» What is liver failure and what are its symptoms?
Liver diseases
Valentin Livanov 06/09/2017
Liver failure is a medical term that refers to a set of symptoms that develop as a result of the destruction of the liver parenchyma and disruption of its basic functions. This pathological condition is manifested by intoxication of the body, since the liver ceases to perform a detoxification function and harmful substances accumulate in high concentrations in the blood and tissues.
Violation of one or more liver functions leads to metabolic disorders, malfunctions of the nervous system and brain. Severe forms of liver failure provoke irreversible processes that can result in the development of hepatic coma and death.
What is liver failure
Liver failure is a pathological condition in which the liver partially or completely ceases to perform its functions. As the disease develops, the detoxification functions of the liver are disrupted, which leads to severe intoxication of the body with breakdown products of ammonia, phenol, and fatty acids, which disrupt the functioning of internal organs and affect the nervous system.
It is known that 450 million people die every year from liver failure, and the disease can occur with equal frequency in women and men. The disease can occur in acute and chronic forms, has severe symptoms, and in the absence of timely and correct treatment will lead to the death of the patient.
In severe forms of liver failure, irreversible processes occur in the patient's body that can cause the development of hepatic coma, damage to the structures of the brain, nervous system and death of the patient. This pathology is a serious illness with serious consequences, but if you pay attention to the symptoms in time, undergo diagnosis and treatment, there is a chance of a good prognosis.
Therapy
If symptoms of liver failure are detected, comprehensive treatment is prescribed.
If the diagnosis is confirmed, the patient is first prescribed a diet, which implies either a complete absence of protein or a decrease in its content.
Nutrition for liver failure. The patient's food should contain less than 30-40 g of protein (sometimes it needs to be reduced to 20-30 g) and no more than 20-30 g of fat, and the amount of carbohydrates should be 200-300 g. If increased development of liver failure is observed, the consumption of fats must be eliminated, and Limit protein content to two to three grams.
The diet should contain plant foods with a high content of easily digestible carbohydrates and potassium compounds. Protein is limited precisely at the expense of animal proteins; for this purpose, plant proteins are consumed instead of milk proteins, adding thin porridges, for example, semolina, to the menu.
Also, lactose or lactulose is added to the diet for liver failure, which stop the synthesis of ammonia and other compounds. Lactulose is contained in the medications Duphalac and Normaz. Food should be taken every two hours. It is served pureed or liquid. Salt is excluded. You need to drink about one and a half to two liters, in the case when the swelling does not progress.
If precoma develops, the patient is provided with parenteral or tube feeding.
Therapy for this disease includes detoxification of the body, improvement of microcirculation, return to normal acid-base balance and electrolyte imbalances.
To do this, using intravenous injections, the patient is injected in volumetric quantities with a 5% glucose solution, B vitamins, lipoic acid, cocarboxylase, panangin and essentiale. The administration of solutions of ornicethyl and glutamic acid is also prescribed.
Treatment of acute liver failure includes components such as vitamin and hormonal therapy, antibiotics, plasmapheresis, blood and lymph cleansing. Some hepatology centers also offer hemodialysis.
In order to prevent further poisoning, it is necessary to cleanse the intestines with enemas and other means. A person is also prescribed antibiotics and lactulose to prevent putrefaction in the intestines.
When a person’s liver coma progresses, it is advisable to treat with prednisolone. If there is oxygen tissue starvation, treatment is carried out with inhalation or hyperbaric oxygenation.
Also, treatment of liver failure includes ultraviolet irradiation of blood, hemosorption, extrarenal blood purification and plasmapheresis.
Types of liver failure
In hepatology, liver failure is divided into several types, classifications and stages of organ damage, each of which has its own characteristics.
According to the clinical course of the disease, it is divided into acute and chronic. In the first case, the disease develops rapidly against the background of severe intoxication of the body with alcohol, medications or viral hepatitis. The chronic course of the disease has a slower course and develops with prolonged pathologies of the organ. Another form of the disease is alcoholic liver failure (ALF), which develops against the background of long-term alcohol consumption and leads to disturbances not only in liver function, but also problems with blood clotting, the development of encephalopathy and coma.
