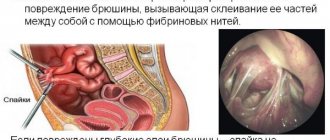
Every woman dreams of becoming a mother. However, it happens that the presence of adhesive formations in the ovaries becomes an obstacle to her happiness. Often, adhesions form between the ovaries and the uterus, its ligaments, fallopian tubes and intestinal loops.
With adhesive formations, conception, ovulation and the movement of a fertilized egg through the fallopian tubes is almost impossible. This is how infertility appears, which becomes a big problem for many couples. That is why you should know all the factors, symptoms of ovarian adhesions and treat them immediately.
Causes of adhesive disease in the ovaries
Ovarian adhesions can form for numerous reasons, but the main factor in their occurrence in the pelvic organs is a long-term process of inflammation. If inflammation of the ovaries and nearby organs is not treated for a long time, the adhesions begin to actively grow and lose their elasticity. Other causes of the disease include:
- Erosion on the cervix, non-compliance with hygiene rules when cauterizing it.
- Rapid labor with numerous deep lacerations;
- External endometriosis subsequently, blood from the endometrium enters the abdominal cavity;
- Surgical interventions in the pelvic organs:
- Appendectomy;
- Myomectomy performed via laparotomy;
- Ovarian resection;
This is important to know! The risk of inflammation and adhesions after surgery directly depends on the individual characteristics of the abdominal cavity of a particular patient, as well as on poor hygiene during surgery.
- Incorrect installation of the intrauterine device;
- The presence of inflammation of the intestines and genital organs;
- Abortion;
- Abdominal injuries;
- Long-term use of antibiotics, sulfonamides;
- Diseases of the pelvic organs:
- Endometritis;
- Oophoritis;
- Salpingitis;
- Sexually transmitted infections;
- Appendix;
- Ectopic pregnancy;
- Hysteroscopy, its illiterate implementation and the introduction of pathogenic bacteria;
- Hypothermia;
- Inflammatory process in the fallopian tubes.
For what reasons does the problem occur?
Adhesions in the pelvis and on the ovaries, in particular, began to appear more and more often. And doctors even identified a whole list of catalysts that become the main cause of pathology. Among them:
- Various types of inflammatory infections in the pelvis
- Inflammation in other organs, appendicitis is often cited as an example
- Past operations: this is explained simply - any operation represents a violation of the integrity of the organ and the subsequent formation of scars at the site of the incision
- Presence of injuries
- Existing hemorrhages in the peritoneum
- Endometriosis
- Previous abortions
- Hypothermia
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Taking antibiotics of a certain spectrum
The adhesions themselves, incl. and on the ovaries, are quite safe. But if they begin to affect neighboring organs, a rather serious disruption occurs in the functioning of the entire organism as a whole. And here it is important not to delay - the sooner you seek help from doctors, the greater the chances of a complete cure and minimizing the consequences.
https://youtu.be/fYgJ6YU5X-A
Symptoms of the presence of adhesions in a woman’s body
Adhesions on the ovaries have their own characteristic symptoms. Very often, a woman cannot even imagine the presence of adhesions, and takes a simple nagging pain in the lower abdomen as the beginning of her period.
The symptoms of the disease are similar to other gynecological diseases, so a woman only learns about the presence of adhesions when problems with conception arise. Therefore, it is important to know the most common signs of adhesions.
So, most often the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- Irregular menstrual cycle;
- Pain during menstruation;
- Infertility or inability to conceive a child for a year;
- Drawing, periodic or stabbing pain in the lower abdomen, sometimes in the lower back;
- Pain during intercourse;
Attention! If you find even minor symptoms of adhesive disease and suspect that you have it, be sure to consult a specialist!
Symptoms and diagnosis
It is impossible to determine the presence of adhesions in the fallopian tubes without examination. After all, the pathology is not accompanied by any symptomatic manifestations: the menstrual cycle and the nature of vaginal discharge do not change, there is no pain.
Certain symptoms appear only during the developing inflammatory process. Acute inflammation manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- Ultrasound shows the presence of accumulated fluid behind the uterus;
- Periodically occurring pain in the lower abdomen;
- Slightly elevated body temperature;
- Pain in the peritoneal area.
Diagnosing the presence of an adhesive process can only be done using hardware methods.
There are several diagnostic techniques that can reliably determine the presence of adhesions in pipes. The most famous of them:
- Salpingography;
- Sonosalpingoscopy.
