Important! A remedy for heartburn, gastritis and ulcers, which has helped a huge number of our readers. Read more >>>
Currently, more and more people are faced with various disorders in the functioning of the digestive system. This is caused by eating disorders, stressful situations, and bad habits. One of the dangerous problems is stomach clogging. If you do not consult a specialist in time, there is a risk of developing dangerous complications.
This term refers to a serious pathology, which is characterized by the accumulation of food in the organ. It cannot move through the digestive tract, which causes stretching of the stomach walls.
This leads to circulatory problems and creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, the very first symptoms of the disease should be a reason for a visit to the doctor.
Causes of stomach blockage
This disorder can be caused by various diseases or mechanical damage, which often occurs during surgical interventions.
The appearance of problems with gastric patency usually results from the following pathologies:
- Tumor formations of a benign or malignant nature. The disease can develop due to the fact that the formation blocks the path of food movement. Radiation therapy can also cause damage.
- Adhesions or scar changes. Similar problems can arise as a result of surgery.
- Inflammation, which leads to a decrease in the diameter of the digestive organ, and stenosis of its walls.
- Cholelithiasis.
- Complex forms of constipation that develop as a result of Parkinson's disease.
- Intussusception of the stomach.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Long-term use of medications that negatively affect the functioning of gastric motility.
Signs of a problem
Symptoms of stomach clogging are not specific and can relate to various pathologies of the digestive system - for example, acute gastritis. Therefore, only instrumental diagnostics will help make a diagnosis.
The main signs of the disease include the following:
- Vomiting with bile impurities. It is a consequence of the fact that the body tries to remove food by any means.
- Symptoms of dehydration. This condition is a consequence of frequent vomiting.
- Rapid onset of feeling weak or tired.
- Nausea.
- Flatulence.
- Severe pain syndrome of paroxysmal nature.
- Diarrhea. This symptom is common when there is not too serious damage. With severe lesions, on the contrary, constipation appears.
- Bloody impurities in the stool.
- Temperature increase.
- Loss of appetite.
When blood appears in the vomit or stool, we can talk about the onset of internal bleeding. If you have such symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor.
In some cases, signs of stomach blockage do not appear immediately, but only after a few days. If treatment is not started on time, the risk of death increases by 20-25%. That is why any suspicious symptoms should be a reason to visit a doctor.
Forecast
Destruction of human microflora is a consequence of gastric obstruction.
Experts say that the probability of death from this disease is 25%. At the same time, every hour of delay has a detrimental effect on the body. In the presence of obstruction, its transition to paralytic obstruction is possible, and the risk of shock is high. Doctors make a prognosis based on the following factors:
- age;
- gender;
- timing of the operation, degree of damage to the body;
- type of obstruction;
- presence/absence of shock. Measures to relieve shock are taken into account;
- presence/absence of pain relief;
- general indicators of the body (temperature, pressure, water level, level of consumption and digestion of proteins/fats/carbohydrates/useful microelements);
- presence/absence of cancer, oncological neoplasms.
The forecast depends on the above factors. Cases of death are common, but if you consult a specialist in a timely manner and follow medical instructions, the operation will be successful.
How to treat
Treatment of pathology can be carried out using the following methods:
- Conservative therapy - in this case, enemas and gastric lavage are prescribed. The doctor may also prescribe IVs using a special solution. This helps restore normal electrolyte balance. In some cases, catheterization is indicated to help determine fluid balance.
- Surgical intervention - during this procedure, excess fluid is removed from the stomach with a flexible tube, after which, if necessary, tissue that has undergone necrosis is removed. The healthy organ fragments are then joined together. Within 6-8 hours after surgery, dehydration should be eliminated and water and electrolyte balance should be restored.
Conservative therapy is indicated in cases of not very serious injuries. In this case, surgical intervention is required in severe stages of the disease.
If symptoms of clogging appear, doctors advise following these recommendations:
- rinse the stomach in any available way;
- take rehydron every 5-10 minutes - you need to do this for 2-3 hours;
- take mezim, festal or other enzyme preparation;
- drink warm water in small sips;
- remove difficult-to-digest foods from the menu;
- drink chamomile decoction to stop the inflammatory process.
Any medications should be prescribed by a doctor only after surgery or conservative therapy. Most often, there is a need for antiemetics, antibacterial drugs and painkillers.
To make therapy more effective, experts advise abstaining from food for several days. At the same time, it is advisable to consume only light foods that are easily digested.
Before using any medications, it is very important to consult your doctor. If therapy is not started in time, the patient may develop a state of shock. There is also a very high probability of infection spreading throughout the body. Without adequate treatment, there is a risk of gangrene and death.
Preventive measures
To prevent poor patency, do the following:
- cure the root cause. which caused obstruction;
- promptly treat gastrointestinal diseases;
- undergo routine diagnostics with your attending doctor;
- normalize physical activity. It is recommended to perform physical therapy, pay attention to exercises in the pool, and spend more time outdoors;
- change your diet. Bad (fatty, carbohydrate, solid) foods should be excluded from the diet. It is recommended to eat more protein foods. Include plenty of fruits and vegetables in your diet. It is allowed to take vitamin complexes and dietary supplements;
- control the development of worms. Parasite prevention should be carried out twice every six months;
- regularly take tests for the presence of cancer and oncological diseases;
- if necessary, take medications prescribed by your doctor;
- refuse self-medication.
Stomach blockage in a child
Clogging in a child under 2 years of age is most often the result of infectious diseases, disorders of the digestive system and problems with blood supply. Sometimes symptoms of the disease appear as a complication of stomach flu, which can lead to inflammatory damage to the organ mucosa.
Identifying a blockage in a young child can be very difficult because the child is not able to describe the symptoms. To do this, you need to palpate the abdomen and identify painful areas. Then the doctor listens to these places using a stethoscope.
