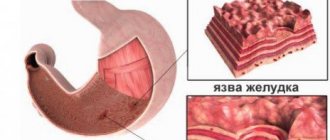
Extirpation of the rectum is the removal of it completely from the human body. Used in the treatment of colorectal cancer. The operation is considered technically difficult due to the topography of the rectum, as it is located close to the walls of the pelvis and the fascia of the sacrum. In addition, it is adjacent to the bladder, large blood vessels and even the ureters, in men with the prostate, in women with the uterus, so when amputating the rectum there is always a risk of damage to them. This is especially true for obesity and a narrow pelvis. Surgery is used only if there is no result from other treatment methods.
Indications for surgery
Extirpation of the rectum is performed:
- in advanced cases of colorectal cancer;
- with tissue necrosis;
- with non-reducible areas of the prolapsed rectum.
The choice of type of operation is determined by the distance of the tumor from the anus. If it does not exceed 6-7 cm, BPE (abdominoperineal extirpation of the rectum) is used. It is also called the Quenu-Miles operation.
If the tumor is located higher (but not higher than 10 cm), this makes it possible to perform sphincter-sparing surgery - BPE with sigma reduction.
Well, if the tumor is 10-12 cm above the anus, another type of operation is performed with preservation of the sphincter (sphincter) - anterior and lower resection, Hartmann's operation, etc.
In what cases is resection indicated?
The most common indications for rectal removal are:
cancer in advanced cases; tissue necrosis; prolapse of the intestine, which cannot be reduced.
Rectal resection is a slightly more complex operation than, for example, colon surgery. This is due to the peculiarities of the location of this part of the intestine. The rectum is tightly adjacent to the pelvic walls and the lower part of the spinal column.
In close proximity to it there are genital organs, ureters, large arteries, and during the operation there is some risk of damage to them. It is larger for patients with significant excess weight and for those who have a naturally narrow pelvis.
In addition, due to the complexity of rectal resection, there is some likelihood that the tumor will grow again.
Hartmann's operation
With this type of intervention, an incision is made in the abdominal cavity along the anterior wall below the middle. The sigmoid and upper parts of the rectum are isolated. The rectum is cut below the tumor. The stump is sutured. The affected area of the intestine is cut off and a stoma is placed in the left iliac region.
But more often than others, abdominal-perineal extirpation of the rectum is used, in 50-60% of all extirpations performed.
It is performed using a two-team method. Indications for WPT:
- rectal cancer localized up to 6 cm from the anus;
- expanded and large tumors involving perirectal tissue;
- cancer recurrence after sphincter-sparing surgery.
In this case, the level of the tumor does not play a role. The only contraindication is decompensation of the heart and liver.
Progress of surgery for rectal extirpation
The affected area is excised to the border of healthy tissue. Perirectal tissue, regional lymph nodes and some healthy tissue are also removed from the intestine. This is done to reduce tumor recurrence. If the tumor is large, the sphincter must be removed. To empty the intestines, an artificial outlet for feces is formed - a stoma. It is attached to a colostomy bag.
Extirpation of the rectum is the operation of choice when deciding whether to preserve the sphincter or remove it, because, accordingly, there are only two types of operations:
- Sphincter-preserving methods include anterior and inferior resection and transanal excision.
- With removal of the sphincter - abdominoperineal extirpation of the rectum (BPE), where a stoma is created instead of the sphincter; pelvic exenteration - removal of the bladder and genitals from the intestine if they are affected.
Contraindications to the procedure
Enemas are not given if the proposed operation does not exclude or is performed for:
- gastrointestinal bleeding;
- internal purulent complications;
- exacerbation of ulcerative and inflammatory diseases of the stomach or intestines;
- suspicion of the disintegration of a malignant tumor;
- cracks and prolapse of the rectum;
- intestinal rupture;
- thromboembolism of mesenteric vessels;
- repeated surgical intervention (for the first - in the last 5 days).
Important! The question of postponing the operation and enema to a later date is decided at elevated temperatures, menstruation in women, against the background of the patient developing general weakness of unknown origin.
