What is hepatomegaly - how to treat it. Signs of hepatomegaly, what does this diagnosis mean?
Hepatomegaly of the liver is a pathological increase in the size of the liver, most often occurring during poisoning with poisons and toxins of various origins. Scientists do not classify hepatomegaly as an independent disease, but define it as a syndrome indicating the general unsatisfactory condition of the organ and the need for urgent treatment.
Articles on the topic
- Hepatomegaly in children, causes of formation and methods of treating hepatomegaly
Author of the article:
Shabanova Anna Alexandrovna
- Therapist
- Gastroenterologist
- Specialist in RDT (fasting dietary therapy)
Views: 48333
Reading time: 3 min.
Hepatomegaly of the liver is a pathological increase in the size of the liver, most often occurring during poisoning with poisons and toxins of various origins. Scientists do not classify hepatomegaly as an independent disease, but define it as a syndrome indicating the general unsatisfactory condition of the organ and the need for urgent treatment.
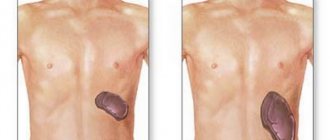
“It is quite difficult to determine a healthy liver by touch, but an enlarged organ can easily be palpated, causing pain in the patient.”
Causes
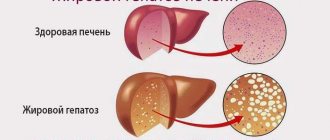
The causes of moderate liver enlargement can be either pathological or completely natural. Signs of small changes in the shape and tissues of the organ are observed when eating too fatty foods, smoked meats and other unhealthy foods. In addition, regular consumption of alcoholic beverages in large quantities leads to an increase in liver volume.
A moderate increase in organ size may also indicate the progression of pathological conditions. Usually the liver enlarges slightly at the initial stage of a particular disease. Most often this syndrome is observed when:
- hepatitis;
- metabolic disorders;
- liver fibrosis;
- cirrhosis;
- hemolytic disease (in newborns);
- parasitic organ damage;
- in the presence of congenital infections, for example, rubella, cytomegalovirus, etc.
Liver enlargement
Dimensions: liver norms by week
The second screening of a pregnant woman's fetus coincides with active growth and development of organs, demonstrating the liver as a semilunar low-echoic area. As the embryo grows, the size and structure change more, so the organ becomes more defined, over time becoming equal in echogenicity to the intestine. Let's look at the sizes by week.
| Term | Length, (mm) | ||
| Longitudinal norm | Vertical norm | Transverse norm | |
| 20 | 32,1 | 18 | 17,7 |
| 21 | 33,3 | 20,2 | 18,1 |
| 22 | 34,9 | 20,4 | 18,3 |
| 23 | 38,9 | 22,3 | 19,9 |
| 24 | 42,2 | 23,2 | 20,6 |
| 25 | 44,4 | 23,9 | 21 |
| 26 | 47,2 | 26 | 23,1 |
| 27 | 47,5 | 26,2 | 23,5 |
| 28 | 47,9 | 26,8 | 24 |
| 29 | 50,5 | 26,4 | 24,9 |
| 30 | 51,2 | 26,9 | 26,6 |
| 31 | 53,6 | 27,5 | 27,1 |
| 32 | 56,8 | 27,8 | 31,5 |
| 33 | 57,4 | 28,8 | 31,7 |
| 34 | 58,3 | 29,1 | 32 |
| 35 | 66,5 | 29,4 | 32,6 |
| 36 | 67 | 30 | 33,3 |
| 37 | 70,8 | 32,8 | 36,8 |
| 38 | 71,2 | 32,8 | 37,1 |
| 39 | 75,3 | 33,7 | 38,5 |
| 40 | 76,3 | 33,5 | 37,5 |
Symptoms
Due to the fact that the liver increases in size slightly, the signs of this condition may be mild or not appear at all. Sometimes people are not aware that they have this syndrome. Usually, such an increase in the size of an organ is discovered by chance - when a person undergoes diagnostics for a completely different reason. When performing an ultrasound, it is possible to identify echo signs indicating that the size of the liver has deviated from the norm.
In some cases, symptoms of moderate enlargement do occur. A person may complain about:
- a feeling of heaviness in the right side of the abdomen slightly below the edge of the costal arch;
- pain in this area when palpated;
- mild nausea;
- feeling of discomfort at the site of liver projection;
- the skin may become icteric;
- general deterioration of health.