During salpingography, adhesions are detected using x-ray examination. To see them, a special solution is injected into the pipes and then X-rayed. A special liquid allows you to clearly see formations and growths in the pipe cavity, so such diagnostics are quite informative.
The peculiarity of this study is the time it was conducted - before ovulation. Indeed, in the event of conception, X-rays will negatively affect the development of the fetus and can cause a miscarriage.
Sonosalpingoscopy is performed at the beginning of the cycle. The technique requires anesthesia, which is administered rectally or by injection. The woman’s entire abdominal cavity is gradually filled with saline, monitoring the process of its movement using ultrasound.
To exclude the presence of adhesions in the pelvis, diagnostic laparoscopy is prescribed. If the adhesive process occurs in parallel with the inflammatory process, laboratory tests are indicated. They will help identify the cause of inflammation and determine how sensitive the infectious agent is to a certain group of antibiotics.
Diagnosis of adhesions in the ovaries
Only a qualified gynecologist can determine the presence of adhesions through a routine gynecological examination. However, it often happens that it is difficult to confirm or refute this disease. That is why the specialist prescribes a number of other examinations, including:
- Ultrasound of the ovaries and uterus;
- Hysterosalpingography;
This is important to know! The examination is carried out between 5 and 11 days of the menstrual cycle on an empty stomach and after an enema. Before carrying out this diagnosis, it is imperative to cure all sexually transmitted diseases!
- Smear for polymerase chain reaction and flora;
- Blood analysis;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
Only after a comprehensive examination and study of its results, excluding other causes of pain in the lower abdomen, the diagnosis is confirmed and appropriate treatment is prescribed. The effectiveness and speed of treatment depends on correctly performed diagnostics and competent interpretation of tests.
Treatment of the disease
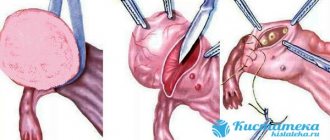
In most cases, ovarian adhesions are treated using laparoscopy. It can be carried out using water pressure, laser or electric knife. This operation will help to quickly and painlessly separate and remove fibrous constrictions. The surgical intervention takes only 40 minutes and is performed under local anesthesia. However, treatment of the adhesive process consists not only in its elimination, but also in preventing neoplasms, eliminating infection and prevention.
In the postoperative period, the woman is prescribed a course of antibiotics, anticoagulants and enzymes to eliminate foci of inflammation and reduce blood clotting. A mandatory step is the application of an absorbable polymer film to the ovaries and the introduction of a barrier fluid to prevent relapse. Based on the results of laparoscopy and the effectiveness of treatment, a certain course of physiotherapy is prescribed.
Attention! During the postoperative period, any physical activity is strictly prohibited in the first two weeks!
The initial stage of adhesions formation involves resorption, elasticity and removal of adhesions with the help of medications.
Adhesions can be treated with the following medications:
- Antibiotics:
- Tetracyclines;
- Sulfonamides;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. They act on the source of inflammation, suppressing and reducing the extent of its spread;
- Fibrinolytic agents. The substance around which adhesions appear is dissolved. These include:
- Chemotrypsin;
- Urokinase;
- Streptokinase;
- Anticoagulants. Reduce the level of blood clotting. This includes:
- Citrate;
- Heparin;
- Enzymes;
- Vitamins;
- Electrophoresis with calcium, magnesium and zinc;
- Balneotherapy. The use of natural mineral waters in the fight against inflammation and neoplasms. May be assigned:
- Irrigation of internal genital organs;
- Washing;
- Using baths or showers.
Possible complications
One of the main risks of having ovarian adhesions is the inability to get pregnant, resulting in infertility. Adhesions can grow rapidly, displace neighboring organs, and disrupt contact between the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries. Reduce peristalsis and patency of the fallopian tubes.
Adhesive junctions worsen the ovulation process, prevent the fertilized egg from penetrating into the uterine cavity, and compress nerves and blood vessels. Increases the possibility of ectopic pregnancy.
Adhesions are a common occurrence in gynecology. Almost any organ in the reproductive system can undergo such a process, which can lead to unpleasant consequences. This article will look at adhesions on the ovaries and what they lead to and how to treat them.
Causes and risk factors
Such cords are formed as a result of the inflammatory process. For example, if, during swelling, two neighboring organs or two often of the same organ are close to each other, then the body tries to restore “integrity” and strives to “grow” them together, achieving this by forming connective tissue.
