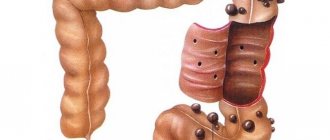
Intestinal diverticulosis is a pathology characterized by the formation of protrusions on the mucous membrane of the digestive structures. Such defects can appear in any part of the organ, however, they are more often detected in the area of the colon. The causes of the disease may be a person’s tendency to constipation, poor diet and hereditary predisposition.
What is diverticulitis
The pathological process develops in the digestive organs, most often affecting the rectum and sigmoid colon. For a number of reasons, diverticula form in the walls - protrusions in the mucous membrane, similar to depressions or hernias. This phenomenon is called diverticulosis. The inflammatory process - diverticulitis - develops when in these cavities:
- processed foods, feces, and worms get stuck;
- bacteria multiply;
- bleeding begins.
If signs of the disease appear, you should consult a gastroenterologist. Diverticulitis is scary because of its complications; the development of:
- fistulas in the intestine, through which its contents enter the vagina, bladder, stomach, causing suppuration and inflammation;
- adhesions that provoke intestinal obstruction;
- peritonitis - inflammation in the abdominal cavity, life-threatening;
- peri-intestinal infiltrate affecting neighboring organs;
- cancerous tumors.
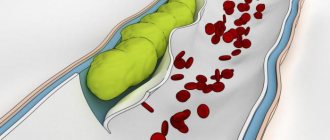
Diverticula in the intestine form in the thin part where the vessels fit. In a normally functioning body, peristalsis is a sequential contraction of the walls, pushing feces to be evacuated from the body. As a result of failures, this process is disrupted:
- solid processed products have difficulty passing through the intestines;
- in thin places the integrity of the mucous membranes is compromised;
- cavities are formed that increase in size - from 5 mm to 10 cm;
- feces fall into the recesses and get stuck, causing the proliferation of microbes;
- inflammation begins with ulcers, erosions, bleeding.
Laxatives
One of the symptoms of intestinal diverticulum is constipation. Boiled beets are used as a natural laxative. Boiled beets are used as a salad with the addition of olive oil. To loosen stools, decoctions of dried fruits are used.
Treatment of diverticulitis with folk remedies becomes an addition to the main therapy. It is not recommended to treat diverticulosis on your own to avoid exacerbation. A dangerous complication is rupture of the diverticulum.
We recommend: First symptoms of cecal cancer and diagnostic features
Causes
The development of the pathological process is caused by diseases of the colon. Diverticulitis is triggered by external factors. These include:
- hereditary predisposition - intestinal diverticulum is transmitted from parents to the newborn as a structural feature of the gastrointestinal tract;
- overweight;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- impaired blood circulation in the intestinal vessels;
- bowel problems - frequent constipation that occurs when eating foods low in fiber;
- age after 60 years – muscle tone decreases, peristalsis worsens, immunity weakens.
Even if infectious intestinal diseases are cured, bacteria continue to multiply in diverticula covered with ulcers. Diverticulitis in the recesses of the walls of the colon develops as a result of:
- atherosclerosis of intestinal vessels;
- bloating;
- flatulence;
- chronic intestinal infections;
- spastic, ulcerative, ischemic colitis;
- reduction of local immunity;
- infectious enterocolitis;
- disturbances of intestinal microflora - dysbacteriosis;
- helminth infestations - worms, spreading in the body, enter the cavities and remain in them.
Symptoms of intestinal diverticulitis
The inflammatory process does not have any special signs. The acute development of diverticulitis resembles in symptoms an ectopic pregnancy, an attack of renal colic, or appendicitis. If, in addition to signs of the disease, there is an increase in temperature, an urgent visit to a doctor is necessary to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe treatment. Characteristic symptoms of diverticulitis include pain:
- localized in the lower abdomen;
- often felt on the left;
- has a monotonous, non-passing character;
- worsens when coughing, pressing on the site of inflammation, physical activity;
- does not subside after defecation.
Diverticulitis has its own characteristics: stool disorder. There is an alternation of diarrhea and constipation:
- spasm in the affected area causes a narrowing of the intestinal lumen, causing stool retention;
- due to disruption of the absorption process, a lot of water accumulates in the intestine;
- when relaxing, diarrhea begins - liquid feces come out intensively.
Diverticulitis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- blood in the stool - comes from ulcers, erosions, is observed after defecation, with heavy bleeding marks appear on the underwear;
- increase in temperature - causes activation of the body's defenses to counteract inflammation;
- signs of intoxication - lethargy, weakness, sweating, loss of appetite, vomiting, headache;
- hard belly - tension of the abdominal muscles to protect the affected area from external influences, such as pressure.