Forms of the disease
Depending on the etiological factor, renal failure is divided into 3 forms:
- Exogenous form - manifests itself in the presence of hepatic or extrahepatic circulatory disorders, often against the background of liver cirrhosis. During the disease process, toxic substances bypass the liver, but affect other internal organs and systems.
- Endogenous or hepatocellular form - develops when liver cells are damaged against the background of hepatotoxic factors. This form of the disease is accompanied by the development of rapid necrosis of hepatocytes.
- The mixed form is a combination of the two above forms of the disease, in which the death of liver cells occurs and damage to almost all organs and systems of the body occurs.
With the development of acute liver failure, all toxic substances that the liver is unable to process enter the bloodstream and are distributed throughout the body, which ultimately leads to hepatic encephalopathy, coma and death of the patient.
3 stages of the disease
As the disease and clinical picture develop, the disease is divided into 3 main stages:
- Initial (compensated stage) - the liver at this stage works in an enhanced mode, exhausting its resources to combat toxic substances. This period can last from several hours to several weeks or months.
- Severe (decompensated) - accompanied by a pronounced clinical picture of the disease, since at this stage the liver is not able to perform its functions, severe intoxication of the body occurs, and the functioning of the entire body is disrupted.
- Terminal (liver dystrophy) - liver cells have completely succumbed to necrosis, the organ does not function, as a result, hepatic coma develops, and the patient dies within 2 days.
Complications of the disease
Liver failure syndrome is extremely dangerous because organ damage can cause the development of severe complications caused not only by a decrease in the functional activity of hepatocytes, but also by an increase in toxic substances in the blood. There are a number of conditions, the occurrence of which reduces the patient's chances of survival.
The accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity increases the risk of secondary infection. In this case, peritonitis develops. Impaired liver function leads to varicose veins of the esophagus, which, combined with a decrease in blood clotting, predisposes to massive bleeding from the upper parts of the organ. The development of this complication ends in death in almost 100% of cases.
The accumulation of toxic substances in the blood often causes the development of deficiency. In addition, in patients with critical liver tissue damage, cases of brain tissue hypoxia and edema are common. Severe respiratory failure may occur. In rare cases, extremely dangerous pulmonary hemorrhages are observed, which in most cases are fatal.
Most patients suffering from chronic liver failure experience atrophy of the mammary glands. Hypogonadism in men is possible. Testicular atrophy and infertility are often observed. In addition to these conditions, patients often experience organ dysfunction due to a chronic course. The development of malignant neoplasms may be observed.
Causes of liver failure
Many causes and predisposing factors can provoke the development of liver failure. Sometimes the disease develops under the direct influence of toxins, and sometimes as a complication of other diseases. Many doctors are of the opinion that this pathology is a consequence of metabolic disorders that are responsible for intoxication and the functioning of the central nervous system. Infections (viruses, bacteria or parasites) often act as provocateurs of the disease; alcohol abuse and long-term use of potent medications also play a significant role in the etiology of the disease.
Acute and chronic forms of liver failure can occur with the following diseases and conditions affecting liver cells:
- herpes virus, Epstein–Barr;
- cytomagelovirus;
- viral hepatitis (C, D, B, G);
- helminthic infestations;
- liver poisoning from alcohol, medications or poisons;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- autoimmune diseases and endocrine diseases;
- disturbance of the metabolism of proteins, copper, iron;
- acute infections;
- hepatosis (dystrophic changes) in the liver;
- severe nervous stress;
- binge eating;
- excessive consumption of fatty, spicy and heavy foods;
- liver injuries;
- blood transfusion.
Liver failure in adults and children can develop under the influence of multiple factors, so it is very important to promptly and correctly treat all diseases, lead a healthy lifestyle, and at the first symptoms, consult a doctor and undergo a comprehensive examination.
Causes of the disease
There are a number of conditions that, as they progress, can cause the development of acute or chronic liver failure. Most often, liver dysfunction is observed in cirrhosis. This disease is characterized by necrotic destruction of organ tissue and further replacement of damaged areas with fibrosis.
Subsequently, the degenerated areas of the liver begin to put pressure on the vessels, triggering the formation of anastomoses and the development of portal hypertension. These processes are often accompanied by the appearance of pronounced ascites. The influence of the following unfavorable factors can provoke first cirrhosis, and then failure:
- viral hepatitis;
- long-term alcohol abuse;
- severe poisoning by toxins;
- taking certain medications;
- drug use;
- some pathologies of the biliary tract;
- poor nutrition;
- eating poisonous mushrooms;
- infectious diseases;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- congenital abnormalities of liver development.
