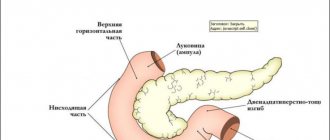
Duodenogastric reflux (DGR) is a pathological process during which bile returns (regurgitation) from the duodenum to the stomach cavity.
GHD of the stomach can be a symptom of a disease of the digestive tract or act as an independent pathology. The passage of bile contents into the stomach cavity is not always accompanied by discomfort.
About a quarter of the entire population does not even suspect that they have such a problem.
People who do not suffer from diseases of the digestive tract may also experience partial reflux of the contents of the duodenum into the stomach cavity.
In this case, the occurrence of this phenomenon is associated with late meals at night or the inability of the pyloric sphincter (the place where the stomach enters the intestines) to relax as much as possible.
This pathological condition is manifested by 2 main syndromes: dyspeptic and pain. What it is, what the causes are and the main aspects of treatment will be described below.
Why does it happen?
Gastroduodenal reflux is a pathology, the essence of which is the release of the contents of the stomach and duodenum into the esophagus. In half of all recorded cases, this problem is accompanied by an ulcer, duodenitis or gastritis. Pathology develops independently in only a third of all patients. Approximately 15% of patients are not even aware of their condition. Often the problem is discovered accidentally during diagnostic tests.
Pathology develops independently in only a third of all patients
Duodenal reflux often develops due to increased acidity if the motility of the upper gastrointestinal tract is impaired or the protective functions of the mucous membrane are weakened. The disease disrupts the natural defense mechanisms of the esophagus - mucosal resistance and esophageal clearance. The latter means the ability of the physiological function of the esophagus to move contents into the stomach.
Risk factors are smoking, stress, excess body weight, diaphragmatic hernia, taking certain groups of medications, and frequent pregnancies.
Causes of duodenogastric reflux
Duodenal reflux can have a number of causes. It becomes a consequence of diseases of the digestive tract such as:
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and intestines (duodenal) in the chronic stage;
- stomach cancer;
- postcholecystectomy syndrome (people who have had surgery to remove the gallbladder);
- resection or suturing of gastric ulcer;
- operations performed on the biliary tract;
- duodenitis and gastroduodenitis;
- duodenostasis - a violation of the motor activity of the duodenum up to its complete cessation;
- dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi;
- uncontrolled use of choleretic drugs and NSAIDs;
- gaping pylorus of organic or physiological origin.
Provoking factors for the development of the disease
There are also a number of reasons that are not an independent etiological factor, but merely create favorable conditions for the development of bile reflux. These include:
- pregnancy status;
- acute and chronic pancreatitis;
- hiatal hernia (especially hiatal hernia);
- cholecystitis (both acute and chronic);
- poor nutrition;
- obesity;
- endoscopic examination of the gastrointestinal tract (rare);
- improper formation of the food tube in the fetus during embryogenesis.
What are the signs of the disease?
Duodeno-gastric reflux has symptoms typical of gastrointestinal diseases. This makes its manifestations similar to other pathologies, which complicates diagnosis a little, but proper differentiation allows you to identify the disease quite quickly.
Duodenal reflux often develops due to increased acidity
Main symptoms of GHD:
- heartburn that occurs after eating;
- lack of appetite;
- belching with a sour or bitter taste;
- unpleasant, often bitter taste in the mouth;
- bloating, feeling of “fullness”;
- urges of nausea;
- bouts of vomiting;
- excretion of bile with vomit;
- the tongue is coated with a yellow coating;
- pain in the abdomen, especially in its upper part;
- profuse salivation.
Less commonly, patients complain of hoarseness, cough, pain in the chest area, which gets worse when bending over. In more severe cases, swallowing impairment (dysphagia) is observed, which can occur due to difficulty in motility or narrowing of the esophagus. Sometimes, against the background of pathology, inflammation occurs and body temperature rises.
