3839
0
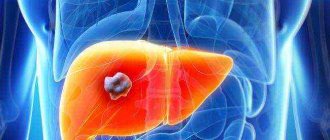
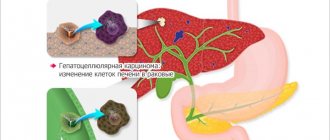
Primary liver cancer (that is, a cancer process that initially began in this organ) is quite rare. It accounts for only 10% of all diagnosed cases of malignant lesions of this gland. The remaining 90% of cases are metastases in the liver, which entered it from another primary cancer site located in other internal organs. The exception is African countries, since these countries have a high incidence of hepatitis, as a result of which the primary tumor is often found in liver cells. In most cases, metastases spread through the blood or lymph from:
- Breasts, that is, the mammary gland (in both men and women);
- Stomach;
- Pancreas;
- Esophagus;
- Lungs and pleura;
- Colon;
- Melanomas (a type of skin cancer).
Most metastatic disease originates from the gastrointestinal tract. This is due to the fact that the gastrointestinal tract is anatomically close to the liver.
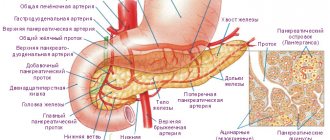
Formation of metastases
Metastases mean cancer cells that can move throughout the body by hematogenous or lymphogenous route. When a certain organ is affected by cancer, its malignant cells are carried to other organs and tissues along with the flow of lymph or blood. After the metastasis attaches to a healthy organ, secondary growth of a malignant neoplasm usually begins on it.
The International Classification of Diseases (ICD 10) assigned this pathology a code - C78.7, which stands for “secondary malignant neoplasm of the liver.” In most cases, breast and pancreatic cancer, as well as lung cancer, are caused by metastasis of pathogenic cells to the liver.
Metastases are formed approximately as follows:
- About 30% of the blood enters the liver through the arteries, 70% of the blood through the portal vein from the intestine.
- Inside the parenchymal organ there are sinusoids (special capillaries), where blood flow slows down and venous blood mixes with arterial blood.
- Next, the mixed blood flow rushes back to the heart, through the inferior vena cava. Thanks to this circulatory system, cancer cells easily penetrate into the liver.
- If the human body is endowed with a strong protective reaction (immunity), cancer cells, as a rule, die or are able to multiply very slowly (sometimes for years).
- But if pathological cells begin to actively divide, a growth factor is produced that can stimulate the formation of new vessels that feed cancerous tumors.
- Thus, a secondary malignant neoplasm develops on a healthy organ or tissue.
Scientists cannot fully establish why pathological cells begin to suddenly multiply, but there are certain factors that provoke the rapid growth of malignant cells:
- decreased immunity;
- patient's age. A young body is more susceptible to metastasis and recurrence of cancer than the body of an elderly person. This is primarily due to the faster metabolism occurring in a young body;
- presence of stage 3 cancer. At this stage of development of a malignant tumor, metastasis is considered an inevitable process;
- formation of a network of branched capillaries near the primary neoplasm.
Metastasis to the liver is observed in more than 30% of patients with cancer of various locations.
The causes of liver metastases are cancers affecting the following organs:
- mammary gland;
- colon;
- stomach;
- lungs.
Sometimes liver metastases form due to cancer of the skin, esophagus, gallbladder, and pancreas. It is extremely rare that the appearance of metastases in a parenchymal organ can be observed as a result of a malignant neoplasm in the prostate or ovaries.
Life expectancy
The following factors influence how long people live with liver metastases:
- What stage is the cancer at?
- The extent of organ damage;
- What is the state of the immune system?
- The effectiveness of treatment methods;
- Presence of chronic diseases;
- The patient's psyche.
According to statistics, the average life expectancy as a result of proper treatment lasts from approximately 6 months to 5 years. If not treated - less than 5 months.
The survival rate for men is much lower than for women. Approximately 13% of men and 17% of women survive to the first year after treatment. About 9% of men and 14% of women survive to 3 years of age. And up to 5 years – 7% of men and 13% of women.
In order to exclude the recurrence of secondary liver cancer, it is necessary to follow all the recommendations of the oncologist: take ultrasound, CT or MRI images, take all the necessary tests every 3-6 months for the first two years, then once every 6-12 months .
Kinds
Modern medicine divides liver metastases into several types, depending on the location, penetration, and the number of malignant cells:
- Unilobar metastases most often affect only the right lobe of the liver.
- Bilobar - cancer cells penetrate immediately into both lobes of the parenchymal organ.
- Single - no more than 2-3 cancerous nodes in the affected organ.
- Multiple - the formation of 5-10 (sometimes more) tumors and nodes occurs.
- Distant - the primary tumor is located far from the liver.