Conditions in which excess fat enters the tissues of the organ predispose to the appearance of such liver damage. In this case, fat begins to accumulate due to a failure in metabolic processes. Adipose tissue gradually replaces dead hepatocytes. Factors contributing to this problem include:
- obesity;
- anorexia and bulimia;
- some gastrointestinal diseases;
- taking alcohol substitutes;
- diabetes.
- Regular consumption of bear and badger fat.
The appearance of liver failure is often a natural result of the progression of parenchymal degeneration of the organ. Factors contributing to this problem include:
- congenital deficiency of enzyme production;
- protein metabolism disorders;
- endocrine disorders;
- hepatitis;
- stagnation of bile in the liver;
- intoxication in certain viral diseases;
- hypo- and vitamin deficiencies.
Less commonly diagnosed is the development of liver dysfunction against the background of parenchymal carbohydrate dystrophy. This pathological condition occurs against the background of metabolic disorders involving glycogen. Lack of vitamins in food, alcohol intoxication and diabetes mellitus predispose to such liver damage. A decrease or complete disruption of liver function is often observed against the background of amyloidosis of this organ.
The occurrence of this pathology is often detected in patients with a predisposition to amyloidosis. Insufficient liver function is caused by gradual deposition of amyloid, i.e., insoluble protein, on the walls of the bile ducts and blood vessels. This contributes to the disruption of tissue saturation with oxygen and nutrients, and in addition, the outflow of bile.
Often the development of liver failure is observed against the background of hepatitis. Both viral hepatitis and liver inflammation caused by the influence of breakdown products of alcohol or toxic substances have a destructive effect on tissue. These conditions lead first to inflammation and then death of large areas of the organ.
The development of renal failure may be the result of malignant neoplasms in this organ. The appearance of a similar problem is often observed in people who have a genetic predisposition to liver cancer. The danger is metastasis from tumors located in other organs.
The long-term adverse effects of carcinogenic substances can also contribute to the formation of malignant neoplasms, and then to failure. As malignant tumors grow, they replace functional liver cells and compress healthy areas of the organ tissue. This leads to the development of inflammation, disruption of the outflow of bile and blocking of blood circulation in healthy tissues. In this case, this pathological condition is accompanied by severe intoxication.
Parasitic infestations can also cause liver dysfunction. When different types of helminths are damaged in the liver tissue, they begin to multiply. When their number reaches a critical level, they not only lead to damage to organ tissue, but also compress the hepatic vessels and bile ducts. However, if detected early, liver dysfunction caused by parasitic infestation can be easily treated.
Some diseases of the cardiovascular system, including aneurysms and atherosclerosis, can also contribute to the appearance of liver dysfunction. Chronic renal failure increases the risk of developing liver dysfunction. In addition, some diseases accompanied by severe hormonal imbalances can contribute to the appearance of such a problem.
There are frequent cases of insufficiency developing in people who have experienced massive blood loss. Contributes to the emergence of the problem of blood transfusion, which is incompatible with the recipient group. In rare cases, the development of pathology is observed after surgical interventions on the gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms in men and women
How does liver failure manifest? Clinical signs of the disease in the early stages of liver failure often go undetected. The patient feels increased weakness, problems with the digestive system appear, and appetite decreases. A person does not pay much attention to such symptoms, but as liver cells die and intoxication increases, other more pronounced ailments appear.
Let's look at the main symptoms and signs of liver failure in men and women:
- acute pain in the right hypochondrium, which may intensify after eating or drinking alcohol;
- red palms;
- increased body temperature;
- yellowing of the skin and sclera;
- urine becomes darker;
- stool discoloration;
- nausea, frequent vomiting;
- feeling of heaviness in the liver area;
- Gastrointestinal bleeding;
- an increase in the size of the abdomen;
- a sharp decrease in body weight;
- increased nervousness;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- increase in blood pressure;
- cough, shortness of breath;
- tremor of the limbs;
- swelling throughout the body.
As the patient's condition worsens, joint and muscle pain appears, there is a smell of rotten meat from the mouth, the patient refuses to eat, quickly loses weight, the liver increases significantly in size, and fluid collects in the abdominal cavity. A few hours after an acute attack of the disease, hepatic encephalopathy develops, affecting the central nervous system and brain structures.
