Reflux gastritis develops due to the fact that the sphincter muscles begin to work in the wrong mode. As a result of the pathology, the contents of the duodenum are released into the patient’s stomach. Reflux is considered a form of chronic gastritis, and therefore requires clear treatment. Diet for reflux is a mandatory part of therapy.
The disease, or rather the discharge, is filled with harmful acids, which significantly damage the mucous-type lining in the patient's stomach, which is the main cause of gastritis.
Almost everyone has heard about gastritis, but not about its reflux form. Therefore, it is important to understand in detail what it is, as well as what diet is necessary for reflux gastritis .
Important! Diseases associated with the gastrointestinal tract require in-depth analysis. That is why it is important not to come up with a treatment for yourself, but to contact a specialist who will think through all aspects of therapy, including dietary nutrition.
Symptoms of the disease
The problem in detecting and further working on this problem is that the pathology itself, as a rule, occurs without pronounced symptoms. However, in some cases, the following signs of the disease are present:
- Dizziness, a state of general weakness.
- Reluctance to eat, weight loss.
- Painful sensations in the stomach, especially after eating.
- A feeling that the stomach is full both during and immediately after eating. Often accompanied by bloating, belching, and a bitter taste.
- Constipation/diarrhea, which may alternate.
- Sometimes severe dry mouth occurs, causing small ulcers to appear on the skin around the lips.
- Nausea and vomiting, which is mixed with bile.
Symptoms, treatment and diet for reflux gastritis should be taken into account by everyone who suffers from problems with the gastrointestinal tract. The thing is that quite often patients do not even suspect that there is a problem. Due to the absence or weak manifestation of signs, this is understandable.
Important! Regularly conduct complete examinations with a gastroenterologist, immediately contact a specialist if there are deviations that may seem unimportant to you. Any little things can signal a serious pathology.
Symptoms and treatments for gastroduodenal reflux
coating on the tongue (yellow);
pain in the abdomen. Causes of pain: activity of the biliary tract and intestines, which leads to spasm;
heartburn (discomfort, burning behind the sternum). In some people, this may be expressed by a feeling of warmth, pressure, or fullness in the abdomen. Heartburn occurs with any acidity, but most often with increased acidity;
belching (food from the stomach entering the mouth). There are voluntary and involuntary belchings. Belching is accompanied by the release of sound and the release of air (from the mouth).
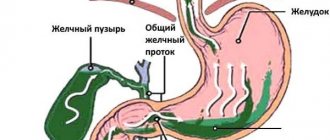
This is due to the fact that bile contained in the intestines (duodenum) goes back to the stomach. This happens because the pressure in the intestines increases, in particular in the duodenum.
What complications does duodenogastric reflux cause?
chemical-toxic gastritis (type C),
reflux gastritis,
gastroesophageal reflux disease,
ulcer.
Symptoms and treatment of complicated duodenal gastric reflux. The disease leads to the formation of ulcers. A mixture of bile with pancreatic juice is an aggressive environment that destroys the gastric mucous barrier. Moreover, over time, duodenogastric reflux causes metaplasia of the gastric epithelium. In addition, lysolecithin is formed, which has a toxic effect on the mucous membrane, gradually damaging it.
Diagnostics
ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity;
determination of the degree of acidity. This is very important, as it will allow the specialist to establish an accurate diagnosis and to what extent the disease is expressed;
conduct electrogastroenterography;
Treatment of the disease can only be prescribed by a specialist, based on the result confirmed by the examination.
Gastroduodenal reflux is a process when bile from the duodenum enters the stomach cavity. This pathological condition can be caused by a number of reasons. It has its own symptoms and, fortunately, can be successfully treated.
In the normal state of the gastrointestinal tract, food moves in only one direction. Special valves do not allow the reverse process. Only vomiting can serve as a protective mechanism for the body, which is trying to get rid of toxins. The lower part of the stomach is connected to the duodenum by the pyloric sphincter, a ring-shaped muscle.
Causes of pathology
The cause of the release of bile into the stomach can be any malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract. But most often it is:
- Duodenitis in the chronic stage. This is an inflammatory process of the walls of the duodenum. It swells, creating pressure for the contents, which are thrown back into the stomach;
- Helicobacter pylori bacterium;
- Operations. If during the intervention the fibers of the pyloric sphincter were damaged, then it will never be able to fully perform its functions;
- Taking medications (muscle relaxants, antispasmodics) also relaxes the pylorus itself, and even bile penetrates through a small lumen;
- Mechanical pressure on the duodenum - hernias, injuries, pregnancy, tumors of the peritoneal organs - all of them can cause the release of bile into the stomach. In fact, this mechanism can be triggered even due to tight compression by the belt.
The clinical picture of the pathology with obvious signs appears only with prolonged and frequent reflux. It is typical that the pain does not have a clear location. Heartburn - it is often associated with the fact that due to strong pressure, bile enters the esophagus, irritating its walls. The patient is bothered by belching, sometimes with a bitter taste in the mouth due to the presence of bile in the stomach.
The most obvious sign of gastroduodenal reflux is vomiting with bile or a yellow coating on the tongue. It is these symptoms that people pay attention to when taking treatment with folk remedies. Indirectly, pathology can be indicated by a feeling of fullness in the abdomen, discomfort and pain.