- Lymphogenic - liver damage occurs through lymphatic fluid.
- Implantation - occurs as a result of the transfer of malignant cells into healthy tissue of the body (for example, during surgery).
Any metastases are considered a very dangerous sign, because this indicates that the primary tumor has been developing in the human body for a long time.
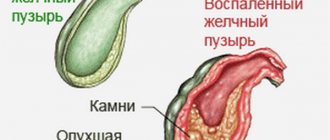
Symptoms
The patient’s further survival depends on timely recognition of signs of liver metastases. Single nodes formed in a parenchymal organ can develop asymptomatically for quite a long time. Most often, a patient consults a doctor when the cancer has reached the last stage of growth and any treatment becomes meaningless. Cancerous tumors are dangerous because when they develop, a person experiences the same symptoms as with most other diseases.
You should immediately contact a specialist if such general symptoms appear as:
- constant weakness and fatigue;
- yellowing of the eyeballs and skin;
- nausea, vomiting;
- darkening of urine, appearance of light-colored feces;
- feeling of heaviness under the right side of the ribs;
- dull pain in the hypochondrium;
- increased liver volume (hepatomegaly);
- the appearance of flatulence;
- ascites (abdominal dropsy);
- appearance of saphenous veins on the abdomen;
- increase in body temperature;
- sudden weight loss, sometimes reaching a state of exhaustion;
- tachycardia;
- the appearance of blood from the veins of the esophagus;
- enlargement of the mammary glands.
The main sign of liver metastases is severe pain under the ribs. This occurs as a result of an increase in the volume of the organ and compression of the cava (lower) or portal vein.
For a certain type of cancer that metastasizes to the liver, there are characteristic symptoms:
- Colon cancer is accompanied by frequent constipation (as a result of intestinal obstruction), high fatigue, weakness, fever, sudden weight loss, and severe pain.
- Skin cancer (melanoma) occurs with loss of appetite, nosebleeds, enlarged liver and spleen, changes in biochemical blood parameters, jaundice and ascites. In addition, during diagnosis, compaction and changes in the structure of the parenchymal organ are determined (the liver becomes tuberous).
- Breast cancer quickly metastasizes to the liver, but the appearance of a clinical picture may not appear for a long time. The presence of metastases in a parenchymal organ is indicated by an increase in liver volume, pain in the epigastric region, increased body temperature, sudden weight loss, and indifference to food.
If you suspect any of the above symptoms, you should immediately visit a specialist, otherwise the cancer will reach the last stage of development and will soon cause the death of the patient.
Diagnostics
If there is cancer of the stomach, skin, mammary glands or intestines, the patient should undergo regular examination of the body, as a result of which it is possible to identify the formation of malignant nodes in a parenchymal organ. To more accurately determine liver metastases, a set of diagnostic measures is carried out:
- Blood biochemistry - allows you to determine elevated levels of transaminase, total protein, the presence of bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase.
- Measurement of tumor markers in blood.
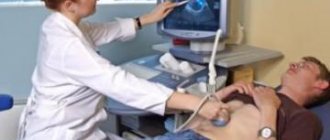
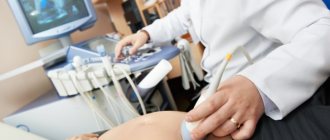
- Ultrasound examination will show the size of the tumor foci, their connection with the vessels, changes in the structure of the liver.
- MRI and CT will help to see the liver layer by layer and determine the location of malignant nodes.
- Organ biopsy - used for histological examination of the tumor. It is performed under local anesthesia and allows you to find out the nature of the tumor.
- Laparoscopy - with its help you can accurately see the presence of metastases, their size and number. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia and allows the surgeon to immediately begin cutting off and resection of malignant tumors.
Diet
To maintain the positive dynamics of the disease, you should follow a daily routine and diet. Eat in small portions, but often. Remove spicy and fried foods from your diet, and do not drink alcohol. Drink more freshly squeezed juices, but with caution. Since if you have stomach or pancreatic cancer, then freshly squeezed juices are contraindicated. In this case, it is better to drink fruit drinks. It is best to exclude meat and fish from food. And replace this with baby food in jars that has been heat-treated. In this case, you will not be able to get poisoned from this product.
Proper nutrition is the key to health, remember this!
Author
Treatment
Treatment methods for liver metastases directly depend on the degree of damage to the organ. The earlier the disease is detected, the higher the chance of saving a person’s life. When stage 4 cancer is detected, it is advisable to select treatment that can prolong the patient’s survival.
Surgical method (resection)
Using surgery, the surgeon cuts off areas of the liver affected by metastases and tumors. Resection is performed only if the number of metastases in the organ does not exceed 4 nodes. If both lobes of the liver are affected, surgery is not performed. The operation is not performed if the tumor develops near blood vessels, or if the patient has cirrhosis of the liver. Relapse of the disease occurs only in 40% of cases after resection.