Other methods of bowel cleansing before surgery
To cleanse the large and small intestines before a planned operation, the doctor prescribes effective laxatives instead of enemas. They are recommended to be taken at home before hospitalization.
- Rectal suppositories - with bisacodyl, glycerin. They, irritating the nerve endings of the rectal canal, stimulate peristalsis. Stool appears after 30-60 minutes. Bisacodyl is less damaging to the mucous membrane. Recommended once a day.
- Microlax - administered as a microenema several hours before surgery.
- Tablet drugs (Senade, Bisacodyl) are prescribed 2 tablets per day for regular bowel movements.
- Powders with macrogol (Relaxan, Tranzipeg) - retain water, increase volume and soften stool, prescribed in the morning and evening before surgery. A good effect is produced by drinking a solution of magnesia (10-30 g).
- Duphalac - a product with lactulose, has an advantage over others - it does not disturb the intestinal bacterial flora.
It is impossible to cleanse the intestines before surgery without the advice of a doctor. The presence of pathology and certain indications for intervention suggest features for a particular case. Unreasonable enema can cause harm.
Bibliography
- Shubin V.N. Pre- and postoperative period. Kazan. 1965
- Mukhina S.A., Tarnovskaya I.I. Theoretical foundations of nursing: A textbook in 2 parts. Part 2. Medicine. 1998
- Kuznetsova V.M. Nursing in surgery. Rostov-on-Don. Phoenix. 2000
- Samoilenko V.V., Bunina M.V., Golovenko E.N. Preoperative period. Publishing house GEOTAR-Media. 2009
Anterior resection
During this manipulation, only part of the affected intestine is removed through the abdominal wall. This technique is applicable when the tumor is located at a distance of 10-12 cm from the anus. The method is as follows: the upper part of the rectum and the lower part of the sigmoid are excised, and the remaining edges are sutured to each other. As a result, the intestines are slightly shortened.
Low anterior resection is used for intermediate or low tumor levels. The affected areas of the intestine with the mesentery are removed. The remaining edge of the colic and rectum is sutured. With this operation, the risk of relapse is minimal.
Transanal excision is successful for small, nonaggressive tumors in the inferior ampulla of the rectum. The affected area on the wall is removed and the intestine is sutured.
Abdominoperineal extirpation of the rectum - Quenu-Miles operation. The name is given by 2 mandatory incisions - in the peritoneum and anus through the perineum. With it, the sphincter is replaced with a stoma. It is performed for large tumors using a two-team method. Resection is carried out from both sides at once - through the anterior wall of the abdomen and through the perineum.
Bougienage
The method refers simultaneously to diagnostic and therapeutic procedures performed to eliminate pathologies in the lower part of the anal canal. Reasons for appointment:
- tissue scarring;
- congenital or acquired stenosis (narrowing of the intestinal lumen).
The purpose of the method is to force the expansion of the walls of a hollow organ. Special tools are used for this:
- bougies or dividers;
- Hegar expander.
In some cases, the procedure is performed with a finger. The principle of the method is a gradual expansion of the lumen of the rectum due to a gradual increase in bougie diameter. The procedure can be carried out in several stages, which are selected by the doctor individually for each patient, depending on the complexity of the pathology. Bougie expansion can be carried out on a daily basis or every other day. After the procedure, massage of the stricture area is required. With the gradual progress of the bougie, the risk of rupture of the intestinal wall is reduced.
The method is carried out without pain relief. But in severe cases of stenosis, it is possible to use anesthesia with nitrous oxide or through intravenous infusion of painkillers. The digital expansion method is used when the scars are sufficiently elastic and can be easily stretched. Before the procedure, the gloved finger is lubricated with lidase-based ointment. Then, slowly, with turning movements, it is introduced into the rectum and the lumen is gradually expanded.
The Hegar dilator is used for severe scarring. In addition to the course of stretching, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed. In the absence of positive dynamics, surgical intervention is performed.
Intra-abdominal stage of extirpation
After lower-median laparotomy, the abdominal cavity is examined and revised to determine operability. The table is tilted at an angle of 45 degrees to the left (Trendelenburg position) - this allows you to raise the pelvis above the head end. The small intestine is pushed up and to the right and covered with gauze pads.