The initial stage of the disease usually does not manifest itself with any symptoms, and gastroenterologists say that sometimes duodeno-gastric reflux occurs in healthy people.
MORE ABOUT: Swiss diet for weight loss
The pathology itself does not pose a danger to the body, but if it is observed frequently and is not treated in a timely manner, it can lead to serious diseases of the duodenum, stomach and esophagus.
For diagnosis, the patient needs to undergo a series of tests: acidity level testing, endoscopy, ultrasound. This data is quite enough for the doctor to make a final diagnosis.
Medication and folk treatment
Although duodenogastric reflux can be successfully corrected with both medications and folk remedies, therapeutic measures can take a long period for the patient.
Treatment includes two main stages: elimination of the cause of reflux and symptomatic therapy. If the culprit is the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, then treatment involves taking antibiotics. Only the last part is usually common to everyone.
It includes:
- Taking selective prokinetics (Cisapride, Motilium). They are aimed at increasing the tone of the sphincters, speeding up the process of emptying the stomach in order to rid it of the irritating properties of bile as soon as possible;
- Taking antacids (Almagel, Maalox) - they reduce acidity in the stomach well, but you need to drink them quite often;
- Taking proton pump inhibitors (Nexium, Pariet) is an alternative to antacids, but more expensive. You need to drink them a little less often, but they also reduce the acid level of gastric juice well and protect the mucous membrane from harmful effects;
- Taking ursofalk - it is especially effective for vomiting with bile or bitter belching. The drug changes the form of bile acids to water-soluble ones.
In addition, the patient will need to adhere to a diet specially developed by the doctor and take medicinal mineral water of the required composition.
If duodeno-gastric reflux has not yet reached the chronic stage, then it is treated with minimally invasive surgical methods. For example, laparoscopic correction can solve the problem of pyloric insufficiency.
In addition, treatment requires compliance with the following recommendations:
- Avoid wearing wide waistbands.
- Follow a diet, exclude harmful foods from the diet that provoke symptoms, saturate the body with vitamins and bile-secreting foods: oatmeal cookies, crackers, rye crackers.
- There should be three main meals a day, with several snacks in between. All portions should be small while on a diet, and even after it you should not overeat.
- For another hour after the main meal, you should not take a horizontal position of the body or engage in physical exercise, in order to avoid the occurrence of painful symptoms.
- It is important to give up alcohol and smoking.
- The diet involves drinking a sufficient amount of warm liquid - herbal teas, compotes, decoctions.
- You need to spend more time in the fresh air, monitor your lifestyle and the strength of your symptoms over time.
Sometimes patients supplement drug therapy with folk remedies to combat pathology, but it is better to coordinate them with a doctor.
Sometimes the symptoms are not obvious, or reflux has not yet developed. In this case, it is treatment with folk remedies and diet that will help normalize the condition of the stomach.
Consequently, duodenogastric reflux is not an independent disease, but only a consequence of one or another reason that caused the release of bile from the duodenum into the stomach. Its treatment can be either conservative or surgical, depending on the stage of development of the pathology, but the prognosis is usually favorable.
What should be in the diet
Important! The diet for autoimmune hypothyroidism or other disorders of this type has its own specific characteristics, which is why only a specialist must prescribe nutrition and create a menu.
It is important to understand that another subtype of the disease, duodenogastric reflux, is not always a pathology and can manifest itself in a completely healthy person. Thus, the problem has been recorded in a significant number of people at night, during sleep. However, if acidity increases by more than 5 percent per day, then such a deviation is already considered pathological and requires special treatment. You also need a diet for duodeno-gastric reflux .
Diet food
Almost all deviations from the norm that are associated with the gastrointestinal tract are accompanied by therapeutic nutrition. This integral part of therapy allows you to restore the correct flow of all processes in the body. This disease is characterized by specific symptoms, so all treatment is aimed at restoring motility function in the intestine. In addition, the treatment ensures the normalization of microflora, binds bile acids, and also neutralizes them. All this helps reduce the negative effect on the gastric walls.
A diet for gastric reflux gastritis works exclusively in conjunction with drug treatment. Only in pairs can therapy restore the body and bring all systems into proper condition. The diet for neutralizing acids should be as gentle as possible, therefore it cannot include the following foods and dishes:
- High fat content.
- Too spicy and spicy.
- Salty.
- Fried.
- Canned, pickled.
- Smoked.
All of the previously listed products can cause severe irritation of the gastric mucosa and also cause damage to it. However, in addition to this, the diet for gastric reflux excludes components that can provoke dumping syndrome. These products include honey, milk porridge, sugar and jam. Alcoholic drinks and cigarettes are completely prohibited.
Dietary nutrition for this pathology is characterized by a number of specific requirements:
- Clear meal schedule by the hour. It should be the same every day. It is worth eating often and in small portions.
- The food consumed should be at room temperature, and be sure to avoid very hot and cold foods. This also applies to drinks.
- Drinking is prohibited during meals. This can be done before/after 15 minutes.
- Based on acid levels, drinking mineral water is often recommended.
