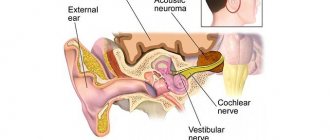
Blood cancer is usually understood as a whole group of acute and chronic diseases caused by mutation and uncontrolled division of hematopoietic cells, bone marrow cells and cells of the lymphatic system.
The disease affects different age groups. However, it most often occurs in early childhood or old age. Statistics show that in children, blood cancer is most often diagnosed at the age of 2-4 years, and in older people - at the age of over 60 years.
Types of blood cancer
Classification is carried out according to the type of flow:
- • Acute blood cancer - grows from immature blasts, extremely rarely becomes permanent.
- • Chronic blood cancer - it takes a long time to develop and affects already mature neurons. It is characterized by periods of exacerbation and remission.
According to cytogenesis, acute blood cancer has the following forms: lymphoblastic, myeloblastic and monoblastic. Permanent is divided into myelocytic, lymphocytic and monocytic.
Determine the type of leukemia (leukemia) and according to the TNM clinical classification:
- • T - size and location of the primary cancer tumor;
- • N - damage to regional lymph nodes;
- • M - distant metastases.
Each type of blood cancer is characterized by an imbalance between white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets (for example, leukemia - the predominance of white blood cells).
Medical certificate
Blood cancer is an anomaly of a malignant nature of formation, which affects, negatively affects and ultimately completely destroys the hematopoietic system of a sick person. Doctors believe that its specific feature is not only the apitastic processes of cell division, but also the excessive accumulation of immature leukocytes.
Pathology can develop in bone marrow tissue, in peripheral blood vessels and in internal organs and systems. As a result, the tumor initially forms in the bone marrow, after which it becomes a replacement for normal hematopoietic processes.
The disease can occur either in an acute form - the prognosis is less favorable - or in a chronic form. In the latter case, the state of remission tends to persist for a long time.
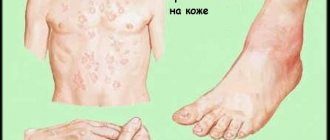
Blood cancer: symptoms and signs with photos
The presentation of cancer differs between children and adults. During the latent period of blood cancer, there are no symptoms, and it is discovered by chance against the background of a test prescribed during a preventive examination, or when it is necessary to obtain a certificate of pregnancy.
All obvious signs of blood cancer are conventionally divided according to the mechanism of occurrence.:
- • anemic - pale skin, shortness of breath, weakness, a finger prick blood test shows a low hemoglobin content;
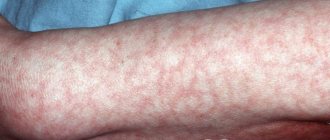
- • hemorrhagic - bleeding gums, extensive subcutaneous hemorrhages after injections, bruises, rashes on the body, women experience uterine bleeding;
- • infectious-toxic - inflammation appears in the wounds, they heal slowly, and ulcerate.
Common signs of blood cancer:
- • in the early stages, the axillary and cervical lymph nodes enlarge, then the inguinal and others, there is no pain on palpation;
- • against the background of a coagulation disorder, bruises on the skin, bruises, and bloody rashes occur; warning signs include unreasonable uterine bleeding in girls;
- • repeated infectious and viral diseases - herpes, sore throat, pneumonia;
- • periodic increase in body temperature, chills, sweating;
- • headache, nausea, vomiting, convulsions, swelling, dizziness and impaired coordination of movements.
Lymphoblastic blood cancer is characterized by weakness, nausea, weight loss, rapid pulse and pallor. In an X-ray photograph or ultrasound, the spleen and liver are larger than normal, and the stomach hurts. Peripheral lymph nodes are enlarged, but the bumps are not painful. If blood cancer is left untreated, breathing problems may occur. Kidney damage rarely occurs, but it is asymptomatic.
Myeloblastic blood cancer is common in older people. Its first symptom is fatigue, later the clinical picture is complemented by weakness, poor appetite, and dizziness. Lymph nodes do not undergo visible external changes. The musculoskeletal system reacts with painful sensations in the spine and lower extremities. Doctors record the patient's complaints of bleeding and extensive bruises that occur without mechanical impact.
Myelocytic blood cancer occurs predominantly in patients aged 30 to 50 years and more often in men. In the early phases it manifests itself as increased fatigue and decreased activity. Shortness of breath and a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen are characteristic of the later phases. Primary indicators are migraines, lack of coordination of movements, late ones include heart attack. The disease progresses rapidly, accompanied by pain in the bones and joints, and infections.