The sigma is excised 15 cm above the tumor. A cap or glove is put on the intestinal stump and bandaged. Then the descending (proximal) portion of the sigmoid is sutured to the parietal peritoneum, forming a colostomy (an unnatural anal opening for subsequent removal of feces). The stoma is formed through an oblique incision in the left abdominal wall.
A hand is inserted into the presacral space and the rectum is separated from the sacral fascia.
The hand should be folded like a boat, like a spatula. This is done without sharp objects because the pelvic fascia with veins can easily be damaged, and then bleeding may occur.
Using scissors, the tupferomrectum is separated in front from the wall of the bladder, then in men - from the prostate, in women - from the vagina and uterus. At the desired level of resection, the colon is cut and the stumps are bandaged.
To prevent infection, a cap or sterile rubber glove is put on the stump. The connection is tightly tied with thread.
The lower distal end of the intestine is lowered into the pelvis and the peritoneum is sutured over it. The incision on the abdominal wall is stitched layer by layer.
Standard patient preparation
Research of primary importance includes:
- identifying the patient’s weight and height;
- measurement of working blood pressure;
- taking blood and urine for subsequent tests;
- determination of the patient’s blood group and Rh factor;
- X-ray examination of organs located in the chest (heart, aorta and other great vessels, esophagus and lungs);
- examination of the state of stool.
Weight indicators are necessary to monitor the dynamics of their changes throughout the entire period of preparation for surgery. For example, they can change greatly in the presence of malignant neoplasms. Growth data is needed to determine the level of basal metabolic rate.
X-ray examination is one of the main methods of standard patient preparation
Blood pressure is measured daily and recorded in the patient's medical history. Very often, people suffering from high blood pressure (hypertension) are admitted to the surgical department and therefore, before the scheduled operation, a set of measures is taken to reduce and normalize it. With low blood pressure, patients, on the contrary, take tonics to increase it.
A blood test is another standard procedure performed upon admission of a patient. It helps the doctor determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
If the patient requires a blood or corpuscle transfusion during surgery, the blood type and Rh factor are determined. In addition, blood is taken to establish the Wasserman reaction - a rapid diagnosis of syphilis.
A urine test is necessary to assess the condition of the kidneys, which are especially stressed in severe diseases.
Stool sampling is also always carried out before planned operations on the gastrointestinal tract. Feces are examined for the absence of worm eggs, and in case of helminthic infestation, anthelmintic therapy is carried out. Otherwise, worms can penetrate between the sutures that the doctor placed during the operation, resulting in a high risk of developing inflammation of the peritoneum. This can cause quite serious complications, and in some cases even lead to death.
Responsibilities of a nurse
The state of the psyche and nervous system greatly influences the outcome of surgery. The behavior of medical staff when preparing a patient for surgery can greatly help him or, on the contrary, harm him. During this period, attention and sensitivity to his complaints are very important for the patient. The ward nurse must be very tactful with patients and take all necessary measures to reassure them and instill complete confidence in the successful course and outcome of the surgical intervention.
Along with this, it is the nurse who must carry out medication preparation for the upcoming surgical intervention. Of course, only as prescribed by a doctor. Her responsibilities also include physical preparation of the patient, which is necessary to prevent and eliminate various complications accompanying the postoperative period. A nurse in a surgical department must strictly follow all the rules for patient care, because even the slightest deviation from the established standards can lead to the most tragic consequences.
It is important to make the patient understand that his life is safe, as well as to strengthen confidence in the doctor who will carry out a complex of surgical measures.
Especially for older people, the nurse should perform breathing exercises. It should not only remind of its necessity, but also make it clear to patients that the rehabilitation period will be much easier and simpler if you follow all the recommendations prescribed by the doctor.
Attentive care from medical staff will reassure the patient and help him fight the disease
Perineal stage
The perineal incision begins. First, a circular tissue incision is made around the anus, then the rectum with the remnants of the sigmoid is removed + the tissues surrounding it.
The perineum and anus are tightly sutured. The anus is sutured with silk ligatures.