To diagnose this disorder in a child, you need to take an x-ray of the abdominal cavity using a contrast agent. Thanks to this, you can see the level of patency of the organ and identify gallstones in the duct.
Prevention
To prevent the development of obstruction, which may occur again after treatment, it is recommended to adhere to certain rules. It is advisable to refuse or limit the consumption of foods that negatively affect not only the functioning of the digestive system, but also the body itself. Bad habits also have a negative impact.
Parasitic organisms have a negative impact on the functionality of all systems and organs of the human body. Despite the fact that children are more at risk of being infected with worms, adults should also be aware of the likelihood of this problem. It should be borne in mind that if one of the family members or close associates has been infected with parasites, the risk of infection increases significantly. For this reason, everyone who is at risk should undergo an appropriate therapeutic course.
To prevent infection, it is necessary to regularly carry out preventive treatment and take tests to detect helminthic infestation if characteristic symptoms occur.
If the patient has a history of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, then in order to avoid exacerbation, which can lead to obstruction, they are treated prophylactically. If it was not possible to avoid a relapse, the symptoms of the pathology cannot be ignored, and you should seek medical help. Obstruction is a serious pathology that does not require self-medication.
Stage 4 gastric cancer in oncology is considered as the terminal stage of the disease, characterized by local spread of the primary tumor, expansion of malignant cells and the formation of metastatic foci in distant organs and tissues.
What factors indicate the presence of late stage stomach cancer? Stage 4 is diagnosed when metastasis damage to distant organs (liver, lungs, bones, brain) is determined.
Possible complications
The consequences that can develop due to a clogged stomach usually depend on the cause of this pathology and the location of the tumor. If food stagnates in the pyloric region, the patient suffers from constant vomiting. However, this form of the disease is very rare.
If the pathological process has affected the distal section, there is a risk of food accumulation for a week or more. In such a situation, a person develops serious stool disorders.
When the pathology is localized outside the stomach, intestinal juice is thrown into this organ. This substance irritates the mucous membranes, which can cause wall perforation or the development of peptic ulcers.
In the presence of congenital gastric obstruction, the most common complication is aspiration pneumonia. Constant bouts of vomiting lead to disruption of water and electrolyte metabolism. As a result, vomit enters the respiratory system or provokes gastric perforation.
Stomach blockage is considered a rather dangerous pathology, which, if complications occur, can lead to the development of serious complications, including death. To prevent this from happening, you should consult a doctor at the first signs of pathology.
Gastroenterologist Vladimir Mikhailovich:
“It is known that for the treatment of the gastrointestinal tract (ulcers, gastritis, etc.) pharmaceutical drugs are used that are prescribed by doctors. But we will not talk about them, but about those medicines that you can use yourself and at home. » Read more >>>
Gastrostasis (popularly called gastric blockage when identifying symptoms and treating it) is a pathological condition of the digestive system in which there is a blockage of the stomach at the point of transition to the intestine (duodenal bulb), as a result of which the food bolus cannot easily pass further along the digestive tract . This condition causes severe bursting pain and discomfort in the patient and can lead to dangerous consequences. Quickly identifying the symptoms of gastrostasis (stomach blockage) will make treatment of the disease more effective. Gastrostasis can be acute or transient and chronic or long-term disturbances in the evacuation of liquid food from the stomach, and then solid food.
The main causes of stomach blockage
Gastrostasis (pathological blockage of the stomach) can occur as a result of the following mechanical reasons:
- Neoplasms. Malignant or benign tumors of the antrum of the stomach can block the lumen of the gastric sphincter - pylorus, thereby preventing the passage of food.
- Changes that occurred after surgery. Scarring and adhesions may appear on the walls of the digestive tract after surgery, which also narrow the lumen of the gastric outlet.
- Inflammatory processes. Inflammation of the walls of the pylorus can impede the passage of food from the stomach into the intestines due to the formation of stenoses (narrowings) of the lumen of the pylorus or duodenal bulb.
- As a result of ulcerative stenosis of the pylorus, hypertrophic stenosis in children or adults with hypertrophic gastritis.
- Formation of stones in the gall bladder.
- Pathological constipation. Severe constipation, which is a consequence of Parkinson's disease, can also cause food to not pass from the stomach through the digestive tract.
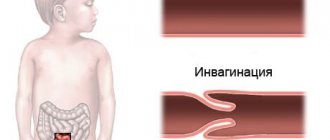
- Intussusception of the upper small intestine. The essence of intussusception is that part of one intestine is inserted into the lumen of another. This pathological condition occurs more often in children than in adults.
- Taking certain medications (opiates, antacids - Almagel, tricyclic antidepressants, anticholinergics). Some drugs may have a side effect, the essence of which is the disruption of gastric contractions and general motility, which can cause spasms of the smooth muscles of the stomach and impaired evacuation of food.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis interferes with evacuation, the so-called diabetic gastric paresis.
- Mental catastrophe - anorexia nervosa
- All serious diseases of internal organs are accompanied by gastric stasis.
Instrumental diagnostics:
- endoscopic examination - FGDS (allows you to assess the location of the tumor, the degree of stenosis (narrowing) of the stomach, take material for histological examination - biopsy);
- radiography;
- magnetic resonance imaging, which records the spread of the tumor to neighboring organs, the localization (location) of distant metastases;
- diagnostic laparoscopy - an operation that reveals the dissemination of cancerous foci throughout the peritoneum;
- histological examination of the structure of a biopsy (tissue taken from an area affected by cancer) for the presence of atypical malignant cells.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of gastric obstruction usually appear very quickly and bring unpleasant, increasing pain. The main signs of a clogged gastrointestinal tract:
- Vomiting, diarrhea. The body strives with all its might to get rid of the food that has entered the stomach, which is why various digestive disorders occur.
- Increased gas formation, flatulence. As a result of intestinal blockage, fermentation occurs, then rotting of food masses.