Risk factors include smoking, stress, excess body weight
Methods for treating duodenogastric reflux
Before prescribing suitable treatment, it is necessary to establish the cause of the problem. So, if reflux has isolated manifestations, it is only necessary to eliminate the provoking factor (in particular, review the diet and diet, give up excessive physical activity, protect yourself from stress and anxiety).
If duodenogastric reflux is a symptom of any disease, the patient needs to be prescribed a set of therapeutic measures, including medication, nutrition and lifestyle correction, physiotherapeutic treatment, and exercise therapy. In severe cases, when GDR has led to the development of serious complications (for example, the formation of cancerous tumors), surgery is prescribed.
Physiotherapy, in particular the use of ultrasound and dynamic currents, allows you to restore damaged stomach cells, return the organ to normal functionality, and eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of the pathological process.
Expert opinion
Tsareva Nadezhda
General practitioner, hepatologist, site expert
Exercise is also an effective adjuvant treatment. Complementing the main treatment regimen. A set of exercises, their intensity and duration are developed by the doctor individually for each patient. The classes are aimed at strengthening the walls of the abdominal cavity and stimulating the motility of the digestive organs.
Classification
With duodenal reflux, pancreatic juice mixes with bile. As a result, a liquid with very aggressive properties is formed, which negatively affects the condition of the gastric mucosa. The composition of the substance is so caustic that it destroys its protective barrier. Gradually, the shell is damaged, these changes lead to serious consequences. The degree of damage determines the forms of DG reflux:
- Superficial. As a result of indigestion, the gastric mucosa is damaged, but for now only its outer layer is affected.
- Catarrhal. The mucous membrane is affected over the entire area. Most often, swelling is observed. Over time, the inflammatory process develops. In response to allergic reactions, long-term use of certain drugs causes so-called catarrhal reflux.
- Erosive. It often occurs if the patient does not adhere to the doctor’s recommendations regarding nutrition and regimen. For example, alcohol consumption or frequent stress can lead to this. As a result, small ulcers appear on the walls of the stomach.
- Biliary. This form of the disease develops when bile excretion is impaired. In severe cases, it can lead to liver dysfunction.
With duodenal reflux, pancreatic juice mixes with bile
In addition, with gastroduodenal reflux it is customary to distinguish the severity of the pathology. It depends on the duration of the process. Throughout the course of the disease, symptoms may change. During diagnosis, the severity of GHD is determined by analyzing contents from different parts of the stomach.
Diagnosis
The doctor diagnoses the disease comprehensively. First of all, he interviews the patient and collects anamnesis. Then the patient is sent for hardware research methods:
- pH-metry. This method helps determine the frequency, duration and manifestation of GDR.
- X-ray. Carried out using contrast, the doctor can visually notice the intestinal contents entering the stomach cavity.
- Electrogastroenterography evaluates the contraction of the duodenum and stomach.
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy. This method helps the doctor determine the site of mucosal lesions, visualize ulcers and assess the severity of the disease.
Diagnostics
Despite the fact that the symptoms of the disease are similar to those of many other gastrointestinal problems, an experienced specialist can easily make a diagnosis. If you suspect a disease, it is important to immediately carry out all the necessary tests. Previously, the leading research method was fibrogastroduodenoscopy, which is now used much less frequently.
In addition, the patient must undergo:
- analysis of daily pH-metry, which determines the acidity of different parts of the stomach;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- X-ray of the stomach and duodenum with contrast;
- electrogastroenterography.
Depending on the patient's complaints or the doctor's decision, additional studies may be prescribed. The examination is carried out comprehensively, that is, it includes different methods - in this way the diagnosis will be determined more accurately. The success of treatment of duodenogastric reflux directly depends on this.
The examination is carried out comprehensively
Prognosis for patients
In general, the disease has a benign course and a favorable prognosis if diagnosed in the early stages of development and subjected to rational therapy.