Diverticulitis in children
In childhood, inflammatory processes of the mucous membranes of the large intestine rarely occur. The main cause of diverticulitis is a genetic predisposition that causes the abnormal development of fetal organs inside the womb - a congenital anatomical defect. The disease in children is provoked by:
- helminthic infestations;
- impaired intestinal motility;
- dry food;
- rare consumption of foods with fiber;
- limited mobility;
- infectious intestinal pathologies.
The inflammatory process of the mucous membranes in a child is characterized by rapid development. The following symptoms of diverticulitis are observed:
- weakness;
- nausea;
- lethargy;
- flatulence;
- vomit;
- monotonous pain in the left lower abdomen;
- lack of appetite;
- the presence of mucus and blood in the stool;
- bowel dysfunction - alternating diarrhea with constipation;
- elevated temperature.
Diagnostics
The task of a gastroenterologist, to whom a patient has approached with symptoms of an inflammatory process in the abdomen, is to distinguish diseases with similar symptoms from diverticulitis. Diagnosis begins with a conversation during which the doctor:
- finds out when and how the disease began;
- establishes the nature of the stool - the presence of constipation, diarrhea;
- clarifies the features of painful manifestations;
- asks about nutrition principles;
- reveals the presence of chronic inflammation in the organs of the digestive system.
Diverticulitis is distinguished by the next stage of diagnosis after collecting anamnesis - examination of the patient. Doctor:
- Performs palpation - feels the abdomen for the presence of spasmodic, compacted areas, round formations. When pressing on the area of diverticulitis, the pain increases, which the patient reports to the doctor.
- They are painfully asked to lie on their side. If this is the side on which there is no complication, then the pain will intensify as a result of the tension of the intestines on the inflamed area as it sags on the ligaments.
The exact diagnosis - diverticulitis - is determined as a result of laboratory and instrumental studies. The gastroenterologist prescribes:
- a general blood test showing the presence of inflammation;
- bacteriological examination of stool confirming colon dysfunction;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, revealing thickening of the walls, the presence of protrusion, fluid accumulation;
- urine test;
- stool occult blood test.
When diagnosing diverticulitis, the following are required:
- colonoscopy - examination of the inner surface of the colon using an electronic optical device - a colonoscope;
- X-ray contrast examination of the intestine with the introduction of a solution of barium sulfate - shows the outline of the inflamed organ in the picture;
- laparoscopy – an endoscopic diagnostic operation using a miniature camera, simultaneous removal of diverticula is possible.
Further management of the patient
An annual doctor's examination and routine outpatient examination are indicated.
After resolution of acute diverticulitis, an examination is necessary to exclude other pathologies of the colon (primarily cancer, detected in 6% of patients with diverticular disease) - colonoscopy is indicated 1 month after resolution of diverticulitis.
After resolution of diverticulitis, careful observation is necessary to exclude its complications (abscess, fistulas, intestinal stenosis): a thorough history taking, if necessary, a plain radiography of the abdominal cavity, irrigoscopy with barium enema, CT scan of the abdominal cavity.
When monitoring a patient with diverticular disease, timely detection of diverticulitis is necessary, the main clinical manifestations of which are abdominal pain and increased body temperature.
Treatment of diverticulosis
The appearance of depressions on the intestinal walls is often asymptomatic. Uncomplicated diverticulosis does not require special treatment. Therapy includes:
- normalization of stool by following a diet rich in plant fiber;
- healthy, nutritious nutrition;
- ban on cleansing enemas;
- refusal of uncontrolled use of laxatives;
- performing regular physical activity that promotes normal intestinal motility and strengthens the abdominal muscles.
Articles on the topic
- Ginger for hypertension - how it affects the body, benefits and harms, how to take it correctly
- Duodenitis - symptoms and treatment with medications, folk remedies and proper nutrition
- Teraflex - instructions for use and analogues of the drug
When diverticulosis becomes complicated, the cavities are blocked, symptoms of intoxication appear, bloody stool appears, and the temperature rises. An inflammatory process develops - diverticulitis, which requires a serious approach, and in severe cases, hospitalization. The treatment regimen includes:
- dietary nutrition;
- compliance with the drinking regime to prevent the formation of hard feces;
- eradication of bad habits - smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages;
- inadmissibility of restraining the urge to go to the toilet.