- An increase in general body temperature as a sign of intoxication. This symptom most often leads to loss of appetite: at high temperatures, digestive enzymes lose their activity, so appetite reflexively decreases.
- Severe sharp pain in the abdomen. Gastrostasis, or blockage of the stomach, is usually accompanied by very unpleasant pain that occurs due to spastic contractions of the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Tendency to bleed. With this pathology, the vessels supplying blood to the organs of the digestive tract experience enormous pressure, as a result of which they can be damaged. This results in intraintestinal bleeding, a sign of which is dark stool.
Important! If any symptoms of gastrostasis occur, you must immediately consult a gastroenterologist who will examine the patient and make an accurate diagnosis.
In terms of diagnosis, patients are prescribed electrogastrography.
Treatment
The choice of treatment procedures that will be carried out to eliminate gastrostasis directly depends on the degree of the disease. But at the first manifestations of symptoms, doctors advise patients to adhere to the following recommendations:
- Perform gastric lavage. There is an affordable and simple way to cleanse the stomach, which is suitable for doing at home. First you need to prepare a weak solution for washing: it can be saline, soda, and the use of potassium permanganate is also allowed. The active ingredients must be used in very low concentrations to avoid burns or irritation of the mucous membranes. The solution needs to be warmed up a little so that it is slightly warm. Then the patient should drink two glasses of the drug and induce vomiting.
- Take any enzyme preparation. There are a lot of remedies that are aimed at normalizing intestinal microflora and improving gastric and intestinal digestion. Such drugs include Mezim, Festal and others.
- Drink as much warm water as possible. Any liquid helps to quickly remove excess from the body. Therefore, you need to drink a lot of water in small sips so as not to create a large load and not cause a gag reflex.
- Adjust your menu. During the period of illness, the food in your diet should be easily digestible; you must exclude any coarse dietary fiber and other difficult-to-digest foods to make it easier for the stomach.
- Use some folk remedies. To achieve an anti-inflammatory effect, you can drink chamomile decoction, which has an anti-inflammatory effect on the mucous membranes of organs.
If the disease has not reached a severe stage, then conservative treatment methods can be used:
- Enema. This procedure is carried out to cleanse the gastrointestinal tract. The duration of the course of cleansing enemas depends on the degree of stomach clogging.
- Dropper. After the stomach and intestines have been cleansed, it is necessary to restore the balance of electrolytes in the patient’s blood. To do this, a dropper with a special solution is placed.
- Prescription of prokinetics: Cerucal, Dompridon, Itopride.
- Patients with gastrostasis who have been fully examined and who have no effect from medications can undergo surgery.
Sometimes there are cases of the disease in which urgent surgical intervention is necessary.
After the operation, the patient may be prescribed antibiotics, antiemetics, and painkillers. It is recommended to fast for several days or adhere to a strict diet, including the lightest possible food.
Thus, gastrostasis is indeed a serious pathology that requires urgent medical intervention. An advanced form of the disease can lead to serious complications: intoxication, acute intestinal obstruction. Therefore, when the first signs of the disease appear, you must immediately contact a gastroenterologist, who will make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment.
https://youtu.be/DM6uOuIPnvs
Due to the accumulation of food and gases in the digestive organ, gastric blockage often occurs. This pathological condition leads to dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract. The gradual expansion of the gastric walls, which is the result of a malfunction, in critical cases causes their rupture. To prevent serious consequences, timely diagnosis of the disease and effective therapy are needed.
Vomiting in stomach cancer and obstruction
Important! A remedy for heartburn, gastritis and ulcers, which has helped a huge number of our readers. Read more >>>
A pathology in which a bolus of food cannot move from the stomach further along the digestive tract is called gastric obstruction. As a result of stagnation of food, the gastric wall stretches, and there are disturbances in blood flow and oxygen supply. Dysfunction of the stomach causes rapid proliferation of bacteria penetrating the duodenum and leakage of fluid through the pylorus into the intestine. The consequences of the toxic effect of bacteria cause vomiting and hypovolemia.
Gastric obstruction accompanies many diseases, one of which is stomach cancer. With a peptic ulcer covering the pyloric region, the pylorus narrows, resulting in congestion. Less commonly, an abnormal phenomenon occurs when eating food containing substances that are unable to be digested and move through the gastrointestinal tract (a classic example is cotton wool). Fecal plugs and the congenital narrow opening (or lack thereof) of the anus in newborns do not create the opportunity for peristaltic movements. The pathology progresses against the background of rapid proliferation of the pathogen Morbus Hirchsprung.
Gastric obstruction is also associated with:
- formation of diverticula in the digestive organ;
- adhesive processes;
- tuberculosis affecting the digestive organs;
- infringement of blood vessels due to hernia;
- the formation of a foreign body in the stomach when hair and other fibrous formations become matted. A bezoar (foreign body) clogs the opening of the pylorus;
- intussusception;
- the formation of gastric fistulas, one of the most common of which is a fistula between the stomach and the gallbladder.
If carcinoma is found in the stomach, then the favorite place for its topography is the cardiac part. The growth of carcinoma is accompanied by constant vomiting, dense and enlarged lymph nodes, weight loss of the patient, icteric skin, ascites, and a feeling of a full stomach.
The clinical picture of the pathology is ambiguous and is tied to the topographic location of the cause of obstruction. In the event of malignant tumors, the upper part of the digestive system (cardiac part) is affected. For this reason, food begins to linger as it passes from the esophagus to the stomach, which is accompanied by inevitable vomiting. The reason for vomiting is also explained by the second reason: the affected cells of the digestive organ cease to perform the function of digesting food, as a result of which undigested food is forced to erupt. Patients with stomach cancer have vomit with a rotten odor; visual examination of it reveals the presence of blood or a large amount of mucus.