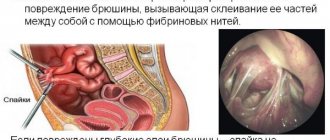
Neglected cases lead to the development of more serious complications, which significantly worsen a person’s quality of life. These include: gastroesophageal reflux disease, toxic-chemical gastritis C, adenocarcinoma, etc.
Treatment
Diagnosis and therapy of this disease require an integrated approach. Pharmacological treatment will undoubtedly have a positive effect, but without a special diet it will be unstable, and after some time the pathology will again make itself felt. The goal of therapy is to normalize the motility of the stomach and duodenum and improve the ability to clot bile acids.
With the help of pharmacological treatment, pain relief, stimulation of motility, and also mitigation of the effect of bile on the stomach environment are produced. Drugs are prescribed to eliminate symptoms - heartburn, pain, flatulence, and so on. The duration of treatment is usually from one and a half to two months. In especially severe cases, therapy is longer - up to six months. The following pharmacological groups are used:
- antacids;
- H2-histamine blockers;
- proton pump inhibitors.
Medicines to relieve symptoms – heartburn, pain, flatulence
Cases when the body does not respond to conservative treatment methods are rare. However, if this happens, as well as when certain complications develop, they resort to surgery.
Symptoms
Duodenogastric reflux occurs with pronounced symptoms, which bring discomfort to the patient:
- There are white patches on the tongue, sometimes with a yellowish tint.
- Painful sensations that lead to spasms.
- Heartburn.
- Belching occurs during the period when the contents of the intestines are released into the stomach cavity.
In the absence of early diagnosis and medical assistance, complications may develop:
- Gastritis develops as type C.
- Gastritis.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease.
- Ulcer.
Important! If a clinical manifestation or feeling of discomfort occurs, you should contact a specialist to make a diagnosis and begin timely treatment therapy.
Diet for GHD
The key to treating many diseases is proper nutrition. This is especially true for gastrointestinal diseases. The Harvard School of Medicine determined the influence of the esophageal sphincter on the occurrence of duodenogastroesophageal reflux. Some foods with GHD not only irritate the walls of the stomach and intestines, but also injure the sphincter.
In addition to limiting the consumption of certain types of food, the diet for GHD has some recommendations regarding diet and cooking:
- preference should be given to food boiled in water, steamed, or baked;
- the temperature of the dishes is strictly warm, not hot or cold;
- fractional meals - 5-6 meals per day;
- it is necessary to exclude all acidic foods, including fermented milk and certain fruits;
- eat chopped food;
- You need to chew each piece very carefully;
- completely eliminate the possibility of overeating.
Some foods with GHD not only irritate the walls of the stomach and intestines, but also injure the sphincter
You can make a list of “bad” foods yourself by observing your condition and recording the results in a notebook. After eating, it is advisable to avoid physical activity and sudden movements for 30-60 minutes. Replacing your usual food with pureed porridge and pureed soups will help reduce the amount of bile secreted. It is allowed to eat low-fat fish and meat. Although fermented milk products are prohibited, milk and curdled milk are allowed.
Diagnosis of reflux
GHD is detected during a visual examination of the patient and history taking. If the doctor has a suspicion, several referrals for examination are prescribed to refute or confirm the disease. Helps identify reflux:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs. During the ultrasound examination, the nature and sources of disturbances in the stomach, gallbladder, pancreas or duodenum are revealed;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy is the most accurate picture for detecting reflux, when the data obtained allow cytological and histological assessment of the degree of damage to the mucosa and the nature of its damage (malignant or benign process);
- chemical analysis of gastric juice, which makes it possible to determine by titration even small concentrations of pancreatic enzymes and bile acids;
- measurement using gastric juice pH indicators throughout the day. If after eating the pH shifts to the alkaline side, it is judged that duodenal fluid has penetrated into the stomach and the two fluids have mixed.
Which products will be beneficial and which will be harmful?
