Gingivitis, periodontitis - behind these incomprehensible names lies a dangerous disease for teeth associated with inflammation of the gums, which, if left untreated, can lead to tooth loss.
What are the causes of this disease and how to deal with it correctly?
Today, more than half of humanity suffers from inflammation of the gums, and the reasons for this are very different - from poor lifestyle to poor heredity or disruption of the body due to hormonal changes.
In this case, inflammatory processes can differ in the nature of their course and treatment methods. In order to correctly decide on therapy and know what to do, you should familiarize yourself with all the possible nuances.
Causes of the inflammatory process
Everyone has encountered the problem of gum inflammation: for some the process was more pronounced, for others less. However, the reaction to the inflammatory process is different - some people try not to make the disease worse and go to the dentist, while others let things take their course, hoping that “it will go away on its own.” Such an irresponsible attitude towards one’s health can ultimately lead to complications that will be difficult to cope with even with the help of a doctor.
To prevent inflammatory gum diseases, you need to know what can cause inflammation and what symptoms can be seen that it already exists.
What could be the reasons
1. Microbes
The human oral cavity contains a huge number of microorganisms that under normal conditions do not pose any danger. The body's general immune system and local immunity cope with the regulation of their numbers, growth and health effects until conditions favorable for microbes occur, when they become a serious threat.
2. Insufficient or poor oral care
In the absence of regular brushing of teeth, or the wrong choice of toothbrush, toothpaste, elixir or mouthwash, plaque accumulates on the surface of the teeth, which serves as an excellent breeding ground for pathogenic microorganisms.
3. Presence of tartar
Soft plaque under the influence of bacterial waste products turns into hard tartar. The appearance of these solid formations contributes to the development of the inflammatory process; The gums become injured and “sag,” and pathogens penetrate into the deeper layers of the soft tissue of the gums.
4. Other reasons
In addition to the above reasons, inflammatory gum diseases can occur:
- due to improper prosthetics and dental fillings
- smoking and vitamin deficiencies
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and endocrine system
Also, gum inflammation can be caused by a hereditary predisposition or weakening of the body's protective functions.
https://youtu.be/_1tGor9xDls
How do the symptoms manifest?
Inflammation does not occur immediately and is strong - it occurs in stages:
- swelling and redness of the gums, excessively soft tissue (this can be felt when palpating with a finger or touching a toothbrush)
- blood vessels are weakened, which is evident from the appearance of blood on the brush or dental floss (at first these are only traces, but later blood can appear at the slightest touch even with the tongue to the gum)
- tooth sensitivity increases, as the gums sag, the neck of the tooth is exposed, and since it is not as protected as the crown by enamel, any impact is noticeable
- the development of the inflammatory process can lead to the fact that the slightest irritation becomes a source of pain: it becomes difficult to chew food, and the contact of cold or hot, sour or sweet food on the inflamed area sometimes causes unbearable pain
- the surface and outline of the gums look uneven, the tissues become loose
- Bad breath becomes a constant unpleasant companion, which cannot be eliminated either by dental elixirs or by brushing your teeth.
General factors
The occurrence of inflammatory gum diseases is caused by a number of factors that weaken the functioning of the human immune system and make the gums susceptible to pathogens attacking them (gum inflammation begins - gingivitis). These factors are often:
- periods of hormonal changes (puberty, pregnancy, menstruation or menopause)
- stressful situations
- disorders of the body's protective functions
- active smoking
Inflammation of the gums can be caused by a disturbance in the composition of saliva, the balance of the bacterial flora in diabetes. Inflammatory gum disease can be caused by a lack of vitamins.
If these risk factors are present in your life, you should carefully monitor the formation of tartar and remove these unwanted deposits as quickly as possible.
Local factors
In addition to general factors, the occurrence of gingivitis is caused by poor oral care, dental plaque, poorly placed fillings and crowns, poor prosthetics, old fillings, malocclusion and the presence of orthodontic structures in the mouth that make normal teeth cleaning difficult. Increasingly growing deposits on teeth contribute to a greater accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms. Periodontal pockets may appear, which means inflammation moves to the gums.
Periodontitis –
In the absence of treatment or improper treatment of catarrhal gingivitis, the latter inevitably turns into chronic generalized periodontitis. And if with gingivitis the inflammation covers only the mucous membrane of the gums, then with periodontitis there is a gradual destruction of the tooth-gingival attachment, as well as the bone tissue around the teeth. As a result, over time this leads to tooth mobility and the need for their removal.
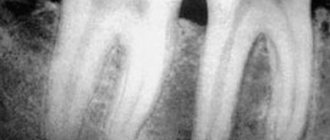
Gum diseases: photos of teeth with periodontitis
Periodontitis can be mild, moderate or severe. The symptoms of a mild form of periodontitis differ little from the symptoms of catarrhal gingivitis, and the patient in most cases will not notice that the condition of the gums has “deteriorated even further.” In addition to the symptoms of catarrhal gingivitis, the patient may notice that the gums begin to move away from the teeth a little, or sometimes tartar peeks out from under the gums (Fig. 5). The characteristic symptoms of periodontitis become noticeable especially in its moderate and severe forms.
Differences between periodontitis and gingivitis - In addition to bleeding and tenderness of the gums, as well as swelling, redness or bluishness of the gums in catarrhal gingivitis, periodontitis occurs:
- destruction of the dental-gingival attachment,
- destruction of periodontal fibers, due to which the tooth is attached to the bone,
- formation of subgingival dental plaque,
- destruction of bone tissue,
- formation of periodontal pockets (Fig. 6),
- suppuration from periodontal pockets (during periods of decreased immunity),
- + Over time, tooth mobility and discrepancy will appear.
Differences between periodontitis and gingivitis: diagram
With mild periodontitis, the depth of periodontal pockets is no more than 3.5 mm (and this still allows for very effective treatment and stabilization of the process). With moderate/severe periodontitis, the depth of the periodontal pockets already reaches 5-6 mm, and the amount of bone destruction around the tooth is such that mobility of first individual and then most teeth appears. Further, under the influence of mechanical loads, the teeth begin to shift in different directions, or fan out (Fig. 6-7).
You can find out more about the symptoms of periodontitis and how it looks on x-rays in the article: → Signs of periodontitis in adults
Important: over many years as a periodontist, I have seen thousands of patients with periodontitis, which always occurs for almost the same reason. The basis is always irregular and/or poor-quality oral hygiene, against which the patient has been using antiseptic rinses, gels and toothpaste for bleeding for many years (believing that this is the best and only protection against gum inflammation). Such patients spend a huge amount of time on various procedures, but cannot bring themselves to spend 3 times 5 minutes brushing their teeth after each meal.
As a result, patients regularly muffle the symptoms of inflammation with the help of anti-inflammatory drugs, while plaque and hard tartar continue to destroy the gums, only more quietly. This is because most patients with periodontitis struggle exclusively with the symptoms of the disease (bleeding, swelling of the gums), and not with the cause of their inflammation - soft microbial plaque and tartar.
Local form of periodontitis –
In addition to chronic generalized periodontitis, with which most patients seek treatment for gum inflammation, there is also so-called localized periodontitis. The latter is characterized by the development of not all, but only 1-2 teeth in the area. Caused by local reasons. This may be an overhanging edge of the filling in the interdental space or, on the contrary, a poorly placed filling, as a result of which there may not be close contact between the teeth in the interdental space.
This could be a traumatic bite, i.e. so-called “super contact” (when the teeth do not close at the same time, but there is premature biting on one of the teeth, which will cause its mechanical overload). These can be poorly made removable dentures, as well as low-quality artificial crowns. The latter, like fillings, can either injure the gingival margin, or have supercontacts, or have poor contacts with neighboring teeth in the interdental spaces.
Treatment of localized periodontitis involves eliminating the traumatic factor. This may result in the need to replace a filling, crown, prosthesis, or, in the presence of supercontacts, in the need for selective grinding of teeth. The rest of the treatment is carried out only after the traumatic factor has been eliminated. It may include anti-inflammatory therapy, as well as curettage of the periodontal pocket.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums caused by local and general unfavorable factors, without a violation of the integrity of the tooth-gingival junction.
Although gingivitis is much easier to cure than periodontal disease or periodontitis, you should not relax: untimely contact with the dentist and delays in treatment can lead to very significant consequences. Firstly, you will need to spend more on treatment; secondly, it is unknown what side effects may appear on general well-being due to “simple” gum inflammation.
The main cause of gingivitis is still non-compliance with basic hygiene rules or a complete lack of oral hygiene. The disease can be caused by injuries of various types, improper installation of prostheses, and weakened immunity. Gingivitis is characterized by shallow inflammation of the gums around a tooth or several teeth. In dentistry, there are several forms of this disease.