The onset of permanent lymphocytic blood cancer is expressed by similar problems, including enlarged lymph nodes. During development, the most common symptoms are frequent infections with fever, pain and burning in the right hypochondrium. Infections lead to modification of the skin, which is expressed in spots or rashes that are not contagious and not dangerous to others. Already at the initial stage, red blood cells and platelets are destroyed, and their lack causes jaundice.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of leukemia requires a comprehensive blood and bone marrow test.
The disease ranks first among other oncological diseases in terms of frequency of occurrence in children and is one of the main causes of death (first place belongs to injuries). The difficulty of making a diagnosis lies in the fact that in the early stages blood cancer in children cannot be detected. This is due to the lack of specific symptoms of leukemia. The disease can be mistaken for arthritis, rheumatism, ARVI, etc.
Immediate consultation with a doctor is required if the following symptoms occur:
- anemic syndrome (pale skin, fatigue, etc.);
- intoxication syndrome (fever, itching, pain in the limbs, etc.);
- hemorrhagic syndrome (bleeding, rash, bruises);
- proliferation syndrome (increase in abdominal size, enlarged lymph nodes).
Causes of blood cancer
The causes of blood cancer have not been fully determined, but the main factors causing the pathology have already been identified.
Provoke a wave of morbidity:
- • radiation;
- • chemical pathogens - carcinogens, the list of which includes some medications and industrial poisons;
- • viruses, the appearance of which in the body leads to the formation of mutagenic neurons.
The possibility of blood cancer is influenced by hereditary predisposition, gender (females are more likely to get sick), and lifestyle. It is impossible to become infected through airborne droplets; the pathology is not transmitted through household items.
Leukemia: symptoms
This diagnosis is fatal for most people. In its lymphocytic form, leukemia manifests itself mainly in children, while this disease affects adults to a lesser extent.
Blood cancer in children has the following symptoms: severe fever with elevated body temperature, decreased immunity, joint pain, enlargement of some internal organs, poor blood clotting.
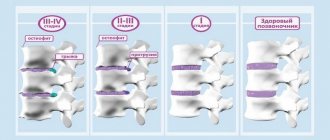
Stages of blood cancer
Stages characterize the degree of development of the disease, the presence of metastases:
- • 0 – precancerous condition, characterized by changes in the composition of biological fluids;
- • 1 - the first degree is manifested by uncontrolled division of atypical cells;
- • 2 - in the early second, blasts accumulate and form tumor tissue;
- • 3 - the third phase is accompanied by damage to regional organs and lymph nodes;
- • 4 - the fourth (and last) is characterized by metastasis to distant organs.
Forecasts
Blood cancer (symptoms, photos of patients with this disease are presented in this article), of course, is a very terrible disease. Its outcome directly depends on the shape of the tumor. Thus, with acute leukemia, death occurs much faster than with other forms of blood cancer. Chronic leukemia is treated better.
Thus, blood cancer is characterized by disturbances in the formation of red blood cells, platelets and white blood cells. This disease can occur in two forms: acute and chronic. In acute forms of cancer, patients die within a few weeks or months. If the form is chronic, then remission of the disease is possible with timely detection of the disease and treatment. If a person notices any of the listed symptoms, he is recommended to seek advice and diagnosis at a medical institution. Timely diagnosis and initiation of treatment can significantly prolong life.
Blood cancer is a disease that develops from a single cell located in the bone marrow. It divides uncontrollably in a short period of time, displacing the growth of healthy blood cells. Accordingly, the symptoms of the disease are directly related to the lack of certain normal cells in the human body. There is no tumor as such; it is, as it were, scattered throughout the body and circulates in the bloodstream.
Malignant diseases often occur in children between two and five years of age. This is most likely due to exposure to radiation, as well as heredity. The disease is manifested by the following symptoms: pain in the back, bones, joints, fatigue, pale skin, enlarged spleen, liver, and so on. Timely treatment increases the chances of recovery or remission for many years. Do not delay your visit to the hospital if you notice the above symptoms.
Diagnosis of blood cancer
Suspicion of the diagnosis appears when a person’s general health deteriorates, diagnosed during an examination, as well as with constant relapses of viral and infectious diseases. The need for additional testing arises when the spleen or liver is enlarged. Diagnosis using oncology tests is prescribed for enlarged lymph nodes, determined visually or by palpation.
Leukemia manifests itself as changes in the composition of biological fluid, which can only be identified after cytology - they are studied by a specialist, determining the complete cytological picture.
An instrumental examination with CT, MRI or X-ray will check for the presence of metastases and will reflect their location on the images.