Important! The diet menu for gastric reflux gastritis should be as thoughtful and balanced as possible. Therefore, it is better to have it compiled by a professional. Remember that treatment of pathology without proper nutrition is usually ineffective and very long-lasting. In addition, harmful products can cause serious deviations and worsening of the condition.
Next, it is worth considering the list of those dishes that are acceptable and recommended for eating with this pathology. These include:
- Slimy types of soups that are prepared from certain types of cereals.
- Not a strong brewed tea, which is best diluted with milk.
- Dairy types of soups, but with ground cereal.
- Kissel/puree/jelly (necessarily from fresh fruits and berries that are well ripened).
- Vegetable-type soups must be pureed, and the broth must be weak.
- Boiled meat, always finely chopped or ground.
- Porridge with milk – preferably slightly viscous and pureed. It is imperative that the cereal is well boiled.
- Boiled or steamed fish.
- Eggs - you can cook them soft-boiled, steamed omelet or use only whites.
- Whole milk, cream.
- Vegetable puree. Potatoes, cauliflower, zucchini, carrots, etc. are suitable for gastroesophageal reflux diet.
- Fresh, non-sour cottage cheese, which is well ground.
- Stale bread made from white flour.
Remember that the best solution is a balanced and thoughtful diet prepared by a specialist. Only he can take into account all the characteristics of a particular organism and know which products are prohibited for a particular person. For example, dairy products are allowed in the diet, but there are patients who cannot eat such foods. Therefore, it is so important to see a doctor who will know about these features.
Nutrition rules
The diet for duodeno-gastric reflux involves the patient observing the following principles:
- Eat small meals at least 4 times a day.
- Do not eat food 3-4 hours before going to bed.
- Don't overeat.
- Do not engage in active sports after meals.
- Avoid eating very cold or hot foods. The temperature of prepared dishes should vary within 50 degrees.
- The main emphasis in the diet is on carbohydrates and proteins.
- Monitor your drinking regime. Drink at least 2 liters of liquid per day.
- If the pathology provokes severe pain, it is better to eat while standing. After eating food, it is not recommended to sit or lie down for about 2 hours.
- During an exacerbation, exclude raw fruits and vegetables from the diet. Preference should be given to soups and porridges with a slimy consistency.
- Chew food thoroughly.
Doctors recommend that patients keep a food diary. With its help, it will be possible to control the body's reaction to certain foods, which will allow you to eliminate foods that can cause belching or heartburn.
Before eating, it is recommended to drink a glass of purified water. With this you will be able to avoid overeating, which provokes a number of complications. Rose hips and chamomile, from which a decoction is made, will help relieve the inflammatory process and speed up recovery. The resulting product is drunk half a glass in the morning and evening. You are allowed to drink non-carbonated mineral water, weak black tea, jelly and compotes from non-acidic fruits. However, it is not recommended to add sugar to them.
Duodeno-gastric reflux - signs
The symptoms of GHD are in many ways similar to those of other diseases of the digestive tract. This is explained by their relationship. Chronic duodeno-gastric reflux can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- heartburn, which usually occurs after eating;
- nausea and possible subsequent attacks of bile vomiting;
- belching with air or a sour taste;
- bloating and feeling of fullness in the abdomen;
- cutting or cramping pain in the abdomen;
- constant bitter taste in the mouth;
- the appearance of a yellowish coating on the tongue.
Very often, duodeno-gastric reflux manifests itself as pain. Unpleasant sensations are usually concentrated in the upper abdomen. The pain is recurrent and generally tolerable. But some patients complain of too intense sharp and burning pain in the pit of the stomach, appearing almost immediately after eating, which unsettles them for several hours.
What should you not eat?
With reflux, patients will need to avoid foods such as:
- spices and herbs;
- legumes;
- mushrooms;
- spinach;
- radish;
- marinades and pickles;
- smoked meats; canned food;
- fatty and spicy foods;
- citrus;
- sauces;
- sweets;
- eggplant;
- chocolate;
- tomato;
- dill and parsley;
- fatty types of fish and meat;
- sunflower seeds.
Return to contents
Sample menu
The diet for reflux esophagitis is determined by the doctor, but each patient should know what approximate diet he will adhere to. Consider a sample menu for 3 days:
- First day:
- Breakfast:
- buckwheat porridge cooked in water;
- veal meatballs cooked in a steamer;
- weak black tea.
- Lunch:
- cottage cheese casserole with permitted fruits;
- berry juice.
- Dinner:
- lean borscht;
- turkey potato casserole;
- vegetable mix;
- compote.
- Afternoon snack:
- biscuits;
- low-fat yogurt.
- Dinner:
- hake fillet baked in the oven;
- tomato and cucumber salad dressed with olive oil;
- Herb tea.
- Second day:
- Breakfast:
- carrot cutlets served with low-fat sour cream;
- green tea.
- Lunch:
- fruit salad with added bananas and apples;
- jelly.
- Dinner:
- cauliflower soup;
- pike perch fillet baked with vegetables;
- rosehip decoction.
- Afternoon snack:
- baked pumpkin;
- freshly squeezed juice from non-acidic fruits.
