Tumors of which organs are accompanied by ascites?
The process of accumulation of excess fluid in the abdominal cavity accompanies about half of all cases of ovarian cancer in women. It also complicates the course of neoplasms:
- colon;
- mammary glands;
- stomach;
- pancreas;
- rectum;
- liver.
The severity of the patient’s condition does not depend on whether the primary tumor caused the pathology or its metastasis. The manifestations of cancer are accompanied by signs of increased intra-abdominal pressure, elevation of the diaphragm, and reduction in respiratory movements of the lung tissue. As a result, the conditions for the functioning of the heart and lungs worsen, cardiac and respiratory failure increases, which brings the death of the disease closer.
Forecast
Among the factors that determine the prognosis of life expectancy with abdominal ascites, the nature of the underlying disease comes first. The most favorable prognosis for ascites that occurs against the background of protein deficiency is that if the balance of nutrients can be restored before serious damage is caused to the body, the symptom disappears without any consequences.
How long a patient with this diagnosis will live also depends on the stage of the disease at which therapeutic measures were started. With transistor ascites, the prognosis is quite good: following doctors’ instructions regarding therapy, diet, and giving up bad habits - drinking alcohol, smoking, overeating, etc.
– a person can live quite a long time – 10-15 years. However, it is not always possible to catch the disease at an early stage - a lot depends on the qualifications and experience of the doctor conducting the examination and making prescriptions. Even if all necessary measures are taken in a timely manner, medicine is not yet able to completely stop the progression of pathologies that cause ascites. And the further the disease progresses, the fewer chances it leaves for the patient.
Ascites in patients with heart failure of 3-4 degrees in 90% of cases leads to death within three to five years. With refractory ascites, half of the patients die within a year. The situation is aggravated by old age - 60 years and older, changes in blood pressure, diabetes mellitus.
What it is?
Ascites in stomach cancer can be fatal. In general, the prognosis for such a disease will not be favorable. The patient may develop pleurisy, that is, fluid will accumulate not only in the peritoneum, but also in the lungs.
It is quite difficult to say how long people live with such a complication, since everything depends on the stage of development of the disease, general history and clinical indicators of the patient. According to statistics, only 50% of patients with dropsy of the abdomen survive for 2 years, but with timely treatment.
Causes and mechanism of development
The abdominal cavity is formed by 2 leaves. One of them (parietal) lines the internal surface, and the other (visceral) surrounds the nearest organs. Both leaves produce a small amount of liquid secretion from their glandular cells. With its help, minor local inflammation is eliminated, organs and intestines are protected from friction.
The fluid is constantly renewed as excess is absorbed by the epithelium. Accumulation is possible if the balance of this state is disturbed. In 75% of cases, patients with ascites have liver cirrhosis. This disease has the maximum number of etiological factors leading to pathology.
These include an increase in hydrostatic pressure in the vessels under the influence of stagnation in the venous and lymphatic systems due to impaired cardiac activity and a drop in oncotic pressure in the blood due to damage to liver function and a decrease in the content of the albumin protein fraction.
Ascites of the abdominal cavity in oncology does not exclude these mechanisms as an addition to the main damaging factor - hyperfunction of the abdominal epithelium with tumor damage to the peritoneal layers. The growth of malignant cells causes irritation and nonspecific inflammation.
The most significant role of contamination with malignant cells is in ovarian and uterine cancer in women. The complication in these cases worsens the general condition of the patients so much that they die as abdominal ascites increases.
Of considerable importance is the direct compression of the liver tissue by the tumor and the creation of conditions for portal hypertension. As venous pressure increases, the aqueous part of the blood is discharged into the abdominal cavity.
Cancer intoxication is accompanied by a lack of oxygen in cells (tissue hypoxia). The kidney tissue very acutely senses any changes and reacts by reducing filtration. This activates the mechanism of action of the antidiuretic hormone of the pituitary gland, which retains sodium and water.
Some authors distinguish hepatic and extrahepatic mechanisms in the pathogenesis of ascites. Using the example of malignant growth, we see how these reasons complement each other. The absorption function of the peritoneum and lymphatic vessels is impaired.
An example of local changes would be abdominal lymphoma. This tumor is accompanied by impaired patency of the intra-abdominal lymphatic ducts. From them, the fluid passes directly into the abdominal cavity.
The provoking causes of ascites in cancer can be such an anatomical feature as the close location of the folds of the peritoneum (adherence), the abundance of blood and lymphatic vessels, which causes the rapid spread of malignant growth to neighboring tissues.
Sweating of fluid can be stimulated by the introduction of atypical cells into the peritoneal cavity during surgery, internal germination of the peritoneal walls by a malignant tumor, as well as a course of chemotherapy.
