Interesting facts about celiac disease
- this disease has been known for several millennia: exactly since people began to grow wheat, rye and other grains
- Celiac disease is much more common in women and is practically not observed in Chinese, Japanese and Africans. Most likely, it’s either a special genetic status or nutritional characteristics
- even now in some regions of Russia doctors are prohibited from diagnosing “celiac disease”, since this pathology is not recognized
- some foreign scientists consider celiac disease as a precancerous condition that increases the risk of developing small intestinal lymphoma, intestinal bleeding, and cancer of various parts of the digestive system
- If parents have celiac disease, the risk of having the same child is one in ten.
How is celiac disease diagnosed?
The pediatrician makes the primary diagnosis based on a general examination of the child and refers the patient to a gastroenterologist. Suspicions are confirmed after receiving laboratory and instrumental diagnostic answers. Laboratory research methods include genetic tests, biochemical and general blood tests, bacteriological, microscopic and biochemical examination of stool.
Among the instrumental ways to diagnose celiac disease are:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- colonoscopy;
- X-ray of the intestine;
- histological analysis of a biopsy taken from the mucous membrane of the tract.
Causes
So why does gluten intolerance occur? As mentioned above, the exact reasons are not known. But there are assumptions expressed in the form of theories. The most common of them are enzymatic and immunological, with the second being trusted by scientists the most.
- Enzymatic
The small intestine lacks the enzyme responsible for breaking down gluten. This reason is probable, but not fully proven, since by following a diet, the enzymatic function of the intestine is completely restored.
- Immunological
Antibodies to gluten and autoimmune antibodies to intestinal cell structures are detected in the blood. In celiac disease, the number of intraepithelial lymphocytes with other receptors is increased. It is these cells that see gluten as an enemy and damage the intestinal walls.
- Unusual Virus Theory
Studies have shown that 90% of patients with celiac disease have an increased amount of antibodies to a certain type of adenovirus. You shouldn’t believe it if one day your doctor says that celiac disease is caused by an adenovirus. It has nothing in common with a congenital disease: the adenovirus and gluten simply have amazing antigenic similarities.
- Pathoreceptor
believes that the composition of proteins on the surface of the intestine is disrupted, which is why the small intestine is hypersensitive to gluten.
Scientists have come to the conclusion that it is worth combining all the theories into one complex, then the expected picture of the development of gluten intolerance will be obtained: there is no enzyme - gluten is not broken down, accumulates, has a toxic effect on the intestines, which reacts with the help of cells with special receptors. When these cells try to “destroy” gluten, they damage the intestinal epithelium, disrupting the digestion and absorption of food. Adenovirus has been implicated as a possible initiator of the immune response to gluten.
Symptoms
Textbooks distinguish three clinical forms of celiac disease. In fact, its manifestations are much more diverse: the symptoms of celiac disease are disguised as various diseases of the digestive system, hypovitaminosis, dermatological pathologies and many others. That is why the diagnosis of celiac disease is given to a limited number of patients, while the rest are endlessly treated for its manifestations.
On the other hand, there are many clinical cases when all the manifestations of one of the forms of celiac disease are present, even a blood test indicates this. But a biopsy of the small intestine does not confirm the doctors' assumptions.
In 1991, celiac disease was presented in the form of an iceberg: at the top there is a small number of confirmed variants that occur with clear clinical signs. Underwater there is a huge number of those same undiagnosed, “masked” cases. And at the base of the iceberg are people who have a genetic predisposition to celiac disease, but the disease develops only when exposed to provoking factors (stress, decreased immunity, eating a large amount of foods with gluten, and so on).
The earlier and in larger quantities gluten is introduced into food (for example, semolina porridge, beloved by all grandmothers), the faster celiac disease occurs and the more severe it is.