- Dinner:
- zucchini boats;
- a glass of kefir.
- The third day:
- Breakfast:
- oatmeal with honey and fruit;
- weak tea.
- Lunch:
- biscuits;
- smoothie.
- Dinner:
- vegetable soup;
- chicken soufflé;
- salad of tomatoes and cucumbers, seasoned with vegetable oil;
- mineral water.
- Afternoon snack:
- syrniki;
- tea with mint.
- Dinner:
- steamed omelette;
- vegetable mix;
- a glass of milk.
Return to contents
Healthy recipes
Chicken soufflé
To prepare, you will need to take chicken fillet, 2 eggs, 200 ml of low-fat milk, 1 onion. First of all, the chicken is peeled, cut into small pieces and sent to a meat grinder. The onions are chopped and added to the resulting minced meat. The yolks are separated from the whites and added to the rest of the ingredients. Pour in milk, add a small amount of salt and grind with a blender. Beat the remaining whites with a mixer with a pinch of salt. The resulting protein mass is carefully added to the minced chicken. Baking molds are greased with butter and the soufflé is placed in them. Preheat the oven to 180 degrees and place the molds to bake for 15 minutes. However, the oven cannot be opened at this time, as the soufflé may fall off. When serving, the dish is taken out of the molds, placed on a plate and decorated with fresh vegetables.
Cauliflower soup
The cabbage is separated into inflorescences and sent to boil. Then, the finished vegetable is crushed using a blender and a small amount of water is added to it. Place a piece of butter and 2 tablespoons of flour in a frying pan and fry until golden brown. Then add half a glass of water and stir to get rid of lumps. Cauliflower puree is mixed with the resulting sauce and heated without bringing to a boil. Served with low-fat sour cream.
Gastrointestinal diseases are very common among people of any age. Many people ignore them, unaware of them until the symptoms begin to manifest themselves more aggressively. Because of this, even ordinary gastritis, which is easily treatable, can lead to such serious pathologies as ulcers or gastroduodenal reflux (GDR). This disease significantly worsens the quality of life of patients - they have to deal with unpleasant symptoms after almost every meal. And the lack of proper treatment contributes to the development of complications, which will not be easy to get rid of.
Duodeno-gastric reflux - treatment with folk remedies
This disease can be treated with alternative methods. But still, most experts recommend resorting to them only as part of complex therapy. When diagnosed with duodeno-gastric reflux, folk recipes should be selected by doctors and only after determining the causes of the disease. Otherwise, the patient's condition may only worsen.
How to cure duodeno-gastric reflux with herbs?
Preparation and use:
- Mix the ingredients in any quantity in one bowl. You can use it “by eye”; you don’t need to follow precise proportions in this recipe.
- The herbs are poured with boiling water and infused for 10-15 minutes.
- It is recommended to drink the resulting tea every day, morning and evening.
Treatment of duodeno-gastric reflux with flax seeds
- flax seeds - 1 tbsp. l.;
- water – 100 ml.
Preparation and use:
- The seeds are filled with cool water.
- The mixture should be infused until the seeds begin to swell. At this stage, beneficial mucus begins to secrete from them.
- The resulting liquid should be drunk on an empty stomach, ¼ – ½ glass.
Calamus and sage against duodeno-gastric reflux
- calamus root – 50 g;
- sage – 50 g;
- angelica root – 25 g;
- water – 1 glass.
Preparation and use:
- Take one teaspoon of each dry mixture.
- Boil water and add herbs.
- The medicine needs to sit for about 20 minutes. After that, you can strain it and drink it.
- To make the mixture more tasty, you can add honey to it.
- You need to take the medicine three times a day, an hour after meals.
Why does it happen?
Gastroduodenal reflux is a pathology, the essence of which is the release of the contents of the stomach and duodenum into the esophagus. In half of all recorded cases, this problem is accompanied by an ulcer, duodenitis or gastritis. Pathology develops independently in only a third of all patients. Approximately 15% of patients are not even aware of their condition. Often the problem is discovered accidentally during diagnostic tests.
Pathology develops independently in only a third of all patients
Duodenal reflux often develops due to increased acidity if the motility of the upper gastrointestinal tract is impaired or the protective functions of the mucous membrane are weakened. The disease disrupts the natural defense mechanisms of the esophagus - mucosal resistance and esophageal clearance. The latter means the ability of the physiological function of the esophagus to move contents into the stomach.
Risk factors are smoking, stress, excess body weight, diaphragmatic hernia, taking certain groups of medications, and frequent pregnancies.
Duodeno-gastric reflux - causes
The disease appears when there is a violation of duodenal patency. As a result, the pressure inside the duodenum increases, and the closing function of the pylorus is noticeably weakened. When the pyloric sphincter cannot perform its basic functions, food that has passed on to the next stage of the digestive cycle returns back to the stomach.
As in some cases of gastritis, duodeno-gastric reflux is caused by the following reasons:
- smoking;
- hiatal hernia;
- dysbacteriosis;
- inflammatory processes in the pancreas or bile;
- taking medications that reduce the tone of the smooth muscles of the esophagus;
- helminthic infestations;
- abnormal development of the duodenum;
- congenital syndromes of incomplete intestinal rotation and short bowel;
- lack of the hormone gastrin;
- pregnancy.