With the development of the terminal phase (last stage), consciousness is impaired, convulsions, nasal and intestinal bleeding, tremors and other symptoms appear, causing hepatic coma (coma). A few days later, the patient dies.
In the chronic course of the disease, the symptoms do not develop so rapidly, but they are still noticeable and ultimately the prognosis will be unfavorable, especially if treatment is not carried out or the patient ignores the doctor’s recommendations.
Symptoms
Symptoms of liver failure manifest themselves in various internal organs and systems of the body. The main ones are divided into groups:
- Cholestasis. This is a violation of the outflow of bile, in which excessive amounts of bilirubin accumulate in the blood. Manifestations of cholestasis affect the skin - they become yellow, severe itching appears, changes in the color of feces and urine - they turn brown. Another pronounced symptom of cholestasis is pain in the right hypochondrium.
- Dyspeptic disorders. Nausea and vomiting are usually the first to appear, often after eating, but sometimes not associated with it. Other dyspeptic disorders are loss of appetite, sudden weight loss, bad breath, and pain in the stomach.
- General intoxication. If there is insufficiency, the general condition of a person worsens and performance is lost. Due to constantly elevated body temperature (up to 37-38 degrees), a person experiences fever, chills, and headaches. Increased irritability, fatigue, sudden mood swings - these symptoms alarm others.
- Nervous system disorders. Toxic substances gradually affect the brain, which is expressed in the following symptoms: dizziness, lethargy, sleep disturbances, apathy, depression. Over time, encephalopathy develops.
Diagnostics
Which doctor should I contact?
When the first signs of illness appear, there is no need to hesitate to visit a gastroenterologist or hepatologist. Modern diagnostic methods will make it possible to diagnose the disease in the early stages, which will reduce its severe consequences.
The initial consultation consists of taking a medical history, examining the skin, and palpating the abdomen. Then the doctor will prescribe a number of laboratory and instrumental examination methods that will help confirm or refute the doctor’s suspicions, determine the stage of the disease and other changes in the body’s functioning.
Which examination to take?
Diagnosis of liver failure consists of:
- General blood test.
- Liver blood samples.
- Blood biochemistry.
- General urine analysis.
- Analysis for antibodies to the hepatitis virus.
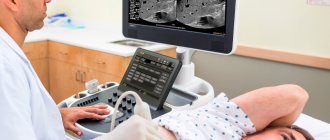
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
- Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- Liver biopsies.
The results of the examination will help the doctor draw up a complete clinical picture of the disease, make the correct diagnosis, and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Propaedeutics and diagnosis
If there is reason to suspect the presence of liver failure syndrome, anamnesis is collected, clarifying the fact of chronic liver diseases and viral hepatitis. You also need to find out whether the person has an alcohol addiction and what medications he takes.
The doctor prescribes an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs, which helps to determine the parameters of the liver and its parenchyma, and in addition, check for the presence of malignant formations.
Studying venous blood analysis in the laboratory helps detect the presence of anemia and leukocytosis. In patients with this disease, it is necessary to examine the serum for albumin, bilirubin, transaminases and potassium.
Hepatoscintigraphy allows you to diagnose mixed liver pathologies. Sometimes the patient is sent for magnetic resonance imaging and multislice computed tomography of the abdominal cavity. In addition, a piece of liver is examined under a microscope.
Clinical guidelines and treatment
Treatment of liver failure is a complex and lengthy process that consists of complex therapy. What clinical recommendations does the doctor give? In addition to taking medications, the patient is prescribed a diet, he also needs to adjust his lifestyle, completely stop smoking and drinking alcohol. Traditional medicine recipes can be prescribed as auxiliary therapy.
When conservative therapy does not bring the desired results or the disease is in advanced stages, there is a chance to save the patient’s life if a liver transplant is performed. At the stage of hepatic coma, hemodialysis and plasmapheresis procedures are performed, which help cleanse the blood of toxic substances.
In case of liver failure, the patient is hospitalized under medical supervision. All medications are administered to him intravenously or intramuscularly, this will allow him to get a faster effect of treatment.
Drug therapy
Drug therapy may include the use of the following medications:
- To improve blood circulation, the patient is injected with saline solutions.