Conservative treatment for diverticulitis includes the following technique:
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs;
- the use of drugs that alleviate the symptoms of the disease;
- the use of natural laxatives – prunes, herbal infusions;
- performing special gymnastics exercises;
- practice of complex exercise therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- use of traditional medicine recipes;
- in difficult cases, surgical intervention is prescribed.
Drug treatment
The therapeutic regimen for counteracting diverticulitis involves the use of medications. Medicines stop the inflammatory process and eliminate the symptoms of the disease. Antibiotics for diverticulitis are a mandatory component of the course of therapy. Broad-spectrum drugs Timentin, Cefoxitin:
- disrupt protein synthesis in bacteria and destroy them;
- relieve inflammation;
- help cleanse the cavities in the intestinal walls from feces and pus.
For drug treatment of diverticulitis, the following is prescribed:
- antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory drug Mesalazine, which reduces the likelihood of relapses;
- antihistamines - Tavegil, Suprastin, which relieve swelling of the intestinal walls;
- laxatives – Normaze, Mukolfak, which facilitate the movement of feces, reducing their pressure on the inflamed area;
- antispasmodics - No-shpa, Meteospasmil, eliminating intestinal spasms, relaxing smooth muscles, relieving pain.
The laxative drug Mukolfak has a plant base. The components in the composition prevent the appearance of dense feces, normalize the functioning of the digestive organs, and regulate bowel movements. The medicine has:
- indications for use – irritable bowel syndrome, constipation, diverticulitis;
- dosage – a package for preparing a solution up to 6 times a day as prescribed by a doctor;
- contraindications – allergies to components, diabetes mellitus, rectal bleeding, disturbances of water and electrolyte metabolism;
- side effects - severe gas formation, a feeling of fullness in the intestines.
The drug Meteospasmil is available in capsules, prevents flatulence, eliminates spasms of smooth muscles. The medicine is characterized by:
- indications – functional disorders of the digestive system, diverticulitis;
- dosage – capsule three times a day;
- contraindications – intolerance to components, age under 14 years;
- side effects - impaired liver function, allergic reactions that disappear after the course of treatment.
Mesalazine tablets have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects. According to the instructions, the medicine is distinguished by:
- indications – diverticulitis, proctitis, ulcerative colitis;
- dosage - determined by the doctor, maximum - 4 g per day;
- contraindications – peptic ulcer, last month of pregnancy, age under two years, sensitivity to components;
- side effects - headache, sleep problems, loss of appetite, nausea, heartburn, skin rashes.
Diet
One of the conditions for recovery from diverticulitis is a change in diet, a diet that prevents constipation. For some patients, at the beginning of treatment, doctors prescribe a three-day fast, replacing food with solutions of electrolytes and glucose. Diet for diverticulitis of the sigmoid colon involves:
- prohibition on eating foods that cause constipation;
- exclusion from the diet of foods that cause fermentation and increased gas formation;
- There should be no fruits or vegetables containing coarse fiber on the table.
For diverticulitis, the following products are prohibited:
- whole milk;
- grape;
- legumes;
- baking;
- products made from yeast dough;
- White bread;
- pomegranate;
- blueberry;
- rice;
- pasta;
- coffee;
- semolina;
- rice;
- fatty fish, meat;
- jelly;
- sausage;
- chocolate;
- a pineapple;
- persimmon;
- carbonated drinks;
- semi-finished products;
- confectionery;
- alcohol;
- strong tea;
- chips;
- radish;
- cabbage;
- zucchini;
- turnip;
- radish.
To normalize the process of defecation and avoid constipation, it is necessary to maintain a water regime - drink more than two liters of water per day. The menu for diverticulitis includes:
- baked vegetables, fruits;
- dishes made from buckwheat and wheat;
- fermented milk products – kefir, yogurt, cottage cheese;
- fruit and vegetable juices without sugar;
- low-fat meat broth;
- vegetable soups;
- vegetable oil.
The diet of patients with diverticulitis requires foods rich in fiber:
- bran bread;
- sweet berries;
- avocado;
- pears;
- peaches;
- seaweed;
- flax-seed;
- muesli;
- flakes;
- prunes;
- dried apricots;
- nuts;
- carrot;
- spinach;
- plantain seeds;
- oatmeal;
- milk soup;
- steam omelette;
- boiled lean fish, meat;
- pumpkin;
- tea with milk;
- baked apples;
- rosehip infusion;
- jelly.
Surgery
If conservative treatment of diverticulitis is successful, a planned operation is performed after three months to exclude relapses. Emergency surgery is performed when there is a threat to life. Indications for:
- heavy bleeding;
- diverticulum suppuration;
- danger of tissue rupture;
- presence of infiltrate;
- the appearance of fistulas;
- intestinal obstruction;
- frequent exacerbations of diverticulitis;
- peritonitis when a fistula ruptures into the abdominal cavity;
- danger of degeneration into a cancerous tumor.