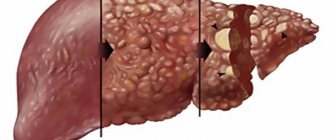
Due to the fact that these symptoms are not pronounced and do not appear often, most people write them off as a common illness or think that they ate something wrong. In fact, when such signs are expressed, it is better to visit a qualified doctor so that he can carry out a diagnosis and identify the cause of this condition. Moderate hepatomegaly is dangerous because without timely treatment it can develop into severe hepatomegaly. In this case, it will still be possible to carry out treatment, but there is a possibility that the healthy tissue of the liver parenchyma will begin to scar, cysts and other pathological formations will form on them (the clinical picture will be complemented by other signs).
Folk remedies
If unpleasant symptoms caused by an enlarged liver appear, before treating the pathology with chemicals, it is recommended to undergo a course of treatment with herbal remedies.
https://youtu.be/t7vLIR3WJT0
A decoction made from a mixture of sage and chicory, widely used in folk medicine, helps improve the condition and restore liver function. Not used for concomitant pathologies of the gallbladder. For the decoction you will need to take equal amounts of chicory root and sage herb, crushed into powder. 1 tablespoon of the mixture is poured into 250 ml of boiling water and allowed to brew. Before use, you are allowed to add 1 tsp. honey
A multi-component composition - sage, chicory, motherwort, peony and dandelion - will help cure hepatomegaly. Plants are crushed and mixed in a 1:1 ratio. Add 1 tbsp to boiling water (200 ml). l. dried raw materials. Leave on low heat for 20 minutes. After this, the broth is infused for 2 hours in a warm place. You need to drink the prepared liquid throughout the day.
Diagnostic measures
There is no way for the patient to identify moderate hepatomegaly on his own, since the signs are not intense, and it is also difficult to visually note an increase in the volume of the organ. To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor studies the patient’s medical history, listens to his complaints, and palpates the abdominal cavity, in particular the hypochondrium area. After the examination, laboratory and instrumental diagnostics are prescribed. It is important not only to confirm the fact of an increase in organ volume, but also to find out the true reason why this happened.
Normal coagulogram values
Diagnostics includes the following procedures:
- blood biochemistry;
- Clinical blood test;
- liver tests;
- immunogram;
- coagulogram;
- tests for tumor markers (if necessary);
- stool analysis;
- ultrasound examination of organs located in the abdominal cavity;
- radiography;
- CT scan.
After receiving all the test results, the doctor describes the most effective treatment regimen.
Stomach
At 16-20 weeks, the fetal stomach is visualized as an anechoic formation of a round or oval shape in the upper abdominal cavity. If the stomach is not filled with amniotic fluid, then we can talk about esophageal atresia (complete absence of lumen).
With a diaphragmatic hernia, the stomach is displaced and also cannot be detected on an ultrasound. Also, amniotic fluid is absent when the central nervous system is damaged in the fetus.
If the fetus swallows blood along with liquid, hyperechoic inclusions are visualized in the stomach. They are also seen in stomach tumors, but they are usually accompanied by other malformations. The size of the organ increases with intestinal obstruction, polyhydramnios, thickening of the walls, and absence of the lesser curvature.
A decrease in the size of the stomach is typical of microgastria, which occurs due to the absence of a bladder or abnormal position of the liver. In 52% of cases, the fetus dies before the 24th week of pregnancy, and the child is born non-viable.
A slit-like stomach is characteristic of underdevelopment in the early stages of pregnancy. This pathology is corrected after the baby is born: a stomach is constructed for the child from part of the small intestine. The operation is extremely complicated, but the anomaly is not an indication for an abortion.
Gastric atresia is characterized by the absence of echoshadow and involves the formation of a film with or without an opening located across the walls of the stomach. If this is an isolated pathology, then in 90% of cases it is eliminated surgically. But usually gastric atresia is combined with fusion of the esophagus, ascites (excessive accumulation of fluid), and underdevelopment of the lungs.
Gastric agenesis involves the complete absence of the organ. This is typical for severe chromosomal abnormalities that cause fetal death during the prenatal period. Ultrasound at week 22 is of great importance in diagnosis. some abnormalities disappear on their own, while others require immediate intervention.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Article rating:
Fetal liver size anomalies prevention Link to main publication
Related publications
- How to recognize the first signs of liver cirrhosis
Therapeutic measures
Moderate hepatomegaly can be eliminated with the help of diet therapy and the prescription of certain medications. Diet is a prerequisite for recovery. It is recommended to eat in small portions 5 times a day. Fatty, salty, spicy and fried foods are excluded from the diet. You should also not consume alcoholic beverages, carbonated drinks, canned food, marinades, fatty meats, etc. The diet includes water-based porridge, vegetables and fruits, heat-treated, lean meats and fish.
Medicinal products include hepatoprotectors, drugs that normalize liver function, vitamin complexes, enzyme agents, and others.
Drugs for the treatment of hepatomegaly
Before treating an enlarged liver, it is necessary to undergo an examination and identify the underlying disease that led to hepatomegaly. This stage is fundamental in the therapeutic course.