Symptoms in children
“Iceberg” of celiac disease: click to enlarge
The typical form has three prominent symptoms:
- frequent stool (up to 5 times a day or more): there is a lot of it, a mushy consistency, shiny due to the presence of fat, smells bad, can be foamy, of different colors, it is difficult to wash off
- bulging belly: the doctor will say that this is due to rickets in the child, the parents will think that the child is just eating well
- lag in height and weight: especially noticeable in the first two years (in weight), and in height - after 2 years. Insufficient weight gain is alarming precisely after the introduction of complementary foods, and until this moment the child gains weight well and grows and develops normally.
Other symptoms of celiac disease in children are associated with insufficiency of nutrients, vitamins and microelements, so they may be different for each child:
- fatigue, lethargy or, conversely, tearfulness, aggressive behavior, increased irritability
- poor skin and hair condition: dryness, weakness, flaking of the skin, atopic dermatitis in a child
- frequent fractures even with minor trauma - this despite the fact that fractures are actually rare in children, their bones are elastic
- incorrect posture
- hypotension - insufficient muscle tone
- manifestations in the oral cavity: bleeding gums, stomatitis in children, caries, crumbling enamel
- anemia (see iron supplements for anemia)
- the child looks unhappy
- a child with celiac disease is compared to a spider due to the presence of a large belly and thin arms and legs
Subsequently, the functioning of the reproductive system in children is disrupted: girls do not get their periods, boys experience sexual dysfunction.
Symptoms in adults
Symptoms of celiac disease in adults are characterized by atypical and latent forms. The atypical form appears only in the third or fourth decade of a person’s life. It represents one of three symptoms of a typical form and two or three accompanying ones. But in general, extraintestinal manifestations of celiac disease predominate:
- neurological: migraine, depression, etc.
- dermatological: herpetiform or atopic dermatitis
- dental: aphthous stomatitis, atrophic glossitis, enamel hypoplasia
- renal: nephropathy
- articular: arthritis, joint pain of unknown cause
- strange changes in biochemical blood tests: decreased cholesterol, increased alkaline phosphatase, transaminases, albumin
- reproductive: infertility
In clinical studies, 4-8% of women unsuccessfully treated for infertility were diagnosed with celiac disease. All of them managed to become happy mothers after being prescribed a gluten-free diet.
The latent form may not manifest itself at all, only occasionally causing concern with minor intestinal disorders or external manifestations (dermatitis and so on). Celiac disease is detected only during random examination.
Myth No. 3. Celiac disease can be contracted or developed as an adult.
No, it's a genetic disease. It cannot be infected, it cannot appear “suddenly” - people with celiac disease are sick from birth. Therefore, there is no “secondary celiac disease” - only “primary”. But, as in the case of many other genetic pathologies, the severity of the disease varies - and this depends on the degree of activity of the mutant genes and on other individual characteristics of the person.
Typically, celiac disease, like most enzymopathies, manifests itself at the time of introducing into the diet those foods for which there are not enough enzymes to process. That is, during the period of introducing complementary foods, in particular flour products, and therefore at the age of six months or more. Most often, this manifests itself in the form of characteristic gray stools and manifestations of malabsorption syndrome (malabsorption of nutrients) - it’s not for nothing that another name for celiac disease sounds like “intestinal infantilism.”
But there are cases when the correct diagnosis is made only in adulthood. At the same time, the person suffered all his life from a “weak stomach”, suffered from indigestibility of food and swelling, acquired osteoporosis, bad teeth, anemia and many other troubles. All I had to do was switch to a gluten-free diet. Often, without treatment, the symptoms of celiac enteropathy weaken in youth, but by the age of 30-40 they return with renewed vigor.
There are also cases of hidden (“silent”) celiac disease - they are often detected in relatives of people with an official diagnosis. Characteristic changes are revealed in the mucosa of their small intestine, but the intestinal microflora sufficiently compensates for the manifestations of the disease. The person ultimately lives a normal, full and healthy life. But the disease can suddenly become more active after suffering a severe intestinal or respiratory infection.