After this, the rectum is mobilized from below, i.e. in the perineum. The intestinal lumen is sealed - to do this, 3-4 cm are removed from the anus, the skin is cut along an oval, the subcutaneous tissue is cut along with it. The skin edges of the intestine are stitched with additional silk interrupted sutures, which are tied on a napkin moistened with furagin solution. The entire abdominal cavity and pelvis are also washed (2 liters of 0.1% furagin solution).
The laparotomy incision is sutured in layers, leaving space in the corners for the administration of antibiotics. A rubber tube is left in the presacral space for drainage. On day 3, she is connected to a low-power vacuum suction unit in the ward. Suction leads to rapid collapse of the cavity. The drainage tube is removed only after 5-6 days.
The sutures are removed on the 10th day. The appearance of bleeding, increased bleeding or infection requires leaving tampons and a rubber drainage tube. In this case, stitches, even rare ones, are not required.
Reduction operation
Abdominal-anal extirpation of the rectum with reduction of the sigmoid and preservation of the sphincter - laparotomy. It can be done when the tumor is located above 7 cm from the sphincter. At a distance of 5-6 cm from the upper border of the tumor, the intestine is ligated, then the level of the healthy portion of the sigma is determined - this is the reductible intestine. When straightened, it should freely reach the inguinal ligament. Its color and pulsation of blood vessels should not be disturbed.
According to the level of normal blood circulation, black ligatures are placed for identification. If these conditions are not present, a Quenu-Miles operation is performed, in which the mobilized sigma is placed in the small pelvis and the parietal peritoneum is sutured. The abdominal wall wound is covered with a large damp cloth.
Laparoscopic method
BPE today is the only operation of the lower intestinal ampulla justified from the standpoint of oncological radicalism. But it also has disadvantages:
- major postoperative trauma;
- it is difficult to fully separate the abdominal organs from the tissue;
- frequent purulent wound infections.
Therefore, new ways of approaching such operations have been developed. Endosurgeons proposed performing the abdominal stage of BPE laparoscopically. This has several advantages:
- trauma is noticeably reduced;
- complications due to purulent processes are reduced significantly;
- The patient's stay in the department is reduced and rehabilitation is accelerated.
During laparoscopic abdominoperineal rectal extirpation, a certain amount of air is forced into the abdominal cavity. Then only a few small incisions are made in the front wall of the abdomen. Through one of them, a laparoscope with a camera equipped with illumination is inserted. And through other incisions, surgical instruments are inserted.
Slag-free diet - contraindications
This method of strict nutrition has a number of disadvantages that should not be overlooked. Many people feel weak and headaches during the diet because the body does not receive enough carbohydrates. Describing the disadvantages of a slag-free diet, it is worth noting that while following it you will have to constantly suffer from hunger, since the diet is low in calories. Doctors indicate that these disadvantages are the norm, since they signal that the body is cleaning. Contraindications to a slag-free diet include:
- individual intolerance to a large number of permitted products;
- period of pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- postoperative period and after serious illnesses.
What is a stoma
Extirpation of the rectum with the formation of a stoma is a surgically created hole in the anterior wall of the abdomen, to which a colostomy bag is attached. Previously, feces were held back by the sphincter.
This hole is formed from the free end of the intestine. An ostomy can be temporary or permanent.
Temporary is needed only for the period of postoperative regeneration of the rectum. After healing, the stoma is closed again surgically after a few months. The stoma becomes permanent with BPE if the tumor was in the lower ampulla of the rectum.
Types of enemas to prepare for surgery
Most often, cleansing enemas are required in preparation for surgery. They allow you to remove feces and gases from the large intestine. Usually boiled water at room temperature and an Esmarch mug are used. Volume for an adult - 2 liters, for a child - 0.5 (babies under one year old from 50 to 150 ml).
Siphon procedure is a type of purification using a funnel, high-level oscillation and reduction of liquid introduced under pressure with passive release of the contents. Washing is done until clean effluent water is obtained.
Siphon enema is used to completely cleanse the intestines of feces and stones. Used before operations.
