important to pay attention to the type of inflammation; depending on it, different symptoms appear:
- Serous mastitis is accompanied by severe pain, the appearance of lumps, and changes in the color of the mammary gland. In this case, the body temperature does not increase.
- The acute infected form is characterized by pain and high fever. When the disease occurs, the skin becomes significantly red. The pain becomes sharp, it is impossible to touch the chest. The patient's condition may deteriorate sharply.
- A chronic inflammatory process in the mammary glands is characterized by tightness in the breasts and slight pain. The temperature can rise no more than 37.5 degrees.
- Breast abscess is a dangerous form of mastitis. When it affects the clear contour of the breast, pus accumulates in large quantities. You may notice how much your breasts swell. The woman feels unwell, her temperature rises sharply - up to 40 degrees.
- The phlegmonous appearance is characterized by a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition, while intoxication of the body is observed, sleep and appetite may be disturbed. On the skin you can notice that the veins are significantly dilated.
- Breast gangrene is very severe. Inflamed breasts become purple or bluish and, over time, completely lose their shape.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Psoriasis and pancreas treatment
If you experience any discomfort in your breasts, consult a mammologist immediately. He will carefully examine and feel your breasts. A more informative diagnostic method is ultrasound; it shows how the inflammatory process proceeds, and also finds out what stage of development it is at.
In the case when a mammologist suspects a malignant tumor, a cancerous tumor, resonance imaging and a biopsy are performed. Differential diagnosis is of no small importance, in which it is important to promptly exclude a breast tumor, abscess, or cyst. Sometimes a biopsy with puncture is required.
It is advisable to treat the acute form of mastitis at an early stage, this way you will prevent complications such as an abscess and purulent lesion. Breast inflammation is most often treated with antibiotics.
Attention! If a woman does not feel better after taking antibiotics, she is admitted to the hospital, fully examined and effective treatment is prescribed.
During lactation, it is necessary to put the baby to the breast as often as possible. You cannot stop feeding; you may have to abstain a little if a woman is taking antibiotics.
Carefully! A breast abscess can only be treated with surgery, during which the abscess is completely opened, then emptied and drained.
After the operation, the woman must undergo a rehabilitation course, during which she takes antibacterial drugs and broad-spectrum medications.
In the case where breast inflammation is caused by erysipelas, it is necessary to use antimicrobial drugs - sulfonamides. Additionally, the method of ultraviolet irradiation is used. It is especially important during this period to take care of strengthening the woman’s immune system.
Every woman must adhere to hygiene rules. This rule especially applies to nursing mothers. It is necessary to take a shower daily, change your bra promptly, and carefully choose personal hygiene products.
After a shower, it is recommended to apply skin moisturizers to the chest - Purelan, Bepanten, solution with vitamin A. If cracks appear, treat them promptly with Rescuer balm, buy sea buckthorn oil at the pharmacy and treat the affected areas of the skin of the chest.
Thus, breast inflammation in a woman is a serious problem that needs to be addressed in a timely manner, otherwise life-threatening complications may arise in the future.
Normally, lymph nodes do not manifest themselves in any way, but enlarge in various infectious and immune diseases
The protection of organs and tissues from foreign microorganisms or substances is carried out by the lymphatic system, which consists of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes and some organs. Lymphatic vessels collect fluid from various parts of the body, and lymph nodes filter it. Lymph nodes are distributed unevenly in the human body.
Axillary (axillary) lymph nodes are divided into 6 groups:
- anterior (pectoral): located along the lower border of the chest (or mammary gland) behind the pectoralis major muscle;
- posterior (subscapularis): located in front of the subscapularis muscle, these nodes receive lymph from the superficial lymphatic vessels from the back;
- lateral: located along the lateral side of the axillary vein, these nodes receive most of the lymph from the lymphatic vessels of the upper limb;
- central: localized in the center of the armpit, receives lymph from the three above groups of nodes;
- Infraclavicular: These nodes are not strictly axillary lymph nodes because they are located outside the armpit. They lie in the depression between the deltoid and pectoral muscles and receive lymph from the superficial lymphatic vessels on the side of the arm and forearm;
- apical: located at the top of the axilla on the lateral border of the 1st rib. These lymph nodes receive lymph from lymphatic vessels from all other axillary nodes.
Normal sizes
Lymph nodes are located throughout the body. Although the functions of all lymph nodes are the same, their size can vary and range from 2 millimeters to 2 centimeters. With the help of lymphatic vessels, lymph reaches the lymph nodes, where it is cleared of microbes, foreign bodies or tumor cells, and then returned to the bloodstream.
In healthy people, the nodes cannot be felt. If the size of the nodes increases beyond 2 cm, this is a sign of diseases of varying severity: from a cancerous tumor to a harmless bacterial infection. There is no generally accepted standard for the size of axillary lymph nodes in the mammary gland.