Catarrhal gingivitis
There is redness of the gums around a tooth or several. Often the gums bleed, there may be slight itching, pain when eating or performing hygiene procedures. This is the most common form.
Ulcerative gingivitis
A severe form of the disease, when large areas of the gums are affected and a characteristic grayish coating is visible. At an advanced stage, the formation of purulent foci, necrosis of soft tissues, and bad breath may appear.
Hypertrophic gingivitis
In the clinic of this form, compaction and proliferation of the soft tissues of the gums are noted, sometimes leading to keratinization of its individual parts.
If the first symptoms of any form of disease appear, you should immediately see a doctor, because self-medication will not help in this case. Relieving the inflammatory process is not an end in itself; it is necessary to get rid of the cause that provoked the inflammatory process. Only a dentist can determine the cause of gingivitis and prescribe appropriate therapy. You may need to consult a specialized specialist, to whom a doctor will give a referral.
What is the danger?
If treatment is not started on time, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, when inflammation affects not only the gums, but also the deeper periodontal tissues. At this stage, the symptoms include itching in the gums, exposure of the necks and roots of the teeth, their mobility and loosening. Periodontal pockets are formed - depressions around the teeth, formed due to the destruction of surrounding tissues. In such places, food debris and microorganisms accumulate, the activity of which aggravates the inflammatory process.
Another possible complication of gingivitis is periodontitis - inflammation of the periodontium, the tissue between the tooth and its bone bed. Its symptoms: severe toothache, swelling of the gums, swelling of the cheeks, lips, loosening of the affected tooth. In some cases, the body temperature rises and the head hurts. Periodontitis can also occur as a result of neglected or untreated pulpitis, trauma, as well as inflammatory processes of surrounding tissues (for example, if a person suffers from sinusitis or osteomyelitis).
Inflammatory processes in the oral area
Today, there are a number of factors that can lead to inflammation of various types in the oral cavity.
Inflammation of the gums causes discomfort in the patient and does not contribute to improving communication with others: it is not very pleasant to talk with a person who has constant bad breath (and this accompanies any inflammation). However, one should not think that everything is limited only to the oral cavity: if infected saliva gets into the stomach, it can provoke quite serious systemic diseases.
Inflammatory process during pregnancy
Pregnancy for almost all women is problematic in terms of the condition of the oral cavity: tooth enamel weakens and begins to deteriorate; gums often become inflamed.
The causes of inflammation and pain in the gums can be different:
- weakening of the protective functions of the whole body and local immunity, as a consequence
- the diet changes, metabolic processes proceed in an unusual mode for the body, which leads to an acceleration of the formation of dental plaque
- neglect of the rules of oral hygiene during pregnancy
Ultimately, an impressive layer of plaque accumulates on the teeth during the day, which serves as an excellent breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria that cause inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.
As such, plaque on teeth does not pose any danger if it is removed on time and well enough. Morning and evening brushing of the oral cavity is enough to avoid the appearance of plaque. During pregnancy, special attention should be paid to the condition of the teeth and gums, without expecting that everything will go away on its own.
If left untreated, gingivitis can develop into periodontitis, which is much more serious and can lead to the loss of completely healthy teeth.
It is necessary to monitor the condition of the gums literally from the first days of pregnancy, since already in the first weeks the first signs of inflammation may appear. If there is pain in the gums, inflammation and bleeding, you should immediately go to see a doctor. You should not put off visiting the dentist and dental treatment until the postpartum period: you simply won’t have time, and most importantly, you will waste time, which will cause more serious consequences.
Prosthetics and installation of crowns
Orthopedic dental operations are not easy procedures in themselves, and additional complications arise against the background of gum inflammation. If prosthetics are necessary, then it is necessary to first treat the oral cavity, remove inflammatory processes, and then install orthopedic structures. In the initial stage, it is easier to get rid of any disease, so earlier treatment of inflammation will be more effective. If you need to install dentures for periodontitis, you need to know:
- the process will be longer due to the need for preliminary treatment
- “loose” teeth cannot be completely reattached to the gums, and if the teeth are too mobile, they will have to be removed; Even apparently healthy teeth, without traces of caries, are removed, since the dentures must have a strong, reliable support
- if you do implantation, then periodontitis will not be a contraindication
With periodontitis, the choice of dentures is small. Even in the remission stage of this chronic disease, one-piece metal-ceramic crowns, made of metal and ceramics, cannot be installed. For reliable installation of permanent dentures, it is necessary that the neighboring teeth are motionless, otherwise the denture will begin to loosen and the supporting teeth may become deformed.
Only an orthopedic dentist can determine which type of design is right for you. Based on examinations and examinations, he decides what kind of surgery is required: installation of a bridge, removable dentures, zirconium crowns or implantation. A good specialist will definitely have an option for you, no matter how difficult the dental situation may be!
Negative effects of wisdom teeth
Wisdom teeth begin to erupt after 18–19 years of age. This third pair of chewing teeth is not easy for a person: the gums become inflamed, swollen, and are literally “torn”. But if the pain or gum swelling is too severe, you should consult a dentist. Medical intervention or the use of special medications and hygiene products may be necessary.
Inflammation of the gums around wisdom teeth can occur for many reasons:
- it is difficult to clean with a toothbrush from food debris and plaque, which leads to the active proliferation of microbes
- the soft tissues of the gums are injured: eruption itself is difficult, plus improper growth of the wisdom tooth is possible
- inflammation around the figure eights can be caused by stomatitis, gingivitis, periodontal disease
In any case, inflammation of the gums around wisdom teeth requires treatment to prevent it from spreading further. Eights are often removed soon after they appear.
Gum disease: treatment
It is unfortunate, but the most adequate patients who follow absolutely all the recommendations of a periodontist are those who have been treated at home for a long time with various rinses, ointments, and used pastes for bleeding.
When such patients come to the periodontist (with loose teeth and suppuration from periodontal pockets), they no longer need to be convinced of the ineffectiveness of such self-medication, and the need to spend money on removing dental plaque and time on brushing their teeth not 2 times a day, but after each eating. Yes, such patients have a difficult situation in the oral cavity, but they are easy to work with. And when, after just a few days of adequate therapy, they see the first results, and you recommend splinting their mobile teeth with fiberglass or curettage of periodontal pockets, they sign up and do it. But there are other patients - they will listen with disbelief to your recommendations for curettage, splinting, prosthetics, ask “how much does it cost” and disappear for 1-2 years.
When they do come, they are ready to do anything to avoid having their teeth removed, but this is most often the only thing that can be done. Therefore, when reading this article, you have 2 choices. The first option is that you can take only the anti-inflammatory therapy regimen for yourself, and then treat yourself at home. The second option is also to undergo a course of home anti-inflammatory therapy, but before that, visit a periodontist and remove the causative factor of gum inflammation (i.e. dental plaque).
Important: remember that gingivitis is reversible, and its proper treatment leads to a complete cessation of inflammation in the gums, and it will not occur again if you normalize the process of oral hygiene. The development of periodontitis begins with the destruction of the tooth-gingival attachment in the neck of the teeth. As soon as the fibers of this attachment are destroyed, a path opens for pathogenic bacteria under the gum and to the destruction of the periodontal attachment of the tooth to the bone.
It is impossible to somehow restore the destroyed tooth-gingival attachment, and from now on you will always be vulnerable to periodontitis. Below we will describe the general principles of treating gum disease, and you will also find useful links where some treatment issues are discussed in more detail.
How to treat gums with gingivitis -
In general, you need to start with a consultation with a periodontist, and if periodontal pockets are found during the examination, the doctor will refer the patient to a panoramic photograph of the teeth - with a preliminary diagnosis of “chronic generalized periodontitis.” If a diagnosis of “catarrhal gingivitis” is made, then this is a reason for joy, because in this case, treatment will consist only of removing dental plaque, a short course of anti-inflammatory therapy + regular hygiene.
Removal of microbial plaque and tartar is most often carried out using ultrasonic cleaning. This is a completely painless procedure, unless, of course, you have increased sensitivity of the necks of your teeth (in this case, you can use anesthesia). Usually, with gingivitis, only 1 visit to a periodontist is enough, who in 1 hour will remove deposits, prescribe medications, teach you how to use dental floss and brush your teeth correctly.
Video of dental plaque removal with ultrasound –
https://youtu.be/8ZZpNsvsPCY
https://youtu.be/VPf7k-fI9Uk
Anti-inflammatory therapy –
For the treatment of catarrhal gingivitis, 8 days are usually sufficient (for periodontitis – 10 days). There is no need to carry out antiseptic rinses and treat gums with gel at a dentist's appointment; you can do this just fine at home. The procedures are carried out 2 times a day - in the morning and in the evening, and each time it is better to do this only after eating and subsequent oral hygiene. The scheme will be as follows..