Causes
Causes of ascites (click to enlarge)
The main reason for the occurrence of ascites in cancer patients is that when tumor cells settle on the peritoneal tissue, it leads to complications in mechanical lymph drainage.
By compressing the veins passing through the liver, hydrostatic pressure increases, which leads to the onset of the disease.
There is also chylous ascites, which occurs as a result of the development of peritoneal lymphoma. This type of disease is characterized by the release of lymph and emulsified fats that penetrate the abdominal cavity and intestines.
Symptoms
In cancer patients, ascites develops gradually over several weeks or months. Patients feel symptoms when a significant amount of fluid accumulates. Main symptoms:
- bursting heaviness in the abdomen;
- belching after eating;
- heartburn or nausea;
- dull pain in the abdomen;
- shortness of breath at rest, especially when lying down.
These signs are associated with the rise of the dome of the diaphragm, impaired peristalsis of the esophagus, intestines, and reflux of acidic stomach contents into the esophagus. Some patients complain of attacks of cardiac arrhythmia. Upon observation, the attending physician reveals an enlarged abdomen. In a standing position, it goes down, the navel protrudes.
Patients with “liver” ascites are characterized by a “jellyfish head” pattern due to the formation of dense dilated veins around the navel. The accumulation of fluid creates difficulties when bending over and putting on shoes.
Unfortunately, there are still frequent cases of identifying young women with an ovarian tumor in an advanced state, who for a long time were confident in their pregnancy, this was facilitated by the cessation of menstruation.
The accumulated fluid itself puts pressure on the tumor, causing decay. Metastasis through the venous system and heart failure is manifested by obstructed blood flow to the heart. This leads to swelling of the feet, legs, and external genitalia.
All the described symptoms do not develop in isolation. In the first place there are signs of a malignant tumor. Ascites requires additional treatment because living with its manifestations becomes more dangerous due to the possibility of other complications.
Stages
Regardless of the causes, the course of ascites is divided into 3 stages. They are also typical for patients with cancer:
- transient - the patient only feels bloating, the volume of accumulated fluid is not more than 400 ml;
- moderate - the amount of exudate in the peritoneum reaches 5 liters, all the described symptoms appear, various complications are possible;
- tense - ascites accumulates 20 liters or more, is considered stable (resistant), cannot be treated with diuretics, is accompanied by a serious condition, disrupts the functioning of the heart and breathing.
Traditional methods of combating ascites
It should be remembered that folk remedies do not help heal ascites, but only relieve symptoms and more quickly remove unnecessary fluid from the body.
Traditional medicine methods are definitely effective, but before using them you should consult your doctor. The total amount of fluid consumed per day for abdominal ascites should not exceed one liter.
Bean pod decoction
Pour 12 dried bean pods into 1 liter of water. Boil over low heat for about 10 minutes. Remove from heat and let steep for 20 minutes. Strain. Drink 200 ml before meals.
Herbal infusion
Pour horsetail and birch leaves with 1 glass of water. Boil for 15 minutes, then let cool. Drink ½ glass on an empty stomach.
Parsley tincture
Pour 300 g of fresh parsley into 1 liter of boiling water. Cook for 30 minutes. Cool. Take ½ glass hourly in the morning and at lunchtime.
Apricot decoction
Pour 1 cup of fresh or dried apricots into 1 liter of water. Cook for about 40 minutes. Cool. Drink 400 ml per day.
Herb tea
Pour hernia and bearberry in the form of leaves (in the same ratio) with 1 glass of water. Boil for a quarter of an hour. Drink the resulting tea on an empty stomach every day in the morning.
"Berry" tea
Pour 1 cup of boiling water over raspberry, lingonberry and currant foliage, rose hips (in equal parts). Next, cook over low heat for about 10 minutes. Then remove from the stove and let stand for a quarter of an hour. Strain. Drink twice a day instead of regular tea.
What complications can follow ascites?
The severity of the underlying disease in the event of ascites reduces the patient’s chances of recovery. The risk of dangerous complications increases even more. These include:
- bacterial peritonitis - infection causes acute inflammation of the peritoneum;
- intestinal obstruction;
- the appearance of hernias in the area of the white line of the abdomen, navel, and groin with possible pinching;
- cardiac decompensation;
- accumulation of fluid between the pleural layers - hydrothorax with acute respiratory failure;
- development of hepatorenal syndrome;
- hemorrhoidal bleeding, prolapse of the lower rectum.
Why can't it be ignored?
Often accumulated fluid causes the formation of umbilical, inguinal and even femoral hernias. In this case, the abdomen becomes asymmetrical, in some area it protrudes more, and the skin in this area often becomes thinner. At any moment, the hernia can be strangulated, so the patient is recommended to wear a bandage.