The phenomenon of duodenogastric reflux has several main risk factors. In most cases, the problem develops due to:
- excessive consumption of fatty and spicy foods;
- unbalanced diet (dry food);
- irregular meals;
- taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or antispasmodics for too long;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- pancreatitis;
- pancreatic insufficiency.
What are the signs of the disease?
Duodeno-gastric reflux has symptoms typical of gastrointestinal diseases. This makes its manifestations similar to other pathologies, which complicates diagnosis a little, but proper differentiation allows you to identify the disease quite quickly.
Duodenal reflux often develops due to increased acidity
Main symptoms of GHD:
Less commonly, patients complain of hoarseness, cough, pain in the chest area, which gets worse when bending over. In more severe cases, swallowing impairment (dysphagia) is observed, which can occur due to difficulty in motility or narrowing of the esophagus. Sometimes, against the background of pathology, inflammation occurs and body temperature rises.
Risk factors include smoking, stress, excess body weight
Causes
The gastrodigestive tract is a conveyor belt, starting from the oral cavity and ending with the rectum. The traffic here is one-way. In some parts of this system, a reverse flow is observed - reflux. The aggressive, opposing environments of the gastrointestinal tract mix, causing a number of other diseases and painful sensations. Causes of disruption of the physiological process:
- Taking medications, especially analgesics, antispasmodics, which paralyze the muscles of the sphincters (valve). This begins the free flow of gastrointestinal fluid in all directions, which causes disease.
- Unhealthy diet: fried, fatty foods, animal products, coffee can provoke diseases of the stomach and esophagus.
- Smoking and drinking alcohol have a detrimental effect on the stomach and the walls of the esophagus.
- Eating large meals stretches the stomach and causes reflux.
Classification
With duodenal reflux, pancreatic juice mixes with bile. As a result, a liquid with very aggressive properties is formed, which negatively affects the condition of the gastric mucosa. The composition of the substance is so caustic that it destroys its protective barrier. Gradually, the shell is damaged, these changes lead to serious consequences. The degree of damage determines the forms of DG reflux:
- Superficial. As a result of indigestion, the gastric mucosa is damaged, but for now only its outer layer is affected.
- Catarrhal. The mucous membrane is affected over the entire area. Most often, swelling is observed. Over time, the inflammatory process develops. In response to allergic reactions, long-term use of certain drugs causes so-called catarrhal reflux.
- Erosive. It often occurs if the patient does not adhere to the doctor’s recommendations regarding nutrition and regimen. For example, alcohol consumption or frequent stress can lead to this. As a result, small ulcers appear on the walls of the stomach.
- Biliary. This form of the disease develops when bile excretion is impaired. In severe cases, it can lead to liver dysfunction.
With duodenal reflux, pancreatic juice mixes with bile
In addition, with gastroduodenal reflux it is customary to distinguish the severity of the pathology. It depends on the duration of the process. Throughout the course of the disease, symptoms may change. During diagnosis, the severity of GHD is determined by analyzing contents from different parts of the stomach.
Classification by severity:
- I – small amount of bile in the stomach, clinical manifestations are mild or absent;
- II – the release of bile increases, the walls of the stomach become irritated, sometimes inflamed, and the first signs of illness appear;
- III – the symptoms of the disease are already clearly observed; a disruption in the process of food digestion may occur.
The progression of the disease is corrected when certain conditions are met. High-quality diagnostics will help determine the severity of the pathology. If patients receive timely help and strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations, then the prognosis for the treatment of duodenogastric reflux is most often positive.
During diagnosis, the severity of GHD is determined by analyzing contents from different parts of the stomach.
Main reasons
Various causes and provoking factors can provoke duodeno-gastric reflux. Experts consider the following:
- congenital or acquired insufficiency of the pyloric segment of the stomach;
- severe disruption of gastric motility, as well as the duodenum;
- a significant increase in pressure in the intestines;
- long-term use of certain subgroups of medications;
- excessively aggressive effect of the contents of the duodenum (DPC) on the stomach tissue.
Duodenogastroesophageal reflux often accompanies many chronic gastrointestinal pathologies, for example, gastritis, ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane, malignant neoplasms, impaired tone of the sphincter of Oddi, duodenostasis.
Often, reflux esophagitis develops in people who have undergone surgical interventions on the biliary tract - bile ducts, duodenal suturing - or gastroduodenal ulcers.
Numerous studies have convincingly proven that bile acids, as one of the components of duodenal juice, not only inhibit the protective barrier of mucous tissue, but also have the ability to provoke reverse diffusion of hydrogen molecules. All this leads to hypersecretion of gastrin by the antral glands - acidity parameters increase many times over. Reflux duodenitis continues to progress without adequate medical care. In severe cases, it becomes the root cause of various complications.
Diagnostics
Despite the fact that the symptoms of the disease are similar to those of many other gastrointestinal problems, an experienced specialist can easily make a diagnosis. If you suspect a disease, it is important to immediately carry out all the necessary tests. Previously, the leading research method was fibrogastroduodenoscopy, which is now used much less frequently.