Less commonly, for depleted and weakened patients in cases of repeated surgery, therapeutic and nutritional enemas are required. Administration of drugs through the rectum is used under conditions of inability to swallow or damage to the upper parts of the digestive tract. In order to improve absorption through the intestinal wall, a cleansing enema must first be given. The volume is 50–100 ml, the temperature is slightly above the body (40–42 degrees). Rubber syringes, ready-made microenemas, a catheter and Zhanne syringes are used. The method is used for administering local anesthetic drugs before short operations and painful dressings.
Important! Nutrient enemas are given by drip solutions with protein and fat mixtures, ready-made preparations for parenteral infusion. Concentrated glucose provides a weakened patient with energy, proteins help speed up healing in the postoperative period.
What is the extralevator method?
According to the standard method of abdominal-perineal extirpation of the rectum, during the operation, the rectum is isolated along the mesorectal fascia to the levators, and then the intestine is isolated from the levators to the anus.
When a tumor grows into the muscular wall of the intestine, this path most likely leads to perforation of the intestine at the site of the tumor.
Since 2007, a modification of the WPT operation has been used - eBPE, which means extralevator WPT. Instead of a circular anal incision, a cylindrical BPT was proposed. The idea of the operation is that there is no need to “unpack” the colon with a tumor from the levators, but it is better to remove it together with the levators, cutting them off from the place of attachment - this is extralevator abdominoperineal extirpation of the rectum. The patient is on his stomach during this manipulation. With this technique, the risk of intestinal perforation is sharply reduced from 23% to 4%.
Prohibited foods for intestinal cancer
First of all, you need to get rid of bad habits, exclude sweets, spices and spices, sparkling water, coffee and black tea from your diet. Fatty meat and fish, canned and semi-finished products, smoked meats and marinades, sausages, fresh bread and milk are removed from the diet for oncology. It is also necessary to give up those vegetables, fruits and berries that contribute to increased gas formation and the fermentation process.
Note! You should not eat foods that have been stored in the refrigerator for a long time, as you may suffer from stomach or intestinal upset.
Doctors recommend avoiding foods that have been cooked in a frying pan, fast food products, and shelf-stable foods. It is best when your diet includes steamed dishes. Particular attention should be paid to products that contain methylxanthine, as this substance promotes fluid retention in the body, provoking the growth of connective tissue. This substance is found in black tea, chocolate and cocoa, coffee and medications that contain caffeine.
Condition after surgery
Rehabilitation of the body begins even before the patient is taken to the ward, in the intensive care unit. The patient gradually recovers from anesthesia.
The staff makes sure there is no bleeding. Pain and discomfort in the wound area are relieved with analgesics.
On the 2nd day, the doctor allows you to sit up in bed. Staying horizontal for a long time only causes harm.
There is drainage in the wound for several days to drain the collecting transudate. All drugs are administered only by droppers.
Complications after extirpation
The most common occurrences are bleeding, damage to adjacent organs, hernia of the midline of the abdomen, non-healing of sutures, thrombosis, and ischuria. Ischuria is the inability to empty the bladder independently, despite its overcrowding due to trauma to the nerve endings responsible for the functioning of the bladder.
Other complications include:
- suppuration of the suture;
- tumor regrowth;
- infection of the abdominal cavity.
The incidence of adverse consequences of abdominal-perineal extirpation of the rectum is 10-15%.
Refusals from surgery
This phenomenon also occurs on the part of some patients. The origin of fear before surgery is psychological - the patient is ashamed that he will always have a colostomy bag with him. He will not be able to control his bowel movements himself. But we are talking about prolonging life, and the choice is made by the patient himself. The cost of extended rectal extirpation in Moscow ranges from 31 to 70 thousand rubles in various leading clinics. The 5-year survival rate after surgery is 30-40%.
Postoperative period
Recovery after surgery depends on the extent of the intervention, the general condition of the patient, and his compliance with the doctor’s recommendations. In addition to generally accepted measures for a quick recovery, including proper hygiene of the postoperative wound, early activation, the patient’s nutrition is of paramount importance, because the operated intestines will immediately “meet” food.
The nature of nutrition differs in the early stages after the intervention and in the future, the diet gradually expands from more gentle foods to those familiar to the patient. Of course, once and for all you will have to give up marinades, smoking, spicy and heavily seasoned dishes, and carbonated drinks. It is better to exclude coffee, alcohol, fiber.