As the volume of fluid increases, breathing becomes difficult, and a dry cough appears, caused by stagnation of effusion in the pleural cavity and lower parts of the lungs. The patient is concerned about shortness of breath, which may worsen at night, in a horizontal position. Heartburn appears, which becomes stronger the more the stomach presses the diaphragm. Varicose veins and hemorrhoids often develop.
But the most dangerous complication of ascites is infection of the pathological effusion. The addition of an infection is indicated by an increase in body temperature, weakness, and sometimes redness of the skin on the anterior abdominal wall, often in the area of the hernial sac. If left untreated, this condition can be fatal.
Diagnostics
A complication such as ascites is expected in advance during the course of cancer. When monitoring a patient, the doctor is required to weigh him. An increase in mass against the background of pronounced weight loss in the arms, legs, and body raises suspicion of hidden edema.
If you make a pushing movement with your hand on one side of the abdomen, then if there is fluid, the second hand will feel a wave on the opposite side. Additional research provides objective confirmation:
- Ultrasound - allows you to detect 200 ml of fluid in the abdominal cavity, at the same time serving as monitoring for changes in the internal organs;
- plain radiography and tomography - require good preparation of the patient before the study, detects fluid when changing body position;
- laparocentesis is a puncture of the anterior abdominal wall for the purpose of pumping out fluid and its laboratory analysis; the procedure is both therapeutic and diagnostic; it allows one to identify the degree of contamination of the peritoneum, the composition of the exudate, and the presence of microflora.
Severity and clinical manifestations of ascites
There are 3 degrees of severity of ascites:
- Initial stage - up to one and a half liters of fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity;
- Moderate ascites - manifested by an increase in the size of the abdomen, edema of the lower extremities. The patient is concerned about severe shortness of breath, heaviness in the abdomen, heartburn, constipation;
- Severe dropsy - from 5 to 20 liters of fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity. The skin on the abdomen tightens and becomes smooth. Patients experience heart failure and respiratory failure. When the fluid becomes infected, ascites-peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneal layers) develops.
The main manifestation of ascites is a significant increase in size and pathological bloating of the abdomen. Signs of abdominal dropsy can increase rapidly or over several months. Ascites is manifested by the following clinical symptoms:
- Feeling of fullness in the abdominal cavity;
- Pain in the abdomen and pelvis;
- Increased gas formation (flatulence);
- Belching;
- Heartburn;
- Digestive disorders;
- An increase in the size of the abdomen;
- Protrusion of the navel.
Doctors at the Oncology Clinic evaluate the clinical manifestations of the disease and carry out a differential diagnosis of cancer with other diseases, the manifestation of which is ascites.
Problems of treating ascites in oncology
Therapy for ascites should theoretically primarily consist of suppressing the growth of malignant cells in the peritoneum. Then we can expect the irritating mechanism to be removed and the fluid absorption function to be restored.
But in practice, chemotherapy methods help reduce ascites only for tumors in the intestines, and when localized in the liver, stomach, uterus, and ovaries, they remain ineffective.
All that remains is to control the intake and removal of fluid with food, and rely on optimal conditions for the action of diuretics (diuretics). You can remove excess water using a restrictive diet. The patient is prescribed a salt-free diet, all dishes are prepared without salt, and, in agreement with the doctor, it is possible to add salt to the plate.
What's happened
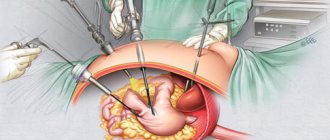
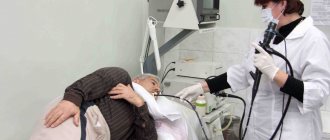
Laparocentesis is a procedure that is prescribed to find out what kind of fluid is present in the abdominal cavity. The puncture is performed by piercing the peritoneal wall.
The preferred place to perform the procedure is a hospital. To perform laparocentesis at home, so that the contents are constantly pumped out, the patient is installed with a permanent peritoneal catheter.
There are several types of this surgical intervention.
With ascites
Can be performed on an outpatient basis. The trocar is inserted in the same way as during the standard procedure.
Diagnostic
This type of laparocentesis is one of the most informative and is used when there is a need to identify primary peritonitis in patients with diagnosed chronic renal failure or with the development of liver cirrhosis.
As a rule, peritonitis is detected after a puncture is obtained followed by laboratory testing. In most cases, the analysis shows an increase in the concentration of leukocytes by more than 300 per milliliter of fluid, as well as a shift in the leukocyte formula by 30 percent.
Laparocentesis for diagnostic purposes can also be prescribed in the presence of acute pain syndrome, or if there is a suspicion of secondary type peritonitis of bacterial origin.
On this topic
Can a stomach ulcer turn into cancer?