Symptoms of the disease almost always occur after eating. But it is not enough to simply give up foods that cause heaviness in the stomach or heartburn. A therapeutic diet involves a gentle effect on the digestive system and at the same time contains all the beneficial substances necessary for the body. Here is a short list of foods that are allowed to be consumed:
Replacing your usual food with pureed cereals and pureed soups will help reduce the amount of bile secreted.
- ground porridge (rice, pearl barley, buckwheat, oatmeal);
- puree soups with weak broth;
- steam omelette;
- fish, always lean;
- fresh whole milk;
- low-fat cottage cheese, casseroles based on it;
- lean meat, preferably in the form of souffle, steamed meatballs or cutlets;
- pureed vegetables;
- butter and vegetable oils in small quantities;
- herbal teas;
- dried fruits compote;
- yesterday's bread.
Where do such pathologies come from?
Duodeno-gastric reflux accompanies such chronic diseases of the digestive system as gastritis and peptic ulcers. This pathology is not considered an independent disease, therefore gastritis and duodenitis are considered to be the causes of disturbances in the unilateral conduction of food along the gastrointestinal tract. In turn, gastritis is associated with serious abnormalities in the functioning of the duodenum. Often, when GDR is detected, a complex disease is detected - gastroduodenitis.
Several factors associated with a violation of a healthy lifestyle can provoke the occurrence of pathology:
- tobacco smoke and drugs;
- alcohol abuse;
- use of unapproved medications during pregnancy.
DGR can be formed under the influence of internal
sources: insufficient tone of the circular muscles of the orifices of the stomach or hernia of the diaphragm in the esophagus. The sources of pathology may be the consequences of too high pressure in the duodenum: cholecystitis, pancreatitis, Botkin's disease. It is possible that pathology may be detected after surgical interventions in the abdominal area: removal of the gallbladder, anastomosis with fastening of intestinal loops. The concentrations in the gastric juice that are contained in the bile acids, pancreatic enzymes and enzymes that break down lecithin contribute to deviations from the norm.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine for gastroduodenal reflux is acceptable and often quite effective. The risk of side effects is minimal. It is important to remember that even the most harmless folk remedies must be agreed with your doctor. Most popular recipes:
- The herbs of chamomile, St. John's wort and yarrow are taken in any proportion, poured with boiling water, and infused. Drink twice a day, adding a small amount of infusion to regular tea. The product will relieve symptoms of gastritis and DH , relieves heartburn, and will help with dysbacteriosis.
- Fumiya herb in the amount of 2 tablespoons is poured with 0.5 liters of boiling water. It takes an hour. Take 50 ml every 30 minutes. Prevents the release of bile with vomiting.
- Mix crushed roots of calamus, sage - 50 g, angelica - 25 g. Pour boiling water at the rate of 1 teaspoon of mixture per glass of boiling water. Let it brew for 20 minutes. Take three times a day an hour after meals.
- One tablespoon of flax seeds is poured into 100 ml of cold water. Infuse them until the characteristic mucus is released. Take a teaspoon of the product on an empty stomach.
Constant relapses “wear out” the stomach and can lead to extremely negative consequences
Traditional medicine mainly uses various parts of medicinal plants, it is important to be careful not to cause allergic reactions. Otherwise, folk remedies are safe and have no side effects.
Drug treatment
To achieve a positive therapeutic result, it is necessary to take medications prescribed by a doctor. Such agents have different actions. This is protecting the stomach, reducing the level of acids in gastric juice and bile, restoring damaged areas of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, preventing the development of complications of GHD, and eliminating pain.