In the early postoperative period, meals are provided up to eight times a day, in small amounts; food should be warm (not hot or cold), liquid in the first two days; from the third day, special mixtures containing protein, vitamins, and minerals are included in the diet. By the end of the first week, the patient switches to diet No. 1, that is, pureed food.
With a total or subtotal resection of the small intestine, the patient is deprived of a significant part of the digestive system, which digests food, so the rehabilitation period can take 2-3 months. For the first week, the patient is prescribed parenteral nutrition, then for two weeks nutrition is provided using special mixtures, the volume of which is increased to 2 liters.
After about a month, the diet includes meat broth, jelly and compotes, porridge, soufflé made from lean meat or fish. If the food is well tolerated, steamed dishes are gradually added to the menu - meat and fish cutlets, meatballs. Vegetables include potato dishes, carrots, and zucchini; legumes, cabbage, and fresh vegetables should be avoided.
The menu and the list of products allowed for consumption are gradually expanding; they are moving from pureed food to finely chopped food. Rehabilitation after intestinal surgery lasts 1-2 years, this period varies from person to person. It is clear that many delicacies and dishes will have to be abandoned completely, and the diet will no longer be the same as that of most healthy people, but by following all the doctor’s recommendations, the patient will be able to achieve good health and compliance of the diet with the needs of the body.
Tumors are treated by oncologists, and the cost of the operation is covered by the compulsory medical insurance policy. In emergency cases (with intestinal gangrene, acute intestinal obstruction), we are not talking about payment, but about saving lives, so such operations are also free.
On the other hand, there are patients who want to pay for medical care and entrust their health to a specific doctor in a specific clinic. Having paid for treatment, the patient can count on higher quality consumables and equipment, which may simply not be available in a regular public hospital.
The cost of intestinal resection on average starts from 25 thousand rubles, reaching 45-50 thousand or more, depending on the complexity of the procedure and the materials used. Laparoscopic operations cost about 80 thousand rubles, closing a colostomy costs 25-30 thousand. In Moscow, you can undergo a paid resection for 100-200 thousand rubles. The choice is up to the patient, whose ability to pay will determine the final price.
Reviews from patients who have undergone intestinal resection are very different. When a small section of the intestine is removed, health quickly returns to normal, and problems with nutrition usually do not arise. Other patients who were forced to live for many months with a colostomy and significant dietary restrictions report significant psychological discomfort during the rehabilitation period. In general, if you follow all the doctor’s recommendations after a high-quality operation, the result of the treatment does not cause negative reviews, because it eliminated a serious, sometimes life-threatening pathology.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the use of special complexes of drugs that are prescribed to cancer patients. The disadvantage of this method is that the chemistry affects both diseased and healthy cells, causing side effects. Atypical cells are destroyed, the growth of metastases and the tumor itself also decreases, but health suffers noticeably. Although the progression of the tumor is slowing down.
There are 2 types of chemotherapy: adjuvant and neoadjuvant.
In the first case, this is the destruction of the tumor with cytostatic poison, and it is carried out for preventive purposes after surgery. In the second, drugs are prescribed to reduce the size of the tumor before surgery.
Chemotherapy is used as the main treatment if surgery is not possible. The procedure involves intravenous infusion of entire cocktails of drugs that kill atypical cells.
Repairing cracks
The procedure is necessary for the surgical removal of any type of fissures in the anal canal. Prescribed in the absence of a positive result of conservative treatment methods. The objectives of the method are to remove the formed scar, which prevents the proper healing of an open crack . To do this, a fresh incision is made, which reverses the process into the acute phase. The problem is then cured with medication.
The operation should be performed under local or general anesthesia. The technique is selected by the doctor according to the individual characteristics of the patient: the presence of hemorrhoids, individual tolerance to anesthesia, etc. The following are used for the operation:
- scalpel;
- ultrasonic scalpel;
- electrocoagulator;
- laser.