Thus, risk factors for this disease are chronic inflammatory processes in the ovaries and in the reproductive system as a whole. In addition, there is a genetic predisposition to accelerate the proliferation of connective tissue.
Treatment
Adhesive disease in the ovaries is fraught with a large number of complications both from the point of view of reproductive function and the reproductive system, and the whole organism as a whole. For this reason, this condition must be promptly diagnosed and treated. In addition, adhesions, regardless of which organ or system they are located in, tend to progress, sometimes quite quickly. Treatment in the early stages is much simpler than in the later stages, therefore, the sooner therapy is prescribed, the better.
Medicines
Drug treatment does not play a leading role in therapy, but it can be quite effective if the ovaries are not severely affected, or if used in combination with physiotherapeutic procedures. In addition, many drugs are used after surgery and before it in order to prevent relapses and the development of severe complications. How to treat adhesions such a condition with drugs?
- Vilprafen is an antibiotic that is most suitable for the treatment of gynecological pathologies. Helps to completely eliminate inflammation in the ovaries and prevent its re-development after the intervention, and hence the recurrence of the pathology. Taken in the form of vaginal tablets (suppositories) 500 mg per day;
- Flamax is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug suitable for the treatment of gynecological diseases. It is taken together with an antibiotic and acts in combination with it. It is also prescribed, most often, in the form of vaginal suppositories. The standard dosage is one suppository per day;
- Longidaza is an enzymatic drug. This enzyme acts directly on the connective tissue, destroying glycopeptide bonds, that is, affecting the adhesive tissue itself, thinning and destroying them. The drug is administered intramuscularly at 3000 IU once a day;
- Trypsin is a drug named after the main active ingredient in the product. The enzyme trypsin acts similarly to Longidase, as a result of which the resorption of adhesions is accelerated and activated. It is used by injection, administered intramuscularly once a day, 10 ml;
- Acylact is a probiotic agent that helps restore the microflora of the genital organs, which is destroyed under the influence of the inflammatory process and the use of antibiotics. Healthy microflora significantly increases resistance to inflammation and other pathologies.
The combination of drugs, their exact dosages and administration characteristics are selected by the doctor. Self-medication in this case is unacceptable, as it can cause a worsening of the condition.
Physiotherapy
This is a fairly effective and popular method of treating adhesive disease, especially in cases where it is not very advanced - the adhesions are not too thick and quite elastic. In addition, this method is prescribed at the stage of preparation for surgery and after it to speed up recovery and prevent relapses. In addition, such methods are used as additional methods during drug treatment.
The patient is prescribed SVYA and/or UHF therapy, and sometimes electrophoresis or other measures may also be prescribed. They are aimed at relieving any remaining inflammation and swelling. In addition, they help increase the elasticity of adhesions, which leads to the ovary becoming less deformed and the symptoms less pronounced. Also, exposure to microwaves causes the adhesions to become thinner and the connective tissue to partially dissolve.
Physical exercise and therapeutic gynecological massage for adhesive disease are also sometimes prescribed. They are also aimed at increasing the elasticity of adhesions, their gradual stretching and thereby eliminating organ deformations. However, with the process in the ovaries, this approach is usually not effective. However, sometimes these measures are still prescribed.
Vitamins
Vitamin preparations do not have a specific effect on this pathology, and as such, targeted treatment is not carried out with them. However, they have an important role in overall increasing immunity, and therefore the body’s resistance to pathologies and its ability to resist inflammation. Vitamins A, B and E are recommended to speed up healing. Magnesium has a beneficial effect on the entire reproductive system.
Operation
Surgery is the most radical and effective way to get rid of the problem. The intervention is carried out when there are severe negative symptoms that cause discomfort, or there is significant deformation of the organ or inhibition of its functioning. In this situation, the adhesions on the ovaries are usually already dense and inelastic, and it is not possible to remove them otherwise.
How is the treatment carried out?
Treatment methods for such a phenomenon as adhesions, incl. and on the ovaries, quite a lot. And each of them meets its own goals and objectives.
Conservative intervention
Adhesions in the pelvic organs - on the ovaries, in the fallopian tubes, etc. - You can try to cure it with medication. This treatment option is used in situations where the problem is only at the beginning of its formation. True, this does not happen so often, because... adhesions are detected only at routine appointments due to the absence of symptoms.