If emergency surgery has almost no contraindications, then they exist for planned operations. These include acute infectious and inflammatory pathologies, severe diseases of the kidneys, liver, lungs, heart, and old age. Operations are unacceptable during pregnancy or during exacerbation of chronic diseases. The appearance of diverticulitis is treated by primary resection:
- remove the affected part of the intestine;
- an anastomosis is performed - healthy parts of the organ are connected to each other for uninterrupted functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- The operation is performed for minor inflammation.
In difficult cases, resection and colonostomy are used to treat diverticulitis. During surgery:
- remove the damaged part of the intestine;
- the proximal end close to the stomach is brought out onto the anterior wall of the abdomen, forming an artificial anus - feces are released into disposable bags - a colonostomy is performed;
- after the inflammation has subsided, the second stage of the operation is performed;
- connect healthy parts of the intestine;
- restore natural defecation through the anus.
Folk remedies
The use of medicines based on plants and natural ingredients is agreed with a doctor. Traditional medicine recipes are becoming part of conservative therapy for diverticulitis. Doctors support the use of:
- A decoction of medicinal fume, which is drunk three times a day, 100 ml. The product relieves pain, spasms, heals ulcers, and improves intestinal motility.
- Bran - up to 40 grams per day, filled with kefir - counteracts constipation.
For diverititiculitis, it is useful to drink a decoction from a collection of herbs. The product eliminates inflammation, flatulence, and relieves spasms. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over a spoonful of the mixture and leave for two hours. Drink half a glass in the morning and evening. The composition includes equal parts:
- stinging nettle leaves;
- dill seeds;
- chamomile flowers;
- rose hips;
- motherwort.
It is easy to cope with flatulence with the help of a decoction of carrot or dill seeds, which are infused for 16 hours, drink 60 ml three times a day. Oatmeal jelly made from flakes and kefir has an excellent healing effect. It helps with diverticulitis:
- normalize intestinal microflora;
- increase muscle tone;
- prevent constipation;
- clear diverticula;
- eliminate bloating;
- normalize stool.
Drug therapy
Patients who are looking for a prescription for how to treat diverticulosis should first make an appointment with a gastroenterologist. The success of therapy largely depends on the accuracy of the diagnosis, and the treatment regimen is drawn up taking into account the nature of the disease. For example, in case of an uncomplicated disease that occurs in a chronic form, one of the main points of the treatment program is diet. The diet includes foods with a high content of indigestible fiber.
Eating such food prevents the progression of the disease and prevents the development of complications. Plant fiber includes pectin, cellulose, polysaccharides, lignin, etc. The main beneficial property of these components is the binding of water inside the intestinal tubes, which leads to increased formation of chyme and a decrease in internal pressure, and this prevents fecal stagnation.
In addition, dietary fiber forms a favorable platform for the placement, growth and activity of beneficial microorganisms (bacteria), which has a positive effect on increasing the body’s immune defense. Beneficial bacteria also actively suppress pathogenic microflora, preventing the development of complications of diverticulosis.
During the diet, it is recommended to reduce consumption of:
- pasta;
- white bread;
- red wine;
- chocolate;
- porridges made from semolina and rice;
- jelly;
- strong tea.
When the disease is characterized by a sluggish, uncomplicated nature, it is enough to adhere to a diet. If the presence of an inflammatory process is confirmed during a diagnostic examination, the gastroenterologist additionally prescribes medications:
- antibiotics (Alfa Normix, Rifaximin), drugs based on 5-aminosalicylic or butyric acid (Mesalazine, Sulfasalazine);
- enzymes that improve the digestion process (Mezim forte, Pancreatin, Penzital);
- peristalsis enhancers (Pasazhix, Metoclopramide, Vasopressin, Aceclidine);
- antispasmodic medications (No-Shpa, Drotaverine);
- laxatives (Guttalax);
- probiotics and prebiotics (Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Probiz, Normaze, Duphalac).
If the disease constantly worsens and conservative therapy does not bring the desired result, there is a risk of perforation (perforation) of the wall, so the doctor prescribes a surgical operation during which the section of the intestinal lining that has undergone a pathological change is removed.