In addition, the patient must undergo:
- analysis of daily pH-metry, which determines the acidity of different parts of the stomach;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- X-ray of the stomach and duodenum with contrast;
- electrogastroenterography.
Depending on the patient's complaints or the doctor's decision, additional studies may be prescribed. The examination is carried out comprehensively, that is, it includes different methods - in this way the diagnosis will be determined more accurately. The success of treatment of duodenogastric reflux directly depends on this.
The examination is carried out comprehensively
Duodeno-gastric reflux – degrees
As with any other disease, GHD has varying degrees of development. Depending on how long and actively the disease has progressed, the manifestations of various symptoms change. The degree of duodenogastric reflux is determined by the amount of bile acids contained in different parts of the stomach. And the earlier the disease is diagnosed, the easier it will be to cope with it.
DGR 1st degree
The “simplest” degree is the initial one. Duodeno-gastric reflux of the 1st degree is diagnosed when a minimal amount of bile is detected in the pyloric gastric section adjacent to the sphincter. Symptoms in the first stage may not appear at all. And if signs do arise, most patients do not pay attention to them, believing that the discomfort appeared as a result of overeating or eating “on the run” and will soon pass.
DGR 2nd degree
Many people learn about their diagnosis just when the disease enters the second stage. Duodeno-gastric reflux of the 2nd degree is diagnosed in those patients in whom bile is found in the higher parts of the stomach - in the antrum or fundus. At this stage, the symptoms acquire clear outlines and constantly remind themselves, which forces the patient to consult a specialist.
DGR 3rd degree
This is the most complex and advanced form of the disease. Severe duodenogastric reflux is determined when the contents of the duodenum reach the fundus of the stomach and the lower esophageal sphincter. The third stage is characterized by the manifestation of all the main symptoms. Moreover, they are all clearly expressed and cause the maximum amount of discomfort.
Treatment
Diagnosis and therapy of this disease require an integrated approach. Pharmacological treatment will undoubtedly have a positive effect, but without a special diet it will be unstable, and after some time the pathology will again make itself felt. The goal of therapy is to normalize the motility of the stomach and duodenum and improve the ability to clot bile acids.
With the help of pharmacological treatment, pain relief, stimulation of motility, and also mitigation of the effect of bile on the stomach environment are produced. Drugs are prescribed to eliminate symptoms - heartburn, pain, flatulence, and so on. The duration of treatment is usually from one and a half to two months. In especially severe cases, therapy is longer - up to six months. The following pharmacological groups are used:
- antacids;
- H2-histamine blockers;
- proton pump inhibitors.
Medicines to relieve symptoms – heartburn, pain, flatulence
Cases when the body does not respond to conservative treatment methods are rare. However, if this happens, as well as when certain complications develop, they resort to surgery.
Successful therapy is impossible without diet. In addition to normalizing nutrition, treatment of duodenogastric reflux requires:
- normalization of body weight;
- quitting drinking alcohol and smoking;
- avoiding heavy physical activity;
- combating physical inactivity;
- regular feasible exercises;
- hiking in the fresh air.
Duodeno-gastric reflux - treatment with drugs
The main goal of drug therapy for GHD is to restore normal functions of the gastrointestinal tract and control the motor-evacuation function of the affected parts of the digestive system. How to treat duodenogastric reflux should be determined by a specialist. Mostly doctors prescribe:
- Prokinetics - Cerucal or Domperidone - which promote rapid digestion of food, its absorption and movement through the ducts of the small intestine.
- To protect the gastric mucosa from the irritating effects of the contents of the duodenum, Omez and Nexium are used.
- Such remedies as Almagel, Phosphalugel, Gaviscon help to cope with heartburn.
- Serotonin receptor agonists – mosapride citrate – help to enhance peristalsis of the upper gastrointestinal tract.
- UDCA (ursodeoxycholic acid) preparations are effective, which make the contents of the duodenum thrown into the stomach water-soluble and less aggressive (in practice, this leads to the elimination of bitter belching, vomiting, and pain relief).
Diet for GHD
The key to treating many diseases is proper nutrition. This is especially true for gastrointestinal diseases. The Harvard School of Medicine determined the influence of the esophageal sphincter on the occurrence of duodenogastroesophageal reflux. Some foods with GHD not only irritate the walls of the stomach and intestines, but also injure the sphincter.
In addition to limiting the consumption of certain types of food, the diet for GHD has some recommendations regarding diet and cooking:
- preference should be given to food boiled in water, steamed, or baked;
- the temperature of the dishes is strictly warm, not hot or cold;
- fractional meals - 5-6 meals per day;
- it is necessary to exclude all acidic foods, including fermented milk and certain fruits;
- eat chopped food;
- You need to chew each piece very carefully;
- completely eliminate the possibility of overeating.
Some foods with GHD not only irritate the walls of the stomach and intestines, but also injure the sphincter
You can make a list of “bad” foods yourself by observing your condition and recording the results in a notebook. After eating, it is advisable to avoid physical activity and sudden movements for 30-60 minutes. Replacing your usual food with pureed porridge and pureed soups will help reduce the amount of bile secreted. It is allowed to eat low-fat fish and meat. Although fermented milk products are prohibited, milk and curdled milk are allowed.