- To stop bleeding - hemostatic drugs.
- You can enhance intestinal motility and cleanse the body using detoxification, infusion of a solution of Rheosorbilact or Neogemadese.
- Osmotic drugs - Sorbitol - will help relieve swelling and stimulate blood circulation.
- Eliminate tissue hypoxia - Cocarboxylase or Cytochrome.
- A solution of Glucose or Albumin can replenish the body's energy reserves.
In addition to the main therapy, the following medications are prescribed to accelerate the regeneration and restoration of liver cells:
- Hepatoprotectors - Essentiale, Essliver Forte, Liv-52.
- Amino acids, B vitamins, PP.
- Drugs to improve cerebral circulation - Actovegin, Cerebrolysin.
- Diuretics - Mannitol, Lasix.
- Sedatives.
All these drugs are intended for the treatment of acute and chronic liver failure.
The choice of drug, route of administration, dose and duration of treatment is determined by the doctor individually for each patient. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe other medications that will help improve the patient's general condition.
In severe cases, the only way to save the patient's life is liver transplantation. The operation is quite complex and expensive. Only a close relative is suitable as a donor. It is important to note that the operation is life-threatening for both the patient and the donor, so it is performed only in extreme cases.
Treatment
After examining the patient and collecting his medical history, the doctor decides on treatment tactics. It should be aimed at treating the underlying disease that influenced the occurrence of liver failure. Most often, the patient is sent to a hospital, where he undergoes a course of therapy under the supervision of medical personnel.
Treatment methods include:
- diet (exclusion from the diet of salt, smoked meats, fried foods and limited consumption of protein foods);
- antibiotic therapy;
- taking hormonal medications;
- infusion therapy;
- vitamin complexes.
If bleeding occurs, a plasma transfusion is prescribed. In cases of progression of liver failure at the third or fourth stage, hemodialysis is performed.
In advanced forms of the disease, a liver transplant is required. Before making a decision on surgical intervention, the patient's condition, age and the ability to maintain the post-transfusion regimen for a long period in full are assessed.
Traditional methods of treatment
Official methods of treating liver failure are often supported by traditional methods of treatment, which cannot cure the disease, but can alleviate the patient’s condition and slow down the destructive processes in the body.
- Decoction of corn silk: To prepare, you will need 10 g of dry raw material, which is placed in a saucepan and filled with boiling water, put on fire for 10 minutes. Afterwards, you need to give the broth time to cool, then filter and take 100 ml 2 times a day.
- Milk tincture of St. John's wort: You need to take 1 tablespoon of dried St. John's wort flowers, pour in 1 glass of milk and put on fire for 15 minutes. Then cool, filter and take ¼ glass three times a day before meals.
- Turmeric tincture: You will need 1 spoon of turmeric, which is poured into 200 ml of cool water, left for 2 hours, added honey and taken half a glass 2 times a day.
- A mixture of honey, lemon, garlic: To prepare the recipe you need to take 2 parts of honey and lemon and 1 part of chopped garlic. All ingredients need to be crushed and taken 1 tsp 2 times a day.
Prevention
Reduce your risk of acute liver failure by taking care of your liver.
- Follow the directions on your medicine packages. If you take acetaminophen or other medications, check the package insert for recommended dosages and do not take more. If you have liver disease, ask your doctor if it is safe to take some acetaminophen.
- Do not take medications without your doctor's consent . Even over-the-counter and herbal medications can cause this condition.
- Drink alcohol in moderation or not at all. Limit the amount of alcohol you drink to no more than one drink per day for women of all ages and men over 65, and no more than two drinks per day for younger men.
- Avoid risky behavior. Use condoms during sex. If you are planning to get tattoos or body piercings, make sure that the solution you choose is certified and safe.
- Get vaccinated. If you have chronic liver disease, a history of any type of hepatitis infection, or an increased risk of hepatitis, talk to your doctor about getting the hepatitis B vaccine. A vaccine is also available for hepatitis A.
- Avoid contact with the blood and body fluids of other people. Accidental needlesticks or improper cleaning of blood or body fluids can spread hepatitis viruses. Sharing razors or toothbrushes can also spread the infection.
- Do not pick or eat mushrooms . It is difficult for an ignorant person to determine the difference between a poisonous and a safe mushroom, which will lead to poisoning if consumed.