Vomiting is not the only sign by which gastric obstruction is judged. The pathology is also accompanied by:
- foul odor of belching;
- a sharp decrease in body weight;
- a feeling of gastric oversaturation that occurs several hours after eating;
- feeling of heaviness in the upper part of the digestive organ.
If gastric obstruction manifests itself with symptoms in the initial stages of its development, then the provoking factor for this is heavy food consumption or excess solid food. In the process of further development, obstruction is detected by symptoms even when eating liquid food in small quantities. Gastric obstruction is not easy to distinguish from peptic ulcers, since all of the listed symptoms are the same in both diseases with a slight difference: with a stomach ulcer, sharp pain in the epigastric region is associated. Pain accompanies not only an ulcer of the digestive organ, but also a malignant neoplasm located in it. The intensity of pain during carcinoma depends on the stage of its development and the degree of metastasis.
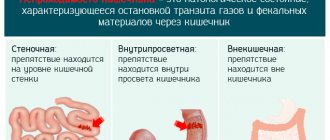
Pathology can be detected using two methods:
- Fibrogastroscopy with the introduction of a contrast agent allows you to detect the cause of obstruction, examine the structure and surface of the detected structure. This method allows you to take a sample of cells for further microscopic analysis (biopsy followed by histology) if there is reason to suspect a malignant tumor.
- An X-ray examination makes it possible to clarify the degree of narrowing of the gastric openings and to detect an object that impedes the normal movement of food mass. If the contrast agent fills the digestive organ evenly, and the pyloric part has an expansion, then a conclusion is drawn about pyloric spasms that occur during peptic ulcer disease.
X-rays detect cancerous tumors in the digestive organ. In this case, the walls of the organ take the shape of a pistol holster, and the borders of the contrast agent have corroded edges. The lumen of the stomach narrows noticeably in size.
The patient needs hospitalization, where, after identifying the cause using diagnostic methods,
When pathology occurs, a treatment regimen is prescribed. If an ulcer has been diagnosed, there may be several treatment options. One of them will concern the excision of the branches of the vagus nerve, when irritated, the secretion of gastric juice increases. The operation will be called vagotomy. The second method is to drain the digestive organ by freeing the pyloric opening. In practice, 2 treatment methods are often combined.
For stomach cancer, symptoms indicate stage 3 or 4 of development, accompanied by vomiting. Patients are subject to radical treatment with removal of the part of the stomach in which the malignant node is found. If surgery is not possible or metastasis has spread to neighboring organs and tissues, the pain symptom is eliminated with strong analgesics and the patient is fed through a tube. The food is ground and introduced warm. So you can introduce jelly, puree soups, broths through a tube, hoping for at least partial absorption of easily digestible food by the stomach.
With slowly developing gastric obstruction, there is no need for first aid. If vomiting occurs, the patient needs sanitary care: provision of dishes for vomiting, napkins for wiping the mouth and hands.
If left untreated, gastric obstruction leads to shock, which has dangerous consequences. A lethal outcome is found in every sixth patient with such a severe pathology . Every hour the probability of death increases by 1%. Mechanical obstruction in the absence of treatment ends in paralysis.
The dangerous consequences of the disease should alert a person and promptly consult a doctor.
source
The gag reflex is a common sign of a malignant tumor of the herbal system, as well as cancer therapy. Vomiting due to cancer occurs in 7-8 people out of 10. Doctors believe that the urge to vomit is caused by the work of the vomiting center of the brain. This condition is quite dangerous because it disrupts the electrolyte balance and can lead to serious consequences for the health of the cancer patient.
Vomiting in stomach cancer dehydrates the body, removes minerals from it, and exhausts the patient mentally and physically. When air is inhaled, vomit can also enter the respiratory tract and cause suffocation. The patient’s health is unsatisfactory: fatigue, difficulty concentrating, slow wound healing, weight loss, etc.
In order to eliminate vomiting, you need to understand what provokes it. The painful condition in patients occurs due to the following circumstances:
The formation reduces the volume of the muscular lining of the organ or blocks the exit holes. When a stomach tumor invades the stomach wall, normal internal movement or normal functioning is interrupted. The result is an accumulation of fluid and food.
- Surgical procedures often cause intestinal obstruction.
- Metastasis.
Conditions that influence the occurrence of vomiting in a progressive disease are:
- The effect of chemotherapy is expressed by two main factors:
- the corresponding reflex pathway is activated. In this way, the so-called stimulation occurs. the vagus nerve, which provides communication between the intestines and the vomiting center. Chemotherapeutic agents affect cells in the gastrointestinal tract. They release the substance 5-HT3, which binds to the vagus nerve and provokes its increased production;
- damage to rapidly dividing intestinal cells, which leads to a violation of its integrity. This obstruction can allow vomiting toxins to enter the bloodstream.
There are different types of vomiting after chemotherapy:
- Acute: occurs within 24 hours after treatment;
- Detained: observed after 24 hours;
- Persistent: does not respond to therapeutic measures;
- Chronic: Predominant in people with advanced cancer.
- Hypercalcemia is a complication that develops when gastric cancer spreads to the bone.
- Radiation therapy works similar to chemotherapy. The provoking factor is the dose of radiation and the size of the affected area: the larger, the stronger the side effects. The gag reflex occurs one to one and a half hours after treatment.
You will be interested in: Vomiting in children during pregnancy
Stomach cancer and vomiting blood is one of the symptoms that occurs in advanced stages. It is caused by problems in the upper intestine, where the first part of the small intestine begins.
The color of the discharge is associated with a specific reason:
- A dark color with a brown tint means that there has been contact with stomach acid. Internal bleeding may not yet have occurred at this stage, but it may soon occur.
- A large amount of bright red blood suggests heavy internal bleeding.