Complications of gluten intolerance
With a long course of the latent form of celiac disease, the risk of developing serious diseases increases:
- gastrointestinal oncology
- autoimmune thyroiditis, autoimmune hepatitis
- type 1 diabetes mellitus
- rheumatoid arthritis
- myasthenia gravis, scleroderma
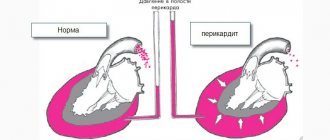
- recurrent pericarditis and others.
Diagnostics
Most often, celiac disease is detected when the whole body is diagnosed for one of the diseases listed above. Targeted diagnosis of celiac disease consists of three stages.
- Stage 1 – immunological blood tests. The level of antigliadin antibodies, the presence of autoimmune antibodies to reticulin, tissue transaglutaminase, and endomysium are determined.
- Stage 2 - if immunological tests are positive, a biopsy of the mucous membrane of the small intestine is performed, and the condition of its villi, the presence of inflammation and lymphocyte cells with altered receptors (discussed above) are determined. The second stage is the most important for making an accurate diagnosis.
- Stage 3 – prescribing a gluten-free diet and monitoring the patient for six months. If there is an improvement in the general condition and a reverse development of the symptoms of the disease, the diagnosis of celiac disease is made definitively.
The third stage of diagnosis is carried out with positive immunological tests and questionable and even negative biopsy results. If after six months the patient’s condition improves, a diagnosis of celiac disease is made. This form of celiac disease is called potential.
A year later, a repeat immunological examination is prescribed. It should reveal positive dynamics. And after one and a half to two years they do a second biopsy: the villi of the small intestine should be completely restored during this time.
What is celiac disease and what are the causes of its occurrence in children?
Celiac disease in children is a disease whose characteristic symptom is intolerance to gluten (cereal protein), associated with thinning of the mucous membrane of the small intestine. In medical terminology, celiac disease goes by several names - celiac enteropathy, Guy-Herter-Heubner disease, non-tropical sprue.
The small intestine digests food, after which beneficial nutrients enter the body. Gliadin, contained in cereal protein, activates the immune system, resulting in inflammation and atrophy of intestinal tissue. The disease is incurable, but completely eliminating gluten will prevent it from developing and completely restoring the mucous membrane.
Celiac disease should not be confused with an allergic reaction to wheat. Completely different principles apply here: allergies lead to skin rashes due to the immune system’s reaction to an allergen, and with celiac disease, the human body cannot absorb the protein of cereals.
The main cause of celiac disease in children is heredity. There are categories of children who are more susceptible to this disorder than others; they suffer:
- diabetes mellitus type 1 (see also: first signs of diabetes mellitus in children and features of treatment of the disease);
- Down syndrome or Shereshevsky syndrome;
- autoimmune diseases of the thyroid gland;
- Addison's disease;
- rheumatoid arthritis (more details in the article: features of rheumatoid arthritis in children).
Differential diagnosis
Doctors are usually in no hurry to diagnose celiac disease and especially to prescribe a procedure such as an intestinal biopsy, performed under anesthesia. Celiac disease is distinguished from food allergies, immunodeficiencies, intestinal infections and other non-hereditary intestinal diseases.
Celiac disease can be distinguished from these pathologies by the absence of mucus in the stool and blood in the stool, the good effect of a gluten-free diet, and a positive immunological test for the above antibodies.
Treatment
Lifelong consumption of gluten-free foods (list) is the only effective salvation. A diet for celiac disease involves excluding bread, pasta, confectionery, some cereals (oatmeal, semolina, pearl barley), sauces, store-bought cutlets, cheap sausages, and sausages. Hidden gluten can be contained in mayonnaise, ketchup, cheese curds, jarred yoghurts and curds, ice cream, canned food, coffee, cocoa, kvass, beer, dyes, and malt extract.
It is critical that 100 grams of product contain more than 1 milligram of gluten.
What then can you eat?