Which products will be beneficial and which will be harmful?
Symptoms of the disease almost always occur after eating. But it is not enough to simply give up foods that cause heaviness in the stomach or heartburn. A therapeutic diet involves a gentle effect on the digestive system and at the same time contains all the beneficial substances necessary for the body. Here is a short list of foods that are allowed to be consumed:
Replacing your usual food with pureed cereals and pureed soups will help reduce the amount of bile secreted.
- ground porridge (rice, pearl barley, buckwheat, oatmeal);
- puree soups with weak broth;
- steam omelette;
- fish, always lean;
- fresh whole milk;
- low-fat cottage cheese, casseroles based on it;
- lean meat, preferably in the form of souffle, steamed meatballs or cutlets;
- pureed vegetables;
- butter and vegetable oils in small quantities;
- herbal teas;
- dried fruits compote;
- yesterday's bread.
It is advisable to consume the above products in the form of purees. Cook food by steaming, in the oven, or boiling it in water. Thus, it does not irritate the mucous membrane, does not contribute to increased acidity and the release of bile.
A therapeutic diet involves a gentle effect on the digestive system
Some products are recommended to completely eliminate or reduce their consumption. We list the products that are not recommended for patients with duodenogastric reflux. Sometimes their use is acceptable, but is strictly prohibited during an exacerbation:
- sour fruits, especially citrus fruits;
- spicy;
- smoked meats;
- marinades;
- roast;
- sauces;
- spices;
- rich broths;
- honey;
- jam;
- vegetables that cause fermentation in the intestines (for example, cabbage);
- dairy products;
- fresh bread;
- alcohol;
- carbonated drinks;
- coffee, strong tea.
You should avoid junk food during an exacerbation period.
These products are more difficult to digest, promote the secretion of digestive juices, and coffee completely stops the processes occurring in the stomach. You should avoid such food during an exacerbation period. Before returning any foods to your diet, you should consult a gastroenterologist.
Disease prevention
To prevent the disease from returning, you need to control your weight.
To avoid the occurrence of a pathological process, it is necessary to carry out its prevention in a timely manner. During the period of exacerbation of the disease, the consumption of alcoholic beverages is strictly prohibited.
If a person smokes, this significantly increases the possibility of duodenogastric reflux. That is why smokers are advised to think about their health.
The patient should minimize the consumption of drinks that contain caffeine. In order to prevent the disease, medications should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor.
A person must normalize his diet. For this purpose, it is recommended to exclude salty and smoked foods from the diet. It is also not recommended to eat spicy and fried foods. The patient should consume garlic and citrus fruits in minimal quantities.
To avoid the onset of the disease, a person must constantly monitor his body weight. For this purpose, he must use dietary nutrition. A person’s diet should consist of lean meat and fish, vegetables, dairy products, berries, fruits, vegetable-based puree soups, etc.
Duodenogastric reflux is a fairly serious pathology that occurs against the background of other diseases of the digestive tract. Despite the minimal number of symptoms, an attentive person can notice them.
In this case, he is recommended to seek help from a doctor who can correctly diagnose and prescribe rational treatment using medications and physical procedures. During the treatment of the disease, the patient must go on a diet, which will ensure its high effectiveness.
Noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter to let us know.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine for gastroduodenal reflux is acceptable and often quite effective. The risk of side effects is minimal. It is important to remember that even the most harmless folk remedies must be agreed with your doctor. Most popular recipes:
- The herbs of chamomile, St. John's wort and yarrow are taken in any proportion, poured with boiling water, and infused. Drink twice a day, adding a small amount of infusion to regular tea. The product will relieve symptoms of gastritis and DH , relieves heartburn, and will help with dysbacteriosis.
- Fumiya herb in the amount of 2 tablespoons is poured with 0.5 liters of boiling water. It takes an hour. Take 50 ml every 30 minutes. Prevents the release of bile with vomiting.
- Mix crushed roots of calamus, sage - 50 g, angelica - 25 g. Pour boiling water at the rate of 1 teaspoon of mixture per glass of boiling water. Let it brew for 20 minutes. Take three times a day an hour after meals.
- One tablespoon of flax seeds is poured into 100 ml of cold water. Infuse them until the characteristic mucus is released. Take a teaspoon of the product on an empty stomach.
Constant relapses “wear out” the stomach and can lead to extremely negative consequences
Traditional medicine mainly uses various parts of medicinal plants, it is important to be careful not to cause allergic reactions. Otherwise, folk remedies are safe and have no side effects.
Treatment methods for duodenogastric reflux
When diagnosing gastric dysplasia at an early stage, it can be easily corrected. However, no treatment can change the sphincter. The patient needs to learn to live with this condition and adhere to the clear recommendations of doctors. The main thing that should be done when treating the disease is taking measures to radically change your lifestyle and diet.
Therapeutic diet
For reflux disease, a health-improving diet is prescribed, which is used for disorders of the duodenum and gastrointestinal tract, called table No. 1. Rules for such nutrition:
- With gastric dysplasia, thermally gentle food is needed: neither hot nor cold.