- Editorial board of Oncology.ru
- October 16, 2020
In most cases, diagnostic laparocentesis is used when the manifested symptoms are not enough to make a final diagnosis.
When choosing a procedure technique, it is necessary to take into account the general condition of the patient and the individual characteristics of his body.
Treatment
Regardless of the cause, ascites must be treated together with the underlying disease. There are three treatment methods: symptomatic, conservative and surgical intervention.
Conservative
At the initial stage of ascites, conservative therapy is used. It consists in normalizing liver function. In the presence of inflammatory liver parenchyma, medications are prescribed to relieve inflammation.
To compensate for the loss of sodium, which is excreted in large quantities in the urine, patients are prescribed diuretics. To normalize lymphatic drainage and reduce liver metabolites, bed rest is prescribed. If the cause of ascites is portal vein hypertension, then the patient is prescribed hepatoprotectors, plasma and albumin administration.
Symptomatic
If conservative treatment is unsuccessful, the patient is prescribed a laparocentosis procedure, which consists of removing fluid from the peritoneum by puncturing its wall and using a special device to suck out the water. This procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
The maximum amount of fluid that can be removed during laparocentosis is 5 liters. The procedure is repeated after 3-4 days. It is worth noting that each subsequent procedure poses an increasing danger to the patient, which lies in the possibility of damage to the intestinal walls .
Therefore, it is repeated infrequently. If fluid fills the abdominal cavity too quickly, a peritoneal catheter is installed in the patient to prevent the formation of adhesions that are possible with ascites.
Surgical
In case of recurrence of ascites, the patient is indicated for surgical intervention.
If the patient has undergone laparocentosis repeatedly, he is prescribed a special diet and blood transfusion.
This method consists of connecting the veins together - the inferior vena cava with the collar vein. This creates collateral circulation.
If the patient requires a liver transplant, he is prescribed a course of diuretics and undergoes surgery. After which, the survival rate for 1 year is 70-75%.
Indications
As a diagnostic procedure, manipulation is prescribed if it is necessary to examine a hollow organ of the peritoneum for the presence of perforation of its walls. This condition often occurs against the background of a gastric ulcer, a diverticulum of the small intestine, or a duodenal ulcer.
In addition, indications for paracentesis are closed-type abdominal injuries, especially if the patient is unconscious, injuries to the abdomen and sternum, in order to exclude pathological processes affecting the muscle tissue of the diaphragm.
The procedure is also carried out when it is necessary to identify the true cause of bleeding and determine the affected organ. Laparocentesis can be performed if the cyst is ruptured or damaged.
On this topic
Blood test for pancreatic cancer
- Editorial board of Oncology.ru
- October 16, 2020
Summarizing
Ascites is a pathological condition in which effusion fluid accumulates outside an organ. This causes compression and poor circulation. In advanced cases, dropsy can cause death. In most cases, abdominal ascites occurs against the background of liver cirrhosis, oncology and heart failure. The main symptom of dropsy is a protruding belly. Patients suffer from edema, shortness of breath, flatulence, and bloating.
Treatment involves primarily combating the disease that led to the accumulation of fluid. To reduce the size of the abdomen, diuretics are prescribed. Patients should follow a salt-free diet and also ensure adequate protein intake. Traditional methods of treatment will help speed up recovery. Alternative medicine offers a wide selection of medicinal plants that have a diuretic effect. If conservative therapy is ineffective, fluid is suctioned - laparocentesis.
Contraindications
If the patient has massive injuries, then the main goal of the procedure is to save his life. In such situations, there are no absolute restrictions on surgical intervention.
However, experts identify several relative conditions in which the procedure cannot be performed. The most common of them include:
- increased gas formation;
- period of bearing a child;
- clotting disorder ;
- development of adhesive processes;
- inflammation of the anterior wall of the peritoneum;
- hernia.
If at least one of the above pathologies is noted, the operation is postponed until it is completely eliminated, since in this case the risk of injury to the pelvic organs increases several times. Against this background, some complications may begin to develop in the postoperative period.
Preparation
For the paracentesis procedure to be successful, it is necessary to properly prepare for it.
First of all, the patient must undergo a series of diagnostic examinations, which includes a urine and blood test, a coagulogram, an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, and radiography. Consultation with a therapist and other specialists is required.
Since the procedure may require laparoscopy or laparotomy, all preparatory measures must be carried out as for a classic operation.
On this topic
Life expectancy for stage 4 gastric cancer with metastases
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- July 9, 2020
Before performing a abdominal puncture, you must empty your bladder. This can be done independently by the patient himself or with the help of a catheter when the person is unconscious. A tube is used to remove the contents of the stomach.
If the patient is in a state of shock, anti-shock therapy is first administered. This is necessary in order to maintain hemodynamics. Also, if there are significant indications, the patient is connected to a ventilator.