Treatment of the underlying disease
If hepatitis B is detected, antiviral therapy is prescribed. A combination of the following drugs is used:
- Interferon alpha-2 has an immunostimulating effect;
- pegylated interferons (in combination with polyethylene glycol) help maintain the required amount of interferon in the blood for 7 days, which increases the effectiveness of treatment and makes taking the drug as suitable as possible;
- nucleosides or substitutes in tablets. The most commonly prescribed drugs are Tenofovir, Lamivudine, Entecavir, Adefovir.
Pegelated interferons along with ribavirin are recommended for detection of hepatitis C. The effectiveness of such treatment is low and is approximately 50%.
Direct-acting drugs have proven themselves better, but only a specialist should prescribe them. The decision about what medications to take for an enlarged liver and what to do to stabilize the condition for fatty hepatosis is made only by the attending physician. The patient is also recommended to switch to a diet and exercise. Changing your diet and proper exercise will help you lose weight and reduce fatty deposits in the liver.
Cardiovascular failure in adults must be treated under the supervision of a cardiologist. He will select complex therapy, taking into account the patient’s condition. In this case, the following groups of drugs can be prescribed:
- beta blockers;
- ACE inhibitors;
- diuretics;
- cardiac glycosides;
- aldosterone antagonists;
- potassium-containing medications.
It is important to know! When treating alcohol intoxication, it is necessary for the patient to recognize the existence of addiction. This is the only way to maintain health and get rid of illness. To prevent the occurrence of cirrhosis, you need to completely abstain from alcohol.
Helminths that infect the liver provoke not only its enlargement, but also cause the development of complications such as hepatitis, cirrhosis and cancer. Antihelminthic therapy is selected after identifying the type of parasites that have settled in the body. The dosage is calculated taking into account the weight, age and general condition of the patient. How to treat an enlarged liver? Medicines used to combat helminthic infestation: “Vormil”, “Azinox”, “Nemozol”, “Helmintox”, “Biltricid”, help get rid of parasites and restore liver function.
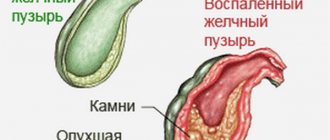
For acute cholecystitis, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used. The first few days a person must follow a strict diet, and then he is transferred to table 5A. Cholecystectomy (removal) is resorted to in case of a serious inflammatory process that threatens complications.
Hepatoprotectors
- Vegetable origin
Essential phospholipids are produced from natural products - soybeans. The resulting components contribute to the natural restoration of liver cells. Preparations obtained from natural raw materials have virtually no undesirable effects; the only contraindication may be individual sensitivity. Popular medications of this type are: “Essentiale Forte”, “Essliver Forte”, “Phosphogliv”, “Rezalute Pro”.
Drugs for liver enlargement, related to plant flavonoids, have a protective effect on the organ, help neutralize free radicals, reduce spasms and enhance the production and outflow of bile. Experts recommend: “Karsil”, “Silimar”, “Hepatofalk”, “Legalon”, “Gepabene”. The natural composition (celandine, milk thistle, turmeric, fume) allows you to avoid many side effects.
- Medicinal origin
Increased symptoms of poisoning and worsening liver failure require the prescription of stronger drugs - amino acid derivatives. Most often in recipes they indicate: “Hepa-Merz”, “Heptral”, “Hepasol Neo”, “Gepasteril”. These products normalize metabolism, help eliminate toxins, restore and support the liver.
Ursodeoxycholic acid, isolated from the bile of the Himalayan bear, allows the bile to be dissolved and removed, leading to a decrease in the death of hepatocytes. This group of hepatoprotectors with immunomodulatory properties includes: Ursohol, Ursolizin, Ursodex, Ursosan. The drugs have contraindications, so before use you must carefully study the instructions. These drugs are not prescribed for liver cirrhosis, liver failure, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, ulcers and gallstones.
Ancillary drugs
The following are used as additional symptomatic therapy:
- enzyme medications that restore the functioning of the pancreas and normalize the process of food digestion (Pepsidil, Festal, Mezim);
- choleretic (“Allohol”, “Holosas”, “Hologon”, “Flamin”);
- glucocorticosteroids (“Prednisolone”, “Dexamethasone”);
- diuretics (“Hypothiazide”, “Lasix”, “Furosemide”), which help remove fluid from the abdominal cavity.
Vitamin therapy
Vitamin A helps restore liver function. It is advisable that it comes from food. It is recommended to drink 125 ml of freshly squeezed carrot juice daily on an empty stomach.
Doctors prescribe vitamin complexes containing vitamin A - “AEvit”, “Retinol”, “Vitrum”.