- legumes
- eggs, natural dairy products
- vegetables fruits
- buckwheat, corn, millet
- meat fish
- sweets - chocolate, marmalade
Children under 1 year of age are prescribed mixtures based on casein hydrolyzate or soy (see the list in the article Milk allergy in children). Special gluten-free cereals are sold for complementary feeding.
After the diagnosis is made, symptomatic therapy is carried out:
- Correction of intestinal microflora: intestinal antiseptics (Enterofuril), probiotics (Bifiform, Linex, Actimel, see list of probiotics), prebiotics (Hilak Forte)
- Treatment of bloating: Espumisan, Plantex (see the list in the article on colic in infants)
- Improved digestion: pancreatic enzymes (Creon, Pancreatin)
- Treatment of diarrhea: decoction of oak bark, Smecta, Imodium
- Treatment of malnutrition: nutritional correction, increasing calorie intake
- Therapy for hypovitaminosis: multivitamins orally; in severe cases, nicotinic acid, vitamins A, B, E, D, K are administered intravenously
- Treatment of autoimmune diseases: glucocorticosteroids
- Correction of water and electrolyte balance: Panangin, calcium gluconate
- Elimination of protein deficiency: mixtures of amino acids, albumin.
At the same time, the patient is treated and observed for concomitant diseases (for example, diabetes mellitus and others).
Attention! You cannot use those medications (tablets and pills) that contain gluten in the shell (for example, Complivit, Mezim Forte, Festal, etc., a list of medications containing gluten). Some liquid preparations contain malt (for example, Novo-Passit), which is contraindicated in case of gluten intolerance.
Drug therapy
Patients with celiac disease are prescribed various multivitamin complexes to prevent vitamin deficiencies. Mandatory components of such preparations should be iron and folic acid (vitamin B9), vitamin D.
For diarrhea, the doctor prescribes binders (Lopedium, Loperamide, etc.). If dehydration develops or is at risk of occurring, rehydration solutions are prescribed. Intravenous infusions of drugs that eliminate the deficiency of vitamins and microelements can be performed.
Normalization of the digestive process occurs through the intake of enzyme preparations and probiotics. If necessary, the patient can be prescribed antihistamines and immunomodulatory drugs. Elimination of inflammatory processes is carried out through the use of hormonal drugs (Prednisolone).
When prescribing tablet medications, it is necessary to take into account that many of them contain starch, which may contain gluten. Therefore, all medications are selected exclusively by a doctor and used under his careful supervision.
Patients with concomitant disorders of the endocrine, digestive or cardiovascular systems undergo additional examination by an endocrinologist, gastroenterologist or cardiologist. The patient is registered at the dispensary and is under the careful supervision of highly specialized specialists throughout the entire period of treatment.
Celiac disease is not a death sentence
Many children are given a disability when diagnosed with celiac disease. But in fact, with strict adherence to the diet, the prognosis is extremely favorable. Within a couple of weeks, the intestinal symptoms of celiac disease disappear, and during the first two months, the vitamin-mineral, water-electrolyte, and protein balance is restored.
Over the course of a year, children catch up with their peers in weight, height and development. However, the diet must be strictly followed for life, otherwise there is a high risk of the return of all pathological phenomena and the possibility of developing gastrointestinal cancer.
Author:
Selezneva Valentina Anatolyevna physician-therapist
Forecast
To date, it is not possible to completely cure celiac disease, so the only option is to follow a special diet. If it is neglected, the risk of death increases.
Compliance with all the doctor’s recommendations gives hope for a complete recovery of the body. This may take from 3 months to six months. In this case, the patient must undergo preventive examinations by a gastroenterologist once every six months. Patients who strictly follow all the recommendations of their doctor have every chance of leading a full life and avoid the adverse consequences of the disease.
Prolonged course of celiac disease without proper treatment has a less optimistic prognosis. In this case, the disease may be complicated by oncology, characterized by a malignant course.
(Visited 200 times, 1 visits today)