Methods to control the gag reflex include the use of pharmaceutical antiemetics, including:
- “Metoclopramide” - affects the intestinal muscularis and its plexus, acting as an antagonist of 5-HT4 and D2, and also promotes gastric emptying. At higher doses it counteracts the 5-HT3 receptor. It is used for partial obstruction of the digestive tract.
- “Haloperidol” is a more powerful selective drug. Recommended for vomiting caused by chemotherapy, hypercalcemia and drug therapy.
- “Cyclizine” - acts on the vomiting center and has antihistamine and antimuscarinic properties.
- “Levomepromazine” is a new generation medicine that is characterized by a wide spectrum of action, affecting all receptors associated with disorders of the brain and vestibular apparatus.
- Dexamethasone also has antiemetic properties.
Non-drug methods of influencing the urge to vomit in stomach cancer include:
- complete rest and tranquility;
- frequent meals in small portions containing easily digestible food;
- using rehydration drinks to restore lost fluids and nutrients;
- after vomiting, drink 30 ml of liquid every 20 minutes for an hour. Gradually increase the dose. This can be water, non-acidic juices, jelly, broth. Carbonated and “spicy” drinks should be avoided;
- if it is impossible to drink liquid, it is advisable to use ice shavings in the form of frozen juices, broths, water, etc.;
- in case of intestinal obstruction, the doctor may insert a probe to facilitate the passage of vomit;
- acupuncture and acupressure;
- relaxation techniques;
- resort to homeopathic remedies.
Studies on the effects of some natural remedies that can relieve the patient's condition include:
- Ginger: You can brew it in tea or add it to cookies or food.
- Chamomile relaxes and helps relieve tension from the nervous system.
- Peppermint comes in various forms: tea, tablets, and capsules.
Circumstances bordering on life include extreme deterioration, which is caused by:
- blood in the vomit or discharge that looks like coffee (black vomit). This is an extremely dangerous condition that should not be delayed;
- inability to take necessary medications;
- prolonged absence of urination;
- vomiting for 24 hours or longer, and more often than 3 times within 3 hours.
Vomiting in stomach cancer is a common symptom, which requires clarification of the exact circumstances and the appropriate choice of treatment, which is based on the complexity of the disease.
source
Vomiting in cancer is a fairly common symptom; there are enough reasons for its development in a cancer patient. Most often, the pathological condition accompanies chemotherapy and is potentially preventable in three quarters of courses; 25% is due to a psychogenic vomiting reaction from the anticipation of vomiting itself. A vomiting reaction is often initiated by taking medications.
Chronic nausea is characteristic of extensive metastatic liver disease. Episodes of severe nausea accompany metastases and brain tumors. Sudden coffee-ground vomiting is a cause for serious concern because it indicates gastrointestinal bleeding.
The vomiting reaction is always formed “in the head,” specifically in two zones of the medulla oblongata. One of the zones is called the vomiting center; a response is formed there to the transmitted impulses in the form of a command to contract muscles in some organs or relax in others. The second area, the chemoreceptor trigger zone (CHZ), also collects “nauseous” impulses from the underlying sections and sends them to the vomiting center for response.
When impulses to the medulla oblongata come from special sensitive cells of the intestinal mucosa, this mechanism is designated as peripheral. Signals coming from the cerebral cortex or from biologically active or toxic substances circulating in the blood directly to the chemoreceptor zone form the central mechanism of nausea and vomiting. In a cancer patient, both mechanisms are activated separately or together.
The central mechanism is believed to occur in the following clinical situations:
- increased intracranial pressure due to tumor or metastatic lesions of the brain is complicated by visual and neurological disturbances, as well as a gag reaction when turning the head, and in severe cases even with synchronous opening of the eyes;
- high concentration of calcium in the blood - hypercalcemia when bone tissue is destroyed by multiple metastases or when the parathyroid glands are involved in a conglomerate of thyroid cancer;
- tumor intoxication , when toxic waste products of a cancer tumor and decay products of a tumor node are constantly released into the blood and poorly eliminated;
- psychogenic vomiting reaction due to fluctuations in psycho-emotional state or from fear of imminent nausea and uncontrollable vomiting during chemotherapy.
The peripheral mechanism is involved in the following cases:
- complications of the use of chemotherapy drugs that are toxic to nerve tissue, causing a significant decrease in intestinal motor activity until contractions stop—intestinal paresis;
- intestinal obstruction or stenosis - narrowing of the outlet of the stomach by a malignant neoplasm;
- tumor damage to the liver with a significant decrease in functionality.
The interaction of both signaling pathways to the vomiting center provides radiation and chemotherapy, in which toxic metabolites circulate in the blood and irritate the sensitive cells of the intestinal mucosa. When using high doses of narcotic analgesics, the effect of metabolites is complemented by a decrease in gastrointestinal motility, but gagging is less of a concern than almost constant nausea.
In the medical literature, there is no classification of emetic reactions by type, since the clinical manifestation is always the same: a sharp contraction of the diaphragm and stomach with the release of gastric contents.
The appearance of the vomit itself can suggest the root cause of the pathological symptom, but not in all situations, including because as cancer progresses, the appetite suffers, the patient does not experience hunger, on the contrary, an aversion to food is characteristic, therefore the scarcity of vomit makes it difficult to analyze.
Depending on the time of occurrence of vomiting after eating, the following types are possible:
- When the passage of food through the gastrointestinal tract is blocked, vomiting mainly occurs some time after eating, when the food masses have already undergone partial digestion; brown inclusions can be detected in them - altered blood.
- During a meal or immediately after eating, the release of stomach contents is caused by an increase in pressure in the brain, psychomotor agitation, and tumor damage to the esophagus.
- In case of intoxication, metastases in the liver, complications of drug and radiation therapy, the release of vomit is possible at any time.