Treatment
When treating a disease such as blood cancer, antibiotics, hormones, antiviral and immunostimulating drugs are prescribed. However, chemotherapy is most often performed, which is the intravenous administration of large doses of toxic drugs that destroy cancer cells. But such a procedure has certain consequences - healthy cells are also damaged. First of all, the hair follicles suffer, so hair falls out, as do the cells of the gastrointestinal tract, reproductive system, and bone marrow. If treatment is not carried out on time, patients die within five months.
Blood cancer, the symptoms of which are also pronounced on the skin (dark spots appear), can be treated with a bone marrow transplant. Using the puncture method, bone marrow cells are taken from a healthy donor and injected parenterally into the patient. But before this, a high dose of a certain chemical drug destroys all the bone marrow cells in the patient. It should be noted that this procedure is quite dangerous and is performed in the presence of particularly malignant tumors.
Blood cancer treatment
Blood cancer can be defeated with medications. Chemotherapy is carried out under the supervision of oncologists and includes steroid hormones, B vitamins, and immunomodulatory agents. Abnormal cell division can be stopped with cytostatics. In order to suppress symptomatic manifestations, effective medications are taken: painkillers, decongestants, anti-inflammatory, antipyretics.
Radiation therapy is also effective against blood cancer. Its action slows down the rate of spread, and positive dynamics are noted after the first procedure.
Transplant surgery will allow you to get rid of atypical cells, replacing them with healthy ones. The duration of rehabilitation after transplantation is high, as is the chance of recovery.
If medical procedures cannot be performed due to medical contraindications, the patient is provided with pain relief and supportive procedures to help alleviate the condition.
Treatment tactics for blood cancer and the chances of recovery are determined by stages and aggressiveness.
Symptoms
Knowledge about the first symptoms of hemoblastosis will help in early diagnosis and its effective treatment. Hemoblastosis can cause many different symptoms. Some of them are common to all species, others are more characteristic of certain species. For example, lymphomas can be characterized by enlarged lymph nodes. One of the most common symptoms of myeloma is bone pain.
The onset of the disease can be recognized by symptoms:
Leukemia symptoms
Leukemia is characterized by acute destruction of the maintenance of healthy red blood cells. Includes symptoms of anemia, weakness and extreme fatigue, and difficulty breathing during regular activities of daily living.
Vulnerability of the nervous system, impaired protection against infection and swelling of the lymph nodes. Blood tests show higher levels of white blood cells. Certain manifestations of leukemia are also associated with cough, nausea, abdominal fullness and extreme fatigue.
Symptoms of lymphoma
Blood cancer symptoms of lymphoma include swollen lymph nodes because this type of cancer mainly occurs around the lymph cells. Swelling of the lymph nodes is mostly painless. Symptoms include loss of weight, loss of appetite, fever, sudden onset of chills and night sweats. A certain variety of leukemia is also associated with cough, nausea, abdominal fullness and extreme fatigue.
Myeloma symptoms
At the initial stage there may be no symptoms. But as the disease gradually progresses, a general feeling of fatigue, soreness, susceptibility to infection, difficulty breathing, bouts of numbness and chest pain appear. Kidney problems may develop. Blood tests taken indicate impaired maturation of granulocytic leukocytes.
Blood cancer, symptoms in women may appear after another cancer, such as bowel or breast cancer. The first symptoms of blood cancer can appear suddenly, so once every six months you need to undergo a medical examination and take a general blood test.
Prevention of blood cancer
To prevent the disease, parents are advised to promptly contact a pediatrician in case of any pathological changes in the child’s behavior, ensure proper nutrition and sleep, moderate physical activity and a proper daily routine. This is especially true in families with a history of blood cancer - there is a possibility that they can be inherited at the gene level.
Elderly people need to adhere to the recommendations of doctors: avoid eating unhealthy foods, eliminate alcohol, lead an active lifestyle, and ensure proper sleep. When working in a toxic environment, it is necessary to protect the body from its harmful effects.
Prevention measures
First of all, you should give up bad habits - smoking and alcohol, a sedentary lifestyle and unhealthy, poor nutrition. All these points and points should be reviewed and adjusted in the right direction, which will reduce the risk of developing and progressing a disease such as blood cancer.
Regarding preventive measures, they are simple and accessible to everyone.
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules and giving up bad habits that can provoke gene mutations in the body.
- Proper and nutritious nutrition, as well as monitoring your own health, combined with an active rhythm of life, is the key to long life.
- It is recommended, if possible, to choose environmentally friendly areas for living, away from industrial regions.
All of these tips are simple and effective, but will ultimately help prevent or minimize the risk of developing blood cancer.