First, have breakfast and brush your teeth after that (not before breakfast, but after!). After this, you need to rinse your mouth with an antiseptic solution. This can be a standard 0.05% solution of chlorhexidine - this concentration will be sufficient for minor inflammation. In case of severe inflammation and bleeding, it is better to use solutions containing chlorhexidine 0.2-025%. The best option here is Lakalut Active rinse aid - with 0.25% chlorhexidine and aluminum lactate, or PresiDent Antibacterial.
To rinse your mouth, you need to put 10-15 ml of solution in your mouth and, without spitting, rinse your mouth for 1 minute. Spit. The second stage of morning treatment is the application of a medicinal gel to the inflamed gums. The strongest option is Cholisal gel; for moderate inflammation, you can also use Parodontocide gel. In order for the gel to adhere better to the moist mucous membrane, the latter must first be dried with a clean, dry gauze swab.
Next, squeeze the gel onto your finger, and, baring your teeth in front of the mirror, apply the gel to the marginal part of the gums, which is adjacent directly to the teeth. Usually the gel is applied to the gums only from the front surface of the teeth. After this, do not drink or rinse your mouth for 30 minutes, and do not eat anything for 2 hours. The resulting saliva does not need to be saved or spat; swallow it as usual. In the evening, repeat the treatment - after eating and brushing your teeth, rinse your mouth again, and then apply the gel.
Useful links -
→ The best mouthwashes, → Rating of the best gels for gums.
An integrated approach to treatment
To stop the further development of the disease and eliminate discomfort, you must do the following:
- diagnose the disease to prescribe appropriate therapy
- remove deposits and stones from teeth
- treatment of inflammation
- sanitize the oral cavity
If necessary, loose teeth are splinted, dentures are placed, and teeth that cannot be treated are removed. After completing the treatment course, maintenance therapeutic procedures are prescribed. Only an integrated approach guarantees complete cure of inflammation, and following the recommendations will avoid relapses.
Consultation and initial examination of a specialist
At the first visit to the dentist, the patient undergoes an initial examination and receives advice on possible treatment methods for the identified disease. After a thorough examination of each tooth, the doctor records data on the condition of the teeth and gums in the patient’s medical record. The visitor is given information about which and how teeth need to be treated, and the approximate cost of the necessary procedures can be calculated.
Anti-inflammatory therapy
The problem of gum inflammation is a common phenomenon, however, self-medication cannot get rid of it. In order not to start the disease and not lose teeth, you should promptly seek the help of a dentist.
The combined use of conservative local therapy and physiotherapy gives good results. Medications used in the treatment of periodontitis are divided into several categories:
- antibacterial agents (antifungals, antiseptics, antibiotics)
- enzymatic, steroidal and non-steroidal drugs
- hormonal, immunostimulating agents, vitamins
If the inflammation worsens, an operation may be prescribed to open the gums so that the accumulated pus can be released. For periodontitis, planned operations are performed:
- patchwork
- gingivectomy
- curettage
Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed after getting rid of severe inflammation.
Treatment of inflammation caused by injury
There are two types of gum injuries - chronic and acute. The former are a consequence of the action of a constant irritating factor - an incorrectly installed prosthesis, unsuccessfully made bridges, crowns, etc. In this case, you cannot do without contacting an orthopedic doctor. Acute injuries can occur when using cutlery, dental floss or a hard brush, as well as in fights and falls.
Anti-inflammatory treatment is carried out by a periodontist. First, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of the inflammatory process:
- replacement of old or low-quality fillings is carried out
- uncomfortable dentures are removed
- It is recommended to buy a soft toothbrush
Next, the treatment course is carried out in stages:
- acute pain is relieved
- anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed
Features of choosing toothpaste and brush
A toothbrush is a personal hygiene item; it should be individual for everyone. The brush should not be used for more than two to three months.
If there are no problems with your gums, a medium hardness toothbrush will do. If there are any gum diseases, then the brush should be soft to avoid injury to the gums.
If you are used to using an electric brush, then you need to know that you should not brush your teeth for more than 3 minutes, and the brush movements are the same as when brushing with a regular brush. To reduce the load on the teeth, the electric brush should be applied to the surface of the teeth with less force compared to a regular one.
The choice of paste and the rules for using it are of great importance. Don’t think that the more toothpaste you squeeze out of the tube, the better you can clean your teeth. The volume of the paste does not affect the quality of the procedure - just squeeze out a little paste, the size of a pea.
The selection of toothpaste is also individual and depends on the condition of the gums and teeth. If your gums are bleeding, then the toothpaste should contain antibacterial and anti-inflammatory components. Most often these are medicinal plants: chamomile, eucalyptus, oak bark, sage, coniferous extracts, echinacea and others. Paste with propolis works well.
As a prophylactic paste, you should use those containing zinc citrate and aluminum lactate. They have an astringent effect and prevent periodontal disease and periodontitis. To restore mucous membranes, you need to buy pastes containing allantoin and bisabolol.
To choose the most suitable paste for your case, it is better to seek the help of a dentist. After examining and assessing the condition of the oral cavity, the doctor will be able to recommend exactly the paste that you need to prevent disease or as part of a treatment course for existing inflammation.
Surgical intervention
Based on the general picture of the situation, the specialist may resort to surgical treatment. Thus, at an early stage of the pathological process, when the periodontal pocket does not exceed 5 mm, subgingival deposits and granulation changes in the gum are removed (closed curettage).
In advanced cases, you will have to make an incision in the gum, and then remove the mucous layer by layer; the doctor will also implant synthetic materials into the gum, and finally apply sutures. Sometimes a flap operation is used to eliminate foci of prolapse: an incision is made in the gingival margin, exfoliated tissue is removed, and a flap of tissue from another place in the oral mucosa is pulled in its place.
Important! Traditional methods of treatment involve rinsing with various medicinal decoctions from oak bark, chamomile, strawberry leaves, St. John's wort, and calendula. However, you should not self-medicate, because... Traditional medicine can only weaken the symptoms, but not eliminate the cause of the pathology.
The postoperative stage usually lasts several months and ends with complete healing of the damaged tissue.
Preventive actions
It is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it. To prevent gum inflammation, a whole range of hygienic and general health measures is necessary. It is necessary to prevent the appearance of tartar; maintain favorable microflora of the oral cavity; prevent the proliferation of microbes that cause inflammation and properly carry out hygienic procedures for caring for the oral cavity.
Comprehensive prevention includes the following measures:
- maintaining oral hygiene, using properly selected care products and a toothbrush for regular care
- mandatory doctor visits twice a year; When the first signs of inflammation appear, go to an appointment with a dentist outside of your plan
- treatment of general somatic diseases
- maintaining a proper diet with the introduction of a large number of foods containing a lot of fiber and vitamins into the menu (it is advisable to consume fruits and vegetables without heat treatment)
- introduce celery, apples, carrots into your daily diet
- the use of mouth rinses with antiseptic properties that do not destabilize the balance of microflora in the mouth
Causes of recession
Recession is not an independent disease. A bare neck of a tooth indicates inflammation of the periodontal tissues – periodontitis or periodontal disease, which in an advanced state in 90% of cases is the reason why the gums move away from the tooth1. These diseases lead to a reduction in the volume of gum tissue and disruption of its metabolic processes.
Helpful information! Periodontal disease is associated with a general disorder of metabolic processes in the body. But periodontitis is caused by infections that have penetrated into the periodontal tissues, which are responsible for holding the tooth in the socket. However, periodontitis is the most common disease. It often occurs in children around 10 years of age. The disease affects unformed tissues that react sharply to the slightest irritants, and causes the gums to recede from a child’s tooth. In some cases, periodontitis develops during pregnancy because... A woman’s body uses nutrients to form a fetus.
Teeth may also become exposed for the following reasons:
- poor hygiene procedures, which leads to the formation of plaque and tartar, which can result in the development of gingivitis, which helps reduce the volume of gingival tissue,
- regular injury to the gums with a hard brush, rough movements when brushing, incorrectly selected dentures or crowns,
- incorrect bite: for example, with an open and deep bite, blood circulation is disrupted, because of this, gum tissue decreases. Recession often occurs against the background of crooked teeth and their crowding,
- unbalanced diet: with a predominance of soft foods, due to the lack of active chewing, the blood flow of the gums weakens, salivation slows down, food deposits form in the oral cavity,
- hormonal changes during puberty, in women during menopause, pregnancy, which make the mucous membrane more sensitive and vulnerable,
- the process of natural aging of the body, as a result of which the epithelium atrophies, gingival tissues lose tone,
- bad habits: for example, the problem of smokers is brown plaque, which subsequently negatively affects the health of the gums.