Reference. In the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (ICD-10), enlarged lymph nodes in the armpit are designated by code R59.0.
An increase and the appearance of pain in the axillary lymph nodes indicates the development of an infectious disease or malignant neoplasm in the body. If such symptoms occur, it is recommended to consult a family therapist. The patient can also contact an oncologist, immunologist, otolaryngologist, phthisiatrician and other specialized specialists.
Mastitis occurs as a result of infection of the mammary gland by bacteria, manifested by swelling of the gland, an increase in size, soreness and increased sensitivity, redness of the skin and fever
Enlarged lymph nodes in the armpits may be due to inflammation of the lymphatic vessels. Bacteria (especially streptococci or staphylococci) that enter the lymphatic vessel through an open skin wound can reach the lymph nodes.
The main symptom of acute lymphangitis is the appearance of a red stripe on the skin. The resulting inflammation is sometimes falsely called sepsis, or "blood poisoning." Lymph nodes in the immediate vicinity of the inflamed lymph vessel become painfully swollen, and the skin becomes overheated and red.
There is a risk of an abscess.
A possible cause of enlarged axillary lymph nodes is mastitis - inflammation of the mammary gland (mainly female) or chest muscles (myositis).
Mastitis most often occurs in breastfeeding women approximately 2-4 weeks after giving birth. Sometimes the disease occurs regardless of childbirth.
In most cases, mastitis is caused by infection with streptococci or staphylococci, which enter the body through cracks in the breast nipples during breastfeeding.
Signs of a breast infection include redness, pain, swelling, swollen lymph nodes on the affected side, and overheated skin. At the same time, fever, chills and general malaise often occur; in more rare cases, purulent abscesses or fistulas develop.
Sometimes the cause of enlarged axillary lymph nodes is acute HIV infection, in which symptoms begin approximately 1-6 weeks after infection. Patients experience headaches, fever, diarrhea and vomiting, as well as inflammation of the lymph nodes, which can be located in different parts of the body.
The Epstein-Barr virus, which is a herpes virus, causes infectious mononucleosis, characterized by pathological enlargement of the lymph nodes. The viral infection is transmitted through saliva, including during kissing, which is why the disease is otherwise called “kissing disease.”
Symptoms of lymphadenopathy
The main sign indicating the appearance of intramammary lymph nodes is a characteristic solid formation measuring 1-1.5 cm near the armpit.
The presence of other symptoms depends on what kind of disease led to the swelling of the lymph node, since each pathological condition is characterized by individual symptoms.
Regarding general signs, there are not very many of them:
- Unreasonable weakness.
- Heavy night sweats.
- Pain in the upper half of the breast upon palpation.
However, lymphadenopathy may generally occur without obvious signs, which is typical for the early stages of oncology.
| Disease | Symptoms of lymphadenopathy due to illness |
| Mastitis (acute) | Redness of the skin of the chest. High temperature (39-40 degrees). Headache. Severe breast swelling. Distension of the mammary glands. Nipple discharge with pus. Swelling of other local lymph nodes. |
| Mastitis (chronic) | It is more difficult to diagnose than the acute form, and therefore requires differentiation from other pathological conditions. With chronic mastitis, the symptoms are few; usually a woman is worried about a slightly elevated temperature (no more than 37-37.2 degrees) and inexpressible pain in the bust. Often, an increased size of the lymph node is the only clinical symptom of chronic mastitis. |
| Mastopathy | The disease is mainly caused by hormonal imbalance. Character of symptoms: 1. Feeling of tension in the mammary gland. 2. Pain in the breast, which gradually increases and reaches its peak towards the end of the monthly cycle. 3. When palpating the chest, a single nodular compaction is detected, however, such formations can also be in the plural. 4. When pressing on the nipple, liquid exudate appears. |
| Rupture of silicone prosthesis in the breast | According to mammological statistics, about 10% of manifestations of lymphadenopathy are associated with the installation of a low-quality silicone implant. Women who have undergone breast augmentation through implantation of endoprostheses should regularly monitor the lymph nodes and monitor the condition of the implant. A sharp change in the configuration of the breast or a decrease in its volume is a sign of a violation of the integrity of the implanted prosthesis. If it ruptures, the silicone contents may leak. Often this situation does not cause any discomfort, but sometimes the patient is worried about: 1. Pain in the mammary glands. 2. Redness of the skin. 3. Unpleasant discomfort in the bust. |
| Malignant neoplasm | In breast cancer with inflammation in the lymph nodes, the following is observed: 1. Apathy. 2. Heavy sweating at night. 3. Rapid weight loss. 4. General weakness. 5. Breast deformation. 6. Modification of the nipple skin. 7. Cloudy or bloody discharge from the nipples. 8. Formation of depressions and other irregularities on the breast. |