Technique
Before puncturing the peritoneal wall, the patient is given a local anesthetic. To perform the technique, instruments such as a trocar, a tube for removing fluid, clamps and syringes are used.
The contents that are removed from the abdominal cavity are collected in a special container. Before sending it to the laboratory for bacteriological examination, it is placed in sterile tubes.
The doctor who performs the operation must wear gloves. If paracentesis is performed for ascites, the patient is covered from above with a film or an oilcloth apron.
On this topic
Diet rules after stomach removal for cancer
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- July 9, 2020
The tactics of performing the procedure do not cause any difficulties for the surgeon. Novocaine or lidocaine is used as an anesthetic. It is injected into the soft tissues in the abdominal area. The place where the puncture will be made is treated with an antiseptic solution.
The patient is in a sitting position when the puncture is performed to remove fluid that has accumulated due to ascites. In other situations, the patient should lie on his back.
The puncture is made along the midline, with a distance of two centimeters down from the navel. Before the trocar is inserted, a small incision is made with a scalpel. In this case, the skin, fiber and muscle tissue are dissected. All actions must be performed with extreme caution, as there is a high risk of damage to internal anatomical structures.
Most surgeons prefer to push the soft tissue apart using a blunt method, which is safer for the patient. As the surgical instrument moves in, it is important to continually control bleeding. This will allow you to avoid obtaining false research results in the future.
A trocar is inserted into the hole in the peritoneal wall, which is then inserted with rotational movements into the abdominal cavity. Its inclination relative to the xiphoid process should be 45 degrees.
To create a space through which the special trocar will move, the specialist grabs the umbilical ring. As a result, a slight elevation of the peritoneal wall occurs. To ensure safety and facilitate puncture, surgical thread is also used. It is inserted into the puncture area through the aponeurosis.
With ascites
In this case, laparocentesis can be performed on an outpatient basis. The trocar is inserted according to the same principle as described above. After liquid appears in its cavity, in order to remove it, the device is tilted towards a previously prepared container. The distal end is held with fingers.
If the ascitic contents are excreted quickly, this process may be accompanied by fluctuations in blood pressure, which can provoke collapse, since in this condition the blood rapidly penetrates into the vessels of the peritoneum, which were previously compressed by the accumulated fluid.
To prevent the sudden onset of hypotension, it is necessary to remove excess contents at a slow pace. Typically about one liter over five minutes. It is important to constantly monitor the patient’s condition.
On this topic
What tumor markers may indicate bowel cancer?
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- July 9, 2020
During the manipulation, the assistant gradually tightens the patient's abdomen to prevent hemodynamic disorder.
After complete removal of the ascitic contents, the trocar is removed. The incision is sutured and covered with a sterile bandage.
It is not recommended to remove the compression towel. This will ensure normal pressure inside the abdominal cavity and gradual adaptation of the patient to the new created conditions for the blood supply to the organs.
How often can you do it
The number of procedures required will depend on the diagnosis given to the patient. Thus, with the development of ascites against the background of cancer of the pancreas, frequent manipulation is not recommended. This is explained by the fact that such intervention can provoke even more frequent accumulation of fluid.
Paracentesis as a therapeutic measure is prescribed in the absence of positive dynamics after the use of medications, as a result of which the stomach takes off its shoes, which causes discomfort.
To alleviate the patient’s condition, this manipulation is prescribed as a large amount of excess content accumulates.
Clinical case
A 59-year-old woman, Sh., was diagnosed with ovarian cancer (adenocarcinoma) stage IV, ascites, and chronic pain syndrome 2 b according to the ShVO. The patient noticed an increase in the abdomen up to 120 cm in circumference, difficulty breathing, and weight loss. Specific treatment at the place of residence was denied. According to the patient, she was “sent home to die.” Read more…
A 59-year-old woman, Sh., was diagnosed with ovarian cancer (adenocarcinoma) stage IV, ascites, and chronic pain syndrome 2 b according to the ShVO.
The patient noticed an increase in the abdomen up to 120 cm in circumference, difficulty breathing, and weight loss. Specific treatment at the place of residence was denied. According to the patient, she was “sent home to die.” Patient Sh. was urgently hospitalized in a specialized department of the European clinic; after active symptomatic therapy aimed at normalizing blood counts and restoring water and electrolyte balance, a peritoneal port was installed. Resolution of ascites was carried out under the control of plasma protein levels. The use of peritoneal ports allows for the removal of ascitic fluid in fractional doses, which ultimately eliminates the occurrence of serious complications in the form of hemorrhagic syndrome associated with hemodilution and coagulopathy as a result of massive entry of ascitic contents into the venous bed.