In addition to local causes, the occurrence of a recession can be influenced by serious chronic human diseases: weak immunity, diabetes mellitus, pathologies of the cardiovascular system of capillary circulation, vitamin deficiency and others. All of them are associated with changes in metabolic processes, which disrupts cell nutrition.
Antiseptic rinses against inflammation
They are good at removing microbes and the toxins they produce, partially destroying pathogens, protecting the enamel and reducing the enzymatic activity of various types of rinses.
Rinses used for inflammatory processes can be divided into:
- antimicrobial action;
- anti-inflammatory action;
- mixed (or combined) action.
Antimicrobial solutions include antiseptics or antibiotics. They don’t just temporarily remove inflammation, they act on the root cause of inflammation – pathogenic microflora.
Important note: when using rinses with anti-inflammatory agents, it is recommended to simultaneously use gum gels containing antibiotics or antiseptics.
How not to do it
Patients often self-medicate and try to get rid of gum disease with hydrogen peroxide. Despite the fact that this is a good antiseptic, it is not suitable for use in the treatment of inflammatory gum diseases and does not give any effect other than foam in the mouth. It is not possible to rinse periodontal pockets on your own using a syringe; certain knowledge and skills are required.
Injuries from fillings and crowns
Non-infectious causes of gum inflammation are overhanging edges of fillings and crowns. The pathology develops due to constant injuries of soft tissues with composite materials or prostheses and is local in nature.
Overhanging edges of the filling not only cause inflammation, but also contribute to the accumulation of food in the interdental space. In this case, it is enough to cut off the excess part or completely change the filling.
Inflammation can develop due to injury to the mucous membrane by poor-quality dentures.
Soft tissue injuries are also caused by poorly made crowns, bridges and dentures. What to do if your gums become inflamed for this reason is determined by the development of the disease. Initially, drug treatment is used. If it gives only a temporary effect, the structure will have to be replaced.
Gels and ointments against the inflammatory process
To treat periodontitis, applications with various therapeutic agents are used. Each has its own recommendations for use, however, during all procedures one should strictly adhere to one rule: hands must be clean (processing can be carried out with cotton swabs)
After eating, you should brush your teeth and squeeze out a small amount of gel from the tube. Apply the product to the affected part of the gum, then do not eat or drink for half an hour. You should not take a lot of gel or ointment: the effect will not increase, and a reaction to the swallowed drug may follow.
However, no ointments or gels used at home can replace dental treatment. They can become a good auxiliary component of a complex of treatment measures prescribed by a doctor. They can relieve discomfort, prevent gingivitis or periodontitis, but cannot replace treatment.
Symptoms
The inflammatory process develops slowly and gradually progresses. It is accompanied by the following symptoms :
- Redness.
- Bleeding when brushing teeth or eating.
- Swelling.
- When the disease is infectious, pus begins to ooze from the gum pockets.
- Unpleasant smell.
- Necrosis of soft tissues.
Healthy gums have an even pink color.
There are several causes of gum inflammation. Treatment will depend on what factor triggered the disease.
Toothpastes against gum disease
If your gums are bleeding, you should choose the right toothpaste. Aluminum lactate has a good hemostatic effect; chlorhexidine and mineral salts are slightly inferior to it.
As for the other components included in the toothpaste for gums - bisabolol, allantoin, medicinal plant extracts - they do not directly affect bleeding gums. They have an anti-inflammatory effect, as a result of which bleeding is reduced and may disappear. Thus, we can only talk about their indirect effect on bleeding gums, which is why a positive result is observed later than when using a paste with aluminum lactate or chlorhexidine.
At the same time, you need to know that even the best paste only temporarily removes bleeding, but in no case is a remedy. To get rid of the disease, you need to see a dentist.
Reasons for the development of pathology
The main causes of gum inflammation can be provoked by both external and internal factors. In addition, they differ in the scale of pathological processes.
The main external factors of gum tissue inflammation are:
- presence of bad habits (smoking, alcohol);
- lack of minerals and vitamins in the body;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, heart problems;
- development of diabetes mellitus;
- hormonal imbalance;
- damage to the body by infectious pathogens;
- long-term use of certain medications (antidepressants, contraceptives, vasoconstrictor nasal drops);
- decreased functioning of the immune system.
Internal provocateurs of gum tissue inflammation include:
- formation of bone tissue of the dentition in an infant (teething);
- injury to soft tissues, chemical or thermal effects on the mucous membrane;
- accumulation of tartar on the enamel;
- insufficient compliance with oral hygiene standards, leading to the development of pathogenic microflora on the mucous membrane;
- an illiterately performed prosthetic procedure leading to injury to soft tissues by the installed crown or filling.
If there are wounds on the gums resulting from incorrectly performed prosthetics, gingivitis and periodontitis develop. This can lead to quite serious complications of a generalized nature, manifested by damage to a large area or the entire oral cavity.
photo: Wound on the gum - gingivitis
Inflammation of the gums can develop due to the use of an incorrectly selected toothbrush or toothpaste. Depending on the condition of the tooth enamel and tooth sensitivity, it is necessary to select a brush of optimal hardness, and before purchasing toothpaste, carefully study the components included in its composition. To prevent the development of inflammation, the best solution when choosing hygiene products is a preliminary consultation with an experienced dentist.
During pregnancy, the female body experiences hormonal changes, which can also provoke gum inflammation. Frequent contact with chemicals and consumption of allergenic foods are the direct cause of inflammation of the mucous membrane. You should be attentive to your health, choosing only foods that are healthy for the body, saturating it with a sufficient amount of minerals and vitamins.
Traditional methods of treating gum inflammation
Alternative medicine offers many ways to treat inflammation in the oral cavity. Gingivitis, periodontitis and periodontal disease are treated with ointments, tinctures, rinses and special “masks”. In addition to medicinal plants, honey, salt, soda, and peroxide are used to prepare medicinal compositions.
But we must understand that traditional medicine cannot seriously become a full-fledged treatment. When you notice the first signs of inflammatory diseases, you should go to see a dentist, and use folk remedies only on his recommendation.
Description of the problem
The receding of the gum from the tooth is called “recession” in dentistry. Recession can be localized (the gum has receded between one or two teeth or from the front tooth) or generalized (the lower or upper gum has receded from all teeth, i.e. the pathology extends to the entire row or even to both jaws at the same time). The problem is often associated with abrasion, peeling of the gum margin and exposure of part of the tooth, its root. This leads to the formation of periodontal pockets and receding gums.
The tooth becomes vulnerable to various pathogens, which easily penetrate into the resulting pockets and cause various dental diseases. If the pathological process is not stopped in time, as a result of the destruction of periodontal tissue, as well as the ligaments around the tooth root, the patient may lose one, several or even all teeth.
In the first stages of development, recession makes itself felt by increased sensitivity of teeth affected by pathology. Also, upon visual inspection, it is clear that these teeth look longer than the rest. The presence of these signs is already a reason for an immediate visit to the dentist.
Prices for treatment of gum inflammation in our clinic
We can talk about the cost of treatment for any inflammatory gum disease only after clarifying the diagnosis, determining the cause and level of neglect of the disease. With a timely visit to the dentist, professional teeth cleaning is often sufficient. In severe cases, surgery may be prescribed. If the examination reveals the presence of concomitant diseases of the oral cavity that complicate the therapeutic treatment of gingivitis, periodontal disease, periodontitis, consultation with a specialized dental specialist - an orthopedist, surgeon or therapist - will be required. This also affects the final cost of treatment.
You should not delay the treatment of periodontitis and gingivitis, because they can quickly develop into a more severe form. If your gums become swollen, red, or begin to bleed; there is pain and itching when eating; If stones and heavy plaque appear on your teeth, you should immediately visit a dentist.
A competent doctor is always aware of the most modern treatment methods and, after examination, will give recommendations and, if necessary, prescribe an appropriate course of treatment.
Gingivitis - we will survive this trouble
The listed factors quite often lead to the development of such dangerous inflammatory processes in the gums as gingivitis and periodontitis. In this case, a generalized nature of inflammation is observed, implying damage to the entire oral cavity.
Catarrhal gingivitis
This form of inflammation occurs most often. The disease can be provoked by both general and local factors.
The following symptoms are characteristic of this type of inflammatory process:
- slight swelling, bleeding and redness of the gums;
- changing the acute shape of the gingival papillae to a dome-shaped one;
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor and taste, itching sensation;
- soreness of the gums upon contact with food;
- fever, general weakness;
- formation of abundant plaque (at the initial stage).