Traditional treatment
There are traditional recipes that cancer patients can take to improve their condition and eliminate tumor cells. The main thing to remember is that treatment in this way can only be done with the permission of the attending physician.
1. Grind 100 g of dried cinquefoil herb, place the leaves in a glass container and pour in 0.5 liters of alcohol. After closing the bottle, leave it in a dark place for a week. Strain the finished tincture and take it, diluting 25 g of this product in 250 ml of water, three times a day.
2. Collect buckwheat inflorescences (50 g), add to them the same amount of rose hips and 1 tsp. Mordovnik seeds. Having combined the necessary components and mixed them thoroughly, 1 tbsp. Pour 500 ml of boiling water over this mixture and, wrapping it in a warm cloth, leave for two hours. To fight cancer, take the finished medicine 250 ml before each meal 3 times a day. In parallel with the infusion, you should also take 1 tsp of propolis tincture. after meal. And after another 20 minutes you need to eat 1 tsp. flower pollen.
3. Collect 5 tbsp. pine and spruce needles from young trees, the age of which does not exceed six months. Chop the needles and fill with water (500 ml) and put on fire. After bringing the product to a boil, keep it on low heat for 10 minutes, then wrap it in a cloth and leave to infuse overnight. The finished medicine should be drunk throughout the day, taking it in small sips. Ideally, 2 tbsp should be added to the decoction. rose hips or onion peels. Take care of yourself!
Diagnostics
Changes in the composition of the blood will be revealed by general and biochemical analysis. The onset of the disease is indicated by a decrease in the number of main blood cells that make up the blood.
In this case, the appearance of atypical cells will signal the beginning of acute leukemia. If granular leukocytes are found, we can talk about the disease - chronic leukemia.
The photo shows a picture of blood cancer in patients with leukemia
A bone marrow biopsy provides information about the course of the disease, clarifying the type and degree of aggressiveness. Computed tomography is used to see if there is metastasis and how far it has spread.
Statistics
Blood cancer affects people of all ages. Middle-aged patients are more protected - the incidence rate in this population group is low. Russian scientists provide the following figures.
In general, leukemia is not very common in the world. American scientists claim that approximately 25 people out of 100,000 people in the United States fall ill with blood cancer every year. Compared to other figures for malignant tumors, this is not much.
“Every year, cancer is initially detected in approximately 5 thousand children and adolescents under the age of 18. The incidence among children under 14 years of age is 15 people per 100 thousand children, over 14 years old - 20 people. Moreover, half of all cancers in children are hemoblastoses - acute and chronic leukemia, malignant lymphoma, histocytosis. That is, in a child’s body, unlike an adult’s, the most favorable soil for the development of tumor processes is the hematopoietic and immune systems.”
| Rice. 2. Cancer cells in leukemia. |
Data on the number of patients with blood cancer in other countries is as follows: from 3 to 10 people per 100 thousand population. Men are affected approximately one and a half times more often than women. Chronic leukemia affects people aged 40–50 years, while acute leukemia affects mainly young people aged 10–18 years.
Healthy cells in the human body divide about fifty times during a lifetime. After this they die.
The essence of cancer in all cases is the same: the cells of our body attacked by cancer change their characteristics and structure as they divide continuously. With each new division, the texture of the cell changes and the accuracy of copying the previous tissue is disrupted. In the next division process, the difference between the “new” cancer cell and the original one is more noticeable. Healthy cells may contain oncogenes that can transform the primary cell into cancer. Mutation of a cellular oncogene leads to the formation of a malignant tumor.
Causes of hemoblastosis
It should be noted that hemoblastosis is not the most common of oncological diseases. According to statistics, no more than two people out of 10,000 people suffer from it. Moreover, most often children aged 2–6 years, as well as elderly people (60–70 years old), suffer from this deadly disease.
Doctors attribute two factors to the main reasons for the development of this condition:
- exposure to radiation (irradiation to which a pregnant woman was exposed at one of the stages of bearing a child);
- genetic factor (hereditary disease).
How does a tumor develop?
Initially, the mutated tissues are localized in the bone marrow, where the production of blood components occurs. Gradually, cancer cells replace normal tissue. Patients experience anemia, other blood cell disorders, bleeding, and fragility of the vascular wall.
One of the types of oncopathology, human T-cell leukemia, is a viral disease.
Metastasis manifests itself as the appearance of leukemic clots in various organs and lymphatic collectors. Damage to areas of the vascular wall due to the formation of a secondary tumor is also possible.
Currently, the causes of this pathology are unknown to science. But doctors identify a number of factors that provoke the development of cancer of the circulatory system:
- genetic predisposition;
- work at chemical plants;
- cases of radio exposure;
- smoking;
- stressful conditions;
- unfavorable living environment.