After stabilization of the general condition, against the background of nutritional support, antiemetic and antisecretory therapy, patient Sh. received specific chemotherapy treatment with good effect. Upon resolution of ascites in the presence of a peritoneal port, intra-abdominal chemotherapy became possible.
Six months after the described hospitalization, the patient returned to her usual lifestyle and continues to receive systemic treatment on an outpatient basis under the supervision of a team of specialists at the European Clinic. The response to treatment is regarded as positive in the absence of ascites and a total reduction in the size of the lesions by more than 70%. Combined treatment in the format of systemic and local (intra-abdominal) therapy with implantation of a port system is the optimal treatment regimen for this group of patients. In the practice of doctors at the European Clinic, such cases occur on a regular basis. Hide
Complications
According to statistics, consequences after laparocentesis are observed only in 8-10 percent of patients. In most cases, the reason for their appearance is non-compliance with the rules of antiseptic treatment, the penetration of infection into the place where the puncture was made.
On this topic
How to properly care for a rectal colostomy
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- July 9, 2020
After the trocar is removed from the cavity, bleeding may occur. During surgery, the patient may faint. This often happens when the blood begins to rapidly distribute through the vessels.
Other complications include:
- injury to the intestinal loops, against which peritonitis may develop;
- vascular damage which leads to the formation of hematomas or extensive bleeding into the retroperitoneal cavity;
- entry of air, which entails the development of subcutaneous emphysema;
- the appearance of phlegmon in the area of the anterior wall;
- puncture of a malignant tumor - as a result, the oncological process can be activated, and the rapid spread of metastases to nearby anatomical structures and systems will begin;
- prolonged release of contents in the puncture area.
Currently, cases of complications are recorded extremely rarely. As a result, laparocentesis began to be considered not only effective, but also the safest method for pumping out fluid accumulated in the peritoneum.
Prognosis for concomitant diseases
When ascites appears as a concomitant severe complication, the prognosis is always negative. In the case of association with cirrhosis, about 50% of patients facing this problem can live no more than two years. The prognosis for concomitant diseases worsens. Infections, metabolic disorders, renal lithiasis and other associated dysfunctions shorten life span.
Ascites may have virtually no effect on life expectancy: this is possible at the onset of the disease - the prognosis in this case is positive.
Ascites is often called dropsy of the abdomen. In fact, this condition is not a separate disease, but a complication of other ailments, the list of which is not small. Most diseases, the complication of which is ascites, are dangerous not only for the patient’s health, but also for his life, so it is important to recognize this condition in time and take all necessary measures.
Rehabilitation period
Since laparocentesis is a low-traumatic procedure and does not require general anesthesia, the recovery period does not take much time. Sutures are removed on days 7-10, provided that the patient’s condition is stable and does not worsen.
However, despite this, in most cases, experts recommend sticking to bed rest for some time, as well as other restrictions until the symptoms of ascites completely disappear.
To prevent re-accumulation of fluid, the patient must adhere to a special diet, which involves limiting the consumption of salt and water. The permissible limit per day is no more than one liter.
If it is necessary to remove fluid from the peritoneal cavity, laparocentesis is performed. During this surgical procedure, a puncture is made in the anterior wall of the abdomen and the contents accumulated there are evacuated. This procedure allows you to obtain biological material for subsequent diagnostic research and reduce intrauterine pressure.
What should be the correct treatment?
Competent treatment of ascites involves:
- treatment of the underlying disease;
- bed rest in the first days of treatment;
- a diet with limited salt and liquid;
- rational use of diuretics (diuretics).
This approach will be considered effective if:
- the patient's body weight decreases;
- abdominal circumference in the waist area decreases;
- peripheral edema disappears or decreases;
- the results of biochemical examination of urine and blood are normalized.
Unfortunately, treatment often does not have an effect because the doctor cannot select the correct dose of the diuretic, or increasing the dose becomes impossible due to impaired renal function of the patient. In this case, the doctor has only one option - to pump out the fluid for ascites. The fluid is pumped out by simply puncturing the anterior abdominal wall (laparocentesis).
Removal of fluid is considered necessary if it causes the anterior abdominal wall to become tense, or if the effusion has accumulated for more than the first time and it is not possible to remove it with medication.
For cancer patients and patients with liver cirrhosis, this procedure is often the only way to alleviate the disease. But so that it leads to an improvement and not a worsening of the patient’s condition, after pumping, infusion therapy is carried out, and the effusion is examined for sterility. According to indications, antibacterial agents are prescribed.
Improper administration of infusion therapy, as well as underestimation of the degree of its significance, is one of the main mistakes doctors make when managing patients with ascites. The second mistake is the excessive use of diuretics, leading to kidney complications. Therefore, you need to approach the choice of a specialist who will control the progress of the process very seriously.