A mild form of the disease (only the gingival papillae are affected) can be replaced by moderate and severe forms with damage to the free part of the gums and their entire space, respectively.
The photo shows a chronic process, the cure of which will require an integrated approach.
Ulcerative gingivitis
In this case, inflammatory processes affect the mucous membranes of the gums, provoking the development of tissue necrosis near the gingival margin and inflammation of regional lymph nodes.
The most likely cause of this process, along with hypothermia, infectious diseases and reduced immunity, is poor oral hygiene.
Symptoms characteristic of catarrhal gingivitis include:
- the presence of dirty gray plaque at the top of the gingival papillae , the removal of which leads to bleeding gums;
- rise in temperature with increased heart rate, pale skin and loss of appetite.
When this form of the disease develops, it is extremely important to start treatment in a timely manner.
The photo shows a severe form of the disease with purulent inflammation, which requires antibacterial and surgical treatment.
Hypertrophic gingivitis
A feature of this form is the reactive proliferation of connective fibrous tissue and epithelial basal cells, caused by chronic inflammation of the mucous membranes of the gums. Most often, such disorders are caused by changes in the functioning of the endocrine system, lack of vitamins and metabolic disorders.
The following symptoms of the disease appear:
- thickening of the epithelium (if untreated, keratinization is possible);
- a significant increase in gum size, a change in its color to dark red (granulating course of hypertrophic gingivitis);
- severe compaction of gum tissue, the appearance of painful sensations on palpation (fibrous development).
Prevention
Like any disease, it is better to prevent such a pathology than to subsequently undergo long-term treatment. This is both troublesome and expensive. The following can be considered as preventive measures:
- increase the consumption of foods rich in calcium - natural vegetables and fruits;
- treat the oral cavity with a solution of pharmaceutical chamomile as often as possible;
- carefully carry out all activities related to personal hygiene in one way or another;
- do not forget about regular visits to a specialized specialist. For the purpose of timely treatment of caries and preventing the development of dental anomalies;
- If there are bite defects, work to eliminate them.
An unpleasant thing - alveolitis
Sometimes after a tooth is removed, inflammation begins in the socket. It gradually spreads to the surrounding tissues - the outer part of the gums and periosteum (if not noticed in time and treatment is not started). This process is called alveolitis. Why does this problem occur? After your tooth is pulled out, blood collects at the site where it was located. The clot covers the bottom of the socket, preventing infection from entering the periodontal tissue. If it is not formed, damaged, washed with a mouth rinse, the hole festers. Not only she suffers, but also the gums in this area. In this case, the patient may feel pain, but not realize that its cause is not trauma from the removal.
In the photo there is alveolitis of the tooth
Doctors recommend not eating, drinking, or brushing your teeth for several hours after tooth extraction surgery. Rinsing during this period of time is also excluded.
It’s especially not worth heating. This will only provoke the proliferation of bacteria and, as a result, the development of the inflammatory process.
Gum treatment: price
The cost of the service is formed from various aspects. It is affected by:
- stage of illness;
- extent of the lesion;
- cost of medicines;
- doctor's workload.
Treatment of gums in dentistry requires careful and long-term therapy. An experienced doctor will examine the oral cavity, identify problems in the gums and teeth and begin the necessary treatment. The price of treatment is also influenced by the cost of injections. How much the patient will spend depends on the characteristics of the disease.
Types of inflammatory gum diseases
Inflammation of the gums is provoked by various pathological processes of the oral cavity, which, according to etiological principles, are divided into groups:
- Damage to soft tissues of a traumatic nature, caused by mechanical, physical or chemical injuries.
- Diseases of the oral mucosa of an infectious or fungal nature:
- periodontitis;
- gingivitis;
- stomatitis;
- periostitis.
Gingivitis
- Oral diseases caused by specific infections.
- Damage to the mucous membranes of the mouth caused by allergic reactions.
Treatment of gums with injections and medications
In some cases, injections of various medications may be required. Antibacterial medications are prescribed strictly individually. Restoration of teeth and gum tissue includes the use of antibiotics and antibacterial drugs. The action of therapy is aimed at eliminating the source of inflammation and stopping the disease. Powerful antiseptics Actovegin and Solcoseryl are used, which have an epithelializing effect. In acute cases, physiotherapy is prescribed.
Vacuum and finger massages are also used as an additional method of therapy. Such measures allow blood to circulate better in the affected areas and trigger the necessary recovery processes.
Important! Regular dental hygiene should be performed to prevent the formation of mineral deposits and the development of disease.
Symptoms of the disease
Gingivitis is an inflammatory lesion of the mucous membrane of the gums, which can be either infectious or of another etiology, and occurs acutely or chronically.
- bleeding from the gums;
- soreness of soft periodontal tissues. It increases during eating, especially when the food is very cold or too hot, as well as hard (rough), peppery, salty or sweet;
- burning, swelling and redness of the gums. This can manifest itself either in individual areas or spread to the entire jaw or even both;
- the appearance of ulcers, ulcers and vesicular formations;
- increase or decrease in gum volume;
- bad breath;
- signs of intoxication (increased body temperature, general malaise, lack of appetite).
Several types of gingivitis are classified:
https://youtu.be/HDsBXDGyyEc
Each of them has different clinical manifestations.
- Catarrhal disease begins with redness, swelling and bleeding from the gums. The mouth feels slightly itchy and sore when eating.
- Ulcerative-necrotic is determined by the formation of ulcerations and areas of necrotization on the mucous membrane, as well as by bad breath (halitosis). There may be an increase in regional lymph nodes and a deterioration in general condition.
- With hypertrophic gingivitis, gingival papillae grow and cover part of the tooth. At first, this does not cause discomfort, but over time, pain and bleeding appear when pressing on the gums. Hypertrophic pathology can be expressed:
- edematous form, in which the gums are painful and enlarged;
- fibrous form. In this case, the mucous membrane, despite signs of inflammation, does not give a pronounced pain reaction, but reacts to touch with mild discomfort. In addition, it does not bleed and can maintain its normal color.
- Atrophic gingivitis is distinguished by the fact that the volume of periodontal tissue along the dentition (or locally) decreases, gradually exposing the roots. Subjectively, a person feels increased sensitivity of teeth and gums to cold and hot food.
Read also: Rinse the flux
Dentists classify into a separate group:
- Gingivitis in pregnant women. It manifests itself with symptoms characteristic of the hypertrophic variety and often occurs in women during pregnancy. The reason is hormonal changes in the body.
- Adolescent gingivitis. It occurs as a mild form of acute catarrhal disease, but due to serious hormonal imbalances it can transform into hypertrophic.
- Herpetic gingivitis. As the name suggests, this variety differs in etiology and develops under the influence of herpes. It often looks like an acute form of necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis, against the background of a chronic viral infection. Erosion and ulcers occur not only on the surface of the gums, but also on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. This form indicates a severe decrease in immunity.
- Desquamative gingivitis. It is determined by the partial rejection of the outer epithelium of the gums. It begins with unhealthy red patches that eventually develop into blisters and then painful sores. The main difference between this variety is that its etiology has not been established. Desquamatous pathology always occurs in a generalized manner and is a chronic inflammation, with alternating periods of remission and exacerbation.
How to distinguish gingivitis from other gum diseases?
One of the goals of diagnosis is to differentiate gingivitis from similar pathologies affecting the gums.
Unlike other conditions that have the same symptoms, gum inflammation is not accompanied by:
- violation of the integrity of the dentogingival junction;
- formation of periodontal pockets;
- loosening of teeth.
It is noteworthy that the pathology mainly affects young people.
If you experience discomfort in your mouth, you should not try to make a diagnosis yourself. It is better to consult a doctor - he will do it professionally and accurately.
How is care provided?
Oral care for inflammation should take place in several stages:
- teeth cleaning;
- rinsing;
- applying ointments or gels to the gums.
Teeth brushing is carried out using a special toothpaste.
Before treating sore gums, you should choose a brush with soft bristles, as hard bristles can cause further injury to the soft tissues of your mouth.
Rinsing will help remove food debris from the mouth, as well as relieve inflammation and alleviate symptoms of the disease.
It is also worth caring for your brush, since bleeding can lead to pathogenic microorganisms accumulating on the bristles.
Gels and ointments are applied directly to the gums, while you should refrain from eating and drinking for a while. During the treatment process, you should avoid eating foods that are too cold or too hot; they can be harmful.
Ointments and gels are used several times a day. They help not only reduce the intensity of pain, but also prevent the proliferation of pathogens.
If the question arises of how to treat gums at home as efficiently as possible, then drug therapy is considered the most effective, since it has a complex effect on the gums.
Other methods to combat sore gums
If medications and traditional methods do not produce results, the doctor may prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures and ultrasound treatment. In the most severe cases, surgery may be required.