- Be careful with aerosol cans. When using aerosol chemicals, make sure the area is ventilated or wear a mask. Take similar protective measures when spraying insecticides, fungicides, paint or other toxic chemicals. Follow product instructions carefully.
- Watch what gets on your skin. When using insecticides and other toxic chemicals, cover your skin with gloves, long sleeves, a hat and a mask.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Obesity can cause a condition called non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, which includes fatty liver, hepatitis and cirrhosis.
Diet for liver failure
Nutritional therapy is considered an important step in the treatment of liver failure. Patients are prescribed table No. 5, which consists of eating protein-free foods. The patient's diet should contain easily digestible foods with plenty of fiber, vitamins and microelements. Daily calorie content should not exceed 1300 - 1500 kcal.
What can you eat
Preference should be given to the following products:
- fruits;
- vegetables;
- cereals;
- honey;
- low fat dairy products;
- lean varieties of meat and fish.
Meals should be fractional, and all products can be served boiled, raw or baked.
What to exclude from your diet
It is strictly forbidden to eat spicy and fatty foods; you should avoid spices, pickles and smoked meats. Any type of alcohol, including smoking, is strictly prohibited.
It is necessary to maintain water balance, normalize mental state, give up physical activity, and establish rest and sleep patterns.
Prognosis and prevention
In both acute and chronic forms of liver failure, the prognosis is unfavorable. In the acute course, death in most cases occurs within 2–3 days to 2 months, unless an organ transplant is performed.
The chronic form of the pathology also has an unfavorable prognosis, although this type of disease manifests itself less aggressively. Even with complex treatment and diet, one can only achieve prolongation of life, but without transplantation the patient will face premature death. The prognosis is worsened by the presence of complications.
To reduce the risk of developing critical liver damage, it is necessary to promptly treat diseases of this organ. As part of the prevention of the described pathological condition, it is necessary to stop taking alcohol and drugs. To reduce the risk of developing deficiency, you should adhere to a healthy diet and exercise regularly.
It is imperative to maintain normal weight. You should avoid eating mushrooms collected in the forest. It is imperative to be vaccinated against hepatitis A and B. It is necessary to take any medications and dietary supplements with caution. Major injuries that would require a blood transfusion should be avoided whenever possible, and all medical procedures should be carried out in a sanitary manner. This will reduce the risk of developing organ failure and avoid premature death.
Causes
There are many reasons why the liver malfunctions. Often the disease is provoked by one or more of the following factors:
- viral hepatitis;
- infectious diseases caused by damage to internal organs by parasites;
- alcoholic and other toxic liver damage;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- tuberculosis, syphilis and other acute infectious diseases;
- dystrophic changes in the liver, tumor formation;
- chronic diseases of the digestive system.
Some reasons that can trigger the disease are related to a person’s lifestyle. By themselves, they cannot develop organ pathology, but in combination with other factors, they can. These include:
- bad habits;
- unhealthy diet: eating fatty, fried, spicy, and other unhealthy foods;
- lack of diet, frequent overeating;
- fasting, mono-diet;
- stress, severe nervous shock.
Symptoms of the development of the disease
The clinical picture of the development of liver failure includes the syndrome of hepatic cell failure, hepatic encephalopathy and coma.
At the stage of hepatic cell failure, the appearance and progression of jaundice and swelling is observed, ascites develops, signs of hemorrhagic diathesis appear, and the development of dyspepsia and abdominal pain is detected. The patient experiences a decrease in body weight and a fever.
In the chronic form of the pathological process, the patient experiences the occurrence of endocrine disorders, which are accompanied by:
- Decreased libido.
- Infertility.
- Testicular atrophy.
- Gynecomastia.
- Alopecia.
Women experience atrophy of the uterus and mammary glands, which complicates the conception of a child and the normal course of pregnancy.
Liver dysfunction leads to the appearance of liver odor from the patient’s mouth.
Laboratory tests at this stage of development of the pathological condition reveal the presence of increased levels of bilirubin, ammonia and phenols in the serum and hypocholesterolemia.
At the stage of hepatic encephalopathy, the occurrence of mental disorders is recorded. The patient develops:
- unstable emotional state;
- anxiety;
- apathy;
- disturbance of night sleep;
- aggression;
- increased excitability.