Such therapy should be comprehensive, incl. and on the ovaries. In addition to taking pills and other medications that directly affect the adhesions themselves, you should also take medications that relieve inflammation. Medicines used for treatment can be in different forms:
- Injections
- Suppositories
- Tablet options
Alternatively, physiotherapy is used to treat inflammation of the ovaries. They contribute to the overall health of the body.
Surgical intervention
If the adhesions have grown to such an extent that they have begun to cause noticeable discomfort, most likely it will not be possible to cope with conventional therapeutic methods. In this case use. To solve the problem, use 2 options:
- Laparotomy
- Laparoscopic
The first option is considered an old, proven and quite successful option for correcting the problem. The second method is considered more modern. It is also considered more productive, because Helps remove even small and thin films.
During surgery, general anesthesia is used. This allows you not to be afraid and significantly simplifies the treatment process.
Traditional treatment options
Often many people try to use unconventional methods to get rid of the problem. However, it is worth remembering that the use of herbal preparations and traditional methods is not prohibited, but without canceling official treatment.
An excellent solution would be various herbal decoctions and infusions. For example, St. John's wort is considered a fairly effective herb. It is not difficult to prepare the medicine - just brew one spoon with a glass of boiling water. Then the product must be put on fire and boiled for 15 minutes. Cool the liquid and strain, after which it can be taken quite calmly. For treatment, you should take it a glass a day.
In addition, bergenia is often used. It also needs to be poured with boiling water and placed in a dark place for 8 hours. The product should be stored in a cool place. A similar decoction is used for douching.
Conclusion
Adhesion of the ovary to the uterus is a serious pathology that tends to progress. Therefore, even if the condition does not bother you at all, this does not mean that it should be ignored. If adhesions are detected, treatment must begin immediately.
The female body is structured very complexly, because by nature a woman is endowed with the reproductive function. In the context of increasing morbidity of the female reproductive system, the proportion of various types of surgical interventions is increasing. They are, in turn, one of the risk factors for the appearance of such pathologies as adhesions on the ovaries. Most often, this disease occurs without a clear clinical picture, but it is dangerous due to infertility.
Is it possible to get pregnant and give birth with an ovarian cyst?
From what is known about this disease, we can conclude that with certain types of it, the possibility of becoming pregnant is not excluded.
Does it interfere with getting pregnant?
Diseases such as polycystic disease, follicular and endometriotic formations make conception almost impossible, and if both organs are affected, the woman is considered infertile.
Adhesions and adhesive disease
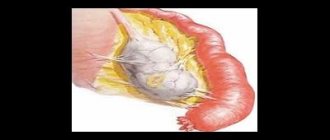
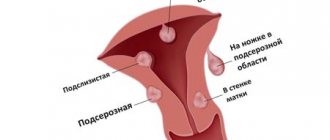
From a morphological point of view, a commissure is nothing more than a cord of connective tissue. It is pathological; normally such a structure should not exist. The cord connects any adjacent anatomical structures to each other. Ovarian adhesions can be fixed by the uterus, fallopian tube, intestinal loops and other organs.
Adhesive disease is a pathological condition in which connective tissue appears between organs and anatomical structures, and there are clinical symptoms. In the vast majority of cases, adhesions form after surgery. The larger the volume of surgery, the higher the risk of connective tissue formation. First, strands of fibrin are formed. This is a protein that accompanies inflammatory reactions, as well as recovery processes. During operations of the fallopian tubes, uterus and ovaries, it is found in large quantities at the site of intervention. If adequate preventive measures are not taken, fibrin clots transform into full-fledged connective tissue, like scar tissue.
Causes of adhesions on the ovaries
The most powerful factor in the appearance of connective tissue is irritation and disruption of tissue integrity. Usually, adhesions are found on the ovaries after laparoscopy or laparotomy surgery (with a full-fledged large incision). Without adequate drainage, absorption therapy, and preventive physical therapy, the likelihood of signs of adhesive disease occurring after ovarian laparoscopy in the future increases.
In general, any surgical intervention
regarding pathology of the pelvic organs are a risk factor for adhesions. This may be removal of the fallopian tube or its excision, treatment of salpingitis, salpingoophoritis (or adnexitis). Adhesions after hysterectomy are not uncommon. This applies to both amputation and organ extirpation. Surgical intervention in both cases is very traumatic. This means that the risk of adhesions increases.
Ovarian diseases themselves become the cause of the described problem. Adhesions in the ovaries are found after suffering inflammatory changes, as well as cysts. This is especially true for the complicated course of these diseases. After removal of an ovarian cyst, adhesions also form, despite the small volume of the operation.