You should consult a doctor at the first signs of the disease, since it is better to treat gum inflammation at an early stage. Advanced acute gingivitis can become chronic or develop into a more serious pathology - periodontitis or periodontal disease.
https://youtu.be/EFhLBoND_70
Diagnostics
At the first signs of gum inflammation, you should seek help from a dentist rather than try to relieve the inflammation on your own. How to treat gum inflammation correctly, the doctor can tell only after an accurate diagnosis and identification of the etiology.
First of all, the doctor conducts a thorough physical examination of the oral cavity, taking into account the medical history. Also, during the initial examination, the dentist can clean and treat the inflamed areas with an antiseptic.
As for the diagnostic program, there is none as such. The doctor may prescribe laboratory and instrumental examination methods if the patient’s condition requires it. However, a general and biochemical blood test, a test for the presence of an allergen, is mandatory.
Basic therapy will depend on the etiology of the pathological process. It is quite possible to treat gum disease at home, but only as prescribed by a doctor. Taking traditional medicine is also possible, but only as an addition to the main course of treatment.
Drug treatment may include taking the following medications:
- spray "Parodontocide";
- solution "Maraslavin";
- "Polyminerol" solution;
- gel "Cholisal".
For severe toothache you can use:
It should be understood that painkillers can only provide a temporary effect, so you should not use it as a basis for self-medication. In addition, drugs of this pharmacological group should be used only in extreme cases, since their abuse can cause poor health. Also, the body gets used to this drug and the desired effect will no longer be achieved.
A doctor may prescribe antibiotics for gum inflammation if this symptom is due to an infectious process. If gum inflammation occurs during pregnancy, then taking medications is kept to a minimum.
In case of inflammation, special solutions for rinsing the mouth effectively help. In this case, the doctor may prescribe both a herbal decoction and the drug “Chlorhexidine”. Your doctor will tell you how to rinse your mouth with chlorhexidine.
You can also treat gum inflammation at home using traditional medicine. In this case, you can use decoctions of the following herbs:
- chamomile;
- thyme;
- a collection of mint, oregano and St. John's wort;
- arnica;
- strawberry leaves.
Read also: Trigeminal neuritis after tooth extraction
You can also rinse your mouth with a solution of furatsilin, soda and potassium permanganate. But before using any product, you should consult your doctor.
Folk remedies
There is a very wide list of folk methods and remedies for treating gum inflammation. They are quite effective if the form of the disease is not acute and quite advanced.
Tinctures and decoctions
The most commonly used are decoctions of oak and sage bark. These two agents have not only an antiseptic, but also a hemostatic and astringent effect.
- Oak bark .
One tablespoon is poured with boiling water and kept in a bowl over low heat for about 5–7 minutes. After cooling, the resulting liquid is filtered. Rinse – 2 times a day. © Alexander Raths / Fotolia - Sage . It is prepared in the same way, but you need to rinse it 3-4 times a day.
- Decoctions of other plants are also successfully used - calamus, marshmallow, serpentine, chamomile, calendula, St. John's wort, walnut leaves and others.
Medicinal plants – juices
To relieve inflammation, pain and disinfection, the juice of some plants is also used, rubbing it in a circular motion into the affected gums without strong pressure.
Kalanchoe, aloe and sorrel are mainly used for this.
Honey
Honey contains many active substances. In addition, it is the most effective natural preservative . This property helps prevent the appearance of pathogenic bacteria.
Honey in the amount of 20 grams should be mixed with regular table salt (5 grams). This mixture is rubbed into the gums to get rid of bacteria.
What are the symptoms of wisdom teeth growth? In addition to temperature, there may be several more.
This article talks about how to treat stomatitis in a child who is already 3 years old.
Here: https://www.vash-dentist.ru/krasota-i-uxod/narashhivanie/ot-chego-zavisyat-tsenyi-na-zubov.html - you will find out what the price of teeth extensions consists of.
Essential oils
Essential oils are used as a means for gum massage. If they do not cause allergic reactions, they are successfully used to improve blood circulation and regenerate damaged tissues, as well as to relieve inflammation.
Typically, peach, sea buckthorn, olive and fir oils are used to solve gum problems. To obtain a strong anti-inflammatory effect, it is better to apply them.
In the following video you will learn how to prevent inflammation and bleeding of gums using traditional recipes:
https://youtu.be/tDo6TJkeHhc
Cleaning process
The process of brushing teeth during gum inflammation has its own characteristics.
Due to pain, you cannot use a toothbrush with hard bristles; you need to change it to another one.
Select a brush with soft bristles that will not injure the tissue.
You need to brush your teeth 2 times a day, moving the brush from top to bottom.
The procedure should be carried out carefully, since there is a high risk of injuring the gums. After cleaning, you need to thoroughly rinse your mouth and rinse the bristles of the brush under running water.
When treating the inflammatory process you can use:
- Lakalut;
- Mexidol dent phyto;
- Parodontax;
- The president;
- Forest balm.
Toothpastes have proven effective in therapy.
But the products are most effective when carrying out preventive procedures. They are not suitable for long-term use if they contain antiseptics.
The pastes contain extracts of plants and herbs that help prevent the occurrence of inflammation in the oral cavity.
Dentists recommend using Forest Balm as a gum rinse. It can be used both as a medicinal product and as a prophylactic agent.
https://youtu.be/LQKoFfOdtqk
What to do
Gum inflammation affects almost all age groups of patients. The intensity of symptoms may vary.
In many ways, the development of the inflammatory process depends on oral hygiene. The more carefully a person monitors the condition of his oral cavity, the higher the chances that the disease will bypass him. The more plaque and other deposits accumulate on the teeth, the greater the risk that inflammation may occur. Dentists note a direct connection between the intensity of the lesion and the presence of plaque. An interesting experiment was conducted to confirm this relationship.
A group of young people with healthy teeth were asked to give up oral hygiene procedures for three weeks. After the allotted time, all members of the experimental group, without exception, experienced the accumulation of a large amount of plaque, as well as the initial processes of inflammation. At the same time, dentists noted that in order for the first signs to appear, it only takes two to three weeks not to pay due attention to oral hygiene! So, in order not to know for a long time exactly how sore gums hurt, you should brush your teeth regularly.
However, the following conclusions of this experiment are of greatest interest: after the members of the experimental group resumed full oral hygiene procedures, after some time all the symptoms of gum inflammation disappeared, and the composition of the oral microflora returned to normal. This suggests that if due attention is paid to oral hygiene at the initial stage of development, the inflammatory process can be stopped. Particular care should be taken to clean the interdental spaces and hard-to-reach areas of the tooth from food debris and plaque, since this is where most of the plaque accumulates.
However, if the disease has progressed quite far, the gums bleed and hurt, hygiene procedures will most likely no longer be possible. And our only advice is to visit a dentist as soon as possible. Only he will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
The causes of gum inflammation can be very diverse, ranging from insufficient oral hygiene to mechanical injuries. Let's look at the most common of them:
- insufficient oral hygiene,
- tartar,
- weakened immunity,
- taking medications that reduce salivation,
- viruses,
- lack of vitamin C,
- pregnancy,
- heredity,
- smoking,
- poor quality dental crowns and fillings,
- menses,
- taking hormonal drugs.
Insufficient oral hygiene . Over time, a film of bacteria and sugar forms on the teeth and gums, invisible to the human eye, and hardens within three days. If you systematically brush your teeth, the film will be removed during the hygiene procedure as it occurs. If you rarely brush your teeth, the film hardens, turns into tartar, and you can no longer remove it yourself. And in tartar, as in plaque, pathogenic bacteria multiply especially quickly. That is why dentists call insufficient oral hygiene one of the main causes of the disease.
Tartar is not only a breeding ground for bacteria, but also one of the causes of gum injury. Therefore, from time to time you should visit the dentist to have your teeth professionally cleaned and tartar removed, since you will not be able to do this on your own. This way you will protect yourself from getting sick.
Weakened immunity . If the human body is weakened, it cannot resist the occurrence of various diseases caused by bacteria or viruses. Since gum inflammation has a bacterial basis, weakened immunity plays a large role in the development and occurrence of the disease.
Taking medications that help reduce salivation . Human saliva is a cleansing substance; it gently and completely naturally cleans teeth and gums of plaque. If, as a result of taking medications, the amount of saliva has significantly decreased, this can lead to changes in the microflora of the oral cavity, and as a result, to inflammation.
Read also: The ball does not hurt on the gum
Impact of viruses . For example, one type of gingivitis, herpetic gingivostomatitis, is caused by the herpes virus. Viruses can trigger the onset of the disease if the body is weakened by previous diseases, so gingivitis most often occurs after previous diseases.