With some degree of probability, the appearance of the vomit can suggest the leading cause of the complication:
- almost unchanged food - cancer of the esophagogastric junction or esophagus;
- partially digested contents smelling sour - swelling of the lower third of the stomach;
- an admixture of bile is characteristic of damage to the initial parts of the small intestine;
- brown - “coffee grounds” occurs when bleeding in the stomach;
- bitter yellow contents are possible when liver function is impaired as a result of tumor damage.
You may be interested in: Medicines for infants for vomiting and diarrhea
Severe nausea and frequent vomiting discredit an effective method of treating malignant neoplasms, so prevention and prevention of extremely unpleasant complications are no less important than selecting the optimal combination of anticancer drugs.
During chemotherapy, an acute vomiting reaction occurs during the first 24 hours, and a delayed vomiting reaction occurs in the following days after the administration of the cytostatic. There are indomitable or breakthrough vomiting and refractory vomiting, that is, not preventable by special antiemetics - antiemetics.
For all chemotherapy drugs, the emetic - emetogenic potential and methods for its prevention and treatment have been determined, and prevention must begin from the first day and be completed 2-3 days after the end of the course.
Every fourth woman after the first course may develop a reflex - psychogenic vomiting reaction; this type of vomiting is not typical for men. To stop a possible reflex reaction on the eve of the course, tranquilizers are used, acupuncture and psychotherapeutic techniques help.
During irradiation, an emetogenic - vomiting reaction does not have typical symptoms; it often depends on the irradiation zone and the patient’s internal mood. The frequency of complications is influenced by being female, youth, nervousness and life experience in the occurrence of vomiting and nausea from other causes.
Oncology has achieved considerable success in the treatment of chemotherapy vomiting, despite an incomplete understanding of the mechanism of action of antiemetics. Not only standard prevention and treatment regimens have been developed, but also basic principles for taking antiemetic drugs:
- early prediction of the intensity of complications and individual selection of a combination of antiemetics;
- start taking it not when a complication develops, but ahead of time and strictly on an hourly basis;
- the advantage of intravenous and rectal forms over those taken orally - orally;
- adding tranquilizers for nervousness;
- introduction of PPI drugs into the regimen that protect the mucous membrane;
- adequate levels of microelements in the blood and a sufficient volume of circulating plasma are maintained by intravenous drips.
When vomiting, the likelihood of gastric contents refluxing into the respiratory tract in a conscious patient is minimal. If the patient is unconscious, which is possible in the terminal stage of cancer, especially with metastases to the brain or liver, the head is turned to the side, trying to tilt it lower.
It is impossible to interrupt the urge to vomit; interference with the process will worsen its course and irritate the patient. After vomiting, it is advisable to rinse your mouth and replenish lost fluid throughout the day by drinking cool water with electrolytes - rehydron - and only in small sips.
In all cases of the development of an emetic reaction, it is necessary to prescribe antiemetic drugs; an initially effective combination does not guarantee a constant result; constant monitoring of the condition and regular adjustment of the regimen are important.
The first symptom of bleeding in cancer is most often sudden vomiting of characteristic contents. Bleeding is possible with a large or very small tumor located next to a large vessel. In almost 70% of patients with a complicated course of the disease, the size of the malignant lesion corresponds to stages 3 and 4 of cancer.
Initially, gastric bleeding in carcinoma is rarely pronounced; as a rule, the vessel corroded by the cancerous tumor periodically secretly sneaks in for some time, leading to anemia or aggravating existing anemia. With cancerous infiltration, the tissues become “hard” and the likelihood of vascular walls sticking together due to thrombosis is minimal, so seven out of ten asymptomatic bleeding patients eventually develop serious bleeding, and one in nine – up to shock due to rapid and severe blood loss. In every fifth patient, bleeding is combined with wall perforation or cancer growth into adjacent anatomical structures.
The most common type of gastric carcinoma is infiltration with ulceration or ulcerative-infiltrative type; the size of the lesion and ulcerative defect can be any size, up to total damage to the organ. A cancer ulcer has rough, protruding and uneven boundaries; its walls and bottom form a kind of folded funnel. Saucer-shaped carcinoma is distinguished when the ulcer has very clear and uniform boundaries.
In addition, cancerous infiltration can pass through the gastric wall and penetrate into the pancreas and pull the abdominal omental bursa into the conglomerate. Even with tiny early cancer with a minimal ulcerative defect, organ-preserving surgery - mucosal resection - is excluded, because the true boundaries of the tumor are in the deep layers of the gastric wall.
The ulcerative form of cancer in appearance is almost no different from a banal chronic gastric ulcer, and that is why during each gastroscopy, a biopsy is taken from the edges of the mucosal defect from all absolutely ulcer patients.
It is almost impossible for carcinoma growing outside the stomach to bypass the vessel, because in the thickness of the wall the arterial vessels form four interconnected vascular networks: inside and under the mucous layer, between the muscular and under the serous layers. That is why bleeding is the most common complication of the disease.
Severe blood loss is manifested by a rapid decrease in blood pressure and associated progressive weakness. Exsanguination is manifested by pronounced waxy pallor with blue lips against the background of an increasing heartbeat, which the cancer patient feels like hammer blows inside the chest. The patient becomes covered in sticky cold sweat and may lose consciousness.
The most common sign of gastric bleeding is bloody vomit, commonly referred to as “coffee grounds.” Bloody vomit is typical for damage to the vessels of the respiratory tract; a sign of acute gastrointestinal pathology is dirty-brown food masses with an unpleasant odor, which may also contain dark clots of coagulated blood. Blood entering the lumen of the stomach undergoes fermentation with the release of iron from red blood cells, which changes the natural scarlet color of the blood to dark brown.
As blood passes through the intestinal tube, iron released from dead red blood cells will color the stool and the color of the stool will also change to black, again due to fermentation by intestinal secretions. Often, in a cancer patient, the stool liquefies and comes out in the form of a tarry paste with an extremely unpleasant odor. Increased frequency of stools with changes in consistency and color is called “melena.”