| Name | Description | Dosage | Price |
| Motilium | The drug facilitates the movement of food from the stomach to the intestines. This allows you to reduce the aggressive effect of gastric juice on the walls of the organ. | 1 tablet 3 times a day 15-20 minutes before meals. Duration – up to 28 days. | 450 rub. |
| Almagel | Neutralizes hydrochloric acid in gastric juice, as well as aggressive bile enzymes, protects the walls of the organ from negative effects. | 1 tbsp. l 3 times a day after meals. | 200 rub. |
| Esomeprazole | The drug reduces the production of gastric juice, thereby reducing the degree of its effect on the walls of the digestive organs. | 40 MG 1 time per day. The duration of treatment is 1 month. If the symptoms do not disappear, a repeat course is recommended. In this case, the dosage is reduced by 2 times. | 1600 rub. |
| De-nol | A protective drug that coats the walls of the stomach. The film that appears after taking the product neutralizes the effects of aggressive substances. | 4 times a day before meals, and also 1 time before going to bed. The duration of treatment depends on the severity of symptoms. | 300 rub. |
| Lactofiltrum | The drug has an adsorbing effect, neutralizes harmful substances that negatively affect the walls of the digestive organs, and promotes their elimination. | Take 3-4 times between meals. Duration of treatment is 1-2 weeks. | 250-400 rub. (depending on package size). |
| Ursofalk | The product converts acidic elements, making them less dangerous and toxic to mucous membranes. | Take once a day (in the evening), the course of treatment is about 2 weeks. | 180 rub. |
Prevention
Even if the treatment was successful, there is a high probability of exacerbation of duodenogastric reflux. Constant relapses “wear out” the stomach and can lead to extremely negative consequences. In order to avoid this, the patient must adhere to certain recommendations for a long time:
- maintaining normal body weight;
- change in diet;
- adherence to diet;
- active lifestyle;
- rejection of bad habits.
Patients have to partly change their lives. For example, they should not overeat, while hunger is also dangerous. To prevent the release of bile, the patient is prohibited from lying on his back for about half an hour after eating.
Over time, patients get used to the new diet and note not only an improvement in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, but also in their physical condition in general. The prognosis of cases detected in the early stages is most often favorable. Conscientious adherence to the prescribed course of treatment and preventive measures will help prevent relapses.
Typologies and degrees of development of reflux
Depending on the progress of reflux, there are 3 degrees of pathology,
Rejection of gastric juice into the esophagus
identified by diagnostic methods when a concomitant disease is detected.
Half of the patients with reflux of duodenal contents had grade 1 GHD, in which the mixing of gastric contents with duodenal contents was insignificant.
With reflux disorder, four out of ten patients had a greater disturbance in the stomach, which corresponds to grade 2 pathology.
Approximately one patient out of ten showed, as a result of diagnosis, serious disturbances in the movement of duodenal contents into the stomach, which characterizes stage 3 of the disease.
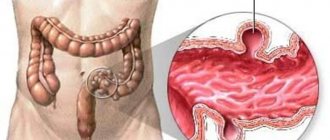
It should be understood that gastric reflux is identical in type to gastroduodenitis. The following manifestations indicate gastroduodenitis:
- halitosis;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- urge to vomit.
There are other signs of gastroduodenitis that make it similar to gastritis:
- violation of stool both in the liquid direction and in the direction of constipation;
- flatulence;
- decreased appetite;
- frequent belching.
According to the typology of destructive processes, there are 4 types of reflux:
- Superficial type, in which only the cells of the mucous membrane are affected. The integrity of the glandular exocrine epithelium is not impaired.
- When reflux is accompanied by inflammatory processes, swelling and redness of the mucous membrane, it is customary to talk about the catarrhal type of pathology.
- With the erosive type of reflux, the mucous membrane is characterized by focal atrophy.
- The biliary variety is associated with a violation of the outflow of bile from the gallbladder into the duodenum.