In addition, this stage of disease progression is characterized by the appearance of neuromuscular disorders, which are characterized by:
- Slurred speech.
- Violations of writing.
- The appearance of finger tremor.
- Impaired coordination of movements.
- Strengthening reflexes.
At the terminal stage of failure, signs of hepatic coma develop. In the precoma phase, increased drowsiness, lethargy, short periods of agitation, muscle twitching, convulsions, uncontrolled urination, and confusion occur.
In addition to these symptoms, the patient may experience bleeding gums, nosebleeds, and hemorrhages from the digestive tract.
When hepatic coma occurs, the patient loses consciousness, his reactions to painful stimuli are lost, and reflexes fade.
The patient's face becomes mask-like, the pupils dilate, there is no reaction to light stimulation, a decrease in blood pressure occurs and breathing is impaired. Usually this stage ends in death for the patient.
Carrying out diagnostics
Diagnosis of hepatic cell failure syndrome is carried out comprehensively, as this allows us to determine the overall picture of the course of the disease. A variety of techniques are used to carry out diagnostics. Initially, anamnesis is collected to clarify the factors that provoked the onset of the disease.
In addition, biochemical diagnostics are carried out aimed at determining the level of bilirubin, blood coagulation pathology, the amount of protein, as well as many other disorders and indicators. An ultrasound of the liver is also required, which will help to accurately indicate the condition of this organ. In addition, other types of diagnostics are indicated, such as:
- tomography;
- biopsy;
- electroencephalography method.
Pathological liver disorder is determined on the basis of total bilirubin, the presence of jaundice, a decrease in liver size, and the presence of encephalopathy.
What it is
At the moment, liver failure refers to a clinical syndrome that appears as a result of a violation of the compensatory functions of the liver.
In case of illness, the liver cannot satisfy the body's metabolic needs and ensure the preservation of the stability of the internal microenvironment - the entire body suffers.
There are no types of metabolism that are not controlled by the liver. Therefore, most emergency conditions can be expressed and aggravated by liver failure.
Complications
If left untreated, the disease leads to serious consequences. Late stages can cause failure of vital organs and death of the patient. Falling into a hepatic coma increases the risk of irreversible changes in brain structures, which causes the patient to become disabled. Other complications include:
- Attachment of a bacterial infection.
- Hypoglycemia.
- Encephalopathy.
- Internal bleeding.
- Blood poisoning.
- Kidney failure.
- Development of systemic portal hypertension.
- Inflammatory lesions of the abdominal cavity.
Main causes
Liver cell failure syndrome occurs for a variety of reasons. The main factors that provoke the occurrence of the disease include the following:
- liver diseases;
- obstruction of the bile ducts;
- chronic diseases of internal organs.
In addition, the disease can occur as a result of drug and toxic poisoning and alcohol abuse. Various types of injuries and damage can have a significant impact on the body.
Clinical signs
During an acute process, which is accompanied by a rapid rate of destruction of hepatocytes, a large number of pronounced clinical signs appear that cannot go unnoticed by a person. Swelling occurs in the lungs, the central nervous system suffers, since the cleansing function of the body’s natural filter is disrupted.
Symptoms of a negative effect on the central nervous system are: lethargy, constant drowsiness, attacks of nausea, or, on the contrary, asthenic manifestations: excessive irritability, hyperexcitability, trembling hands or even convulsive seizures. Additionally, renal dysfunction occurs.
Forecast for life
Predicting the prognosis can be difficult. Important prognostic variables include:
- Degree of encephalopathy (brain damage): Worse when the encephalopathy is severe.
- Patient's age: worse when age < 10 or > 40 years.
- Cause of acute liver failure: The prognosis is better for acetaminophen overdose, hepatitis A, or hepatitis B than for specific drug reactions or Wilson's disease.
Many people get better with therapy. If a transplant is not necessary, most patients return to their daily activities within 6 months. People who receive a transplant need medical care throughout their lives, including medications to prevent the body from rejecting the new organ.
Advantages and disadvantages of the liver diet
Like any medical nutrition, a diet for liver and gallbladder diseases has its advantages and disadvantages. The hepatic dietary table in some cases requires a lot of time and imagination due to its long duration (in case of impaired liver function, it is necessary to follow the principles of the diet constantly, during periods of exacerbation of the underlying disease and in remission). The advantages of this diet are:
- Balanced and complete diet.