The result does not depend on what instrument the doctor used to perform the operation. The procedure lasts on average 8 minutes. The time may vary depending on the type of anesthesia used. Longer operations are necessary in cases where the patient is diagnosed with hemorrhoids. In this case, resection of the anal fissure includes simultaneous removal of hemorrhoids. Special care promotes wound healing. Full recovery is possible in 3-6 weeks.
Radiation therapy
According to official studies, the relapse rate after surgery ranges from 20 to 50%. To prevent this from happening, another treatment method is used - radiation therapy. X-rays or electron beams, sources of ionizing radiation, are used as treatment.
The essence of the method is that radiation is more harmful to cancer cells than to healthy ones. In atypical cells, mutations that are unfavorable for them occur, leading to their death. The course can last 4-5 weeks. If it turns out to be ineffective, the treatment is completed altogether and no other methods are used.
What can and cannot be included in the menu
The diet helps to cope with the disease more easily and to avoid the occurrence of repeated cancer lesions during treatment. The main goals of the treatment menu include:
- exclusion of an inadequate diet;
- restoration of immunity;
- reduction of side effects when exposed to chemotherapy and radiation therapy;
- does not allow metastasis to neighboring organs;
- reduces pain sensitivity, alleviates the patient's condition.
To do this, you must follow all prescribed recommendations.
Eligible Products
The list of acceptable dishes is selected individually. Allowed foods for bowel cancer include:
- dried or dried white bread;
- one egg - soft-boiled or steamed omelet;
- boiled sea fish, without fat;
- soup in a weak broth, with cereals and vegetables;
- fermented milk products and cottage cheese with minimal fat content;
- it is permissible to add sour cream, butter, cream to ready-made dishes no more than 10 g;
- cereals on water;
- boiled chicken, turkey, rabbit meat, without skin;
- green dill, parsley;
- carrots, beets, potatoes, cauliflower, zucchini;
- a small amount of sweets - marshmallows, marmalade, caramels, jam;
- peeled sweet fruits;
- in the absence of bloating - green beans, green peas;
- still water, weak tea or coffee with milk, compote, jelly, weak rosehip decoction, drink with added juice.
The list of dishes is suitable for making a diagnosis of cecal cancer. For this type of malignant tumor, it is permissible to eat lamb, beef without fat, pasta, yeast-free bread, and vegetable oil.
Unauthorized products
After surgery and long-term treatment, strict adherence to the diet is mandatory. The outcome of the therapy provided and the restoration of weakened organs and systems depend on this. The patient must completely remove the following from their diet:
- meat with fat, strong broth;
- milk;
- products made from wholemeal flour or whole grains;
- garlic, radishes, onions, celery, cilantro, sorrel - have an irritating effect on the intestinal mucous membranes;
- legumes;
- sauces and seasonings - pepper, ketchup, mustard;
- carbonated drinks, beer;
- smoked meats;
- canned foods;
- mushrooms, cabbage;
- synthetic additives – dyes, emulsifiers, sweeteners;
- fried foods;
- peanuts, instant coffee.
The inclusion of whole grain cereals, lean meat, vegetables, and fruits in the diet is allowed in the final stages of chemotherapy treatment. Animal fat is replaced with vegetable oil. Grinded food is replaced with heavily boiled slimy dishes. New products are being introduced gradually. You need to monitor how the digestive system reacts, whether constipation or diarrhea occurs. The absence of disruptions in the functioning of the intestines indicates the restoration of the organ after surgery.
The advantages of a therapeutic diet - a balanced diet helps provide the body with the necessary substances for recovery and has a gentle effect on the intestinal mucosa. Disadvantages include long-term use of approved products.
Example menu
The morning meal can be divided into three meals:
- 200 ml juice or water;
- porridge (oatmeal, rice, millet or buckwheat), half a glass of kefir, herbal tea, nuts, raisins;
- juice, fruit.
For lunch, eat vegetable soup, chicken broth, and vegetable salad. A small amount of liquid is acceptable.
For an afternoon snack, flour products and herbal tea are acceptable.
Dinner – stewed or boiled vegetables, rice porridge, pasta. Before going to bed, drink half a glass of juice.
Fasting should not be allowed; daily consumption of fermented milk products is mandatory. Food should be easily digestible and not linger in the intestines.