Causes of pathological intestinal reflux
Reverse evacuation of the contents of the duodenum into the stomach occurs when the pressure in the intestinal cavity increases and the contractile activity of the muscle closure at the border with the pyloric region of the stomach decreases. The cause of these processes is an imbalance in the nervous and humoral regulation of gastrointestinal motility. Mixed reflux irritates the walls of the stomach. Episodes of small intestinal release periodically occur in healthy people, but are not accompanied by unpleasant sensations. Pathology in children manifests itself against the background of congenital anomalies of the small intestine or helminthic infestations. Causes of gastric reflux in adults:
- increased motility of the duodenum;
- inflammatory and ulcerative pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- operations performed in the abdominal area;
- pregnancy;
- diaphragmatic hernia;
- taking medications that cause hypotonicity of the gastrointestinal tract muscles;
- chronic stress;
- overweight;
- frequent drinking of alcohol;
- smoking;
- Irregular diet with an abundance of junk food.
Disease prevention
To avoid the occurrence of gastroduodenal reflux, you must:
- Stop smoking.
- Do not abuse alcoholic beverages.
- Carefully monitor your diet, limit the consumption of fast food, canned and fried foods.
- Normalize your emotional state, avoid excessive mental stress.
- Avoid static physical activity, which can lead to increased intra-abdominal pressure.
- When taking medications, carefully monitor possible gastrointestinal symptoms.
- If the first signs of dyspepsia occur, seek qualified medical help.
Disease prevention
Even after complete healing from duodenogastric reflux, it is necessary to constantly take care of your health, listen to the signals sent from within and carry out prevention in order to avoid a relapse of the disease. Preventive measures are:
- Maintaining a stable weight. People prone to reflux disease are not allowed to gain extra pounds, because... their presence increases intragastric pressure, predisposing to the release of acid into the esophagus.
- Avoid fast food.
- To prevent the disease, it is necessary to increase physical activity: fast walking, basic daily exercise, morning jogging will make the metabolism work better and have a beneficial effect on the condition of the stomach and esophagus.
Find out what kind of disease gastric polyposis is, its symptoms and treatment.
Frequency of occurrence of the disease
GHD occurs in more than half of people.
Wherein:
- In 10-15% of them, bile is thrown into the stomach periodically, which is associated with high physical activity or being in a horizontal position. In this case, the person does not experience negative symptoms. Accordingly, reflux is not considered as an independent disease.
- Pathological bile reflux occurs in approximately 28-32% of the population. Both women and men are equally susceptible to the disease. Most often, the pathology is diagnosed in young people who eat improperly.
- 45-100% of patients with diagnosed GHD have other disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
In patients with chronic gastrointestinal pathologies, duodenogastric reflux is not always detected. Doctors attribute this to an incomplete examination.
Dietary nutrition for illness
Diet for duodeno-gastric type of reflux should be a prerequisite for therapy. It is necessary to exclude completely fried, too salty, fatty and spicy foods from the patient’s diet. Some foods lead to a decrease in the tone of the gastric sphincter - pylorus. This applies to the following foods:
- Coffee.
- Fresh bread.
- Cocoa.
- Garlic.
- Oranges.
These products are prohibited if the patient has duodenal gastric reflux. It is also necessary to avoid those foods whose consumption causes an increase in acidity in the stomach. These are cabbage, apples and various pickles. Alcoholic products are completely prohibited.
The patient, if he has duodenogastric reflux, must follow some tips for organizing his diet. The mode of eating food must be fractional. The number of meals reaches 5-6 per day. It is useful to drink mineral water enriched with magnesium. You should not rush while eating. Foods must be chewed thoroughly.
Food must be warm. Hot or cold is not allowed for consumption. Duodenal reflux requires a competent approach to food preparation. It can be baked, steamed or boiled. This condition is mandatory.
Symptoms of the disease
The symptoms of GHD are similar to other diseases of the digestive system due to their interdependence. But such similarity is only external. The main symptoms of this disease are few:
- heartburn that occurs after eating;
- belching with normal air or with a sour taste;
- bloating after eating, feeling of fullness;
- pain and spasmodic pain in the epigastric region that appears after eating;
- there is a bitter taste in the mouth;
- feeling of nausea followed by possible vomiting of bile;
- coating of the tongue with a yellow coating.