- The diet is easily tolerated by patients and improves their well-being and general condition.
- There are benefits not only for the liver and gallbladder, but also for the entire digestive system.
Symptoms of the disease
Clinical manifestations of liver failure are quite pronounced, and it is characterized by all the signs of liver disease. As a result of the pathology, the process of bile outflow significantly worsens. In this case, total bilirubin increases greatly, which can be determined clinically by performing a general blood test. The liver ceases to function fully, and its cells die.
One of the clearest signs of the disease is the appearance of jaundice, the intensity of which largely depends on the level of damage to the biliary tract. However, if it develops into a chronic stage, then this sign may not exist. Other symptoms of the disease may also be observed, such as:
- death of liver tissue;
- feverish condition;
- presence of discolored stools;
- liver enlargement;
- circulatory disorders;
- presence of tachycardia;
- pressure changes.
As the disease progresses, when the synthetic function of the liver is suppressed, the nervous system begins to suffer greatly, as the general cleansing function is disrupted. This means that there is a lethargic state or, on the contrary, excessive excitability, severe drowsiness, loss of consciousness, nausea, and limb cramps. In addition, there may be significant accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal area.
Classification of the disease
Hepatocellular failure syndrome can occur in chronic and acute forms. The chronic form of the disease occurs as a result of the development of cirrhosis of the liver and can last quite a long time. The acute form of the disease occurs quite sharply and suddenly, mainly due to viral hepatitis or as a result of poisoning or drug overdose. Each type of disease corresponds to several stages of the pathological process, namely:
- initial;
- expressed;
- terminal;
- hepatic coma.
The acute form is characterized by a complete loss of the liver's ability to function. This disease can occur even in a completely healthy person. There are also several forms of this disease, such as:
- endogenous;
- exogenous;
- mixed.
In some cases, the disease can be fatal. Hepatocellular failure syndrome is characterized by the death of the tissues of this organ. After cell death, many dead components enter the blood. Their quantity can be determined by conducting a biochemical analysis.
Treatment at home
If you decide to be treated at home, the course of medications is still only prescribed by a doctor. The process of treating liver failure directly depends on the type of disease and its complexity.
In particularly difficult cases with a severe and dangerous course of the disease, treatment should only be inpatient. In milder forms, the fight against the disease can be carried out at home, under the close supervision of a doctor. Taking medications and vitamins aimed at combating the disease gives good results in our time. By following a course of treatment and a special diet, you can get rid of the disease in a certain period of time.
Interesting to know! The human liver has half a thousand functions. 20 million chemical reactions take place in this small organ per minute.
Diet
In this condition, therapy primarily involves following a diet. It is important to reduce your intake of protein foods and salt. It is also recommended to exclude the consumption of fried, fatty, spicy, smoked foods. Alcoholic drinks are completely excluded.
It is important to maintain a drinking regime - drinking at least two liters of clean water per day.
To prevent the development of pathology, doctors advise: get vaccinated against hepatitis, eat right, do not abuse alcohol, take hepatoprotectors if there is a need for treatment with antibacterial drugs, carefully follow all the rules of personal hygiene, and do not use other people’s hygiene products.
Liver transplant
Transplantation is considered the most effective treatment for failure. Replacing an organ with a healthy one eliminates all the consequences of pathology and prevents the recurrence of the disease. The operation is performed in late stages, when other methods of therapy have practically no effect. Indications for transplantation:
- Oncology.
- Late stages of cirrhosis, hepatosis.
- Severe form of viral hepatitis.
- Cirrhotic cystic fibrosis.
Extensive testing is required before the procedure, after which the patient is placed on a waiting list for a donor liver. In this case, the compatibility of the organ is taken into account. The transplant operation is performed urgently and usually takes no longer than 6 hours.
Reasons for formation
Together with the blood, toxins enter the liver.
Most often, liver failure is formed due to deviations in the balance of narrowing and dilation of liver vessels. These disorders occur due to poisoning of the body with ethyl alcohol or other toxic substances. There are also other reasons that can provoke intoxication of the body and, as a consequence, liver failure:
- Mushrooms: toadstool;
- lines;
- cross
- "Aspirin";
- hepatitis virus of various etiologies;
- staphylococcus;