If it is necessary to remove fluid from the peritoneal cavity, laparocentesis is performed. During this surgical procedure, a puncture is made in the anterior wall of the abdomen and the contents accumulated there are evacuated. This procedure allows you to obtain biological material for subsequent diagnostic research and reduce intrauterine pressure.
Indications and contraindications for pumping free fluid from the abdominal cavity
The described operation is performed to alleviate the condition of a patient with ascites, if there is a suspicion of massive internal bleeding or possible perforation of the gastrointestinal tract caused by perforation of the ulcer. The resulting liquid is examined for the presence of hidden blood, bile inclusions, and feces.
Laparocentesis is not performed in the following cases:
- a history of abdominal adhesions;
- bleeding disorder (there is a risk of bleeding);
- severe flatulence;
- the likelihood of damage to the wall of the intestinal loops;
- development of a large tumor in the peritoneum;
- purulent-inflammatory processes;
- pregnancy.
A ventral hernia of the anterior abdominal wall, which occurred after a previous surgical operation, is another direct contraindication to the described manipulation. It is not recommended to puncture and pump out fluid if palpation of the abdomen reveals a large tumor or an enlarged organ.
Preparation for the procedure
When performing routine laparocentesis, laboratory tests of blood and urine tests, as well as ultrasound of organs located in the peritoneum, are indicated. The patient is asked to do a coagulogram and x-ray. Depending on the indications for abdominal puncture, the range of diagnostic measures can be expanded.
Surgery is performed under local anesthesia. To perform laparocentesis, a minimal set of surgical instruments is used. You need a trocar with a sharp end, a polyvinyl chloride tube a meter long, a clamp, several ten-millimeter syringes and a container in which to collect the liquid. If the patient is conscious and his condition allows him to prepare in advance for the procedure, first the intestines are cleansed with an enema. The patient is also asked to empty the bladder.
Classification of ascites
Based on the severity of the condition and the amount of fluid accumulated in the abdomen, ascites is divided into the following types:
- Small, in which the volume of liquid does not exceed three liters. At the same time, the pathology is not visible externally. The presence of ascites can be diagnosed by ultrasound or laparoscopy.
- Medium - the volume of liquid is more than three, but less than 10 liters. The shape of the abdomen changes, but the muscles of the abdominal wall do not stretch, and the level of the diaphragm remains the same. Liver failure progresses, irreversible changes in brain activity occur (hepatic encephalopathy occurs).
- Large - the volume of liquid reaches 10 - 20 liters. The abdomen is modified, stretched, the diaphragm is raised by the enlarged abdominal cavity. Breathing problems occur (constant shortness of breath), the functioning of the cardiovascular system becomes difficult, and significant swelling is noted throughout the body.
Depending on how ascites can be treated, the disease is divided into 3 types:
- Transient or transient ascites. With adequate treatment, no symptoms of the disease are observed.
- Stationary ascites. The body does not respond to conservative treatment, hospitalization and surgical intervention are required.
- Tense or progressive ascites. All therapeutic measures do not produce results. The disease progresses, the volume of fluid increases.
Ascites during oncology has three stages of development:
- transient - no more than 400 ml of fluid has formed in the peritoneum;
- moderate - about 5 liters of watery substance;
- tense - about 20 liters of fluid have accumulated in the peritoneum.
Execution technique
The surgeon initially determines the puncture point. It is located on the midline of the abdomen, three centimeters below the navel. The area is first thoroughly treated with a liquid antiseptic, after which anesthesia (1% novocaine solution or 2% lidocaine solution) is injected into the tissue layer by layer.
When the medications begin to take effect, the doctor makes a small incision with a scalpel, dissects the skin and tissue, then pierces the abdomen with a trocar. To create the necessary hole for the movement of the instrument, the umbilical ring is grabbed and the peritoneal wall is slightly raised. One end of a PVC tube is inserted into it, the other goes down into the pelvis. Liquid is released through it.
The first part is collected into sterile tubes and sent for cytological examination. The rest of the contents very slowly (one liter every five minutes) descends into a deep container. If we are talking about ascites, up to ten liters can be removed in one procedure. With rapid extraction, surges in blood pressure occur (even to the point of collapse), because the released vessels become overfilled with blood. The surgeon's assistant tightens the patient's abdomen with a towel as the fluid is removed. This technique helps to avoid hemodynamic disorders.
The surgeon is able to determine by the color of the extracted biological material what caused the accumulation of fluid in the peritoneum. If the resulting substance is the color of meat slop, the patient most likely has internal bleeding. In such a situation, the patient begins to urgently prepare for further extensive surgery. When transudate flows through the tube, the patient will be examined for cirrhosis of the liver, the presence of malignant tumors and tuberculous peritonitis. The appearance of turbid fluid with a predominance of neutrophils is characteristic of bacterial peritonitis.