Inflammation from adjacent and neighboring organs becomes a powerful triggering factor for the realization of pathological connective tissue connections between various structures of the pelvic cavity. This fact confirms the detection of adhesions between the ovary and other organs in the following conditions:
- Salpingitis;
- Salpingo-oophoritis;
- Ophooritis;
- Adnexitis;
- Abscess formation of the intestines and uterus.
A large group of triggering factors for adhesions are various interventions and conditions of the uterine mucosa. With endometriosis and erosive damage to the organ, adhesions can be detected. In this case, the right or left ovary is soldered to the uterus. Endometriosis causes a small but sufficient amount of blood to enter. It is enough to form fibrin strands, which later become scar or connective tissue.
Ovary in adhesions: what does it mean?
Pathology affects the organ in the following cases:
The operation violates the integrity of the ovaries and leads to disruptions in the processes of blood clotting and cell renewal. The body is trying to restore tissue structure. Failures in this process lead to the formation of connective tissue that glues organs together. Moreover, the pathology spreads to neighboring organs. At risk are women after an abortion or cesarean section. If there are other ovarian diseases: cyst, endometritis, hypoplasia, the likelihood of adhesive disease increases;
surgical intervention.- chronic or acute inflammatory diseases of the ovaries. These processes are accompanied by fluctuations in the number of leukocytes in the blood. The affected cells injure the ovarian stroma - the dense membranes that connect the tissues. The stroma contains blood vessels that supply the follicles with the necessary substances for functioning. Damage to the membranes creates favorable conditions for tissue growth and division of “infected” cells. As a result, tissue sticks together and scars form. The situation is aggravated by increased synthesis of fibrin, a protein that forms fibers, the clots of which form a blood clot.
There are frequent cases when adhesions form after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst.
- internal bleeding. When the ovary is damaged, blood or intercellular fluid is released. This material forms films that glue organs together;
- incorrect insertion of the intrauterine device;
- sexually transmitted infections;
- endometriosis is a gynecological disease characterized by the growth of endometrial tissue beyond the organ;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- treatment with antibiotics, antimicrobial agents;
- ruptures during childbirth;
- hypothermia;
- hysteroscopy – examination of the uterine cavity with a special device for diagnostic or treatment purposes.
Manifestations of adhesive ovarian disease
Clinical signs of the described disease include discomfort in the abdomen or lower back. Their analogue can be pain. Depending on what the ovary is fused to, the symptoms may have different localization. When fixing to the fallopian tubes, for example, pain occurs on the sides. They can radiate. The pain is not acute. More often they are dull, as with pyelonephritis.
With adhesive disease, the menstrual cycle is disrupted. Your period may be delayed or come earlier than usual. The volume of menstrual flow may also change, either down or up. Pain from adhesions on the ovary is not associated with the onset of menstruation. At the same time, it does not occur in the middle of the cycle, which distinguishes it from apoplexy. The pain syndrome is generally not tied to time intervals, but is permanent (constant) in nature.
During the adhesive process, patients turn to the doctor with unpleasant and painful sensations during sexual intercourse.
Women have been avoiding sexual relations for a long time. This leads to dysphoric disorders - irritability, depression. When connective tissue cords connect the ovaries to the fallopian tubes, the patency of the latter is disrupted. They are known to be hollow structures and promote pregnancy. When the lumen is blocked, its patency is partially or completely impaired. Then pregnancy cannot occur. The next serious problem arises - tubal infertility.
Relying only on clinical symptoms is incorrect. Only instrumental studies are important in making a diagnosis.
Adhesions in the fallopian tubes
After termination of pregnancy or other operations, inflammation may begin in the fallopian tubes due to an infection that has entered there. As a result of inflammation, adhesions can form - films that block the cavity of the fallopian tube partially or completely. If a woman does not consult a doctor in a timely manner, the process becomes irreversible. Due to adhesions, the fallopian tubes cannot function normally, increasing the risk of an ectopic pregnancy. Very often, all this leads to the removal of the fallopian tubes.