The combination of dark vomiting food masses and black feces are the leading signs of gastric bleeding of any etiology, including carcinoma. Foul-smelling vomit is typical of gastric or colonic outlet obstruction, but its color is not dark brown, although it differs from the food eaten the day before. The clinical situation requires immediate seeking emergency medical help, especially in combination with black stools, even against the background of good health.
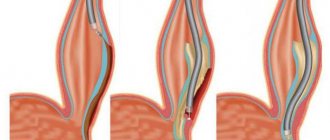
All patients with hematemesis are referred for urgent gastroscopy, during which they try to detect the source in the form of a gaping vessel and carry out conservative measures to stop the bleeding.
Many methods have been developed for local control of bleeding during endoscopy; often several methods are used in one patient. They resort to hypothermia with an ice solution, hemostatic agents and various methods of coagulation and vascular embolization. It is especially difficult with profuse leakage, when the blood seems to be oozing from the wall and not a single damaged vessel is visible.
The frequency of relapses after endoscopic control of blood loss is also significant, so the possibility of performing surgery on a cancer patient is mandatory. A radical measure is removal of the stomach, but emergency intervention immediately after the bleeding has stopped results in high postoperative mortality, therefore, if possible, the patient is actively prepared for a planned surgical intervention within several days.
You may be interested in: Diarrhea and vomiting in a cat, what is the best medicine to give?
Treatment of a bleeding stomach is a very difficult task, requiring only an individual therapeutic approach with the clinic being well equipped with modern operating and diagnostic equipment. To this, our clinic adds vast experience in endoscopic interventions in complex cancer patients.
source
November 17, 2020, 12:23 0 13,745
A sign of developing stomach cancer is the gag reflex. The symptom may occur as a reaction to antitumor therapy. The incidence of stomach cancer is 8 out of 10. There are different types of vomiting - with undigested food masses, bloody impurities or mucus. Vomiting is accompanied by nausea and occurs against the background of irritation of the reflex center in the brain. Frequent, intense vomiting leads to electrolyte imbalance, dehydration and other serious consequences.
The painful condition in cancer patients can be caused by the following factors:
- Tumor growth in the stomach. As the volume of the tumor increases, muscle tissue decreases. If cancer develops near the inlet or outlet, it can become blocked, causing gastric obstruction and vomiting. When a tumor affects the gastric walls, internal mobility is disrupted and the functioning of the organ is interrupted, as a result of which the accumulated food and liquid will be released back.
- Surgery that can cause intestinal blockage.
- Narrowing of the esophageal tube.
- Metastasis.
There are 2 scenarios for the development of vomiting:
- The occurrence of nausea and vomiting immediately after eating. In this case, the food bolus appears in its original form without traces of digestive juice.
- Sudden onset of vomiting without eating food and nausea. The reason is poisoning of the body by dead tumor cells during its disintegration. The number and strength of spasms determine the power of the vomit flow and its concentration.
The color and consistency of the etched masses determines the degree of development of stomach cancer. Bloody vomiting is considered the most dangerous, as it indicates the development of bleeding and blood plasma entering the stomach. In this situation, urgent hospitalization is needed to provide emergency measures. Unreasonable vomiting indicates the early stages of cancer, especially if it is accompanied by accompanying symptoms.
This symptom appears with varying frequency, character and strength. Depends on the degree of development and rate of progression of tumor growth. At the first stage, vomiting may not appear at all, but nausea may occur. Provocateurs of urges are the breakdown of cancerous tissue and the development of catarrhal putrefactive processes in the affected organ. In this case, vomiting occurs regularly.
With a single spasm, the etched liquid will contain semi-digested products, and with multiple spasms, liquid contents in the form of:
- yellow mass, which indicates the normal functioning of the bile ducts;
- light liquid masses, which indicate blockage of the ducts, metastasis to the liver (especially with frequent urges);
- a clot-like mass with dark red veins, which indicates hidden bleeding.
With cancer, the volume of vomit is usually small and has a sour or otherwise unpleasant odor of decaying tissue and undigested food. If food etching develops, then remnants of undigested food are found in the masses. If the symptom develops immediately after eating, contains pieces of food and is not abundant, it is provoked by oncology located in the pyloric zone. Such vomiting is accompanied by swallowing dysfunction and regurgitation. If the evacuation function is impaired due to a tumor in the lower parts of the stomach, large volumes of semi-digested, semi-decomposed food are poisoned several hours after the end of the meal.
This type of etched masses is a clear symptom of developed oncology in the stomach. Typically, the presence of blood indicates vascular damage, which occurs against the background of rejection of foreign structures by the internal gastric mucosa. Blood may appear due to damage to the tumor itself, which often contains a dense network of vessels that feed it for growth. The vomit may be scarlet, which indicates massive bleeding. Black vomiting indicates hidden blood loss.
If there is mucus in the masses, then a possible reason is increased acidity in the stomach.
If clear mucus appears in the masses, a failure in the secretory function of the stomach should be suspected. This occurs against the background of a sharp increase in acidity in the digestive organ, which the body cannot cope with. As a result, the stomach tries to reject excess acid along with protective mucus, which provokes frequent mucous vomiting with severe discomfort due to overstrain of the stomach in the absence of fuel to process excess acid.
The main provoking factor for the appearance of vomiting in the last stages of stomach cancer is the result of exposure to chemotherapy drugs, against which:
- the vagus nerve is stimulated, connecting the nerve centers of the intestine and the vomiting center, which causes a surge in the secretion of the substance 5-HT3, which increases the urge to vomit;
- rapidly dividing intestinal cells are damaged, disrupting the integrity of the tumor, resulting in intoxication.
Radiation for cancer is similar to chemotherapy.