Lack of vitamin C. It would seem, what is the relationship here? But it turns out that the lack of vitamin C can lead to such a serious disease as scurvy.
Pregnancy . During pregnancy, complex hormonal changes occur throughout a woman's body, as a result of which the woman complains that her gums are inflamed. In this case, you should pay increased attention to oral hygiene and visit the dentist in a timely manner so as not to lose all your teeth by the end of pregnancy.
Bad heredity and smoking . If parents suffer from sore gums, their children are more likely to suffer as well.
Poor quality dental crowns and fillings . If a filling or dental crown constantly injures the gums, then over time it begins to become inflamed. Therefore, if you have a feeling of discomfort, and some crown scratches your gums, immediately consult a doctor and replace the low-quality crown with a better one.
Menstrual cycle or taking hormonal contraceptives . Therefore, women during this period should be especially careful about oral hygiene.
Let us note a few more reasons that can cause inflammation of the gums around the tooth:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract,
- of cardio-vascular system,
- diabetes,
- presence of infectious diseases.
If you suffer from one of these diseases, this does not mean that you will definitely develop gum disease. However, you should understand that you are at potential risk.
Symptoms of gum inflammation may appear gradually and increase in intensity over time. We list the main ones:
- redness,
- increased bleeding,
- swelling,
- bad breath.
At an early stage of the development of the disease, redness appears, which turns bright red. Therefore, if your gums have changed color, this is a reason to consult a doctor, even if no other symptoms are observed.
- At the next stage of development of the inflammatory process, increased bleeding appears. Most often, gums bleed during hygiene procedures, as well as when touched carelessly. Bleeding is a rather serious symptom, which indicates that the process has gone far. Therefore, adequate treatment should be started immediately. Soft tissues can bleed on their own or even due to a light touch or microtrauma. The affected gum becomes sensitive to any touch, and even eating can cause unpleasant pain and bleeding.
- At the next stage of inflammation, everything around the tooth swells, and pus can accumulate in the periodontal pocket, which causes bad breath. It also happens that bad breath is the only symptom of the disease.
- The most dangerous sign is tooth loss . It occurs at a late stage in the development of the disease, as a result of gum atrophy . It is very important not to let this happen, so inflammation must be treated in a timely manner, at an early stage of the disease.
Since we are often asked the question: “The gums are inflamed, what should I do?”, in this article we tried to tell you in detail everything that is known today about this disease. We hope that our article will help you keep your teeth healthy for as long as possible.
Regional distribution of gum diseases in the world
Traditionally, things are best in Western European countries. Here, oral hygiene has long been part of social culture. There is another “pole” - the poor countries of the Middle East, small Asian states like Burma and Cambodia. Here people live in such conditions that not every family can afford toothpaste to protect their gums. The same is true in Russia. There are entire territories, like the Far North and Chukotka, where local peoples have lived for centuries in unsanitary conditions.
Symptoms of periodontal disease
However, there are exceptions. When people live in remote places, but their gums are in order. How can this be explained? In most cases, they are saved by various natural remedies containing antiseptics. This can be pine resin, bee propolis, various decoctions and infusions from pine needles, natural herbs, etc. Similar products are recommended for use by modern science.
Speaking of Europe. There are also problem regions there - Romania, Albania, certain regions of Greece, Italy and Spain.
Healthy teeth and gums
If the diet does not have enough nutrients and vitamin C, inflammatory processes in the gums begin. This, unfortunately, is inevitable. What do experts recommend for residents of such places? The easiest way out is to purchase multivitamins and mineral complexes. Popular folk remedies can also be used.
Therapy at home
Medicines
Antibacterial agents are used only after consultation with a doctor.
Among the most popular means are:
- Amoxicillin, Augmentin;
- Tsiprolet, Nolitsin;
- Metronidazole.
Amoxicillin
Augmentin
Tsiprolet
Nolicin Metrnidazole
The treatment course is 7-10 days.
The best pharmaceutical products:
https://youtu.be/-0a2DG0VnXo
Gels
A high antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effect is noted in:
- Cholisal - gel. The product penetrates perfectly into the gums.
- Metrogyl - Dents containing the antibiotic and antiseptic Chlorhexidine.
- Kamistad, characterized by a strong analgesic effect.
- Periodonticide, consisting of essential oils.
Holisal
Metrogil Denta
Kamistad
Periodonticide
For information! Since gels are water-based, while ointments are fat-based, they are more often used to treat gums. They are able to stay on the mucous membrane longer.
Rinse aids
The following will help relieve inflammation:
- Chlorhexidine (solution).
- Miramisin.
- Furacilin (solution).
Chlorhexidine
Miramistin
Furacilin
Toothpastes
- Lacalut Active.
- Lacalut Phytoformula.
- Parodontax.
- Forest balm.
Lacalut Active
Lacalut Phytoformula
Parodontax
Forest balm
Review of pastes for bleeding gums:
https://youtu.be/j3_QJ-K73rE
Hydrogen peroxide
- For rinsing, you need to prepare a solution of 10 drops of the product and 50 ml of clean water.
- Treatment of gums with 3% hydrogen peroxide using a cotton swab.
- To brush your teeth, you need to make a mixture of ½ tsp. baking soda, 20 drops of hydroperite solution and 10 drops of freshly squeezed lemon juice. Use the mixture with toothpaste.
Traditional methods
- A decoction of chamomile, calendula, sage, and yarrow is prepared as follows: 1 tbsp. l. one type of herb is poured with 1 glass of boiling water.
- Infuse for 30 minutes.
- After which, the broth must be filtered and used for rinsing.
Effective folk method:
https://youtu.be/1YgikSb7OS0
Vitamins
- Ascorutin (quickly eliminates bleeding).
- Calcium – D3 (for calcium deficiency).
- Dentovitus (protection against gum disease).
Askorutin
Calcium D3
Dento Vitus
Diet
- Legumes (they contain a lot of phosphorus).
- Various vegetables, fruits.
- Cereals, nuts.
- Lean meat, fish.
- Greenery.
Surgical methods for treating periodontitis
In our clinic, if necessary, various surgical methods are used, and the price for gum treatment is acceptable for all patients. The disease can be eliminated using advanced techniques:
- opening of an abscess due to periodontal disease;
- closed curettage of periodontal pocket;
- increase in attached gum tissue;
- splinting of teeth;
- using fiberglass to strengthen teeth.
Treatment of gums with surgical methods helps strengthen teeth and prevent their destruction and loss. Periodontal disease can be eliminated if you contact a periodontist at our clinic in a timely manner.
Laser gum treatment
Elimination of periodontal problems is also carried out using laser equipment. The method allows you to deeply disinfect all gum tissue and the oral cavity. The laser has a powerful regenerating effect. Its use is safe and appropriate for periodontitis. The procedure has fewer contraindications and is accessible to most of our patients. After the procedure, rehabilitation is faster and easier. Laser restoration of teeth and gum tissue is an innovative method that is widely used in Europe.
Therapy is carried out in a course prescribed by the doctor. Already after the first procedure, partial restoration of tissue cells occurs. The laser provides non-contact, minimally invasive dental care and positive results. The technology allows a specialist to eliminate all problems with the disease, as well as eliminate stomatitis and gingivitis.
Complex treatment has a more positive result. The use of antibacterial medications, laser exposure, and surgical curettage make it possible to forget about the disease. Statistics show that complex therapeutic methods are 65% more effective than monotherapy.
Methods of therapy
Already with the primary signs of the development of inflammatory processes in the gums, it is extremely necessary to contact a medical institution, where an accurate diagnosis will be carried out and the optimal treatment regimen for the pathology will be selected.
Depending on the stage of progression of the disease, the doctor will clean the tooth surface from excess deposits, localize the abscess, and take preventive measures. As a rule, therapy is carried out comprehensively and may include a number of methods and techniques.
We learn about why it is important for treatment to be prescribed by a dentist in this video:
https://youtu.be/SNrZ9JnOsCI
Medications
The modern pharmacological market is able to offer a number of effective drugs to eliminate this problem in the form of tablets, ointments, creams and sprays.
Holisal
Available in gel form. The main components are Cetalkonium chloride and salicylate. These substances perfectly eliminate pathogenic microorganisms and effectively relieve pain.
3-4 minutes after application, your health improves significantly. The approximate cost in a pharmacy chain for a 10 gram package is about 300 rubles.
Is treatment of flux with antibiotics always indicated? Find out about this in the article prepared for you. And here we will explain why the jaw clicks when opening the mouth.
"Forest Balm"
It is used as a complex remedy in the fight against pathology. Used as a rinse. It is characterized by a rich medicinal composition based on five components of medicinal plants. It disinfects well and localizes foci of infection.