The volume of pumped out fluid has great diagnostic value. The more it is, the more accurately the pathology can be determined by its qualitative composition. Even a minimal amount (300-500 ml) can help clarify the disease in 80%.
After completion of the manipulation, sutures and a tight sterile bandage are applied to the wound. The patient is turned onto the right side. The postoperative period proceeds favorably. The stitches are removed on the seventh day. Restrictions in the regime depend on the underlying pathology, the development of which led to the need to puncture the abdominal wall and pump out fluid. For example, with cirrhosis, the patient is prescribed a strict diet.
The restraining towel does not need to be removed immediately: it will help to form intrauterine pressure that is familiar to a healthy person and gradually adapt to new conditions of blood supply.
Water in the pelvis in women
Free water can accumulate in the pelvis in particular and inside the abdominal cavity in general. In the second case, the accumulation of water in the peritoneum is called ascites.
. It can develop in women and men. In the first case (in the pelvis), water appears for exclusively “female” reasons. They can also lead to ascites, but not always.
Perhaps the most common reason for the appearance of fluid in small quantities is ovulation. In women of reproductive age, it occurs monthly. When the follicle ruptures, it pours its contents into the abdominal cavity. Such water dissolves on its own without posing a threat to health.
In addition, the causes of water inside the abdomen in women can be pathological processes that require urgent treatment:
- Inflammatory processes of the reproductive system
. For example, inflammation of the ovary, even its rupture. This condition is accompanied by severe pain; it cannot go unnoticed. - Ectopic pregnancy
. The embryo must attach to the wall of the uterus, but it attaches to the wall of the fallopian tube. As it grows, the pipe cannot withstand it and ruptures. Internal bleeding causes fluid to accumulate. - Other internal bleeding
, for example, due to injury, after surgery, cesarean section. - Intra-abdominal tumors
provoke the development of a complication - ascites - the accumulation of a large amount of water inside the abdomen;
Symptoms of the presence of fluid in the pelvis
Fluid accumulation is not a disease, but one of its signs
. You cannot make a diagnosis based on the presence of free water alone; there must be other symptoms. You should be wary of the following:
- Nagging pain in the lower abdomen
. It accompanies every gynecological problem and can have different intensity and frequency. The most dangerous type of pain is sharp, acute, and appears suddenly. Seeing a doctor should be urgent: this condition is life-threatening.
These reasons indicate gynecological problems.
Free water in the pelvis can appear for natural reasons; fluid inside the abdominal cavity is a sign of serious diseases
Possible complications and consequences
At first glance, it seems that pumping out fluid from the abdominal cavity is a simple and safe procedure. Like any other surgical procedure, it may result in unwanted reactions. The most harmless of them is the formation of a hematoma. It is formed in cases where the surgeon damages small and large vessels while performing a puncture.
Very rarely, careless actions of medical personnel can lead to damage to internal organs. Then laparocentesis can be complicated by massive bleeding and death of the patient.
If antiseptic rules are not followed, phlegmon of the abdominal wall is formed. This disease causes acute diffuse purulent inflammation of fatty tissue. It spreads quickly and involves muscles in the pathological process. The patient develops a red swelling in the affected area. It has severe pain. The skin above it is shiny. Palpation reveals a compaction without clear boundaries, hot to the touch, motionless. Lack of treatment leads to the formation of softening in the area of compaction and the appearance of a fistula. The development of abdominal phlegmon causes an increase in body temperature to 40 degrees. The patient feels weak and very thirsty.
The consequence of laparocentesis for ascites can be bleeding.
How many times can fluid be pumped out of the abdominal cavity?
It all depends on the patient's diagnosis. If ascites develops as a complication of pancreatic cancer, frequent removal of peritoneal contents will stimulate greater accumulation. Treatment by laparocentesis is performed when it is not possible to solve the problem with the help of diuretics and traditional medicine, and the development of the disease leads to the appearance of a dense, bloated abdomen, which causes great discomfort to the patient. In order to alleviate the condition, the procedure is performed as needed, with maximum accumulation.
Conservative therapy
Conservative therapy is used in the treatment of small and moderate ascites. In other words, if there are no tiring and debilitating symptoms: pain, rapid breathing (tachypnea), etc. Up to 65% of patients have an improvement in their condition when treated with diuretics - this way you can remove up to 1 liter of fluid per day. Spironolactone is considered the “gold standard”; it is prescribed in a dose of 100 to 200 mg 1-2 times a day. It is also used in combination with furosemide at a dose of 40–240 mg per day. How long and to what extent such therapy will be carried out depends on the rate of fluid loss, which is determined by changes in body weight.
In the later stages of cancer, reducing salt and water intake can reduce quality of life. Therefore, in the European clinic such diet correction is rarely prescribed.