- If you have stomach diseases, you should not eat spicy, sour or fatty foods.
- If you are ill, you should not consume foods that relax the lower esophageal sphincter: sweet carbonated drinks, strong coffee, tea, sour citrus juices.
- To eliminate the disease, it is necessary to avoid foods that cause bloating: legumes, grapes, dairy products.
- Taking mineral waters alleviates the condition at the initial stage of the disease or during its remission. In case of acute inflammatory processes in the stomach, they should not be consumed.
- During treatment of the disease, tea lovers should drink this drink with caution. It is allowed to be consumed chilled and not combined with honey.
- People prone to stomach diseases are recommended to eat at least four times a day in divided portions.
Drug therapy
To treat gastroduodenitis, many doctors prescribe drug therapy for the disease. Its duration is prescribed by the attending physician, but any treatment with drugs should not exceed one month. Reflux therapy consists of:
- Antacid drugs. The most famous: baking soda, Almagel, Rennie tablets, Gastal, Maalox. These medications neutralize the acid in the stomach, thereby relieving heartburn.
- Prokinetics that stimulate gastrointestinal motility and prevent disease: Motilak, Ganaton, Metoclopramide.
- H2 blockers that minimize the amount of acid in the stomach: Cimetidine, Ranitidine, Famotidine.
- Birch sap - homemade recipes
- How to reduce an adult's temperature
- Pregnancy test at home. How to determine pregnancy using traditional methods and test results
Surgery
In advanced cases, when the patient’s condition is accompanied not only by burning heartburn, but also by constant hiccups, patients cannot do without surgical intervention to treat gastric dysplasia. In modern conditions, the operation takes place through punctures, thanks to which the following actions are performed:
- Formation of a new valve from stomach tissue, which prevents the reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus.
- Restoring the normal physiology of the stomach that was before the disease.
Physiotherapy
To consolidate the results of the main treatment, doctors prescribe physical procedures. They are carried out using high-frequency devices “Azor-IK” and “DiaDENS”. The procedure is carried out in the morning, on an empty stomach. The course of treatment ranges from 10 to 20 sessions. When exposed through the skin, physiotherapy:
- Affects pathological changes in the esophagus and stomach: has a healing, anti-inflammatory effect.
- It tones the muscles of the esophagus and stomach, which improves its functioning.
- Increases blood circulation in the walls of the stomach, which triggers metabolic processes in the body.
Folk remedies
To alleviate the condition of reflux disease, many resort to traditional methods. Herbalists successfully treat heartburn using herbs and tinctures:
- Freshly squeezed yarrow juice (aloe) is taken in the amount of 1 tsp. before meals for diseases of the esophagus and stomach. This plant has antiseptic and antimicrobial effects. The juice, getting on the walls of the esophagus, has an enveloping and analgesic effect.
- To reduce stomach acidity, it is recommended to take a decoction of flax seeds. For cooking you need 2 tbsp. l. grains and 500 ml of water. It is necessary to cook over low heat until a sticky state appears. It is recommended to take when cooled, before breakfast. The solution has a beneficial effect on the entire digestive tract, healing ulcers and erosions. In addition, flax is rich in vitamins and vegetable proteins, which are necessary to maintain strength during a therapeutic diet.
- Herbal mixture: chamomile (1 tbsp), St. John's wort herb (1 tbsp) pour boiling water (300 ml) and leave in a water bath. Take half a glass 3 times a day before meals.
Prevention
Even if the treatment was successful, there is a high probability of exacerbation of duodenogastric reflux. Constant relapses “wear out” the stomach and can lead to extremely negative consequences. In order to avoid this, the patient must adhere to certain recommendations for a long time:
- maintaining normal body weight;
- change in diet;
- adherence to diet;
- active lifestyle;
- rejection of bad habits.
Patients have to partly change their lives. For example, they should not overeat, while hunger is also dangerous. To prevent the release of bile, the patient is prohibited from lying on his back for about half an hour after eating.
Over time, patients get used to the new diet and note not only an improvement in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, but also in their physical condition in general. The prognosis of cases detected in the early stages is most often favorable. Conscientious adherence to the prescribed course of treatment and preventive measures will help prevent relapses.
Causes
There are several possible reasons for the reflux of duodenal contents into the stomach cavity, among them the most common and key are:
- Incomplete closure of the pylorus at the border of the duodenum and stomach. Thus, the content is thrown in the opposite direction.
- Chronic form of duodenitis.
- High level of pressure in the cavity of the duodenum. The most common causes of this are certain diseases, including cholecystitis, hepatitis and chronic pancreatitis.
- Chronic or long-term gastritis.
In medical practice, it is customary to divide the causes into two subtypes:
- functional;
- anatomical.
Functional disorders include disorders that are directly related to the work of the sphincter and give corresponding symptoms.
The second group includes tumors that are located at the junction of the duodenum and the stomach. Tumors provoke duodenogastric reflux.
It is these factors that provoke complex lesions in the part of the mucous membrane of the organ that is adjacent to the duodenum.
Important: Under the influence of bile acids, salts, pancreatic enzymes and the contents of the duodenum, gastritis develops in the stomach, which is based on chemical-toxic root causes.