Completely natural based. The cost, depending on the manufacturer, varies on average across the country from 80 to 120 rubles for 250 - 280 ml. The effect is achieved with regular use.
Balm “Asepta”
The very name of the product suggests that we have an excellent antiseptic. Prevents the spread of infection, kills germs. Requires regular use. Localizes bleeding.
The composition includes the components benzydamine and chlorhexidine. An innovative drug with an improved spectrum of action. Price – approximately 380-400 rubles.
Traditional medicine recipes
Almost any inflammation of the gums is in the nature of infection, and traditional methods of treatment at home, proven by many years of practice, will perfectly help to cope with it.
Salt
It relieves swelling well and soothes soft gum tissue. Suitable in any form - both sea and regular, table. Preparation: 1 teaspoon per 200 g of warm boiled water. Rinse every 2 hours until the situation improves.
It is recommended to rub sea salt into the infected area every day, as well as treat the jaw row with a toothbrush dipped in this solution. Relief occurs within 2-3 days.
Celandine
Grind a tablespoon of dry herb, pour in 250 g of water and boil over low heat for 20 minutes. Leave for an hour. Strain well. Rinse the cavity in the affected area. Fast and pronounced effect. After a few days, the pathology will disappear without a trace.
St. John's wort
It has a powerful healing effect. Suitable for the treatment of any pathological processes in the oral cavity. Brew a strong decoction and leave overnight. Once a day, before going to bed, rinse not only your gums, but also your throat.
You can use a pharmacy tincture and dilute the concentration recommended on the package. If the disease is not advanced, positive dynamics are observed after several procedures.
Aloe
Effective in the form of a paste made from fresh leaves of a plant that is at least 3 years old. Bring the mixture to a boil in an enamel container, strain and cool. Leave for half an hour. Rinse 5-6 times during the day, store in a dark place.
The drug is effective in combination with drug therapy as an auxiliary treatment.
Coffee
The preparation process is long, but the result will bring the desired relief quickly enough. As a rule, after several manipulations, the infection stops, the pain goes away, and the swelling subsides. Promotes soft tissue regeneration.
Lightly fry the grains and grind to a powder. Mix with powdered sugar in a ratio of 1:2. Massage your gums 3 times a day. You can do this with your finger, or with a toothbrush.
After this, treat the cavity with a disinfecting solution. The course of treatment until complete recovery is several weeks, while the symptoms disappear almost immediately.
Use of antibiotics
At the stage of disease progression, taking antibiotics is a necessary condition for its elimination. The choice of drug should be made only by a doctor in accordance with the nature of the occurrence, as well as the severity of the pathology.
Metronidazole
A broad-spectrum drug with a pronounced antibacterial focus. An excellent antimicrobial agent for localizing foci of damage by pathogenic microorganisms. The course of therapy is 7-10 days.
The main component of the product is oxyethyl. Auxiliary components – sodium chloride, disodium acid. The cost of a blister with 20 tablets is from 70 rubles.
Lincomycin
Representative of the glycosamide group. An effective therapeutic drug. Duration of treatment – 10 days. Available in tablets, capsules and injections. Suitable for the treatment of any inflammation of the oral cavity, has contraindications.
Quickly relieves sepsis and is indicated for osteomyelitis. Ingredients: lincomycin component. Cost: injections (10 ampoules) - from 50 rubles, capsules (20 pieces) - from 120 rubles, tablets (packaging) - about 160 rubles.
Clindamycin
A derivative form of the antibiotic described above. Release form: capsules, injections. Ingredients: hydrochloride component of clindamycin.
Indications: infections and inflammations of the oral cavity and gums, acute forms of dental diseases. The price of a capsule is from 160 rubles, ampoules – from 600 rubles.
We will tell you how to treat submandibular lymphadenitis in children in a separate article. By going to the following address: https://dentist-pro.ru/lechenie/bolezni-polosti-rta/stomatit-bpr/zarazno-li-zabolevanie-i-kak-s-nim-borotsya.html - you will find out if it is contagious stomatitis in children.
In this review you can find a recipe on how to get rid of caries at home.
Gum pain around wisdom tooth
We all know that wisdom teeth are a headache for all humanity. They grow from 18 to 25 years, sometimes longer. Moreover, they often do it either very slowly or too painfully, sometimes at some unimaginable angle. Sometimes a situation arises when a hood of soft tissue grows over the tooth. “Biological debris” begins to accumulate between it and the tooth, including waste products of bacteria. Ultimately, you have to resort to surgical treatment methods - excision of the gums in this area.
Hood over wisdom tooth
In most cases, pain in the gums is associated with the teething process itself. Unfortunately, it is long-lasting and can be accompanied by bursts of inflammatory processes, with an increase in temperature to subfertile levels and other unpleasant symptoms. This is not to mention the constant aching pain. It is impossible to cure the natural process for obvious reasons. But warm rinses and NSAIDs help relieve the condition.
However, you should not abuse Nurofen, Nimesulide and other drugs. They have an extensive list of side effects.
Surgical and non-surgical treatment methods
To prevent gingivitis, as well as in the absence of an acute form, the following methods can be used:
- carrying out professional cleaning. The procedure is carried out every six months. Professional cleaning will reduce the risk of developing pathology;
- special cleaning and polishing. By polishing the roots of the tooth, plaque and stones are removed.
Professional cleaning and polishing is carried out under local anesthesia
Advanced forms of the disease are treated with surgery:
- flap surgery. The void between the gum and tooth is reduced by raising the gum. During the procedure, plaque and tartar are removed;
- tissue grafting operation. In order to strengthen the gums, palatal tissues are replanted with the gums;
- tissue restoration. The operation is performed when the bone that supports the teeth is severely weakened. A special cellular material is planted in the area that is located between the bone and gum.
How to treat gingivitis
The treatment of gingivitis uses a set of medical measures aimed at getting rid of painful symptoms, eliminating the causes of pathology and restoring gum health.
An integrated approach to treatment
It consists of a combination of local and general types of therapy. This allows you to successfully cope with different forms and types of pathology. Treatment includes:
- Removing dental plaque. This is extremely important for the catarrhal variety, because it is plaque, almost 100% consisting of pathogenic microflora, that is considered the cause of inflammation. Ultrasonic cleaning, which is carried out in a dental office, allows you to completely get rid of deposits. This cannot be done using traditional methods or a homemade toothbrush. At the end of the procedure, the enamel is polished, which in the long term makes it possible to reduce the rate of formation of dental plaque.
- Anti-inflammatory treatment. This is the next stage, which consists of rinsing the mouth with special compounds, as well as applying bandages with medicinal ointments, and performing other procedures - in the clinic and at home.
- Use of special medications. Their choice is determined by the type of gingivitis, the form of its course and other factors. These could be, for example: antibacterial, antifungal or antiviral medications, which will need to be used both externally and internally.
- Sanitation of the oral cavity. It consists, first of all, in removing carious lesions, which are a constant source of infection. This is performed immediately after the acute symptoms of gingivitis are relieved, and allows you to minimize the risk of relapse.
- Eliminating circumstances that aggravate the impact of infection:
- getting rid of traumatic factors (replacing dentures and structures);
- correction of the frenulum attachment (performed using plastic surgery).
- Learning how to properly brush your teeth. That’s right, because gum inflammation indicates, among other things, that daily oral care was not carried out properly. If you do not pay attention to this, the result of treatment will not last long. To correct the situation, the dentist will advise which brushes are best to use, how to brush your teeth correctly, and also recommend the most suitable toothpastes.
- To stimulate the regeneration process, keratolytics (agents that cause exfoliation of dead cells) are used. For this purpose, applications with sea buckthorn and rosehip oil, as well as special gels, are recommended.
- Vitamin complexes, adaptogens (to increase the body’s nonspecific resistance to harmful influences), antioxidant drugs, as well as medications that help improve metabolism are prescribed as general tonics
An integrated approach forms the basis of treatment for gingivitis. Other methods only complement it.
Individual approach
Properly selected therapy necessarily takes into account all pathologies of the body and other circumstances characterizing the general health and immune status of a person. Great importance is attached to:
- severity and etiology of gingivitis;
- age factor.
Systematicity
To maximize periods of remission and reduce the likelihood of exacerbations, there are intermediate treatment courses.
Gingivitis can be cured in 7-10 days if it occurs in an acute form and therapy is started in a timely manner.
Getting rid of gum inflammation is the last chance to stop the process of destructive periodontal changes and prevent more serious pathology, which ends in the loosening and loss of normal teeth. It should be borne in mind that periodontitis is much more difficult to treat. Therefore, if you have problems with your gums, you should immediately rush to the doctor.