There are the following types of vomiting:
- acute – fast-flowing, develops in the first day after the start of treatment;
- delayed, appearing after 24 hours (often black);
- persistent, unresponsive to medications;
- chronic, typical for cancer patients with diffuse cancer;
- as a symptom of hypercalcemia, when cancer cells attack the bones.
Irradiation can cause etching of gastric contents at stage 4 of oncology. Its action is similar to chemotherapy. The higher the dose of radiation used and the size of the affected area, the stronger the side effect. Usually the gag reflex appears 1-1.5 after treatment.
To control the gag reflex, special antiemetic medications and other aids are used.
Selected depending on the cause of the side effect:
- in case of excessive production of the vagus nerve stimulator (5-HT3), partial obstruction of the stomach or esophagus, consequences of chemotherapy or radiation, Metoclopramide, Ondasetron, Granisetron, Tropisetron are prescribed;
- in case of adverse effects of the tumor itself, peripheral drugs “Cerukal”, “Reglan”, “Domperidone”, “Motilium”, “Dimetpramide”;
- for cancer with metastases - glucocorticoid hormone "Dexamethasone" or "Cortisone", antipsychotics "Amitriptyline", "Risperidone", "Olanzapine", "Quetiapine";
- for hypercalcemia - selective medication "Haloperidol";
- to act directly on the emetic.
Return to contents
What to do to reduce the number of gags? Recommended:
- rest and peace;
- small-portion fractional meals;
- light food;
- taking restorative fluids.
After an attack, it is important to drink 25 ml of light broth, water, juices and jelly.
After an attack, in the first hour it is important to drink 25 ml of light broth, water, weak non-acidic juices, liquid jelly every 15 minutes. The consumption of soda and other “spicy” drinks is prohibited. If a person cannot drink liquid, frozen juices, broths, and water in the form of chips are allowed. If intestinal blockage has developed, it is recommended to install a tube to remove vomit.
Other supporting measures:
- acupuncture, acupressure;
- breathing relaxation techniques;
- homeopathy.
Return to contents
You can fight vomiting with the help of proven folk remedies, such as:
- ginger powder: tea is brewed with it, cookies are made, food is seasoned with it;
- chamomile tea;
- mint in the form of teas, tablets, capsules.
Return to contents
Any deterioration that could lead to death requires urgent medical intervention. These include:
- the appearance of scarlet blood or blackened thick matter in the masses;
- immediate rejection of any antiemetics taken;
- no urge to go to the toilet;
- vomiting for more than 24 hours or more than 3 times in 3 hours.
source
Manifestation of obstruction
Without specific individual manifestations characterizing obstruction of the digestive organ, the disease is often confused with other gastrointestinal pathologies. Common symptoms of stomach blockage include:
- attacks of vomiting, sometimes with bile;
- the presence of diarrhea due to mechanical obstruction;
- constipation as a consequence of paralytic obstruction;
- general weakness due to loss of electrolytes due to dehydration;
- increased gas formation in the intestines;
- acute attacks of pain;
- increased body temperature;
- blood in the stool;
- deterioration of appetite or its complete absence.
Return to contents
Causes of intestinal obstruction in cancer patients
Intestinal obstruction develops due to its compression from the outside by a tumor conglomerate or the growth of a tumor deep into the intestine. Feces cannot move through the intestines, which leads to stasis and the appearance of characteristic symptoms. Similar conditions are observed with cancer:
- intestines;
- ovaries;
- uterus;
- Bladder;
- prostate gland.
The oncological process in the above organs can develop both primarily and as a result of metastasis of a malignant tumor of a different localization.
Symptoms of the disease in children
Developing as a consequence of a gastric infection, a clogged stomach leads to inflammation and poor circulation. The manifestation of obstruction in children implies the same symptoms as in adults. However, diagnosis is complicated by the inability to accurately collect anamnesis, due to the inability of a child under 2 years of age to describe pain and the difficulty of identifying blockages at an early stage. The disease is diagnosed in children by palpation, listening with a stethoscope and using radiography using a contrast agent. Having determined the location of the blockage, the doctor prescribes therapy. An external sign of the disease is the child's lying position. Knees pressed to the stomach indicate the presence of pain.
If there is blood in your child's stool, you should consult a doctor immediately.
Diagnostic procedures
Diagnosis of the disease begins with collecting anamnesis and its analysis. The main diagnostic measure is radiography. The first step is to administer a contrast agent to the patient using an enema or probe. It is possible to take an x-ray of the abdominal cavity in the side position to detect the area where the stomach is clogged. Among other measures, colonoscopy is an instrumental diagnostic method. Using a colonoscope, the condition of the colon and rectum is visually assessed and clogging of the stomach is determined.
Diagnostics
Intestinal obstruction does not manifest itself as a sharp deterioration in condition. This is often preceded by intestinal dysfunction in the form of constipation, bloating and rumbling in the abdomen. Symptoms gradually increase, accompanied by nausea, vomiting and pain.
The pain is spastic in nature. The higher the obstruction (blockage), the faster vomiting will begin. If the colon is affected, only nausea and later vomiting are possible. It initially consists of gastric contents, but later acquires a yellow-green tint with a fecal odor.
Also, bloating and rumbling are disturbing. As the intoxication syndrome increases, the pressure decreases and the pulse quickens.
Instrumental techniques include barium radiography, abdominal ultrasound, colonoscopy and laparoscopy. Using tomography, the extent of the cancer process is assessed and the extent of surgical intervention is determined.
Consequences and complications of pathology
A clogged stomach becomes the basis for disruption of the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, and if you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, it becomes a source of infection. Pathologies of the distal intestine cause prolonged accumulation of food and lead to the release of acidic contents onto the mucous membranes, which contributes to the formation of ulcers. As a consequence of stagnation in the pyloric section of the stomach, vomiting develops. Aspiration pneumonia is a consequence of congenital pathologies and occurs when vomit enters the respiratory organs.
https://youtu.be/KOUC6JacyHk