Basically, the formation of adhesions occurs without visible symptoms, and very often their presence is discovered only when it is impossible to get pregnant. That is, the woman herself cannot determine whether she has adhesions. The formation of adhesions in the fallopian tubes does not disrupt the menstrual cycle, does not lead to the appearance of discharge or anything else unusual, so the diagnosis can only be made by a specialist after an ultrasound or laparoscopy.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of the pathology is difficult. Indeed, without the use of endoscopy or tomography, it is extremely difficult to detect adhesions. Any diagnostic study begins with general clinical tests: general blood and urine tests, determination of biochemical parameters. This is important in order to make a differential diagnosis. Pain in the abdomen and lower back can occur with a variety of pathologies. Therefore, first of all, the most dangerous and acute diseases that require urgent intervention are excluded. These are appendicitis, intestinal obstruction, acute pyelonephritis and others. Ultrasound examination is a good help in this case. It excludes diseases of the liver, pancreas, spleen, including those of a traumatic nature. Sometimes plain radiography is used. This method is needed to exclude ulcerative perforation of the stomach or duodenum.
Acute pyelonephritis is detected by changes in the general urine test or the Nechiporenko, Zimnitsky test. The symptoms and treatment of this disease differ from those of adhesive disease. Therefore, it is important to carry out adequate differential diagnosis. Ultrasound imaging of the pelvic organs can confirm the presence of adhesions on the ovaries. If no pathological changes are detected, it is important to pay attention to the anamnestic data.
Of particular interest are situations with previous laparoscopic or laparotomic interventions. The risk of adhesions in these cases increases significantly.
Then the diagnostic search does not end there. Hysterosalpingography is another important diagnostic method. It is used to identify obstructed patency of the fallopian tubes. If the fears are confirmed, it is worth starting to prepare the patient for planned laparoscopy. It will initially be of a diagnostic nature, but if adhesions or other pathologies are detected, it will be possible to immediately carry out therapeutic measures.
For planned laparoscopy, a whole series of tests and studies are again prescribed. These include blood and urine tests, identification of pathogens of syphilis, hepatitis, and HIV infection. It is very important to take a smear from the woman’s genital tract. In this way, all acute sexually transmitted infections are excluded. According to the research standards, it is also necessary to conduct electrocardiography, fluorography or an x-ray of the chest organs, as well as consultation with a therapist.
Only a full range of studies will confirm the presence of adhesions. The main thing is to exclude other pathologies.
How to treat ovarian adhesions
The easiest way is to prevent the development of adhesions on the ovaries. To do this, after any surgical intervention, you need to prescribe physiotherapy, a course of supportive and restorative therapy, as well as measures to resolve the developing fibrin threads and strands. Physiotherapy includes electrophoresis with lidase and other enzymes. At later stages, balneotherapy is applicable. Antibacterial treatment is prescribed to prevent infectious complications. B vitamins are effective.
Surgical treatment allows you to radically get rid of adhesions. This is the only method of therapy. There are the following types of surgical intervention for adhesive disease:
- Aquadissection.
- Electrosurgical methods.
- Laser therapeutic techniques.
https://youtu.be/JSxRSz9Jrgo
Prevention of possible complications
It is worth getting rid of education before conception. With some types of disease, pregnancy cannot occur. In others it can, but during pregnancy it continues to grow, creating risks for the health of the baby and the expectant mother. There is a situation in which the bubble disappears as the fetus grows.
In any case, the doctor should monitor the condition and changes in the formation during pregnancy, and if the condition worsens, prescribe appropriate treatment or offer to remove the cyst surgically.
When planning a child with an ovarian cyst, constant medical supervision is required. Only he will be able to determine its type and predict how the formation will affect conception and gestation.
Prevention of adhesions
- avoid hypothermia and the appearance of inflammatory processes in the body;
- maintaining local immunity;
- preventing the occurrence of infections;
- regular sex with a regular partner;
- using a condom during sexual intercourse;
- avoiding termination of pregnancy;
- timely diagnosis of cystic formations of female ovaries;
- avoidance of promiscuity with different partners;
- regular visits not only to the gynecologist, but to the gastroenterologist, since with pathologies in the gastrointestinal tract, adhesions can form between the ovary and the intestines;
- control over the menstrual cycle;
- moderate exercise is necessary;
- adherence to a diet regimen (overeating and fasting are not allowed).
- use of high-quality threads for suturing wounds;
- Powdered gloves are not allowed;
- instruments must be sterile;
- normalization of blood circulation during surgery;
- insertion of drainage for the outflow of blood and inflammatory fluid;
- it is necessary to avoid electrical or laser exposure to the peritoneum;
- do not allow the peritoneum to dry out.
Is it possible to get pregnant with this pathology? After correction, there is a chance to fulfill this desire on your own. But without surgery, there is only one option left - in vitro fertilization.