Often, when performing fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) to diagnose a third-party disease, the doctor can detect duodenogastric reflux in the patient. At the same time, the disease does not manifest itself in everyday life. In such cases, it is periodically activated during sleep or when performing certain physical activities. At the same time, it does not have a negative effect on the patient’s digestive system.
Diet
For GHD, it is recommended to include low-fat meat and fish in the diet. Porridge, low-fat milk and cottage cheese are useful. It is allowed to eat sweet fruits - bananas, pears.
You need to steam the dishes, then grind the resulting mass in a blender to obtain a puree.
It is necessary to take crushed meals, in small portions, every 4 hours. Portions should be balanced, that is, proteins, fats, and carbohydrates should be present in each serving, which helps reduce the load on the digestive tract. Rough food should be completely avoided. In order to reduce stomach acidity, it is necessary to avoid acidic foods and dishes (citrus fruits, cabbage, tomatoes, garlic, apples, plums).
The use of drinks containing caffeine, chocolate, baked goods, especially warm bread is not allowed.
You need to exclude smoked, fried, salted foods from your diet, and give up canned foods.
Gastric reflux duodenitis can be completely cured at an early stage. Proper nutrition, an active lifestyle, and regular examination by a specialist will help prevent the development of pathology, and if you have GHD, avoid its exacerbation.
Drink to normalize intestinal motility
Take 1 tbsp. l. dry grass plantain, buckthorn. The collection is poured into 250 ml of boiling water, left for an hour, taken 3 times a day.
Currently reading: What you can and cannot do with duodenitis - the best dishes, diet and menu for the week with recipes
For biliary dysplasia, the following are recommended:
- Rue leaves. The leaves of the plant are used fresh. After each meal you need to chew a few leaves.
- Aloe. Before each meal, drink 1 tsp. freshly squeezed juice from the leaves of the plant.
- Infusion of fume grass. 2st. l. dried herbs pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. The resulting composition is infused for an hour. The finished infusion is taken in 50 ml doses every 2 hours.
Folk remedies
Many plants and herbs can help overcome symptoms caused by duodenitis and gastric reflux.
The most effective and safe way to treat duodenitis is a decoction of flax seeds. It is a natural antacid. The decoction can reduce acidity no worse than medicine. The following herbs are also useful:
- lemon balm - normalizes the state of the nervous system;
- chamomile - removes inflammatory processes;
- rose hips - heals tissues and mucous membranes;
- sea buckthorn oil - relieves pain.
Products with beneficial properties
Among the healthy products, potato juice is especially worth highlighting. The starch contained in the product envelops the internal organs of the gastrointestinal tract and relieves pain. Fresh juice can be taken on an empty stomach or immediately after breakfast.
Fermented milk products can also relieve symptoms of reflux and duodenitis. Kefir, milk and low-fat fermented baked milk can help with healing. But the main property of these products is to fight heartburn. Just a sip of milk can soothe your internal organs and reduce acidity.
Traditional methods are harmful
There are a number of plants, decoctions and compositions of which should never be used during inflammation. Among them:
- Rowan;
- mint;
- plantain;
- dandelion.
Important: These plants stimulate the production of gastric juice and significantly improve appetite. You can relieve the symptoms of reflux at home, but you need to do it with extreme caution so as not to make it worse for yourself. The most important thing is to coordinate each method with your doctor, and not to start taking any medications without the permission of the treating doctor.
Diagnosis of the disease
Since bile reflux does not cause clear symptoms, it is often discovered incidentally during examination for other gastroenterological diseases.
A comprehensive examination consists of the following stages:
- laboratory blood and urine tests;
- ultrasound examination of the digestive tract;
- endoscopic examination, which involves inserting a special tube with a camera into the stomach to detect inflammation;
- intragastric measurement of acidity level;
- examination of the stomach contents to detect traces of bile;
- electrogastrography, which determines the frequency and degree of gastric motility;
- contrast radiography;
- antroduodenal manometry, which studies the pressure indicator in the gastrointestinal tract.