Prognosis and prevention
With timely treatment, diverticulitis does not cause complications. A favorable outcome of the situation is observed. The patient’s life expectancy depends on his desire to comply with all the doctor’s instructions and the nature of the development of the disease. The appearance of an unpleasant disease can be easily avoided if you take preventive measures:
- play sports - Pilates, yoga;
- eat foods with fiber to prevent constipation;
- observe drinking regime;
- do not eat preservatives, fried, smoked, spicy foods;
- avoid trauma to the colon during medical procedures, research, and anal sex.
Measures to prevent diverticulitis include:
- quitting smoking and drinking alcohol;
- adherence to daily routine;
- walks in the open air;
- maintaining immunity by hardening, taking medications;
- Seeing a doctor if signs of illness appear;
- taking fiber supplements;
- weight loss;
- increasing local immunity by taking fermented milk products and vitamins;
- eating a spoonful of flaxseed oil or olive oil on an empty stomach in the morning;
- timely treatment of all intestinal diseases;
- restoration of microflora balance.
Therapy using folk remedies
Therapy for diverticulosis of the colon and sigmoid colon involves the regular use of home medications.
Traditional healers recommend using products prepared on the basis of olive and linseed oils.
Olive oil is added to various dishes (salads, cereals). Flaxseed oil is drunk in the evening before bed, one tablespoon at a time. You can also use the following recipes:
- Decoction of slippery elm. The product has an enveloping effect and effectively eliminates heartburn. To prepare, take a teaspoon of crushed bark, add two cups of boiling water, and heat in a water bath for 20 minutes.
- Infusion of slippery elm. The tree bark is ground in a coffee grinder. Fine powder (1 teaspoon) is diluted with a small amount of cold water until a thick, homogeneous mass is obtained, poured with boiling water (1 glass), honey is added, and drunk warm before meals. The drug helps get rid of constipation.
- Wheat bran. Take 1-2 spoons throughout the day with water.
- Thorn tincture. Alcohol tinctures from medicinal plants, fruits and berries, if taken in small quantities, bring significant relief. These drinks relax the intestinal walls, which helps reduce internal pressure. Sloe fruits are poured into a glass container to the top, poured with alcohol so that the berries are covered, the container is tightly closed, and left to infuse for four months. After this period, the tincture is filtered, 100 g of sugar and 2 sticks of dry cloves are added for each liter. When the sugar has dissolved, the tincture is bottled, sealed tightly and infused for another six months. Take a tablespoon half an hour before meals, twice a day.
- Herbal collection. Rose hips, dill seeds, nettle and motherwort greens, chamomile flowers are crushed and mixed in equal parts. A tablespoon of the mixture is poured into a thermos, a glass of boiling water is added, and left for 1.5 hours. Drink half a glass of infusion after meals. The duration of the course is one month.
- Elderberry infusion. A tablespoon of berries is poured with boiled water (1 glass), infused, and consumed once every day in full.
- Herbal collection. Nettle greens, mistletoe, peony roots (100 g each) are mixed. The raw material in the amount of two tablespoons is poured into a liter of water, brought to a boil (do not boil), removed from the heat, infused, filtered, and drunk a glass twice a day an hour after meals. The duration of the course is 14 days. The composition is also used to give enemas for constipation.
- Fresh apples. Traditional healers advise eating two apples daily. This fruit is rich in pectin, which generally improves intestinal function.
- Chamomile infusion enemas. This remedy significantly reduces pressure on the intestinal walls. An infusion of 1.5-2 liters, previously brewed and cooled to a temperature of 37°C, is injected into the anus. Procedures are carried out once a week, gradually reducing their number to once a month. It is also recommended to drink chamomile infusion throughout the day.
Treatment with folk remedies is an effective program with which you can achieve high therapeutic results. However, patients should be aware that eliminating the manifestations of the disease is only possible with an integrated approach to treatment. This means that traditional medicine must be used in conjunction with pharmaceutical drugs prescribed by the attending physician. Compliance with other rules prescribed by the therapy program (diet, exercise, giving up bad habits) is also required.
Today, hundreds of people are susceptible to gastrointestinal diseases. A common case is intestinal diverticulosis. The disease involves the formation of diverticula (bag-like protrusions) in multiple quantities, usually provoked by weakness of the connective tissue, and is inflammatory in nature. The most common location is colonic diverticulosis, the rarest is the duodenum.
The disease can be congenital or acquired. The first option is rare and involves the formation of growths already at a young age. In the second case, it occurs much later and is provoked by a lack of plant fiber in the body or increased pressure in the intestines.
At risk are people of both sexes over the age of forty. Especially those suffering from obesity, flatulence, stomach infections or using laxatives. With age, the likelihood of developing diverticulosis increases.