Oncological diseases are among the most dangerous, because their treatment is a rather complex process. Many of them are diagnosed too late, leading to failure of any kind of therapy. You can find out what a Klatskin tumor is, what the symptoms of this disease are, and what treatment methods are available.
Chemotherapy
Depending on the patient’s age, the nature of the tumor and the stage of the process, the doctor prescribes the patient to take cytostatics (drugs that suppress the division and growth of cancer cells). The specialist selects the selection of the drug, dosage and course of treatment for each patient strictly individually.
The following drugs are used:
- Cisplatin, costs about 841 rubles;
- Cyclophosphamide, costs from 121 rubles;
- 5-fluorouracil, costs from 58 rubles.
Chemotherapy produces a visible effect in only 30% of cancer cases and is accompanied by side effects (infertility, hair loss, exhaustion, leukemia).
Radiation therapy
This type of treatment allows you to get rid of severe pain and destroy tumors, while preserving healthy liver tissue. Radiation therapy is carried out in several ways:
- Powerful focused radiation.
- Selective internal radiation therapy.
- Local hyperthermia (destruction of foci by temperatures above 700ᵒC).
- Using the “cyberknife” method (point impact of photon beams on metastases no more than 1 mm in diameter).
Diet
When metastases are detected in the liver, it is important to eat food that will not overload the diseased liver. The patient is strictly prohibited from: alcoholic and carbonated drinks, salty, spicy, fried foods, sweets, smoked foods, canned food.
You can eat:
- moderate amounts of lean fish or meat;
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- fermented milk products;
- cereals;
- sprouted raw grains;
- vegetable soups;
- freshly squeezed juices.
Some cancer patients prefer to seek help from alternative medicine. Is it possible to treat liver metastases with folk remedies? Many medicinal herbs can have a healing effect on metastases, relieve severe pain, and strengthen the liver. But folk recipes alone cannot cure cancer. Before using any product derived from medicinal plants, you must obtain specialist permission. For the treatment of liver cancer, plants such as:
- hemlock;
- celandine;
- oats;
- potato inflorescences.
The listed plants are used to prepare medicinal tinctures or decoctions for oral administration.
How to prolong life using folk remedies?
Folk remedies can be used as auxiliary measures to combat metastases. However, we must not forget that the plants that are used for this are poisonous, so all proportions must be strictly observed when preparing healing infusions and decoctions. It is important to understand that it is impossible to remove metastases using traditional medicine; these are only additional measures to strengthen the liver.
Take 25 g of hemlock seeds and pour half a liter of vodka into it. The product should stand in a dark place for 40 days. It needs to be shaken from time to time. After this, the medicine should be strained and drunk according to the following scheme: the medicine should be taken half an hour before meals.
The first day - 1 drop, then 2, then 3 and so on until 40 drops accumulate. For the first 2 weeks, the product should be added to 100 g of water. If signs of intoxication appear, the dosage must be reduced.
The next remedy is from potato flowers. Pour half a liter of boiling water into a thermos and put a tablespoon of flowers there, take purple or white. Leave to infuse for 4 hours. Then strain and take 100 g three times a day. The course of treatment is at least a month. The tincture must be stored in a cool place.
Finely chop the fresh celandine herb, put it in a glass jar and fill it with 70% alcohol. Leave for a day, then take 25 g for 5 days, then increase the dose to 50 g and take for another 20 days.
Forecast
The prognosis of the disease depends primarily on the stage of cancer at which treatment was started. In the early stages of metastasis development, properly selected treatment allows the patient to live for at least another 5 years. Without proper therapy, a person dies within a year. Stage 4 cancer cannot be treated; only palliative therapy is possible, helping to improve the patient’s quality of life (support from family and friends, use of painkillers, adherence to a special diet).
Metastases in the liver are a rather serious sign indicating organ cancer. Without timely diagnosis and treatment, the patient will soon die. Prompt and accurate diagnosis, as well as effective treatment, selected taking into account the stage of cancer, can give a sick person several more years of life.
You can also get acquainted with the classification of liver metastases, and how you can get rid of them, depending on the specific type, using the traditional method.
https://youtu.be/ogxJhfkpxMY
Folk remedies
In some cases, desperate patients resort to self-medication - folk remedies, which are a supportive method of treating the disease. The main role in getting rid of the disease is given to drug treatment. Therefore, drinking herbal infusions is not prohibited. But it is best to consult your doctor before using them. Since each treatment method has its own contraindications.
There are a great variety of tinctures that can improve liver performance, which has a positive effect on the effect of medications on the liver.