Based on a comprehensive examination, the doctor can make a diagnosis, determine the degree of development of GHD and prescribe appropriate treatment.
What it looks like, photo
Pathological changes in the gastric mucosa during GHD depend on the type of pathology. With the superficial form of duodeno-gastric reflux, destruction of the mucosa can be observed, without damage to the glandular exocrine epithelium. When a catarrhal type of pathology is detected, an inflammatory process is observed; in the photo you can see swelling and redness of the mucous membrane.
The erosive appearance is expressed by the initial processes of atrophy, the mucous membrane atrophies in places. With biliary duodeno-gastric reflux, there is an incomplete transfer of the required amount of bile to the duodenum.
Preventive actions
To avoid the need for treatment with synthetic drugs for duodenal or gastric reflux, it is necessary to carry out preventive measures to prevent them:
- strive for a healthy lifestyle - eat right, exercise more, take long walks, for example, and also adjust your work and rest schedule;
- treat all gastrointestinal diseases promptly and in full - follow all recommendations of specialists;
- do not wear tight or tight clothing;
- spend the night resting on an orthopedic mattress, with the head end moderately raised;
- annually undergo a full preventive medical examination, with mandatory fibrogastroduodenoscopic examination.
As you know, every person is the creator of his own health. If you adhere to the above preventive measures, then a person will not even know what reflux is.
Reviews
Dear readers, your opinion is very important to us - therefore, we will be glad to hear your feedback on reflux duodenitis - how to eat and treat correctly in the comments, this will also be useful to other users of the site.
“For many years I suffered from reflux duodenitis due to a congenital bend in the gallbladder. I save myself only with gastric mixture and (during severe attacks) Phosphalugel. The doctor recommended both remedies. On his recommendation, I started taking up ballroom dancing - I thought my condition would get worse, but the attacks, on the contrary, became much less frequent.”
Elena
“When treating reflux duodenitis, it is important to follow a diet and completely avoid carbonated drinks. If possible, it is better to drink spring water, but in no case drinks with artificial colors. Occasionally you can have coffee, but only instant coffee. And no alcohol. This is the only thing that helped me."
Dmitriy
Diagnosis methods
Symptoms of duodenal gastric reflux should be a reason to urgently seek medical help. It is not recommended to delay a visit to a specialist. This also applies to self-treatment of duodenogastric reflux at home.
The first event that the patient has to undergo is characterized by an initial examination. This is done by a gastroenterologist. His tasks include interviewing the patient, identifying complaints, collecting anamnesis and drawing up a plan for further action.
The next stage of diagnosis is carried out using laboratory methods. They are more informative, unlike an examination, and therefore allow you to obtain more information about the patient’s condition and determine the tactics for further action. The following methods are used for diagnosis:
- Acidity monitoring.
- Fiberoptic spectrophotometry.
In the first case, the acidity indicator is subject to study, and the degree of value is determined. With fiberoptic spectrophotometry, the absorption spectrum of bilirubin, which is located in the patient’s esophagus, is studied. The study occurs regardless of acidity.
Specialists also have instrumental techniques. During fibrogastroduodenoscopy, the alimentary tract and its mucous membrane are examined. This is achievable thanks to a special device with an optical system. Ultrasound examination can detect inflammatory processes and pathologies of the abdominal area.
Contrast radiography of the duodenum and stomach helps to recognize the presence of defects or changes that are associated with the structure of the organs. This is possible due to the introduction of a special contrast agent into the stomach. During the X-ray, specialists will receive the necessary information about the patient’s condition. Electrogastroenterography is used to study the electrical activity of the stomach and determine disorders that are associated with the motor activity of the gastrointestinal tract.