Kinds
Cancer in a person’s blood can be acute or chronic. The difference lies in the nature and stage of maturity of the cells that have undergone the change. The acute form of blood cancer significantly inhibits the blood clotting process, is practically untreatable and leads to lymphoblastic leukemia (in 80% of cases). With this form of cancer, there is a sharp increase in blast cells and they, being immature, also begin to divide.
More often, the acute form of cancer in the blood affects children; in them, the infiltration process develops faster and the number of affected organs increases. At the initial stage, the patient experiences general malaise and often suffers from chronic diseases.
The chronic form of blood cancer progresses more slowly only to a state of “blast crisis.” If treatment is started before this point, there is every chance of achieving remission. This form of blood cancer cells is considered relatively benign because it contains a higher number of mature cells. Such particles divide more slowly, and, therefore, the disease is not so aggressive. There are no pronounced symptoms in the initial stage of chronic cancer. You can suspect something is wrong using a blood test, paying attention to the increase in the number of immature granulocytes. Further, the disease becomes malignant and leads to the appearance of tumors.
The chronic form of leukemia never becomes acute, just as the reverse transition is impossible.
Another criterion for dividing the disease lies in the nature of the diseased cells: small granules - myeloid leukemia, without granules - lymphocytic.
Chronic leukemia in humans is more common in people over 40 years of age.
Chronic leukemia
The most common chronic leukemia is myeloid leukemia. The development of this disease is due to the presence of the so-called Philadelphia chromosome, which is obtained as a result of the transfer of part 9 to chromosome 22. Major changes in blood tests:
- Leukocytosis can reach up to 450x 109/l. A shift in the leukocyte formula to the left is characteristic, which is manifested by the presence of myelocytes, promyelocytes, myeloblasts, that is, all forms of differentiation. The absence of “failure” is a distinguishing feature of chronic leukemia from acute leukemia.
- An increase in basophils and eosinophils; the presence of immature forms of these cells is possible.
- Formed elements are characterized by anisocytosis - a change in size, shape, structure, which affects the functional activity of the cell.
- Anemia appears in the advanced phase of the disease. The etiology of the decrease in the number of red blood cells is associated with an increase in the size of the spleen and, in connection with this, an increase in the utilization of red blood cells.
- The platelet concentration is increased, but in severe cases of leukemia in the final stages of the disease, it is possible to diagnose thrombocytopenia.
- The course of chronic leukemia can be complicated by blast crisis - a condition reminiscent of acute leukemia: an increased number of blasts, the presence of a “failure”, severe anemia, thrombocytopenia.
Subleukemic myelosis is one of the types of chronic leukemia, which can be detected by a clinical blood test for cancer. Characteristic features:
- The disease develops as a result of damage to the pluripotent red bone marrow cells, so in a general blood test we will see changes in all indicators.
- Thrombocytosis reaches up to 2000 x 109/l, erythrocytosis and increased hemoglobin are characteristic of the first phase of the pathology
- Leukocytosis up to 25-30 x 109/l, there is a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left
True polycythemia or erythremia is formed from the myeloid series of hematopoiesis. With this hemoblastosis, hyperplasia of the red bone marrow occurs, that is, an increase in the number of cells. The course is more favorable than with other hemoblastoses. Polycythemia vera can be determined by a blood test:
- Increase in hemoglobin up to 200g/l
- Increase in red blood cell counts to 8 - 9x 1012/l
- Leukocytosis up to 14x109/l, thrombocytosis more than 1500x109/l
- An increase in hematocrit - the number of formed blood elements compared to the liquid phase of blood - plasma. Depending on the hematocrit level, the degree of bone marrow damage is determined.
- Increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- The final stage of leukemia is blast crisis.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is a blood cancer that is most common in the adult population. The tumor is represented by lymphocytes, which, due to improper differentiation, are not able to perform their function. A blood test can help detect cancer:
- Leukocytosis from 10 to 160 109/l. An increase in leukocytes occurs due to an increase in lymphocytes; their number can increase to 89-90%.
- The presence of Botkin-Gumprecht shadows - remnants of destroyed lymphocytes that circulate in the blood in the form of clumps of chromatin, half-destroyed cell nuclei.
- Morphologically changed lymphocytes with a kidney-shaped or double nucleus.
- The formation of autoimmune anemia is observed when pathological lymphocytes produce autoantibodies against red blood cells, which shows the neglect of the process
- A decrease in platelet count occurs due to suppression of the megakaryocyte lineage by lymphoid tissue.